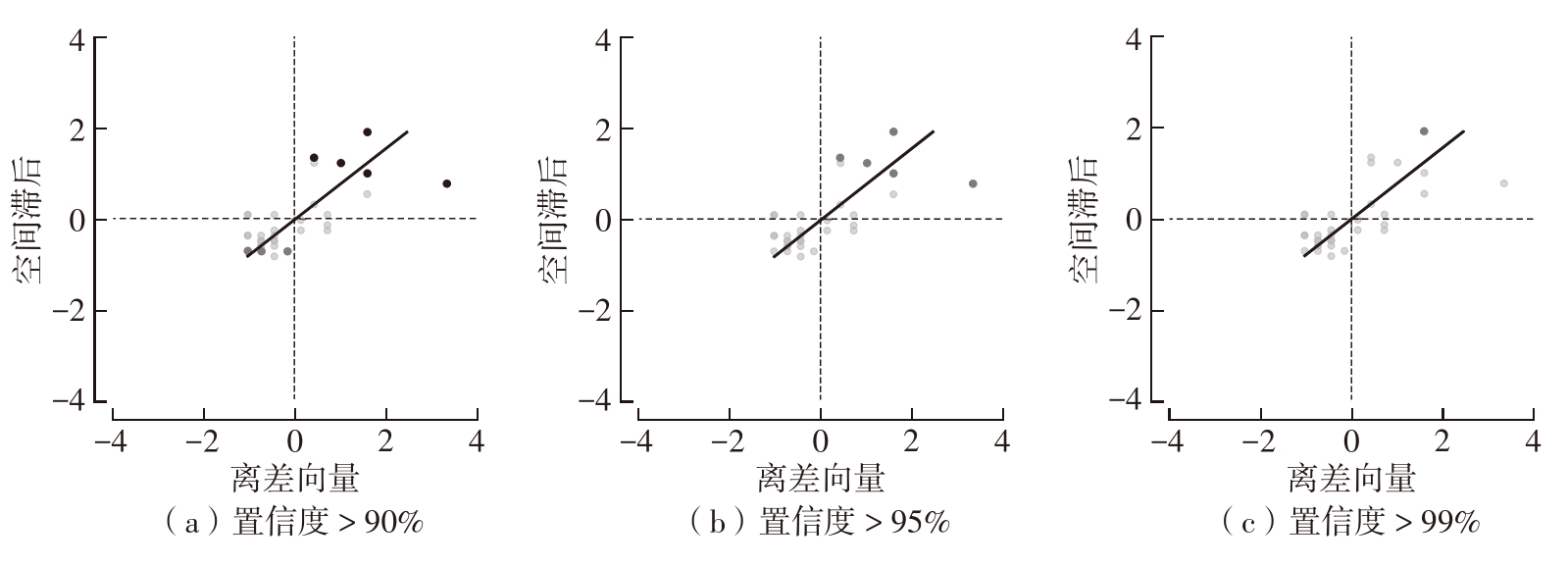
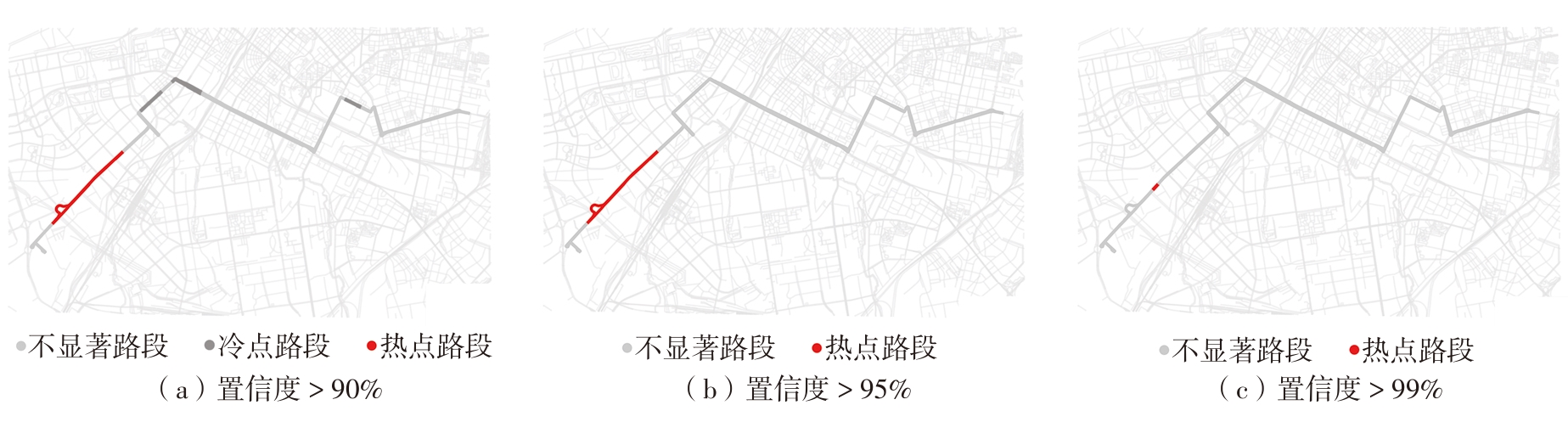
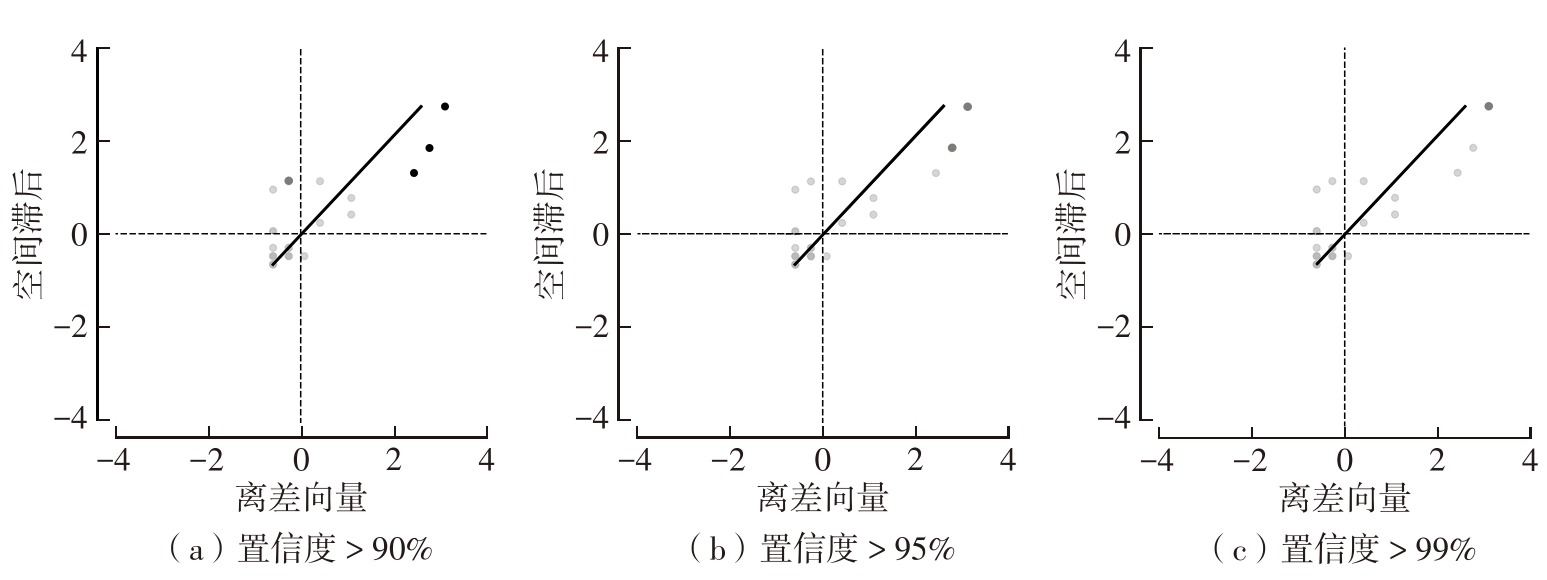
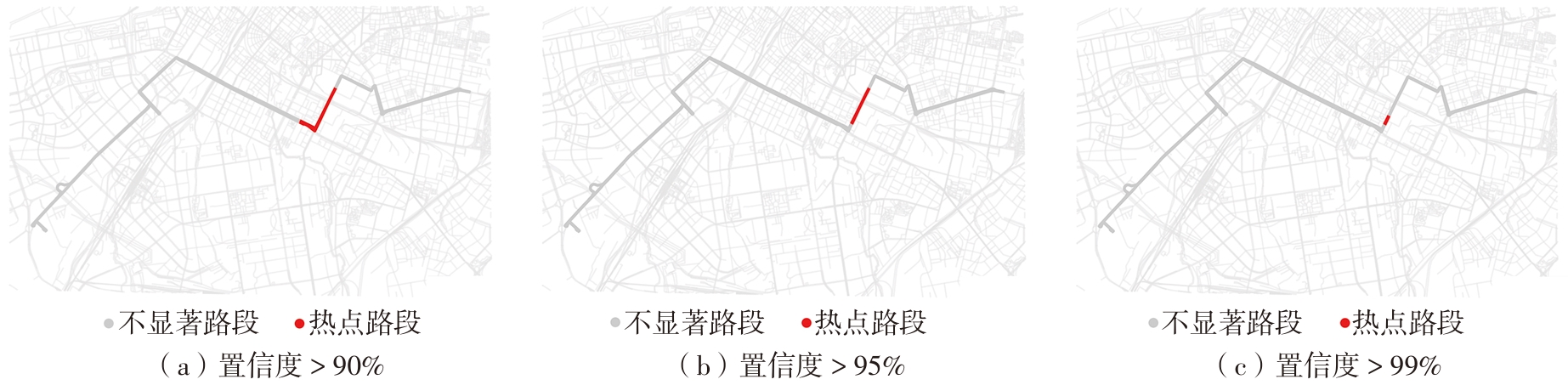
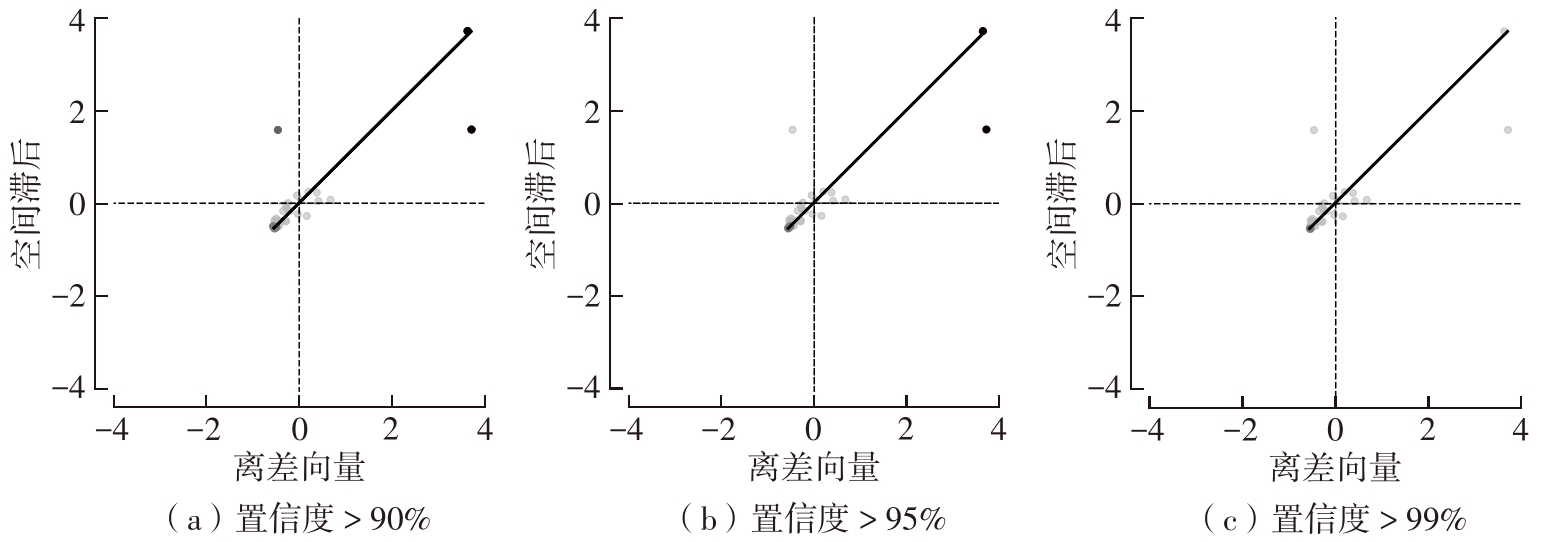
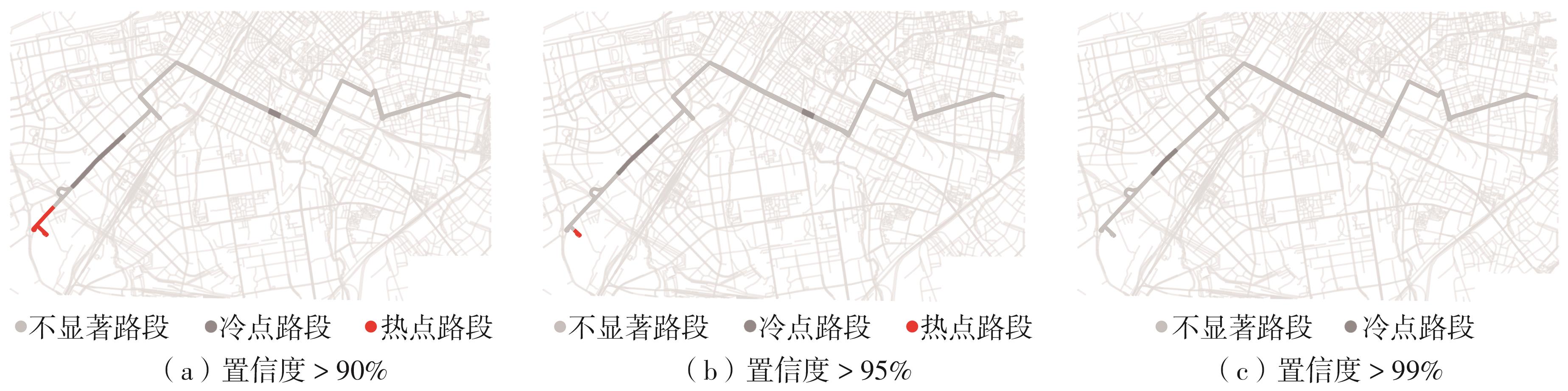
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 138-150.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230026
• Traffic Safety • Previous Articles
Identification of Hazardous Driving Hotspots of Conventional Urban Bus Based on Spatial Autocorrelation
ZHANG Wenhui1 LIU Tuo1,2† SONG Yajing1 SU Jiaqi1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin 150040, Heilongjiang, China
2.Commercial Vehicle Research Institute, BYD Auto Industry Company Limited, Shenzhen 518118, Guangdong, China
-
Received:2023-01-19Online:2024-04-25Published:2023-05-09 -
Contact:刘拓(1990-),男,硕士,主要从事交通安全研究。 E-mail:liutuo901010@163.com -
About author:张文会(1978-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事交通安全研究。E-mail:rayear@163.com -
Supported by:the Key R&D Program of Heilongjiang Province(JD22A014)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Wenhui, LIU Tuo, SONG Yajing, et al. Identification of Hazardous Driving Hotspots of Conventional Urban Bus Based on Spatial Autocorrelation[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(4): 138-150.
