| 1 |
SCHMIEDT M, HE P, RINDERKNECHT S .Target state optimization:drivability improvement for vehicles with dual clutch transmissions[J].Applied Sciences-Basel,2022,12(20):1-30.
|
| 2 |
边扬,俞洁,赵晓华,等 .导航播报措辞对驾驶行为的综合影响研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(11):30-37,54.
|
|
BIAN Yang, YU Jie, ZHAO Xiaohua,et al .Research on the comprehensive influence of navigation broadcast wording on driving behavior[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2020,48(11):30-37,54.
|
| 3 |
LIU P H, ZHANG T, ZHAO X B .Vehicle drivability evaluation and pedal-acceleration response analysis [J].International Journal on Advances in Information Sciences and Service Sciences,2013,5:506-513.
|
| 4 |
WI H, PARK J, LEE J .The influence of noise in vehicles on the driver’s subjective evaluation of driveability [J].Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part D:Journal of Automobile Engineering,2018,232(11):1494-1500.
|
| 5 |
林彦名,蒋贤芳,蒋华梁 .基于驾驶性主观评价和AVL-Drive客观测试的整车驾驶性主客观评价方法 [J].时代汽车,2022(21):13-15.
|
|
LIN Yanming, JIANG Xianfang, JIANG Hualiang .Subjective and objective evaluation method of vehicle drivability based on subjective evaluation of drivability and objective test of AVL-Drive[J].Auto Time,2022(21):13-15.
|
| 6 |
吴文文,陈帅 .插电式混合动力汽车驾驶性主观评价方法[J].汽车实用技术,2023,48(19):127-132.
|
|
WU Wenwen, CHEN Shuai .Subjective evaluation methods of driving performance for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles[J].Automobile Applied Technology,2023,48(19):127-132.
|
| 7 |
张宸维,林方圆 .电动汽车驾驶性主观评价研究 [J].汽车实用技术,2019(18):8-11.
|
|
ZHANG Chenwei, LIN Fangyuan .Subjective evaluation research of drivability of pure electric vehicle[J].Automobile Applied Technology,2019(18):8-11.
|
| 8 |
逯家鹏,杨雪峰,张丽雪,等 .用户常用加速工况车辆驾驶性客观评价指标的设定与试验研究[J].汽车技术,2022(6):40-46.
|
|
LU Jiapeng, YANG Xuefeng, ZHANG Lixue,et al .Research on drivability objective index setting and test on cceleration condition in common use[J].Automobile Technology,2022(6):40-46.
|
| 9 |
朱翔宇 .车辆起步加速驾驶性客观评价及优化[J].汽车工程学报,2022,12(1):47-54.
|
|
ZHU Xiangyu .Objective evaluation and optimization of vehicle starting performance[J].Chinese Journal of Automotive Engineering,2022,12(1):47-54.
|
| 10 |
SHIN C W, KIM H, KIM M K,et al .Development of an evaluation method for quantitative driveability in heavy-duty vehicles (Article)[J].Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology,2014,28(5):1615-1621.
|
| 11 |
SCHOEGGL P, RAMSCHAK E .Vehicle driveability assessment using neural networks for development,calibration and quality tests[J].SAE Transactions,2000,109(6):1052-1061.
|
| 12 |
李立治 .混合动力汽车驾驶性研究[D].天津:河北工业大学,2022.
|
| 13 |
李波 .基于底盘测功机的整车驾驶性客观测试与评价方法研究[D].合肥:合肥工业大学,2023.
|
| 14 |
莫易敏,胡恒,王骏,等 .基于神经网络的车辆急加速工况驾驶性评价研究[J].汽车技术,2021(4):12-18.
|
|
MO Yimin, HU Heng, WANG Jun,et al .Research on driveability evaluation of vehicles on tip-in condition based on neural network[J].Automobile Technology,2021(4):12-18.
