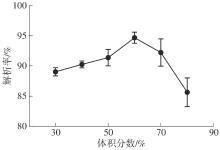
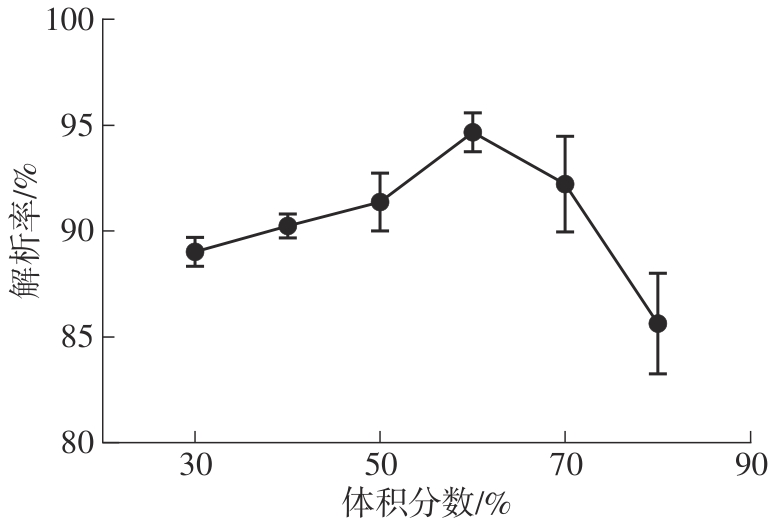
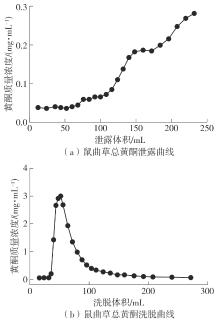
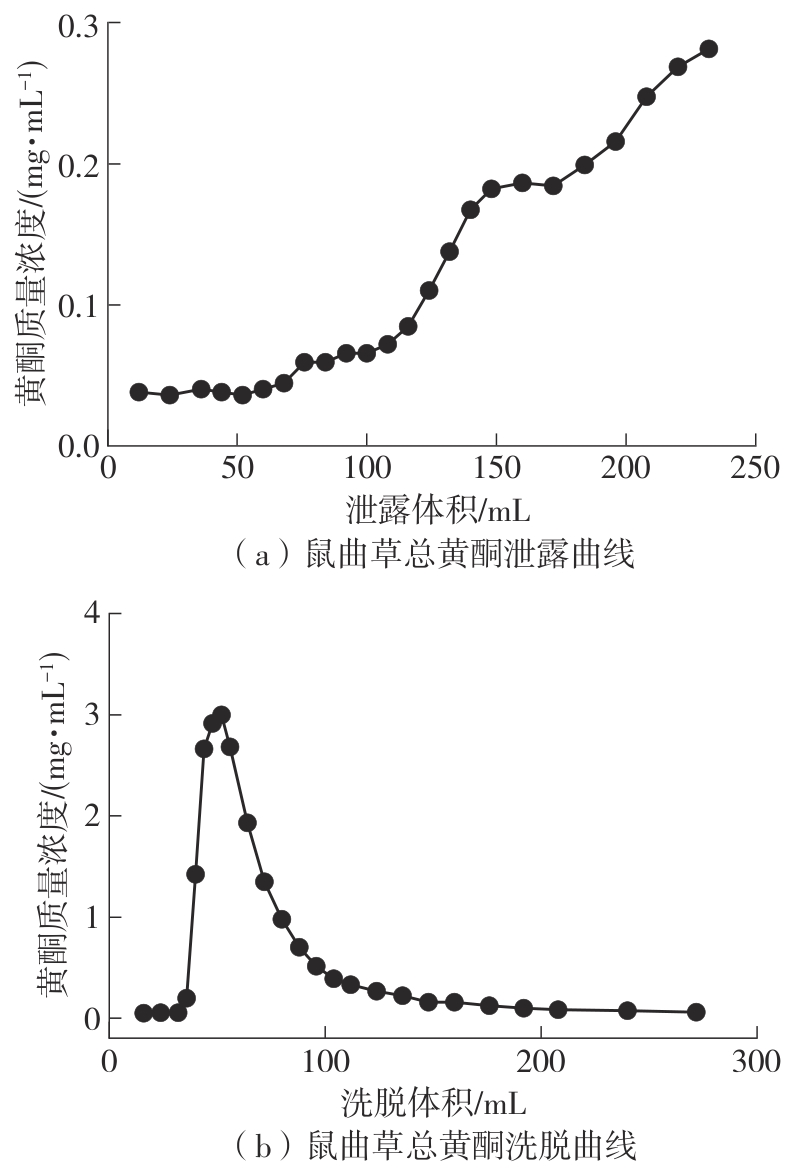
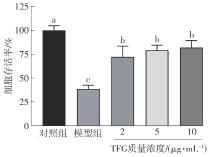
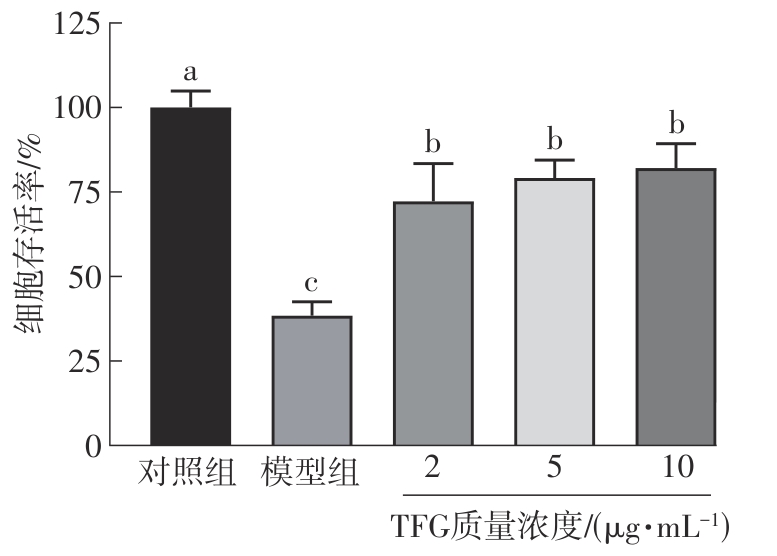
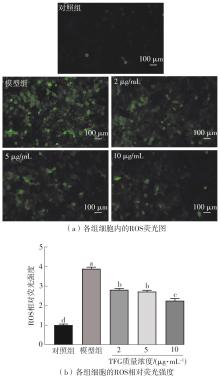
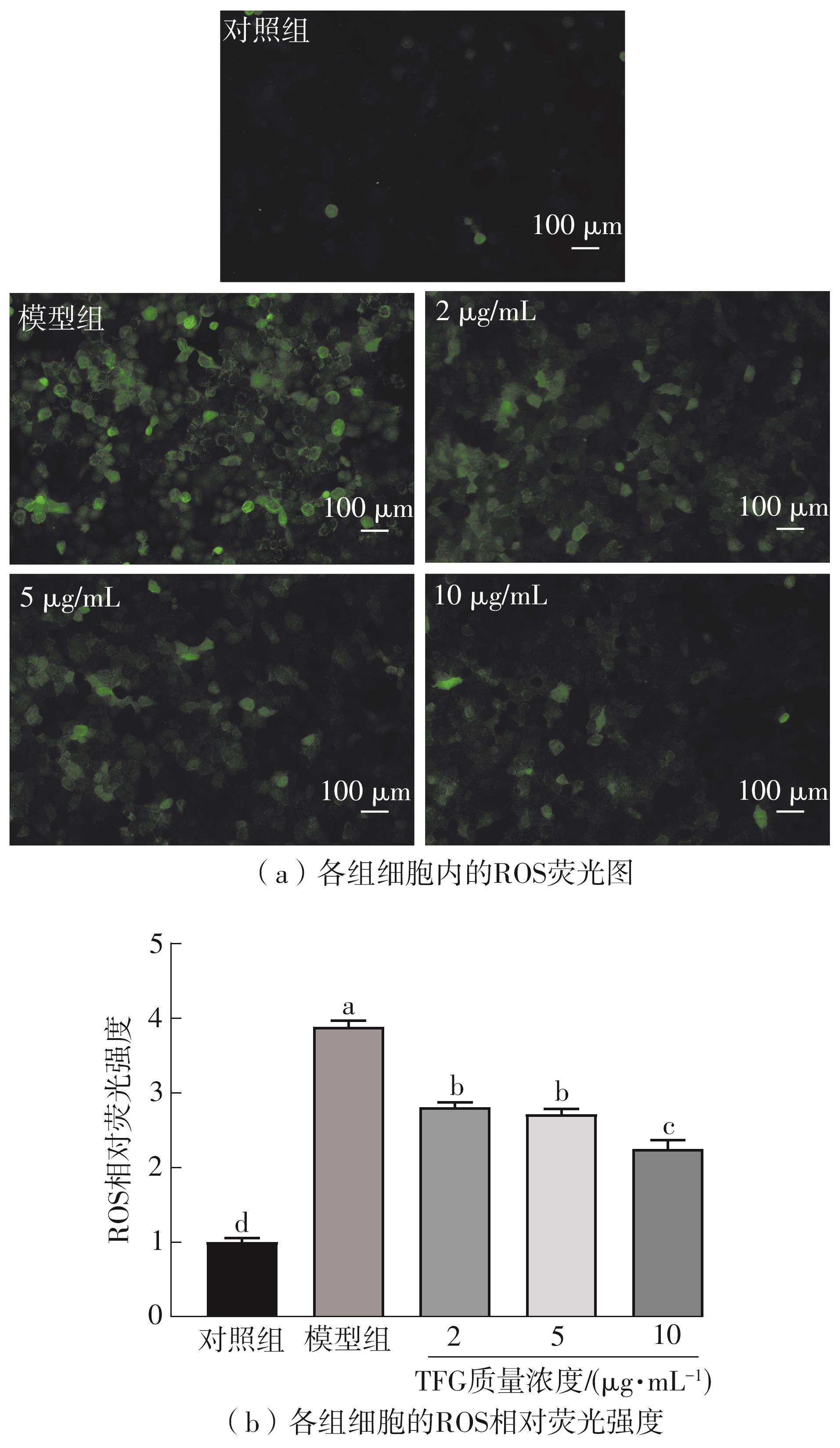