share this article
Table 10
Comparison between average values of AIC and BIC in four models"
| 危险驾驶状态 | AIC平均值 | BIC平均值 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | |
| 速度过快 | 470.392 | 449.513 | 449.781 | 446.734 | 485.049 | 462.170 | 464.438 | 441.391 |
| 急加速 | 183.228 | 178.090 | 173.676 | 179.220 | 197.885 | 190.747 | 188.333 | 173.877 |
| 急减速 | 158.788 | 146.418 | 146.338 | 150.546 | 173.445 | 159.075 | 160.995 | 145.203 |
| 急转弯 | 469.708 | 452.771 | 453.771 | 453.553 | 484.365 | 465.428 | 468.428 | 448.210 |
Table 11
Calculated results for over speed data in four models"
| 变量 | 变量的系数 | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | |
| k1 | 0.002 | 0.473 | 0.623 | 0.598 | 0.010** | 0.012* | 0.000*** | 0.001*** |
| k2 | 46.463 | 2.446 | -14.642 | -20.065 | 0.304 | 0.908 | 0.454 | 0.289 |
| k3 | 2.320 | -2.393 | -0.671 | 1.806 | 0.067 | 0.038* | 0.083 | 0.054 |
| k4 | 277.868 | -34.783 | -309.339 | 3.039 | 0.061 | 0.089 | 0.012* | 0.099 |
| k5 | 1.353 | 4.656 | 8.908 | 0.421 | 0.917 | 0.448 | 0.282 | 0.958 |
| k6 | -124.513 | 997.205 | 4 389.910 | 9 474.280 | 0.988 | 0.806 | 0.280 | 0.014* |
| k7 | 98.505 | 18.076 | -25.140 | -1.799 | 0.266 | 0.662 | 0.469 | 0.959 |
| k8 | -203.237 | -117.154 | -43.982 | -42.111 | 0.024* | 0.015* | 0.052 | 0.025* |
| k9 | -121.983 | -71.183 | -24.651 | -18.955 | 0.001*** | 0.000*** | 0.020* | 0.033* |
Table 12
Calculated results for sharp acceleration data in four models"
| 变量 | 变量的系数 | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | |
| k1 | -0.002 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.072 | 0.070 | 0.021* | 0.010* |
| k2 | 0.001 | -0.068 | 0.019 | -0.383 | 0.999 | 0.844 | 0.953 | 0.260 |
| k3 | -0.015 | 0.009 | 0.025 | -0.041 | 0.808 | 0.830 | 0.589 | 0.463 |
| k4 | -2.232 | -2.288 | -3.214 | -1.984 | 0.716 | 0.589 | 0.358 | 0.564 |
| k5 | -0.070 | -0.048 | -0.089 | -0.217 | 0.632 | 0.632 | 0.450 | 0.140 |
| k6 | -86.015 | -37.951 | 16.775 | -0.469 | 0.379 | 0.572 | 0.800 | 0.995 |
| k7 | 0.569 | 0.639 | 0.577 | -0.388 | 0.564 | 0.346 | 0.325 | 0.546 |
| k8 | -0.178 | 0.388 | 1.069 | 0.198 | 0.926 | 0.770 | 0.358 | 0.869 |
| k9 | -0.597 | -0.420 | -0.338 | -0.471 | 0.013* | 0.011* | 0.026* | 0.010** |
Table 13
Calculated results for sharp deceleration data in four models"
| 变量 | 变量的系数 | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | |
| k1 | -0.003 | -0.002 | 0.770 | -0.003 | 0.268 | 0.061 | 0.107 | 0.184 |
| k2 | 0.002 | -0.023 | 0.019 | 0.061 | 0.996 | 0.078 | 0.627 | 0.770 |
| k3 | -0.004 | 0.013 | 0.129 | 0.078 | 0.927 | 3.215 | 0.401 | 0.019* |
| k4 | 3.049 | 3.213 | 0.313 | 3.215 | 0.469 | -0.092 | 0.220 | 0.129 |
| k5 | 0.203 | 0.086 | 0.787 | -0.092 | 0.052 | 11.785 | 0.531 | 0.313 |
| k6 | -42.835 | -24.614 | -41.489 | 11.785 | 0.519 | 0.530 | 0.301 | 0.787 |
| k7 | 1.566 | 1.399 | 1.216 | 1.771 | 0.027* | 0.000*** | 0.000*** | 0.000*** |
| k8 | -0.074 | 0.181 | 0.044 | 0.584 | 0.955 | 0.815 | 0.949 | 0.425 |
| k9 | -0.310 | -0.343 | -0.642 | -0.631 | 0.239 | 0.026* | 0.001** | 0.004** |
Table 14
Calculated results for sharp turn data in four models"
| 变量 | 变量的系数 | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | OSL模型 | SLM模型 | SEM模型 | SDM模型 | |
| k1 | 0.337 | 0.336 | 0.232 | 0.307 | 0.396 | 0.120 | 0.249 | 0.148 |
| k2 | 2.046 | -8.331 | 6.479 | 8.330 | 0.963 | 0.732 | 0.781 | 0.717 |
| k3 | 12.012 | 7.464 | 10.613 | 15.373 | 0.036* | 0.014* | 0.003** | 0.000*** |
| k4 | -38.273 | -231.718 | -468.536 | -363.328 | 0.943 | 0.434 | 0.054 | 0.012** |
| k5 | -3.505 | -0.472 | 2.868 | 8.337 | 0.785 | 0.947 | 0.760 | 0.403 |
