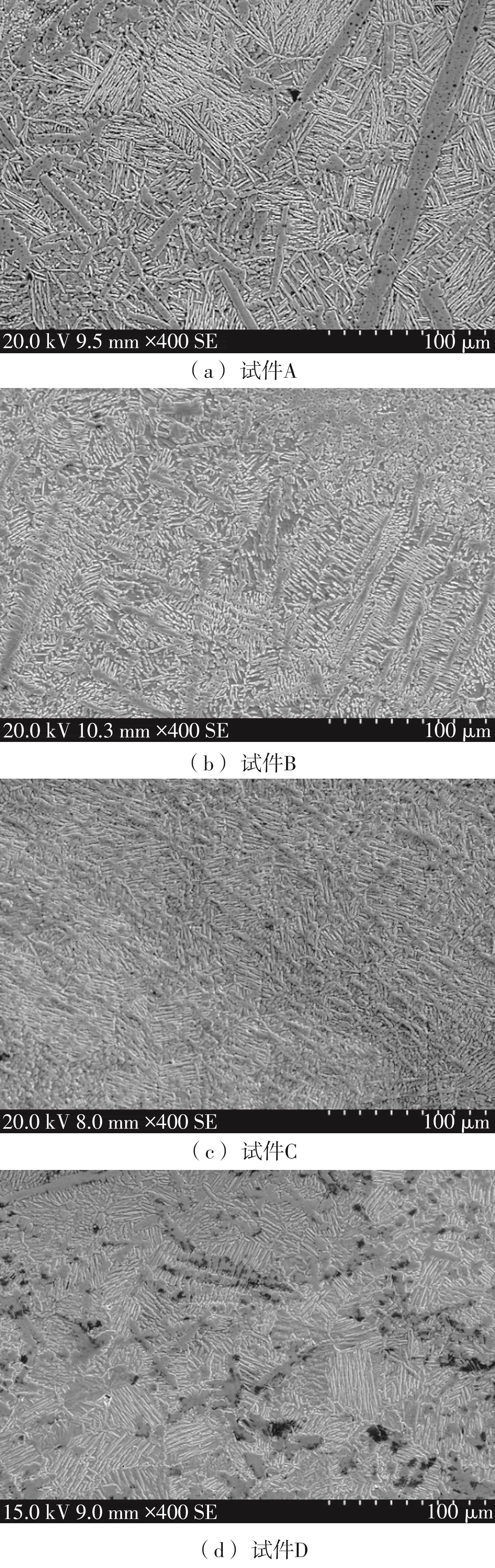
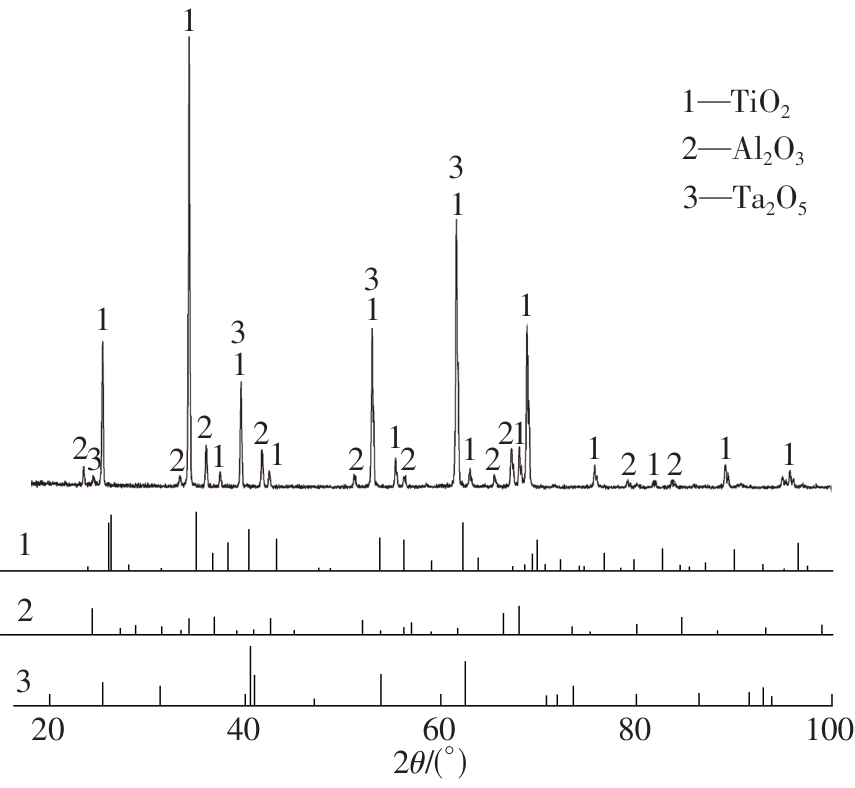
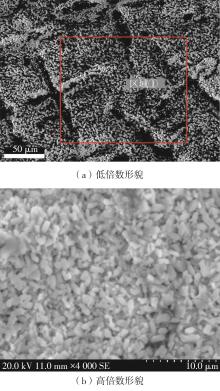
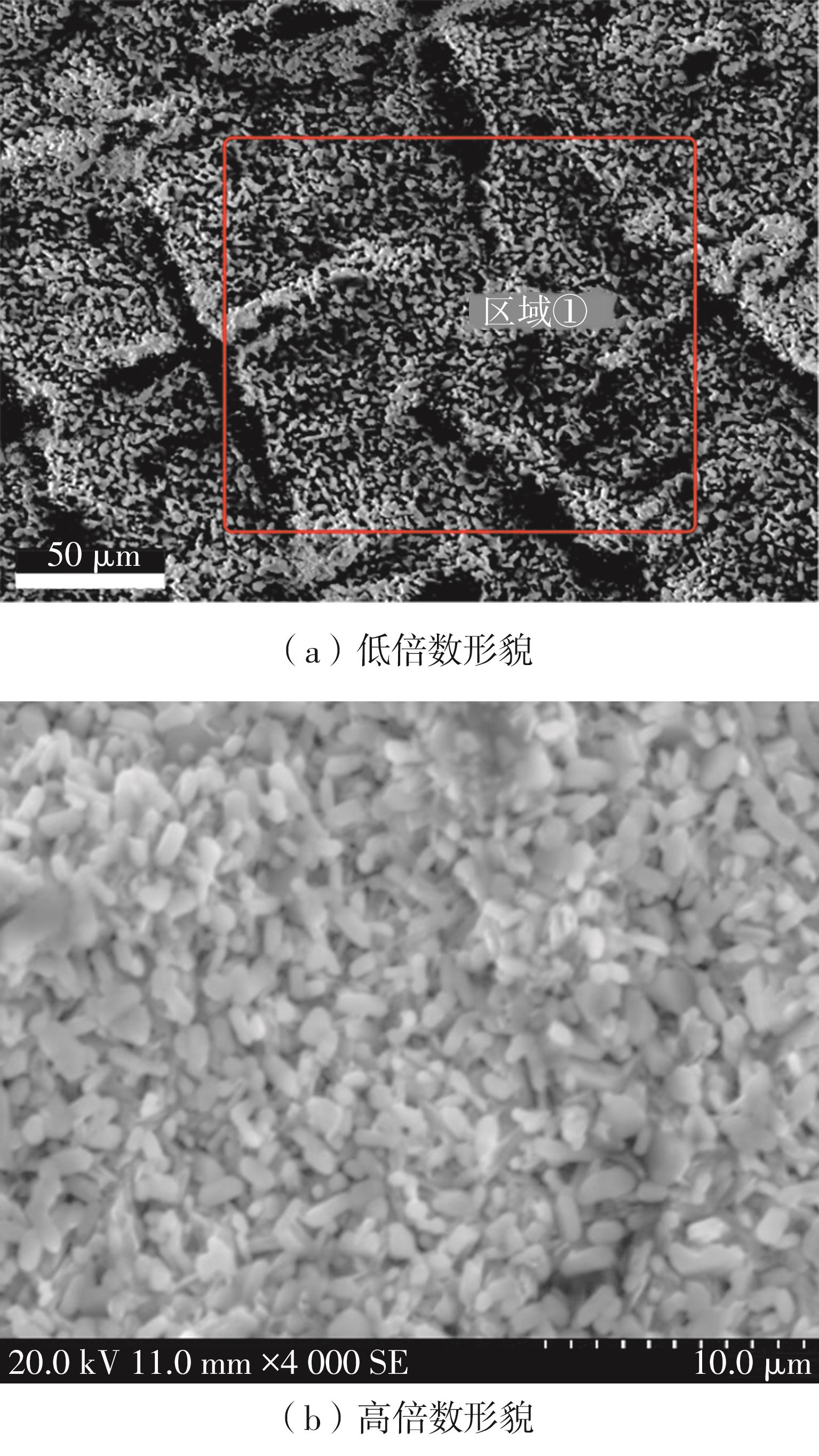
| 1 |
LIU Z, ZHANG D C, GONG L J,et al .Microstructures and mechanical properties of in situ TiC-β-Ti-Nb composites with ultrafine grains fabricated by high-pressure sintering[J].Scientific Reports,2018,8:9496/1-9.
