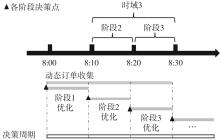
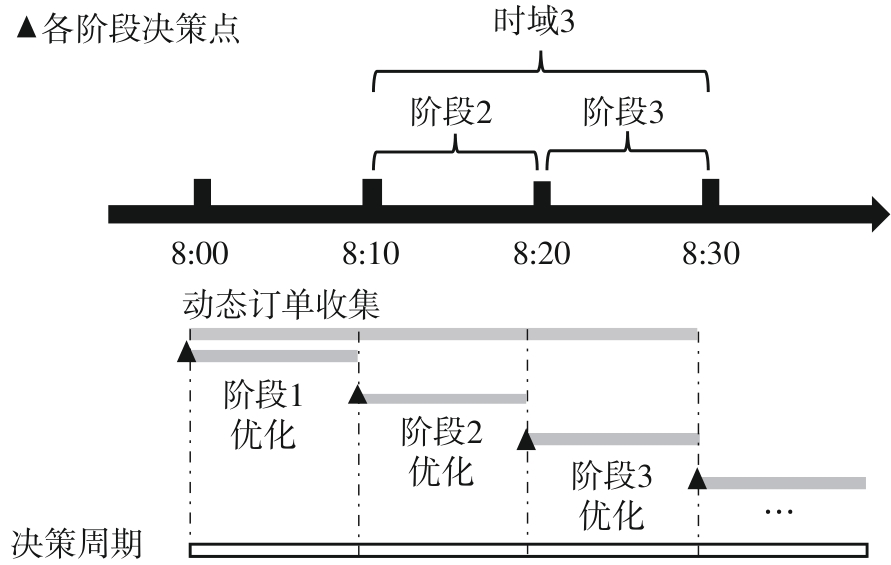
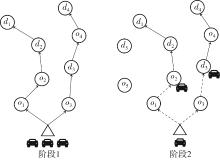
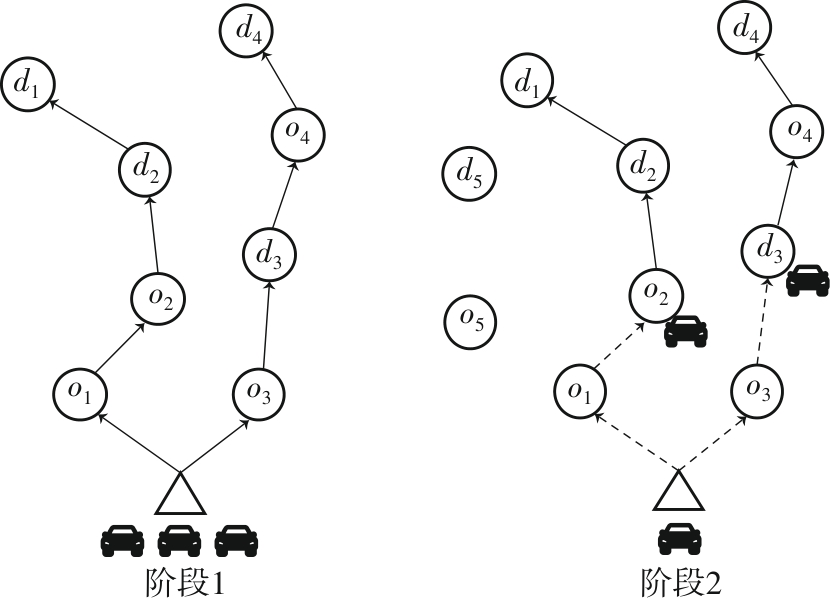
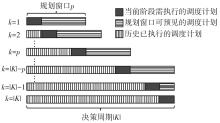
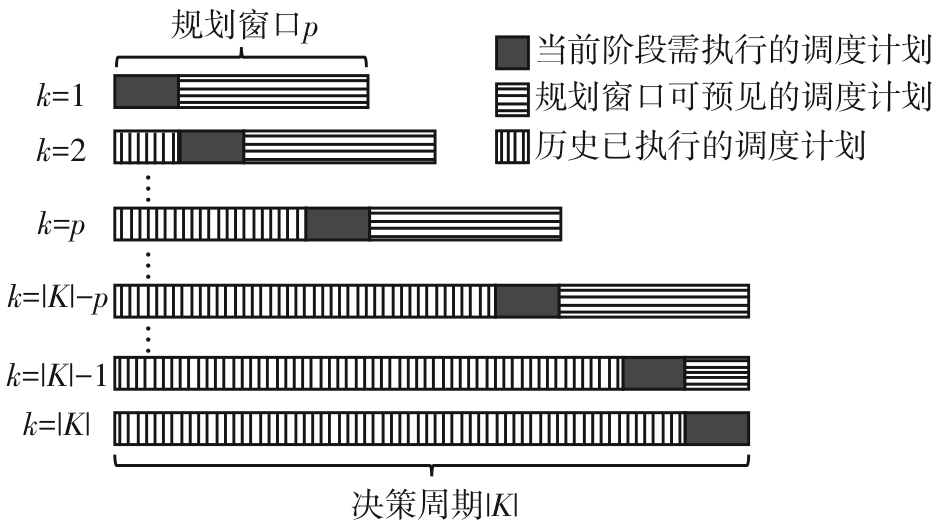
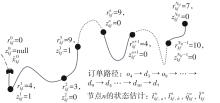
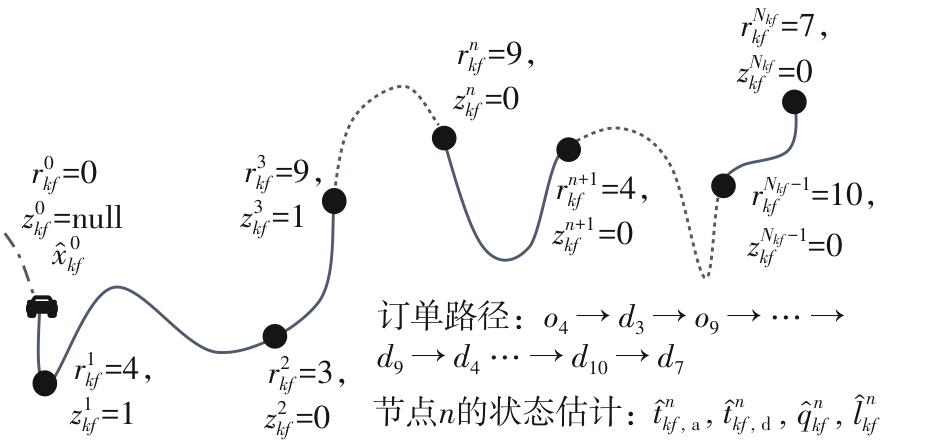
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 77-90.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240331
• Intelligent Transportation System • Previous Articles Next Articles
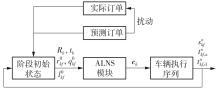
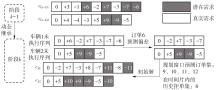
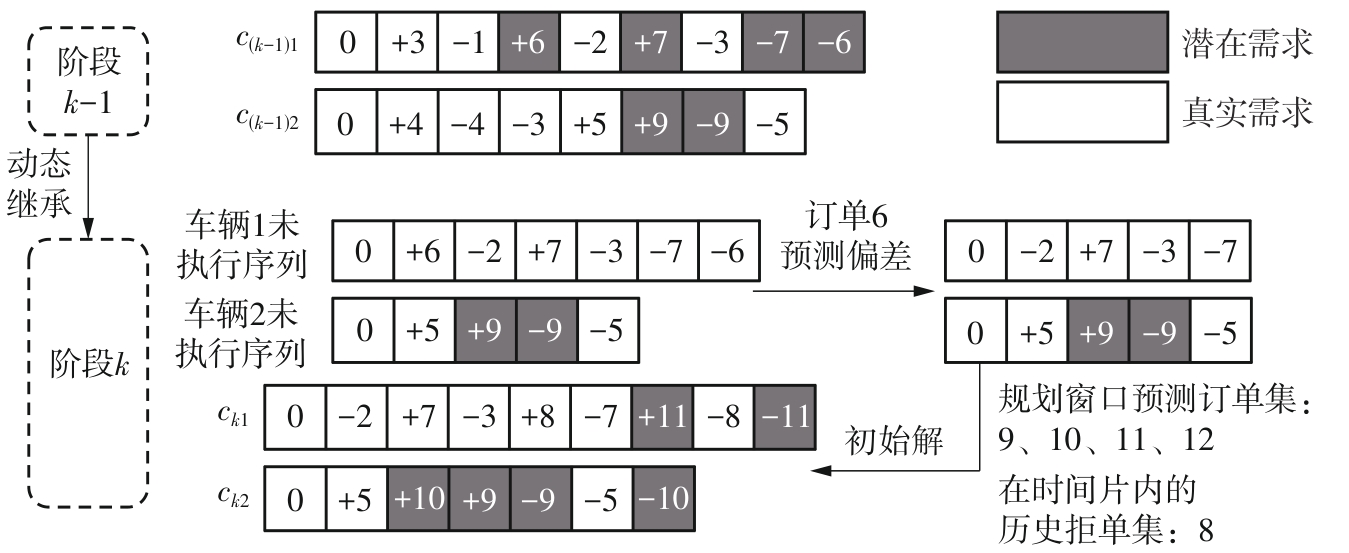
Dynamic Scheduling of Demand Responsive Transit Based on Model Predictive Control
JIN Wenzhou( ), ZHANG Yong, SUN Jie
), ZHANG Yong, SUN Jie
- School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2024-06-26Online:2025-06-10Published:2024-12-06 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52072128)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIN Wenzhou, ZHANG Yong, SUN Jie. Dynamic Scheduling of Demand Responsive Transit Based on Model Predictive Control[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(6): 77-90.
share this article
Table 2
Final vehicle route"
| 车场编号 | 车辆编号 | 车辆服务订单路径 |
|---|---|---|
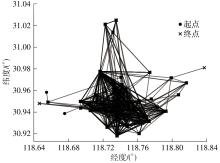
| ① | 1 | p6→o3→o6→o13→p2→d13→o26→d6→d3→p27→d26→o60→o41→p3→o43→p11→d41→d43→o74→o68→o79→d60→o82→p9→d82→o104→d68→d79→o116→o114→d104→d74→d114→d116 |