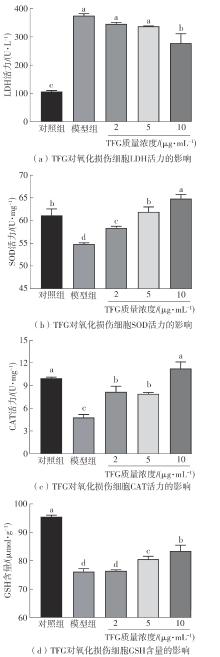
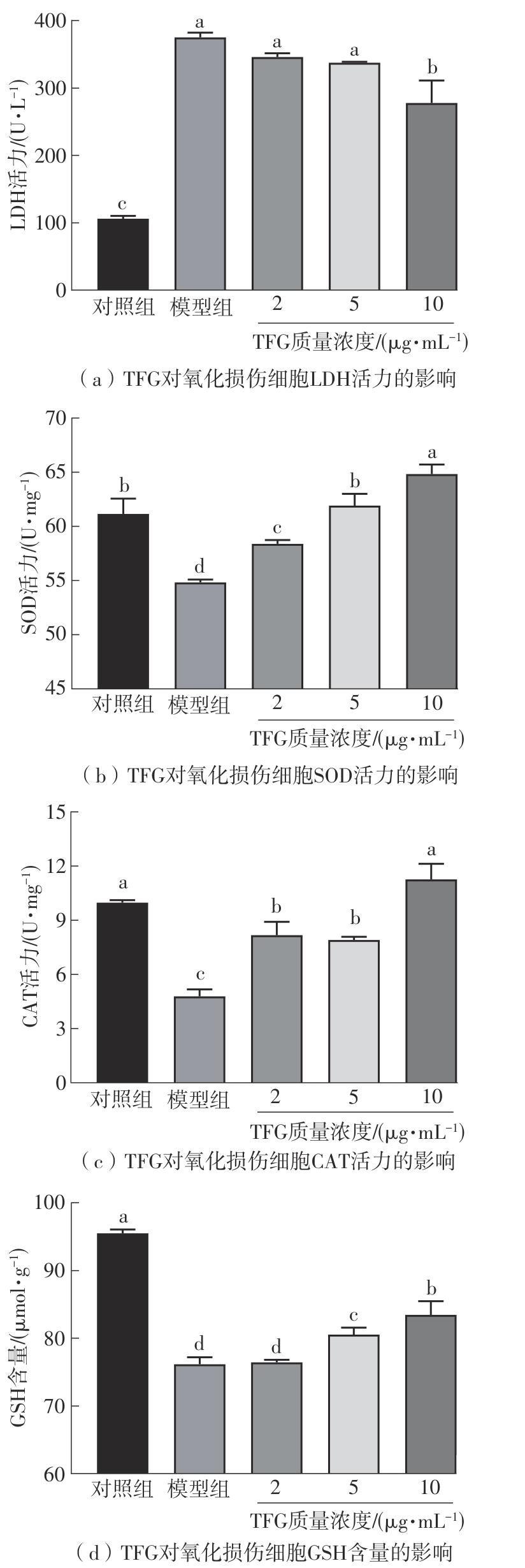
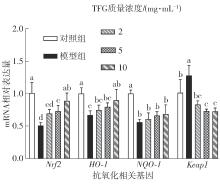
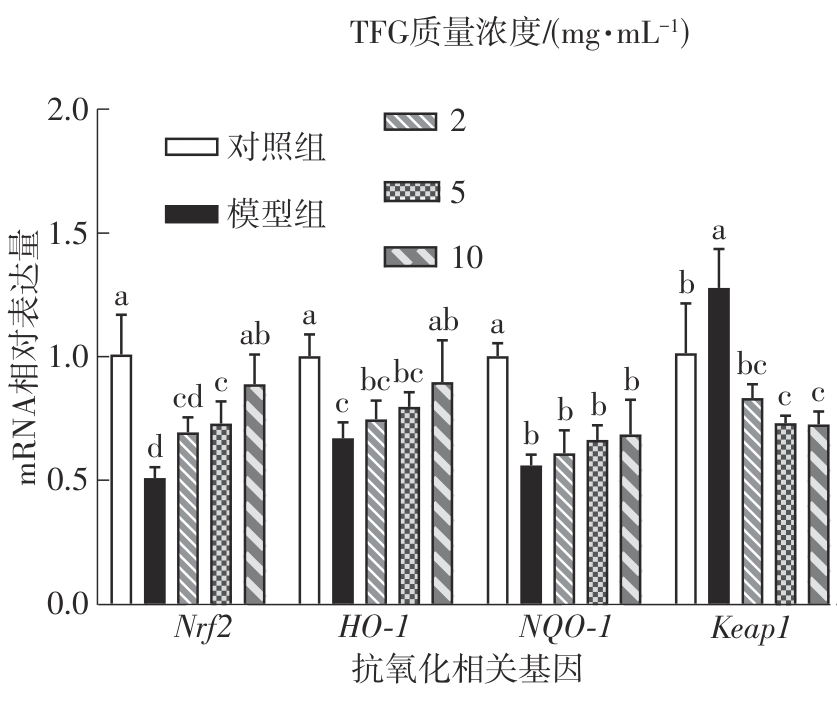
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 174-182.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.250082
• Food Science & Technology • Previous Articles
Purification of Total Flavonoids from Gnaphalium affine and Analysis on Its Antioxidant Stress Activity
ZHENG Bisheng, XU Yanting, XU Qiuxiong, FAN Xinlühui
- School of Food Science and Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2025-03-24Online:2025-10-25Published:2025-05-16 -
About author:郑必胜(1966 —),男,博士,副教授,主要从事天然产物活性及功能应用等研究。E-mail: febzheng@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2021A1515012110)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHENG Bisheng, XU Yanting, XU Qiuxiong, FAN Xinlühui. Purification of Total Flavonoids from Gnaphalium affine and Analysis on Its Antioxidant Stress Activity[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(10): 174-182.