|
| 2 |
付宇明,马顺芯,刘绍峰,等 .TC4表面激光熔覆硬质复合涂层组织与性能[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2024,52(3):10-17.
|
|
FU Yuming, MA Shunxin, LIU Shaofeng,et al .Microstructure and properties of laser cladding hard composite coating on TC4 surface [J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2024,52(3):10-17.
|
| 3 |
ZHANG D C, MAO Y F, YAN M,et al .Superelastic behavior of a β-type titanium alloy[J].Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials,2013,20:29-35.
|
| 4 |
SONG R, LI J, SHAO J Z,et al .Microstructural evolution and wear behaviors of laser cladding Ti2Ni/α(Ti) dual-phase coating reinforced by TiB and TiC[J].Applied Surface Science,2015,355:298-309.
|
| 5 |
GUO S Q .Densification of ZrB2-based composites and their mechanical and physical properties:a review[J].Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2009,29(6):995-1011.
|
| 6 |
LI Z, GOBBI S, NORRIS I,et al .Laser welding techniques for titanium alloy sheet[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology,1997,65:203-208.
|
| 7 |
XU X, YU Y, HUANG H .Mechanisms of abrasive wear in the grinding of titanium (TC4) and nickel (K417)alloys[J].Wear,2003,255:1421-1426.
|
| 8 |
QIN Y, XIONG D, LI J .Tribological properties of laser surface textured and plasma electrolytic oxidation duplex-treated Ti6Al4V alloy deposited with MoS2 film[J].Surface and Coatings Technology,2015,269:266-272.
|
| 9 |
KUMAR S A, RAMAN S G S, NARAYANAN T S N S, et al .Influence of counterbody material on fretting wear behaviour of surface mechanical attrition treated Ti-6Al-4V[J].Tribology International,2013,57:107-114.
|
| 10 |
覃鑫,祁文军,左小刚 .TC4钛合金表面激光熔覆NiCrCoAlY-Cr3C2复合涂层的摩擦和高温抗氧化性能[J].材料工程,2021,49(12):107-114.
|
|
QIN Xin, QI Wen-jun, ZUO Xiao-gang .Friction and high temperature oxidation resistance of laser cladding NiCrCoAlY-Cr3C2 composite coating on TC4 titanium alloy[J].Journal of Materials Engineering,2021,49(12):107-114.
|
| 11 |
周璇,肖华强,赵欣鑫,等 .TC4合金表面激光熔覆TiAl涂层的高温循环氧化行为[J].中国有色金属学报,2023,33(2):400-412.
|
|
ZHOU Xuan, XIAO Hua-qiang, ZHAO Xin-xin,et al . High-temperature cyclic oxidation behavior of laser cladding TiAl coating on TC4 alloy surface[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2023,33(2):400-412.
|
| 12 |
单晓浩,王存山,于群 .钛合金表面激光熔覆Nb-Al-Ti高温合金涂层组织与性能[J].中国激光,2016,43(8):0802015/1-8.
|
|
SHAN Xiaohao, WANG Cunshan, YU Qun .Microstructure and property of Nb-Al-Ti high temperature alloy coatings by laser cladding on Ti alloy surfaces[J].Chinese Journal of Lasers,2016,43(8):0802015/1-8.
|
| 13 |
于多,殷杰,张步豪,等 .碳化物超高温陶瓷材料研究进展[J].航空制造技术,2019,62(19):53-64.
|
|
YU Duo, YIN Jie, ZHANG Buhao,et al .Recent research progresses on ultrahigh temperature carbide ceramic materials [J].Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2019,62(19):53-64.
|
| 14 |
YOO H, KIM H S, HONG B G,et al .Hafnium carbide protective layer coatings on carbon/carbon composites deposited with a vacuum plasma spray coating method [J].Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2016,36(7):1581-1587.
|
| 15 |
董天下,孟凡桂,陈红梅,等 .石墨表面TaC涂层的熔盐法制备及表征[J].表面技术,2023,52(2):297-306.