| ① | 2 | p6→p5→o24→o22→o30→p11→d24→d30→d22→p4→o58→o61→o143→p38→o64→o89→o78→d61→d143→p6→o92→d64→d89→d78→d58→o111→d92→d111 |
| ① | 3 | p6→o7→o8→p21→d7→o31→p6→o54→p53→d31→o59→d8→d54→o70→o50→o55→p6→d50→o73→d70→d55→p57→d73→d59→o101→o99→o113→o110→d99→o119→d113→o120→d101→d110→d120→d119 |
| ① | 4 | p6→o1→p11→d1→o21→o20→o19→p38→o46→o36→d20→p39→d46→d21→p35→d19→d36→p42→o76→o83→o98→d76→d83→o106→d106→d98 |
| ② | 5 | p1→o18→p28→o16→d18→o17→o135→p13→o29→d16→o37→o56→d135→d17→p12→o52→d29→d52→d37→o69→p51→p40→d69→o88→d56→o102→d88→d102 |
| ② | 6 | p1→o9→p50→d9→o27→o12→o32→p6→o34→d27→d12→p8→d34→o53→d32→o62→o51→p29→o72→d62→d51→p4→d53→o103→d72→o108→o112→d103→o115→d108→o117→d115→d112→d117 |
| ③ | 7 | p50→o11→o5→p32→d5→d11→o15→o40→p43→d40→p28→o47→d47→p27→o63→d15→o84→p52→d84→o160→o95→o118→o94→d63→d95→d118→d160→d94 |
| ③ | 8 | p50→o14→p53→d14→o39→o33→o38→p27→d33→d38→p3→d39→o80→p9→o100→o96→o93→o85→p17→d80→o105→o90→o107→d105→o168→d85→d93→d107→d168→d90→d96→d100 |
Table 4
Comparison of key indicators under different scales"
| 规模场景 | 对比算法 | 目标函数值/元 | 乘客服务率/% | 额外时间系数 | 人均惩罚时间/min | 车均行驶里程/km | 车均等待时间/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
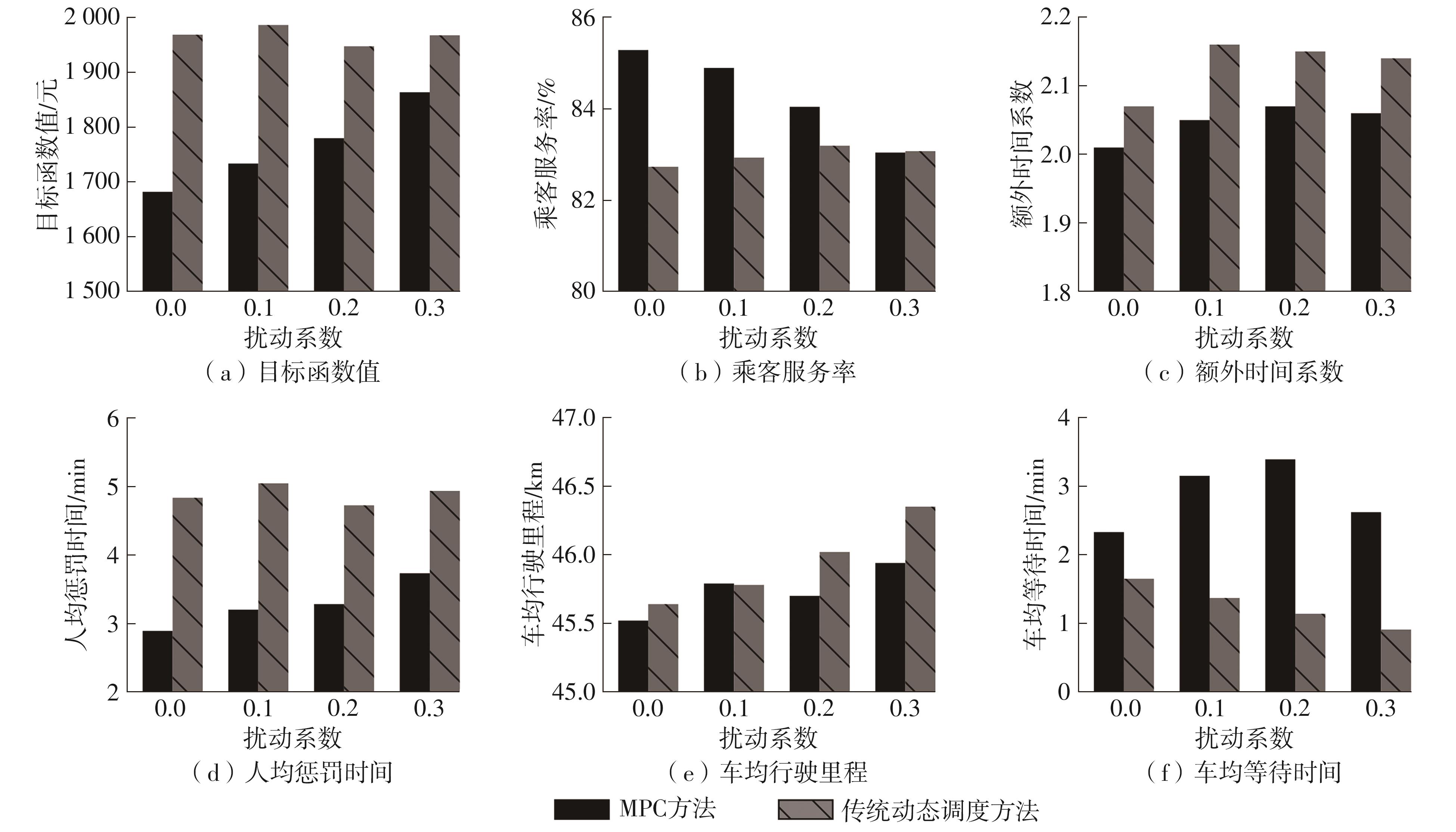
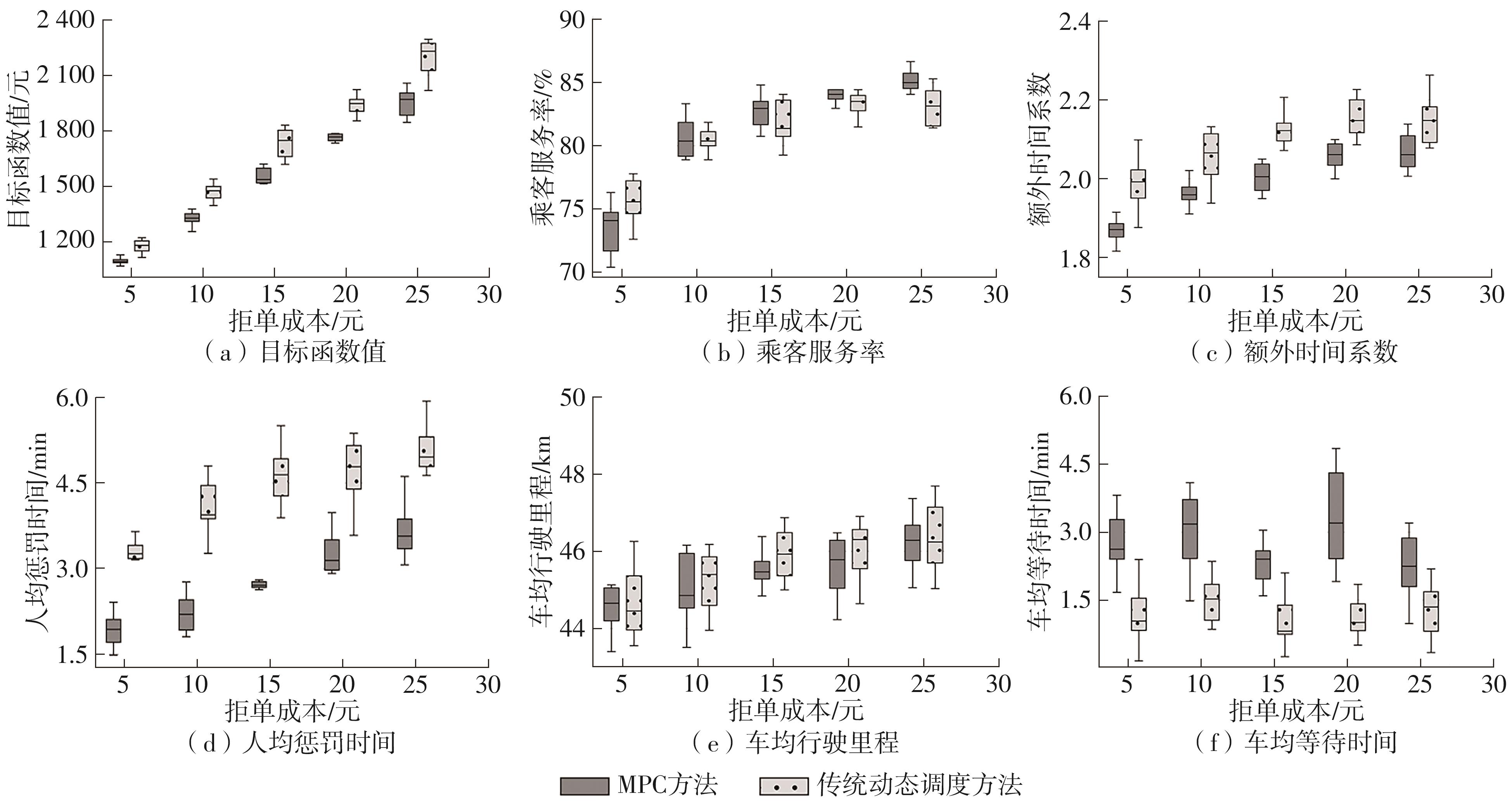
| 120个订单,8辆车 | MPC | 1 779.50 | 84.04 | 2.07 | 3.28 | 45.70 | 3.39 |
| 传统动态调度 | 1 946.93 | 83.19 | 2.15 | 4.72 | 46.02 | 1.14 | |
| 180个订单,12辆车 | MPC | 2 591.93 | 85.12 | 1.94 | 3.06 | 46.46 | 3.41 |
| 传统动态调度 | 2 886.35 | 84.21 | 2.12 | 4.53 | 46.40 | 2.14 | |