share this article
Table 2
Qualitative and quantitative analysis results of total flavonoids from Gnaphalium affine"
| 物质名称 | 标准曲线方程 | 分子式 | m/z(母离子) | m/z(特征碎片离子) | 含量/(μg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 木犀草素 | y = 12 020.625 30x+4 729.323 55,R2= 0.999 59 | C15H10O6 | 285.0 | 133.0 | 289.57±7.50 |
| 金丝桃苷 | y = 43.555 58x+221.583 28,R2= 0.997 56 | C21H20O12 | 465.1 | 314.9 | 391.91±40.69 |
| 槲皮素 | y = 12 322.286 34x+8 480.388 26,R2= 0.999 7 | C15H10O7 | 301.1 | 151.0 | 228.44±4.12 |
| 圣草酚 | y = 4 904.533 10x+17 18.43 311,R2= 0.998 34 | C15H12O6 | 287.1 | 135.0 | 184.53±8.95 |
| 芹菜素 | y = 10 546.478 98x+3 461.369 17,R2= 0.999 78 | C15H10O5 | 269.1 | 117.0 | 165.30±7.52 |
| 野黄芩苷 | y = 10 471.028 93x+2 570.485 38,R2= 0.999 58 | C21H18O12 | 461.1 | 285.1 | 238.24±20.13 |
| 槲皮素-3-O-葡萄糖醛酸苷 | y = 17 298.137 41x+1 083.097 28,R2= 0.99 951 | C21H18O13 | 477.1 | 301.0 | 235.30±20.54 |
| 异鼠李素 | y = 21 684.797 56 x+3 282.213 40,R2= 0.999 84 | C16H12O7 | 315.1 | 300.0 | 53.97±0.78 |
| 绣线菊苷 | y = 6.077 28e4 x+20 680.97 361,R2= 0.998 88 | C21H20O12 | 463.1 | 301.0 | 40.17±1.20 |
| 二氢槲皮素 | y = 4 097.122 65 x-6 642.076 74,R2= 0.999 8 | C15H12O7 | 303.1 | 125.0 | 13.55±0.53 |
| 芹菜素-7-O-葡萄糖醛酸苷 | y = 14 375.38 407 x+4 848.90 482,R2= 0.999 54 | C21H18O11 | 445.1 | 269.1 | 17.25±0.88 |
| [1] | 曾建飞,霍春燕 .中国植物志(第75卷)[M].北京:科学出版社,1979. |
| [2] | ZENG W C, ZHANG W C, ZHANG W H,et al .The antioxidant activity and active component of Gnaphalium affine extract[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2013,58:311-317. |
| [3] | 陈桢 .鼠鞠草的生药学研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2010. |
| [4] | 王利民,何春梅,刘彩玲,等 .鼠曲草属植物的活性成分及其功效研究进展[J].江西农业学报,2019,31(10):63-69. |
| WANG Li-min, HE Chun-mei, LIU Cai-ling,et al .Research progress in chemical compounds and their multiple function of Gnaphalium affine [J].Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2019,31(10):63-69. | |
| [5] | 徐任生,赵维民,叶阳 .天然产物化学导论[M].北京:科学出版社,2006. |
| [6] | RANI V, DEEP G, SINGH R K,et al .Oxidative stress and metabolic disorders: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies[J].Life Sciences,2016,148:183-193. |
| [7] | KUBBEN N, MISTELI T .Shared molecular and cellular mechanisms of premature ageing and ageing-associated diseases[J].Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2017,18(10):595-609. |
| [8] | FATOKUN A A, TOME M, SMITH R A,et al .Protection by the flavonoids quercetin and luteolin against peroxide- or menadione-induced oxidative stress in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cells[J].Natural Product Research,2015,29(12):1127-1132. |
