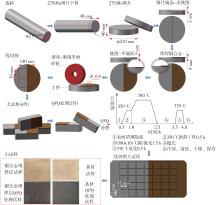
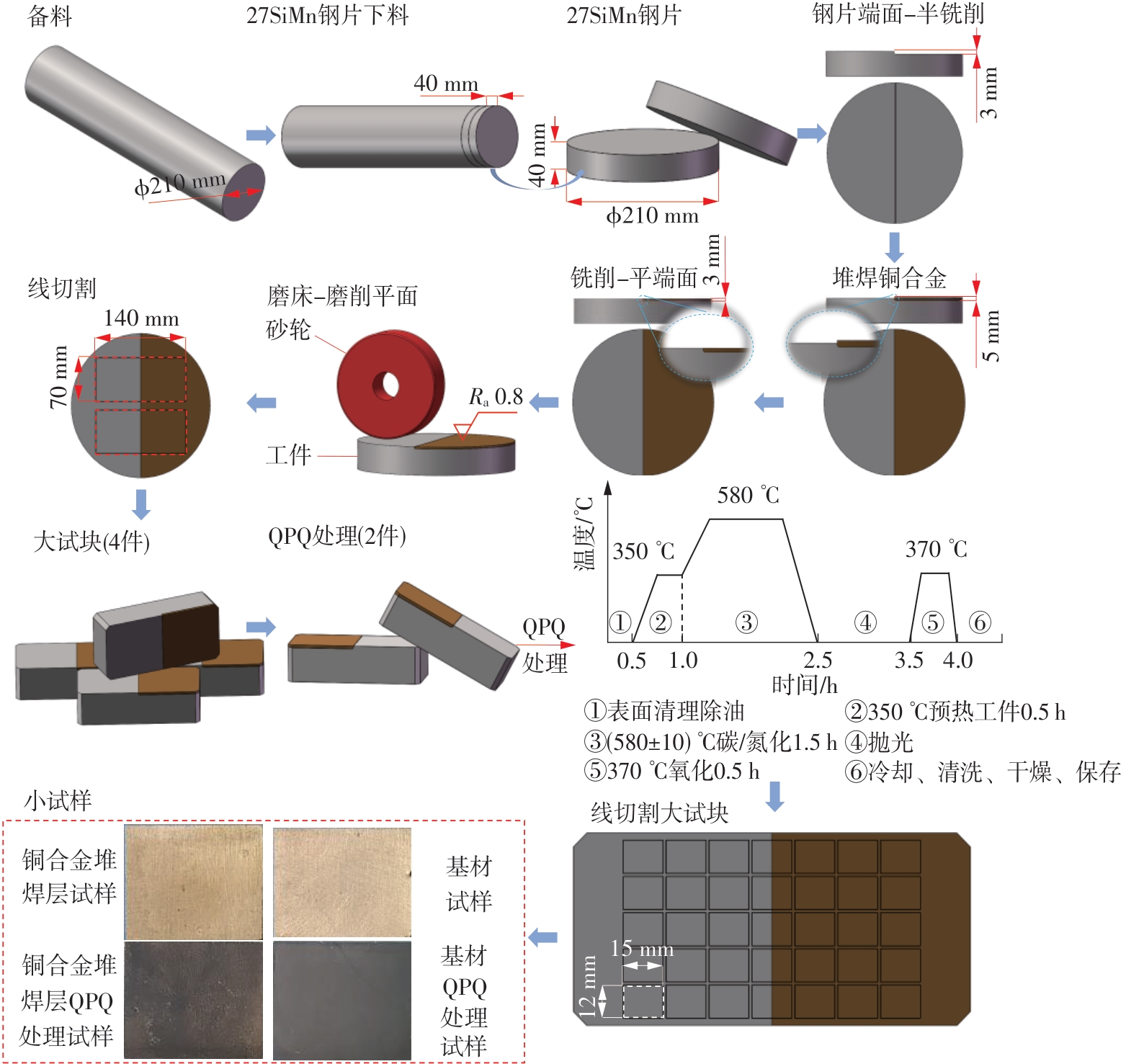
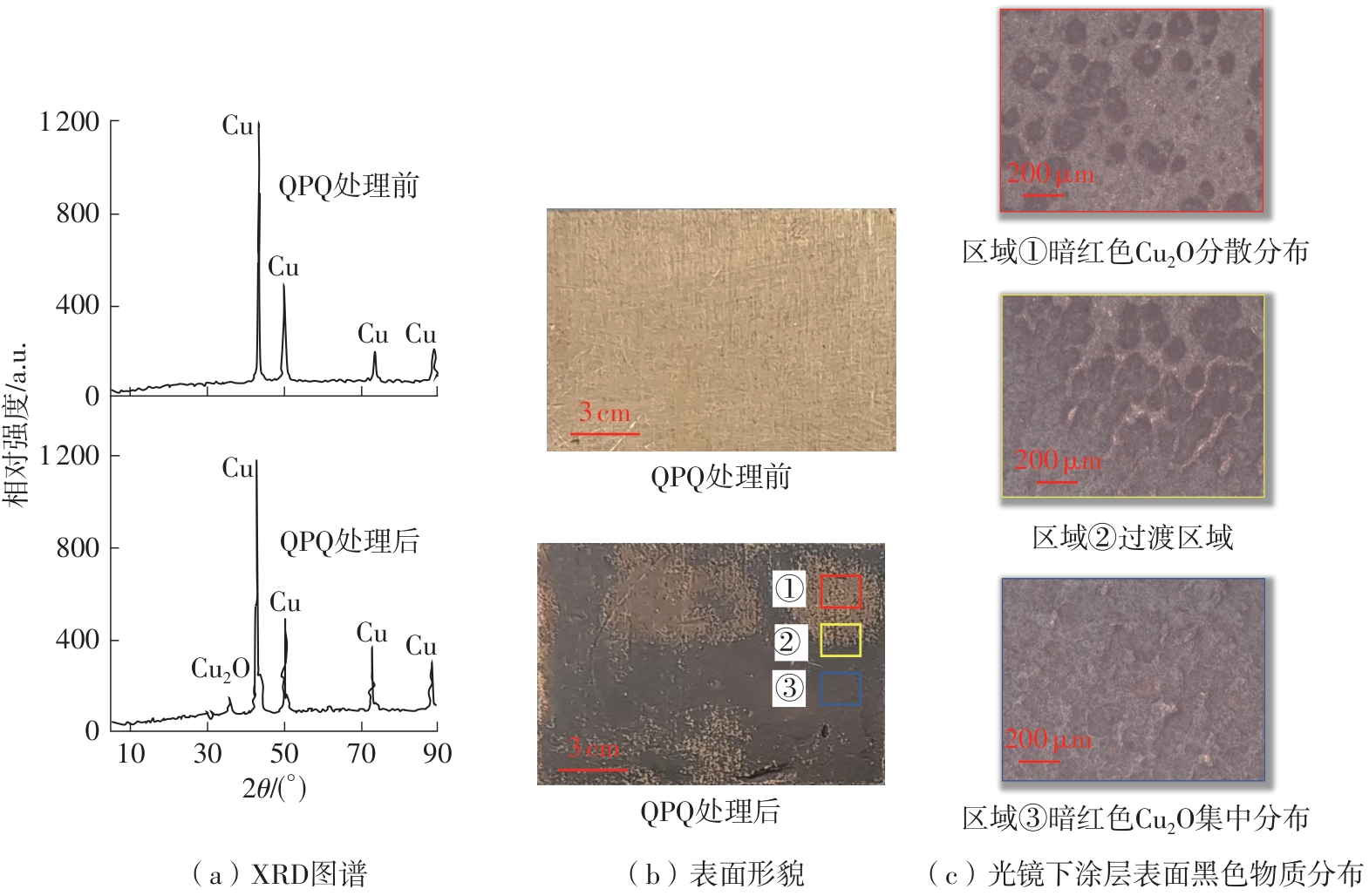
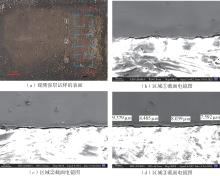
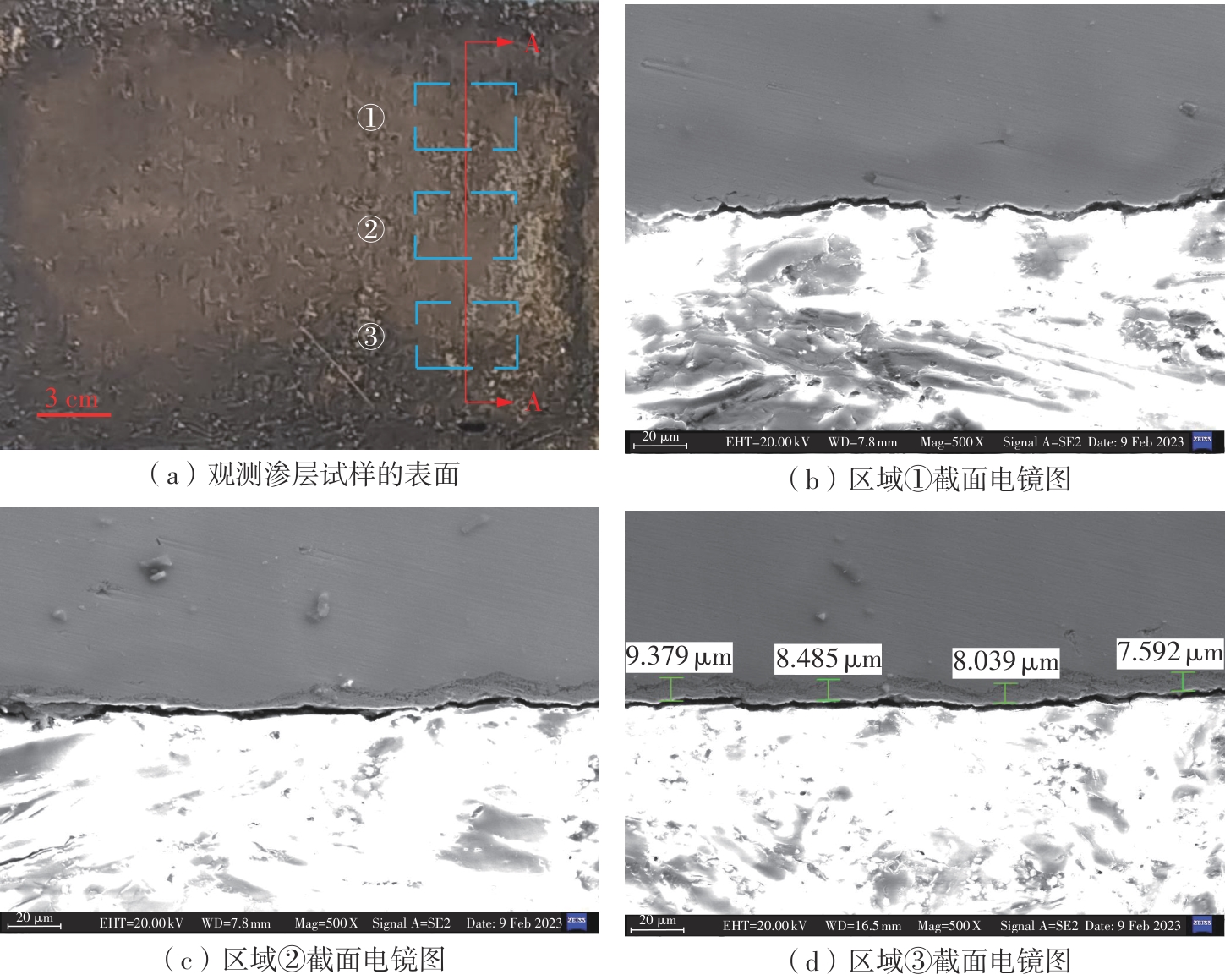