| k6 | 19 564.800 | 9 071.940 | 622.866 | -62.169 | 0.030* | 0.054 | 0.898 | 0.990 |
| k7 | 42.748 | 38.389 | 4.989 | 18.188 | 0.621 | 0.418 | 0.906 | 0.669 |
| k8 | 231.132 | 210.451 | 262.946 | 180.185 | 0.180 | 0.025* | 0.001** | 0.024* |
| k9 | -11.124 | -23.757 | -9.689 | -42.520 | 0.739 | 0.198 | 0.673 | 0.074 |
| 1 | 左精力,王秋平,陈君 .城市公交GPS数据与IC卡数据时空特性融合算法[J].交通信息与安全,2021,39(2):101-108. |
| ZUO Jingli, WANG Qiuping, CHEN Jun .A fusion algorithm based on spatiotemporal characteristics of the GPS data and IC card data in urban public transportation[J].Journal of Transport Information and Safety,2021,39(2):101-108. | |
| 2 | 吴红波,郭敏,杨肖肖 .基于地图API和GIS路径分析的城市公交车路网优化[J].北京交通大学学报,2022,46(1):69-78. |
| WU Hongbo, GUO Min, YANG Xiaoxiao .Optimization of urban bus network based on map API data and GIS path analysis[J].Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University,2022,46(1):69-78. | |
| 3 | 陈辉,蒋圭峰,姜桂圆,等 .基于海量公交轨迹数据挖掘的地图匹配算法[J].计算机应用,2018,38(7):1923-1928. |
| CHEN Hui, JIANG Guifeng, JIANG Guiyuan,et al .Map matching algorithm based on massive bus trajectory data mining[J].Journal of Computer Applications,2018,38(7):1923-1928. | |
| 4 | LI P, ABDEL-ATY M, YUAN J .Using bus critical driving events as surrogate safety measures for pedestrian and bicycle crashes based on GPS trajectory data[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention,2021,150:105924/1-8. |
| 5 | 薛清文,蒋愚明,陆键 .基于轨迹数据的危险驾驶行为识别方法[J].中国公路学报,2020,33(6):84-94. |
| XUE Qing-wen, JIANG Yu-ming, LU Jian .Risky driving behavior recognition based on trajectory data[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2020,33(6):84-94. | |
| 6 | TIMMERMANS C P M, ALHAJYASEEN W K M, ROSS V,et al .Introducing a multi-variate classification method:risky driving acceptance among different heterogeneous driver sub-cultures[J].Journal of Safety Research,2020,73:81-91. |
| 7 | HAN W, ZHAO J .Driver behaviour and traffic accident involvement among professional urban bus drivers in China[J].Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour,2020,74:184-197. |
| 8 | 纪少波,张珂,李伦,等 .基于纯电动汽车高频数据的驾驶风格分类方法[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(2):273-282. |
| JI Shaobo, ZHANG Ke, LI Lun,et al .Driving style classification method based on high frequency data from pure electric vehicles[J].Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2022,50(2):273-282. | |
| 9 | 王海星,王翔宇,王招贤,等 .基于数据挖掘的危险货物运输风险驾驶行为聚类分析[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2020,20(1):183-189. |
| WANG Hai-xing, WANG Xiang-yu, WANG Zhao-xian,et al .Dangerous driving behavior clustering analysis for hazardous materials transportation based on data mining[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2020,20(1):183-189. | |
| 10 | 孙川,吴超仲,褚端峰,等 .基于车联网数据挖掘的营运车辆驾驶速度行为聚类研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2015,15(6):82-87. |
| SUN Chuan, WU Chao-zhong, CHU Duan-feng,et al .Driving speed behavior clustering for commercial vehicle based on connected vehicle data mining[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2015,15(6):82-87. | |
| 11 | 李彦瑾,罗霞 .突发环境下城市道路网关键路段集识别[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2018,18(2):128-135. |
| LI Yan-jin, LUO Xia .Identification of urban road network’s critical links set under emergency environment[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2018,18(2):128-135. | |
| 12 | 李君羡,吴志周,沈宙彪 .基于行程时间影响的关键路段识别与查找[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2020,20(6):129-135. |
| LI Jun-xian, WU Zhi-zhou, SHEN Zhou-biao .Identification and retrieval of critical segments based on travel time effect[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2020,20(6):129-135. | |