| [9] | SPORN M B, LIBY K T .NRF2 and cancer:the good,the bad and the importance of context[J].Nature Reviews Cancer,2012,12(8):564-571. |
| [10] | WARDYN J D, PONSFORD A H, SANDERSON C M .Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways[J].Biochemical Society Transactions,2015,43(4):621-626. |
| [11] | LEE J W, PARK H Y, PARK J .Enhanced extraction efficiency of flavonoids from Pyrus ussuriensis leaves with deep eutectic solvents[J].Molecules,2022,27(9):2798/1-11. |
| [12] | 荆常亮 .紫花苜蓿总黄酮的提取、纯化及其抗氧化活性研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2016. |
| [13] | WU S, WANG Y, GONG G,et al .Adsorption and desorption properties of macroporous resins for flavonoids from the extract of Chinese wolfberry (Lycium barbarum L.)[J].Food and Bioproducts Processing,2015,93:148-155. |
| [14] | 魏瑞敬 .木棉花黄酮的提取分离及祛痘功效研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2022. |
| [15] | 肖琨珉 .龙胆苦苷对过氧化氢诱导HepG2细胞氧化损伤的保护作用及机制研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2020. |
| [16] | WANG X, SU J, CHU X,et al .Adsorption and desorption characteristics of total flavonoids from Acanthopanax senticosus on macroporous adsorption resins[J].Molecules,2021,26(14):4162/1-19. |
| [17] | ALJAWARNEH R Y A, CHE Z M S, ZAKARIA F .Macroporous polymeric resin for the purification of flavonoids from medicinal plants:a review[J].Journal of Separation Science,2024,47(15):2400372/1-14. |
| [18] | ZHANG Y, LI S, WU X,et al .Macroporous resin adsorption for purification of flavonoids in Houttuynia cordata Thunb.[J].Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering,2007,15(6):872-876. |
| [19] | CHE Z M S, LEE S Y, TEO C Y,et al .Adsorption and desorption properties of total flavonoids from oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) mature leaf on macroporous adsorption resins[J].Molecules,2020,25(4):778/1-17. |
| [20] | 石青浩,李荣,李书启,等 .LC-ESI-MS/MS结合标准品比对鉴定野菜鼠曲草中的黄酮类化合物[J].食品研究与开发,2021,42(20):154-159. |
| SHI Qing-hao, LI Rong, LI Shu-qi,et al .Identification of flavonoids from a wild vegetable,Gnaphalium affine by LC-ESI-MS/MS coupled with standard comparison method[J].Food Research and Development,2021,42(20):154-159. | |
| [21] | 张美静 .金丝桃苷与槲皮素的抗氧化作用及其机制研究[D].天津:天津科技大学,2023. |
| [22] | KANG J, LI Z, WU T,et al .Anti-oxidant capacities of flavonoid compounds isolated from acai pulp (Euterpe oleracea Mart.)[J].Food Chemistry,2010,122(3):610-617. |
| [23] | PAREEK A, GODAVARTHI A, ISSARANI R,et al .Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of Fagonia schweinfurthii (Hadidi) Hadidi extract in carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cell line and rats[J].Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2013,150(3):973-981. |