| 240个订单,16辆车 | MPC | 3 309.88 | 86.73 | 1.94 | 2.57 | 45.94 | 5.21 |
| 传统动态调度 | 3 713.23 | 85.25 | 2.01 | 3.84 | 45.89 | 2.78 |
| 1 | VANSTEENWEGEN P, MELIS L, AKTAS D,et al .A survey on demand-responsive public bus systems[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2022,137:103573/1-39. |
| 2 | 宋翠颖,王鹤玲,田泽尚,等 .需求响应式公交车辆调度模型和算法研究综述[J].北京交通大学学报,2023,47(4):31-44. |
| SONG Cuiying, WANG Heling, TIAN Zeshang,et al .Review of demand-responsive transit vehicle scheduling models and algorithms[J].Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University,2023,47(4):31-44. | |
| 3 | LIU Y N, OUYANG Y F .Mobility service design via joint optimization of transit networks and demand-responsive services[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2021,151:22-41. |
| 4 | 靳文舟,胡为洋,邓嘉怡,等 .基于混合算法的需求响应公交灵活调度模型[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(1):123-133. |
| JIN Wenzhou, HU Weiyang, Deng Jiayi,et al .Fle-xible scheduling model of demand response transit based on hybrid algorithm[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(1):123-133. | |
| 5 | 胡迪,靳文舟 .基于站点优化的需求响应公交调度研究[J].深圳大学学报理工版,2022,39(2):209-215. |
| HU Di, JIN Wenzhou .Flex-route demand response transit scheduling based on station optimization[J].Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering,2022,39(2):209-215. | |
| 6 | LI X, WANG T Q, XU W H,et al .A novel model and algorithm for designing an eco-oriented demand responsive transit (DRT) system[J].Transportation Research Part E:Logistics and Transportation Review,2022,157:102556/1-33. |