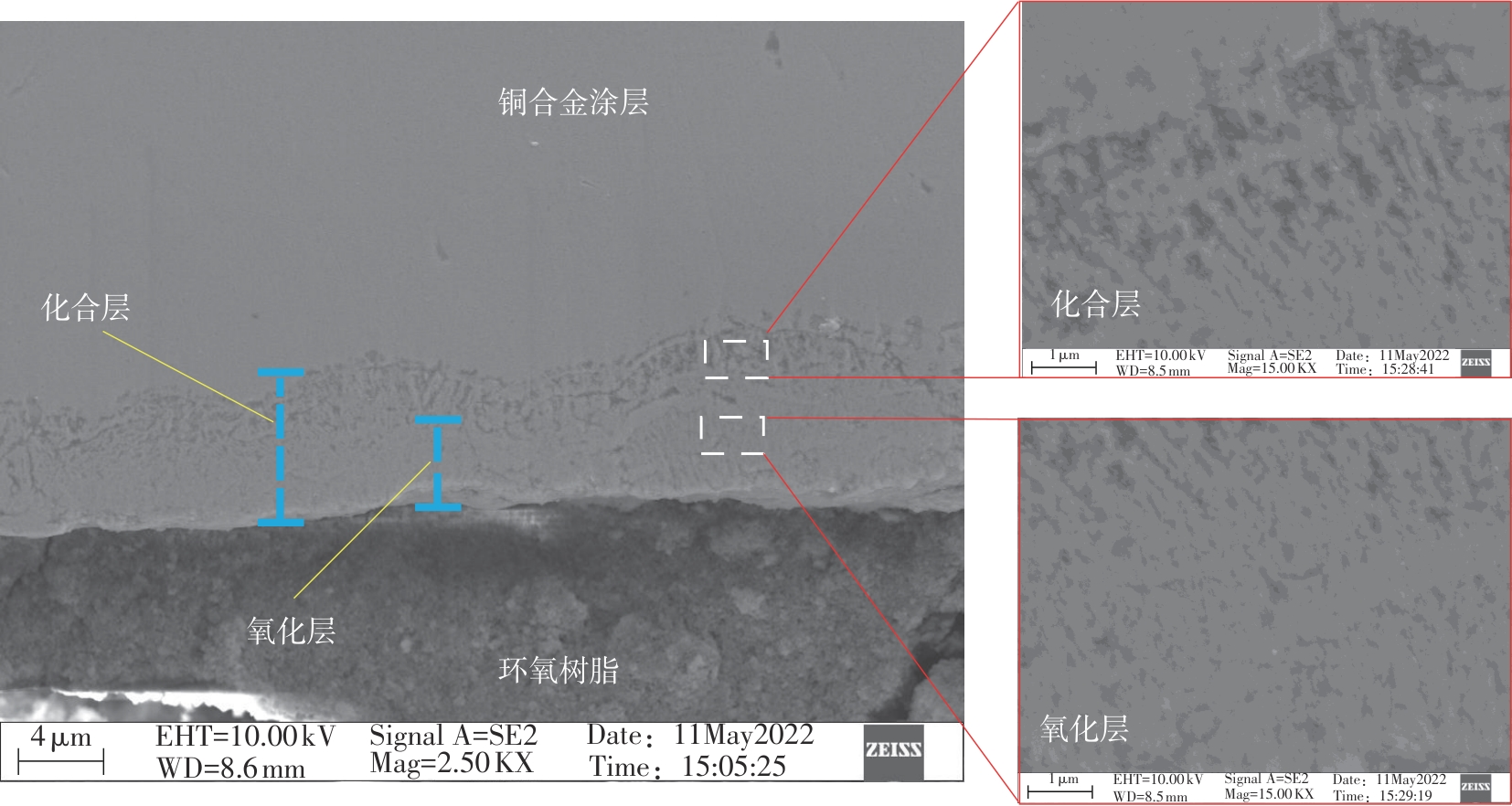
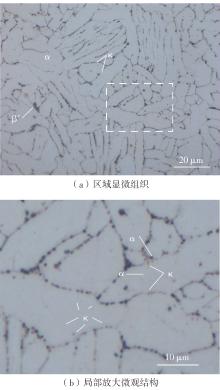
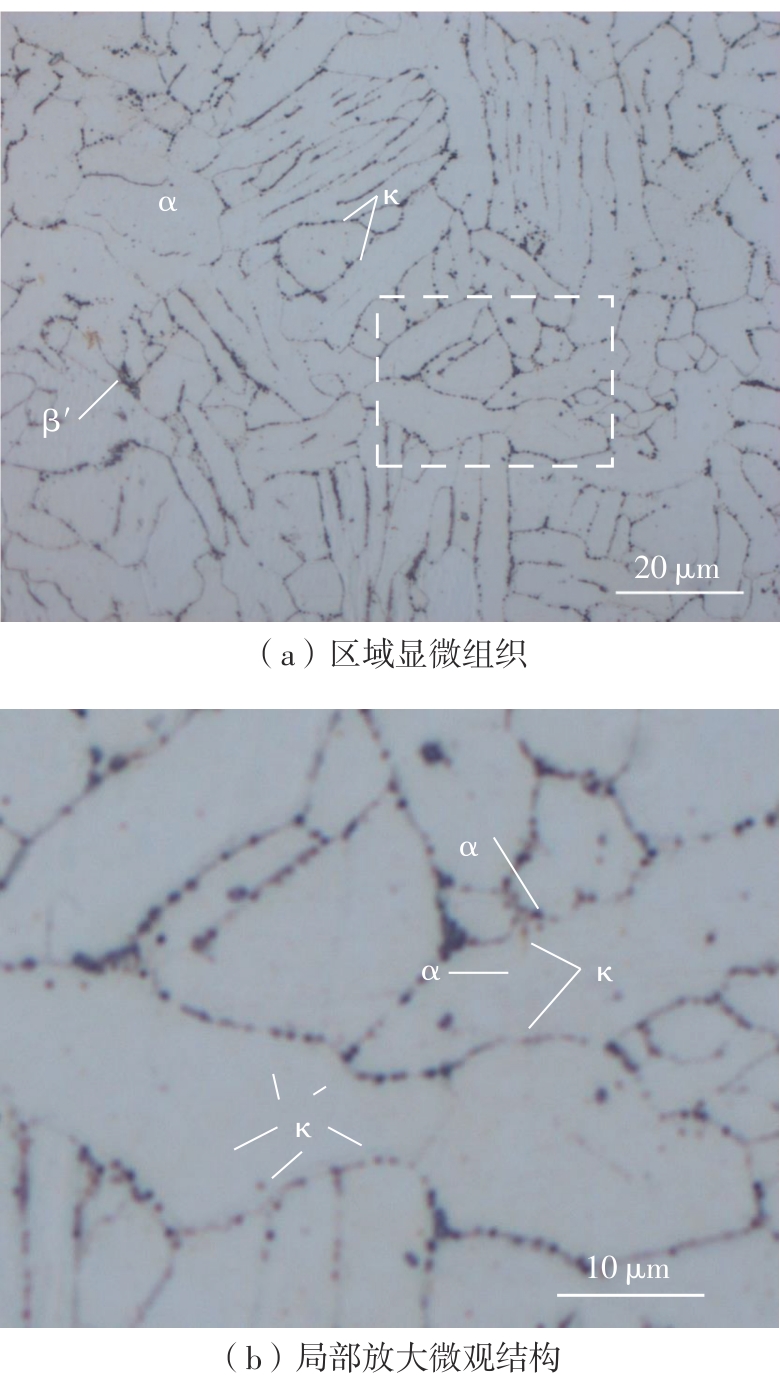
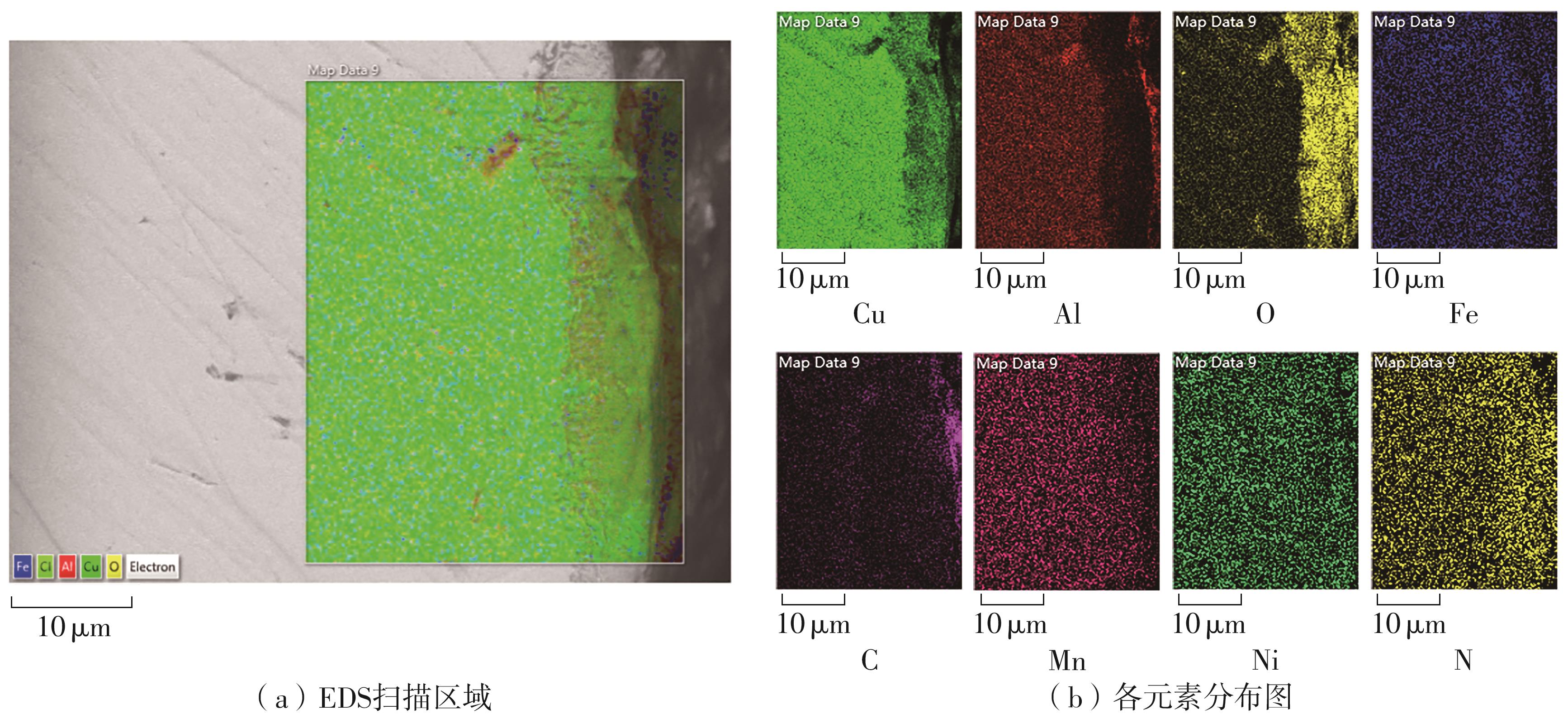
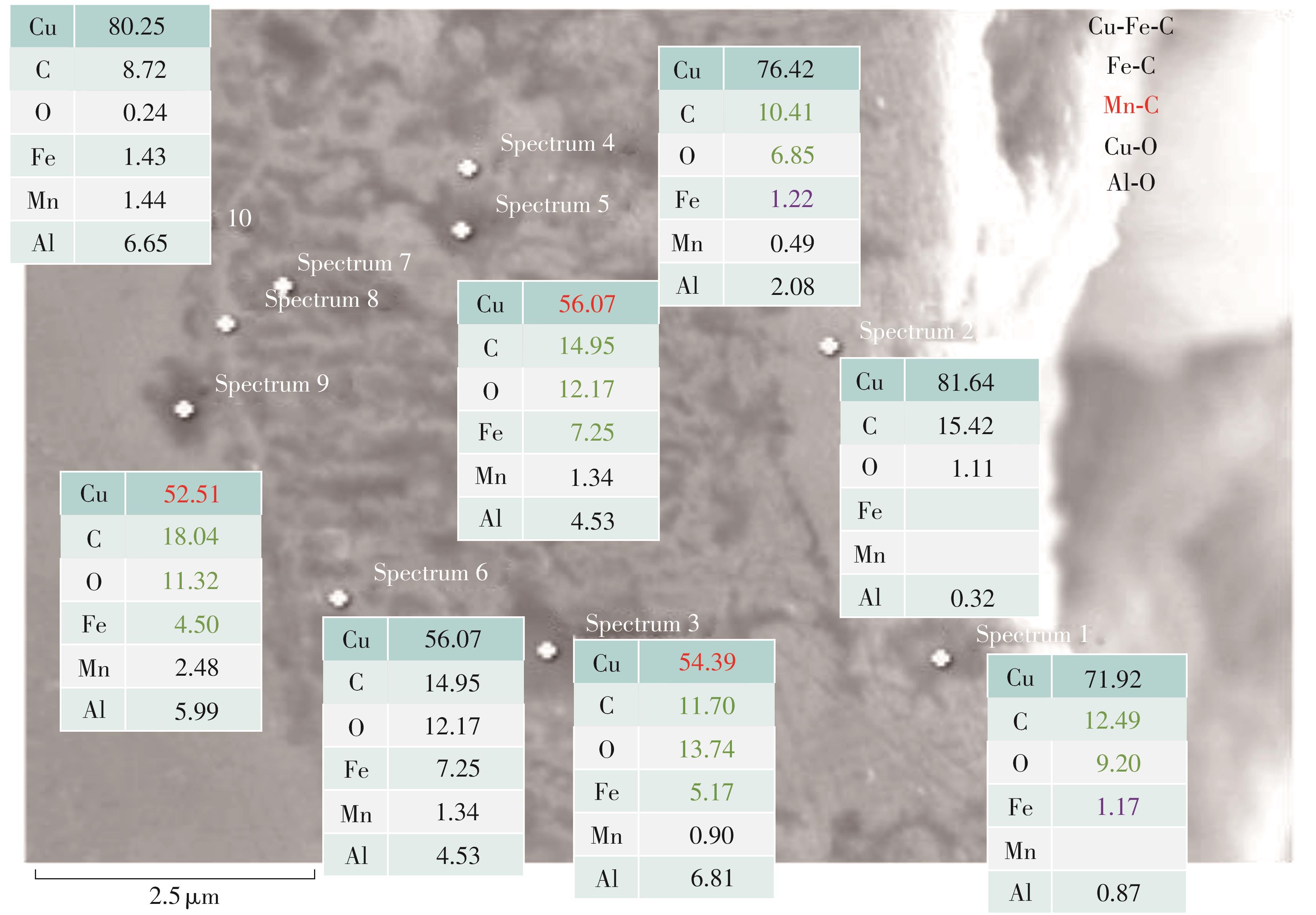
| 1 |
郭辰光,孙瑜,吕宁,等 .液压支架缸体内壁面再制造粉流场影响规律分析[J].表面技术,2022,51(3):304-314.