| 13 | 邓红星,白伊杨 .考虑轨迹数据的公交运行状态识别[J].重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2023,37(2):233-240. |
| DENG Hongxing, BAI Yiyang .Research of state recognition and application of GPS-based bus operation[J].Journal of Chongqing University of Technology(Natural Science),2023,37(2):233-240. | |
| 14 | 赵建东,贾卓瑾,梁营力,等 .基于浮动车数据的城市区域路网关键路段识别[J].北京交通大学学报,2021,45(4):54-60,78. |
| ZHAO Jiandong, JIA Zhuojin, LIANG Yingli,et al .Identification of key road sections in urban road network based on floating car data[J].Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University,2021,45(4):54-60,78. | |
| 15 | 苏飞,董宏辉,贾利民,等 .基于时空相关性的城市交通路网关键路段识别[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2017,17(3):213-221. |
| SU Fei, DONG Hong-hui, JIA Li-min,et al .Identification of critical section in urban traffic road network based on space-time correlation[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2017,17(3):213-221. | |
| 16 | 刘家良,孙立双 .结合空间相关性的城市热点路段提取方法[J].测绘通报,2018(6):73-77. |
| LIU Jialiang, SUN Lishuang .Extraction of urban hot sections based on spatial correlation[J].Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2018(6):73-77. | |
| 17 | 杨洋,邵哲平,赵强,等 .基于厦门港的海上交通事故地理空间分布及风险预测研究[J].地球信息科学学报,2022,24(9):1676-1687. |
| YANG Yang, SHAO Zheping, ZHAO Qiang,et al .Geographical spatial distribution and risk prediction of maritime traffic accidents in port of Xiamen[J].Journal of Geo-information Science,2022,24(9):1676-1687. | |
| 18 | 廖聪,邬伦,蔡恒,等 .城市电动自行车违规充电隐患的空间分布及其影响因素[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2021,57(4):671-678. |
| LIAO Cong, WU Lun, CAI Heng,et al .Spatial distribution and influencing factors of unsafe charging for electric bicycles in urban areas[J].Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,2021,57(4):671-678. | |
| 19 | HUANG W, ZHANG Y, YIN D,et al .Urban bus accident analysis:based on a Tropos goal risk-accident framework considering learning from incidents process[J].Reliability Engineering & System Safety,2021,216:107918/1-10. |
| 20 | 刘辉,章国鹏,王羿童,等 .无控制交叉口交通安全影响因素分析[J].公路交通科技,2019,36(9):110-116. |
| LIU Hui, ZHANG Guo-peng, WANG Yi-tong,et al .Analysis on factors affecting traffic safety at uncontrolled intersection[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2019,36(9):110-116. | |
| 21 | 朱建全,石琴 .城市快速路路段车速分布特征及影响因素研究[J].合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,41(1):95-101. |
| ZHU Jianquan, SHI Qin .Research on vehicle speed distribution characteristics of urban expressway section and influence factors[J].Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science),2018,41(1):95-101. | |
| 22 | GITELMAN V, KORCHATOV A, ELIAS W .An examination of the safety impacts of bus priority routes in major Israeli cities[J].Sustainability,2020,12(20):8617/1-17. |
| 23 | 张道文,母尧尧,王朝健,等 .城市道路交通事故特性及严重程度研究[J].安全与环境学报,2022,22(2):599-605. |
| ZHANG Dao-wen, MU Yao-yao, WANG Chao-jian,et al .Research on characteristics and severity of urban road traffic accidents[J].Journal of Safety and Environment,2022,22(2):599-605. | |
| 24 | 郭淼,赵晓华,姚莹,等 .基于驾驶行为和交通运行状态的事故风险研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(9):29-38. |
| GUO Miao, ZHAO Xiaohua, YAO Ying,et al .Study on accident risk based on driving behavior and traffic operating status[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(9):29-38. | |
| 25 | 任慧君,许涛,李响 .利用车载GPS轨迹数据实现公交车驾驶安全性分析[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2014,39(6):739-744. |