| 7 | 靳文舟,杜昊,巫威眺 .基于ALNS-TS算法的半灵活型需求响应公交调度问题[J].深圳大学学报理工版,2023,40(4):425-434. |
| JIN Wenzhou, DU Hao, WU Weitiao .Semi-flexible demand responsive transit scheduling based on ALNS-TS algorithm[J].Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering,2023,40(4):425-434. | |
| 8 | 郭梅雪,靳文舟,巫威眺 .考虑充换电的模块化需求响应公交路径优化[J].交通运输工程与信息学报,2024,22(3):34-51. |
| GUO Meixue, JIN Wenzhou, WU Weitiao .Optimization of modular demand-responsive transit routes consi-dering charging and battery swapping[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information,2024,22(3):34-51. | |
| 9 | 韩博文 .考虑实时需求的需求响应式公交调度方法研究[J].广西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2019,37(3):9-20. |
| HAN Bowen .Demand responsive transit scheduling method considering real-time demand[J].Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2019,37(3):9-20. | |
| 10 | HUANG D, GU Y, WANG S,et al .A two-phase optimization model for the demand-responsive customized bus network design[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2020,111:1-21. |
| 11 | 巫威眺,周霄,朱彦辰,等 .考虑乘客时空灵活性的需求响应客货联运动态调度[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2023,23(4):211-227. |
| WU Wei-tiao, ZHOU Xiao, ZHU Yan-chen,et al .Demand-responsive dynamic scheduling considering passengers’ spatio temporal flexibility for passenger and freight transportation[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2023,23(4):211-227. | |