|
|
GUO Chen-guang, SUN Yu, Ning LÜ,et al .Analysis of the influence law of the remanufactured powder flow field on the inner wall of hydraulic support[J].Surface Technology,2022,51(3):304-314.
|
| 2 |
史学琦 .煤矿井下液压支架油缸泄漏故障及维修探析[J].现代工业经济和信息化,2017(18):57-58,68.
|
|
SHI Xueqi .Leakage failure and maintenance of cylinder of hydraulic support in coal mine[J].Modern Industrial Economy and Informatization,2017(18):57-58,68.
|
| 3 |
魏传君 .液压支架立柱缸筒维修与再制造技术分析[J].冶金管理,2019(17):77,79.
|
|
WEI Chuanjun .Analysis of repair and remanufactu-ring technology of hydraulic support column cylinder barrel[J].Metallurgical Management,2019(17):77,79.
|
| 4 |
刘翔宇 .液压支架立柱的维修及再造技术分析[J].机电工程技术,2019,48(12):236-238.
|
|
LIU Xiangyu .Analysis of repair and reconstruction technology of hydraulic support column[J].Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Technology,2019,48(12):236-238.
|
| 5 |
高锋,万滋雄,黄昭明 .激光熔覆液压支架立柱工艺特点分析[J].矿山机械,2013,41(6):125-126.
|
|
GAO Feng, WAN Zixiong, HUANG Zhaoming .Chara-cterization of laser cladding process for hydraulic su-pport column[J].Mining Machinery,2013,41(6):125-126.