|
|
DONG Tian-xia, MENG Fan-gui, CHEN Hong-mei,et al . Preparation and characterization of TaC coating on graphite via molten salt method[J].Surface Technology,2023,52(2):297-306.
|
| 16 |
GOWTHAM A, CHAITANYA G, KATIYAR J K,et al . Experimental investigations on laser cladding of NiCrBSi+WC coating on SS410[J].Materials Today:Proceedings,2020,27:1984-1989.
|
| 17 |
MOSTAJERAN A, SHOJA-RAZAVI R, HADI M,et al . Evaluation of the mechanical properties of WC-FeAl composite coating fabricated by laser cladding method[J].International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2020,88:105199/1-10.
|
| 18 |
YAO J, ZHANG J, WU G,et al .Microstructure and wear resistance of laser cladded composite coatings prepared from pre-alloyed WC-NiCrMo powder with different laser spots [J].Optics and Laser Technology,2018,101:520-530.
|
| 19 |
吴腾,师文庆,谢林圯,等 .激光熔覆铁基TiC复合涂层成形质量的控制方法[J].激光技术,2022,46(3):344-354.
|
|
WU Teng, SHI Wenqing, XIE Linyi,et al .Forming quality control method of laser cladding Fe-based TiC composite coating[J].Laser Technology,2022,46(3):344-354.
|
| 20 |
侯锁霞,赵江昆,李强,等 .对激光熔覆形成缺陷的影响因素的探究[J].材料导报,2022,36(Z1):22030105/1-4.
|
|
HOU Suoxia, ZHAO Jiangkun, LI Qiang,et al .Study on the influencing factors of laser cladding defects[J].Materials Reports,2022,36(Z1):22030105/1-4.
|
| 21 |
张杰,张群莉,姚建华,等 .激光熔覆工艺参数对IN718合金组织及元素偏析的影响[J].热加工工艺,2022,51(19):30-34,40.
|
|
ZHANG Jie, ZHANG Qunli, YAO Jianhua,et al .Effect of laser cladding process parameters on microstructure and element segregation of IN718 alloy[J].Hot Working Technology,2022,51(19):30-34,40.
|
| 22 |
赵晖,孙旭,杜春燕,等 .TC4合金表面激光熔覆材料研究进展[J].沈阳理工大学学报,2022,41(1):31-37.
|
|
ZHAO Hui, SUN Xu, DU Chunyan,et al .Progress in research of laser cladding materials on TC4 alloy surface[J].Journal of Shenyang Ligong University,2022,41(1):31-37.
|
| 23 |
许明三,周春辉,张正,等 .激光熔覆过程中的粉、气、光耦合温度场[J].中国机械工程,2022,33(1):70-77.
|
|
XU Mingsan, ZHOU Chunhui, ZHANG Zheng,et al . Temperature distribution of powder-gas-optical coupling temperature field in laser cladding processes[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2022,33(1):70-77.
|
| 24 |
BARIN I, KNACKE O, KUBASCHEWSKI O .Thermochemical properties of inorganic substances[M]. Berlin/Heidelberg:Springer,1977.
|
| 25 |
张伟祥,唐超兰,陈志茹,等 .退火温度对激光选区熔化成形TC4钛合金组织及力学性能的影响[J].金属热处理,2019,44(6):122-127.
|
|
ZHANG Weixiang, TANG Chaolan, CHEN Zhiru,et al .Effect of annealing temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4 titanium alloy formed by selective laser melting[J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2019,44(6):122-127.
|
| 26 |
肖振楠,刘婷婷,廖文和,等 .激光选区熔化成形TC4钛合金热处理后微观组织和力学性能[J].中国激光,2017,44(9):0902001/1-9.
|
|
XIAO Zhennan, LIU Tingting, LIAO Wenhe,et al . Microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4 titanium alloy formed by selective laser melting after heat treatment [J].Chinese Journal of Lasers,2017,44(9):0902001/1-9.
|
| 27 |
CHEN Dong, WANG Quansheng, LIU Yanbo,et al .Effect of Ta2O5-Y2O3 dopants on phase structure, fracture toughness and thermophysical properties of zirconia[J].Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2021,50(6):1890-1895.
|
| 28 |
李浩,王松,余艺平,等 .Ta-Hf体系材料研究进展[J].中国陶瓷,2020,56(11):10-18.
|
|
LI Hao, WANG Song, Yu Yiping .Research progress of Ta-Hf system materials[J].China Ceramics,2020,56(11):10-18.
|