| 12 | ALBAREDA-SAMBOLA M, FERNÁNDEZ E, LAPORTE G .The dynamic multiperiod vehicle routing problem with probabilistic information[J].Computers & Operations Research,2014,48:31-39. |
| 13 | NÚÑEZ A, CORTÉS C E, SÁEZ D,et al .Multiobjective model predictive control for dynamic pickup and delivery problems[J].Control Engineering Practice,2014,32:73-86. |
| 14 | 刘亚杰,吴志永 .灾后动态环境下基于MPC的应急运输实时调度[J].控制与决策,2018,33(12):2131-2141. |
| LIU Ya-jie, WU Zhi-yong .Real-time relief transportation planning based on MPC in post-disaster dynamic environment[J].Control and Decision,2018,33(12):2131-2141. | |
| 15 | 石建力,谢丽蓉 .近似动态规划求解随机需求分批配送车辆路径问题[J].运筹与管理,2023,32(5):16-22. |
| SHI Jianli, XIE Lirong .Approximate dynamic programming for the split delivery vehicle routing problem with stochastic demands[J].Operations Research and Management Science,2023,32(5):16-22. | |
| 16 | LI G L, CHEN Y X, WANG Y M,et al .City-scale synthetic individual-level vehicle trip data[J].Scientific Data,2023,10(1):96/1-18. |
| 17 | 刘小寒,马晓磊,刘钲可 .面向公共交通的电动自动驾驶模块车调度优化[J].中国公路学报,2022,35(3):240-248. |
| LIU Xiao-han, MA Xiao-lei, LIU Zheng-ke .Dispatch optimization of electric autonomous modular vehicles for public transport[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2022,35(3):240-248. |
| [1] | WEN Shengping, SU Yilong, QU Hongyi. Design of a Cascade Controller of Trajectory Tracking for Omnidirectional AGV Driven by Mecanum Wheels [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(1): 49-61. |