|
| 6 |
王瑞 .矿用掩护式液压支架立柱维修技术研究[J].机械管理开发,2019(2):255-256,259.
|
|
WANG Rui .Research on maintenance technology of mine cover hydraulic support column[J].Mechanical Management and Development,2019(2):255-256,259.
|
| 7 |
黄杰,贺定勇,杜开平,等 .FeCrNiMo激光熔覆层组织与电化学腐蚀行为研究[J].表面技术,2020,49(12):228-234.
|
|
HUANG Jie, HE Ding-yong, DU Kai-ping,et al .Microstructure and electrochemical corrosion behavior of FeCrNiMo layer fabricated by laser cladding [J].Surface Technology,2020,49(12):228-234.
|
| 8 |
杨毅 .矿用液压支架维修关键技术分析[J].矿业装备,2021(4):240-241.
|
|
YANG Yi .Analysis of key technology of mining hydraulic support maintenance[J].Mining Equipment,2021(4):240-241.
|
| 9 |
潘岳军 .矿用液压支架立柱外缸和中缸内表面损伤的修复工艺:CN107671488A[P].2018-02-09.
|
| 10 |
韩启勇,朱征宇,张磊,等 .采用中间层的高强钢表面CMT堆焊耐腐蚀铜合金研究[J].江苏科技大学学报(自然科学版),2019,33(4):13-17.
|
|
HAN Qiyong, ZHU Zhengyu, ZHANG Lei,et al .CMT surfacing of corrosion-resistant copper alloy on the high strength steel with an interlayer[J].Journal of Jiangsu University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition),2019,33(4):13-17.
|
| 11 |
罗德福 .QPQ技术在我国的发展[J].金属热处理,2022,47(7):227-233.
|
|
LUO Defu .Development of QPQ technology in China[J].Metal Heat Treatment,2022,47(7):227-233.
|
| 12 |
张占辉,薛家祥 .熔滴冲击方向对焊缝质量的影响[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(4):138-144.
|
|
ZHANG Zhanhui, XUE Jiaxiang .Effect of the direction of droplet impingement on the bead quality[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2019,47(4):138-144.
|
| 13 |
马莉 .液压支架立柱维修与再制造技术的应用研究[J].当代化工研究,2019(14):65-66.
|
|
MA Li .Application research on maintenance and remanufacturing of hydraulic support column[J].Mo-dern Chemical Research,2019(14):65-66.
|
| 14 |
李炯辉 .金属材料金相图谱[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2009.
|
| 15 |
吕维洁,王立强 .镍铝青铜合金组织结构优化及腐蚀疲劳性能[M].北京:科学出版社,2018.
|
| 16 |
WHARTON J A, STOKES K R .The influence of nickel-aluminium bronze microstructure and crevice solution on the initiation of crevice corrosion[J].Electrochim Acta,2008,53:2463-2473.
|
| 17 |
SABBAGHZADEH B, PARVIZI R, DAVOODI A,et al .Corrosion evaluation of multi-pass welded nickel-aluminum bronze alloy in 3.5% sodium chloride solution:a restorative application of gas tungsten arc welding process[J].Materials & Design,2014,58:346-356.
|
| 18 |
宋德军,胡光远,卢海,等 .镍铝青铜合金的应用与研究现状[J].材料导报,2007,21(专辑Ⅸ):450-452,459.
|
|
SONG Dejun, HU Guangyuan, LU Hai,et al .Survey of progress on the research and practice of nickel-aluminum braze[J].Materials Reports,2007,21(Special Ⅸ):450-452,459.
|
| 19 |
秦真波 .镍铝青铜合金的腐蚀行为及其表面改性研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2018.
|
| 20 |
都春燕 .镍铝青铜合金的耐蚀性及表面处理的研究[D].镇江:江苏科技大学,2014.
|
| 21 |
孙梦龙,谢春生 .热处理对新型铝镍青铜组织与性能的影响[J].金属热处理,2016,41(1):97-100.
|
|
SUN Menglong, XIE Chunsheng .Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of new aluminum-nickel bronze alloy[J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2016,41(1):97-100.
|