| [24] | RASTOGI R P, SINGH S P, HÄDER D P,et al .Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by the oxidant-sensing probe 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate in the cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis PCC 7937[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2010,397(3):603-607. |
| [25] | XU J, ZHANG Y, REN G,et al .Inhibitory effect of delphinidin on oxidative stress induced by H2O2 in HepG2 cells[J].Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2020,2020(1):4694760/1-12. |
| [26] | LIANG R, CHENG S, DONG Y,et al .Intracellular antioxidant activity and apoptosis inhibition capacity of PEF-treated KDHCH in HepG2 cells[J].Food Research International,2019,121:336-347. |
| [27] | WILLMORE W G, STOREY K B .Purification and properties of glutathione reductase from liver of the anoxia-tolerant turtle,Trachemys scripta elegans [J].Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry,2007,297(1):139-149. |
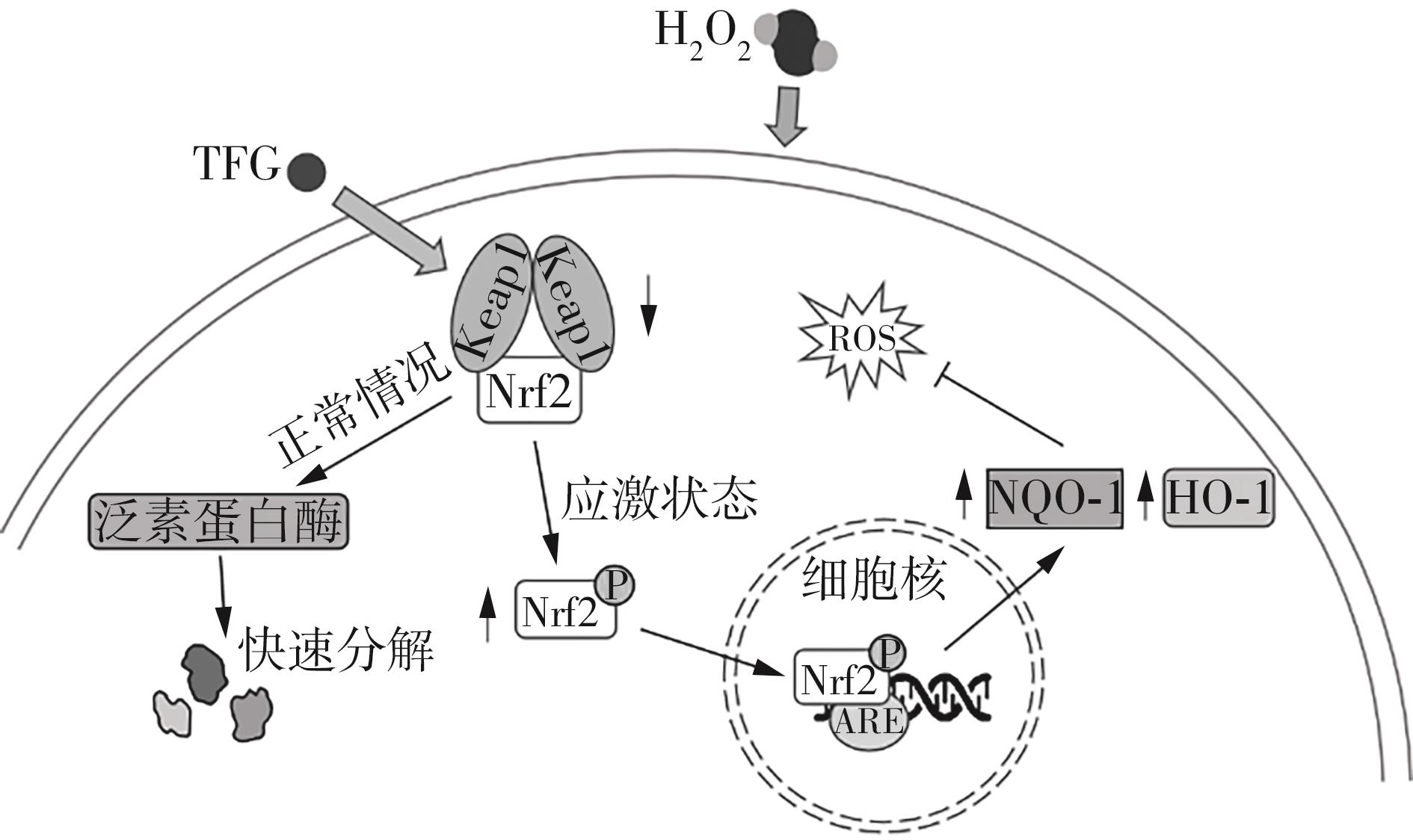
| [28] | JIANG J, ZHU Y, WANG M,et al .Protective effect of Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc.) pomace wine on oxidative stress of hydrogen peroxide by regulating Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in HepG2 cells[J].Foods,2023,12(9):1863/1-15. |
| [29] | DAVINELLI S, MEDORO A, INTRIERI M,et al. Targeting NRF 2 -KEAP1 axis by omega-3 fatty acids and their derivatives:emerging opportunities against aging and diseases[J].Free Radical Biology & Medicine,2022,193:736-750. |
| [30] | BOORMAN E, KILLICK R, AARSLAND D,et al .NRF2:an emerging role in neural stem cell regulation and neurogenesis[J].Free Radical Biology & Medicine,2022,193:437-446. |
| [31] | HUANG W, ZHONG Y, GAO B,et al .Nrf2-mediated therapeutic effects of dietary flavones in different diseases[J].Frontiers in Pharmacology,2023,14:1240433/1-18. |
| [1] | ZHENG Bisheng, WEI Ruijing, GUO Chaowan, et al. Purification of Kapok Flavonoids by Macroporous Resin and Its Anti-Acne Efficacy [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(4): 119-128. |
| [2] | SU Jianyu HU Han WU Ping MENG Xiaofeng XU Zhenbo ZHENG Huade. Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities of Myricetin In Vitro [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(3): 101-108,152. |
| [3] | XIONG Jian XIE Liping ZHANG Ting LIANG Min YUAN Erdong REN Jiaoyan. Interaction Between Memory-Enhancing Chinese Herbal Medicine and Walnut Peptides#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(11): 1-8. |