| [2] | YUAN Renteng, WANG Chenzhu, XIANG Qiaojun, ZHENG Ou, DING Shengxuan. Trajectory Data-Driven Model for Vehicle Lane Change Intention Recognition [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(6): 34-44. |
| [3] | LONG Xueqin, WANG Han, WANG Ruixuan. Taxi Trajectory Characteristics Analysis Based on Frequent Sequence Mining [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(6): 24-33. |
| [4] | ZHANG Wenhui, LIU Tuo, SONG Yajing, et al. Identification of Hazardous Driving Hotspots of Conventional Urban Bus Based on Spatial Autocorrelation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(4): 138-150. |
| [5] | ZHAO Xiaomei, ZHU Xiangyuan, WANG Qin, et al. Operational Reliability Optimization Strategies of Multi-type Bus Lines [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(8): 32-39. |
| [6] | WENG Jiancheng, WANG Maolin, LIN Pengfei, et al. Cross-line Combined Bus Scheduling Optimization Method Based on Passenger Flow Characteristic Identification [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 39-48. |
| [7] | YAO Qiangqiang, TIAN Ying, WANG Shengyuan, et al. Research on Path Tracking Control Strategy of Intelligent Vehicles Based on Force Drive [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(2): 33-41,57. |
| [8] | Chao-Yi Li. Model predicted control for underactuated ship path following based on extended state observer [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(12): 143-152. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jiaxu, YANG Xiong, SHI Zhengtang, et al. Path Planning and Tracking Control for Emergency Lane Change and Obstacle Avoidance of Vehicles [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(9): 86-93,106. |
| [10] | YIN Huajie, GUO Zhiyu, ZENG Jun. Simplified Predictive Torque Control for Induction Motor with Sliding Mode Speed-Sensorless [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(12): 18-26. |
| [11] | ZHANG Nian LUO Xia ZHANG Ke. Bus Travel Choice Reversals Based on the Equate-to-Differentiate Theory [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(9): 61-67. |
| [12] | QIN Datong QIN Ling. Energy Management Strategy for a Power-split Hybrid Electric Vehicle Based on Explicit Stochastic Model Predictive Control [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(7): 112-120. |
| [13] |
SUN Chuanyang ZHANG Xin XI Lihe CHEN Hongwei .
Design for the Steering Controller of Autonomous
Vehicles at the Limits of Handling
|
| [14] | DU Guiping DU Fada. Application of Finite Set Model Predictive Control in VIENNA Rectifier [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(10): 9-14. |
| [15] | CHAI Linguo CAI Baigen SHANGGUAN Wei WANG Jian WANG Huashen. A Construction Approach Based on Kinematic Simulation Environment for Networked Intelligent Vehicles [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(1): 66-77. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||