|
| 15 |
HUANG W, LIU H J, MA Y F .Drivability evaluation model using principal component analysis and optimized extreme learning machine[J].Journal of Vibration and Control,2019,25(16):2274-2281.
|
| 16 |
徐福来 .汽车驾驶性能的评估方法研究 [D].长春:吉林大学,2023.
|
| 17 |
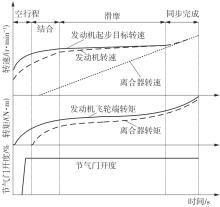
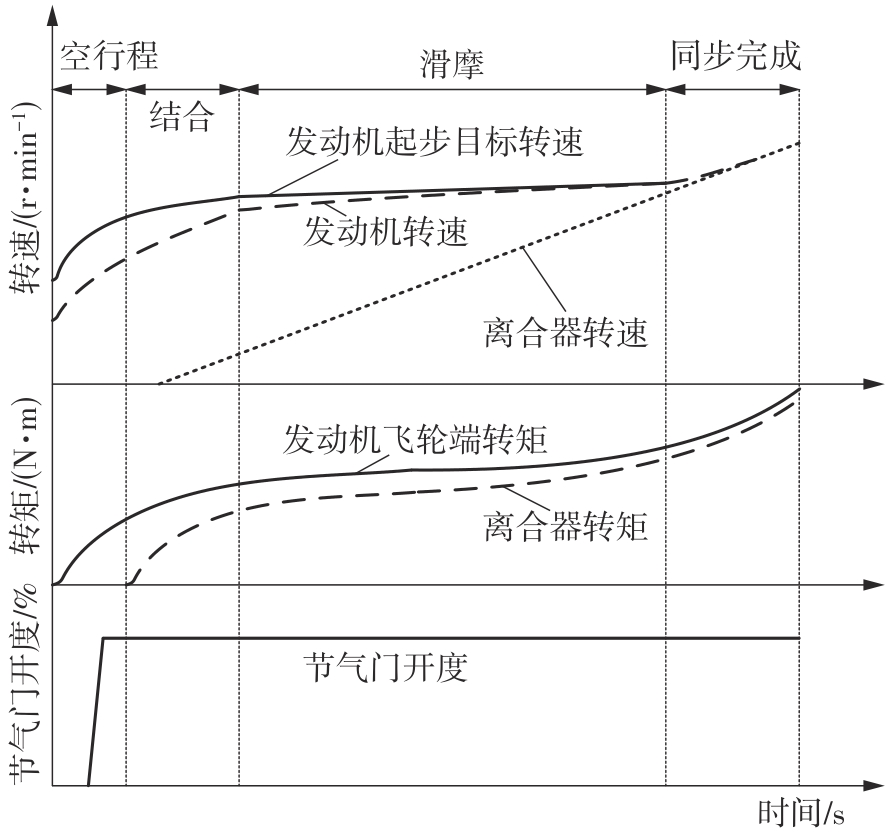
宋世欣,张元侠,刘科,等 .双离合器自动变速器控制品质评价指标分析[J].汽车工程,2015,37(8):925-930.
|
|
SONG Shixin, ZHANG Yuanxia, LIU Ke,et al .Analysis on the evaluation metrics of control quality for vehicles with dual clutch transmission[J].Automotive Engineering,2015,37(8):925-930.
|
| 18 |
BENTÉJAC C, CSÖRGŐ A, MARTÍNEZ-MUÑOZ G .A comparative analysis of gradient boosting algorithms[J].Artificial Intelligence Review,2021,54(3):1937-1967.
|
| 19 |
VIMBI V, SHAFFI N, MAHMUD M .Interpreting artificial intelligence models:a systematic review on the application of LIME and SHAP in Alzheimer’s disease detection[J].Brain Informatics,2024,11:10/1-29.
|
 ), SUN Xiankui, WANG Pengcheng
), SUN Xiankui, WANG Pengcheng