| [4] | Ren Jiao-yan Lai Ting Jiang Yan-qing Lu Yun-jun Liu Peng Liao Wen-zhen. Enzymatic Preparation,Separation,Purification and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Whey Protein Peptides [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(2): 1-7. |
| [5] | Zhao Qiang-zhong Feng Meng-ying Lin Lian-zhu Zhao Mou-ming. Separation,Identification and Antioxidant Activity of Glycoproteins from Millettia Speciosa Champ. [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(11): 8-15. |
| [6] | Fan Xiao- jiang Lei Ying Zhang Xi- hui Chao Meng Hiroshi Noguchi. Investigation into a New Integrated Water Purification Process of Half Coagulation/Ozonation/Ceramic Membrane Filtration [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(5): 54-59. |
| [7] | Li Li-feng Ren Li Liu Sa Wang Ying-jun. Production and Cell Compatibility of Medical Bacterial Cellulose [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(10): 44-49,56. |
| [8] | Liu Xiao-lan Zhang Wen-shu Zheng Xi-qun Shen Yuan Sun Ying. Isolation and Purification of Novel Fibrinolytic Enzymes Obtained from Fermentation of Cordyceps militaris [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(5): 107-114. |
| [9] | Fu Kai Fu Shi-yu Zhang Li Zhou Pan-deng Zhan Huai-yu. Production and Enzymatic Properties of Laccase from a Subtropical Wood-Rot Fungus [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(9): 152-157,164. |
| [10] | Deng Ming-rong Zhu Chun-hua Guo Jun Zhu Hong-hui. Isolation and Identification of Violet-Blue Pigment from Streptomyces vietnamensis [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(5): 132-137. |
| [11] | Lin Qi-ling Wen Qi-biao Ou Shi-yi Wu Lei-yan Lai Fu-rao. Scavenging of In Vitro Hydroxyl Free Radical Using Feruloyl-Arabinose [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(12): 110-114. |
| [12] | Zhang Xiao-yuan Guo Yong Wu Hui Zhao Qi Huang Min. Purification and Structure Identification of Phytohemagglutinin-L4 [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(12): 145-150. |
| [13] | Dong Xin-fa Liu Wen-yue Gao Jun Lin Wei-ming. Purification of CO via Selective Methanation Using Microchannel Reactor [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(12): 44-48,69. |
| [14] | Wang Wen-ping Guo Si-yuan Li lin Wang Ming-li Mo Li-ping . Extraction, Separation and Structural Analysis of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides from Chaenomeles cathayensis [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(7): 128-133. |
| [15] | Zhang Yun-feng Wei Dong Guo Si-yuan Chen Feng. Separation of Active Components from Andrographis paniculata Using High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(4): 127-132. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||