| REN Huijun, XU Tao, LI Xiang .Driving behavior analysis based on trajectory data collected with vehicle-mounted GPS receivers[J].Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2014,39(6):739-744. | |
| 26 | SUN Chao, CHEN Xiaohong, ZHANG H M,et al .Evaluation of driving behavior based on massive vehicle trajectory data[J].Journal of Southeast University (English Edition),2019,35(4):502-508. |
| [1] | TANG Qianlong, PENG Limin, DENG E, et al. Safety of Existing Intersection High-Speed Railway Trains Under the Condition of Sheild Tunnel Penetration Construction Considering the Stochastic Field [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(4): 95-103. |
| [2] | CHEN Guohua, XIE Mulin, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Study on Hydrogen Leakage-Explosion and Risk of Hydrogen Bus in Station [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(2): 84-94. |
| [3] | ZHAO Xiaomei, ZHU Xiangyuan, WANG Qin, et al. Operational Reliability Optimization Strategies of Multi-type Bus Lines [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(8): 32-39. |
| [4] | HAN Le, JIANG Yihua. Robust TruncatedL1-L2Total Variation Sparse Restoration Models [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(5): 45-53,140. |
| [5] | ZHANG Wenhui, SU Jiaqi, HA Zihong, et al. Location and Capacity Optimization Model of Battery-Swapped Electric Bus Charging Station [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 126-134. |
| [6] | HU Xinghua, CHEN Xinghui, WANG Ran, et al. Optimization Model of Bus Priority Control Considering Carbon Emissions with Stochastic Characteristics [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 160-170. |
| [7] | BIE Yiming, ZHU Aoze, CONG Yuan. Electric Bus Scheduling Method Considering Differences in the State of Health of Batteries [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 11-21. |
| [8] | YANG Min, CHEN Shantao, JIANG Ruiyu, et al. Flexible Bus Scheduling Optimization for Integrated Hub Connections in the Context of MaaS [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 22-30. |
| [9] | WENG Jiancheng, WANG Maolin, LIN Pengfei, et al. Cross-line Combined Bus Scheduling Optimization Method Based on Passenger Flow Characteristic Identification [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 39-48. |
| [10] | LONG Xueqin, LI Jingtao, WANG Jianjun, et al. Collaborative Optimization of Departure Timetable for Common Bus Lines Under Real-Time Information [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(2): 23-32. |
| [11] | WU Jiaorong XIE Jinhong WANG Yuqin. The Profiling Method of Instability of Bus Route Operation and Its Application [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(2): 15-22. |
| [12] | SHEN Chan SUN Yao CUI Hongjun. Collaborative Optimization of Urban Conventional Bus and Customized Bus Under Epidemic Prevention and Control [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(7): 34-41. |
| [13] | SONG Xianmin, LENG Ning, JIANG Jingling, et al. Bus Priority Signal Control Method Based on Variable Phase in Internet Vehicles Environment [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(5): 18-27. |
| [14] | CHENG Wenming, ZHANG Daoyu, CHEN Qingrong, et al. A Directly Robust Adaptive Neural Network Controller for an Underacuated Crane [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(5): 120-128,144. |
| [15] | LIAO Yanfen, ZHANG Manyu, CHEN Shunkai, et al. Study on MILD Combustion of MSW Pyrolysis Gas Based on FLUENT [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(2): 9-16. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||