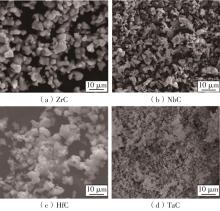
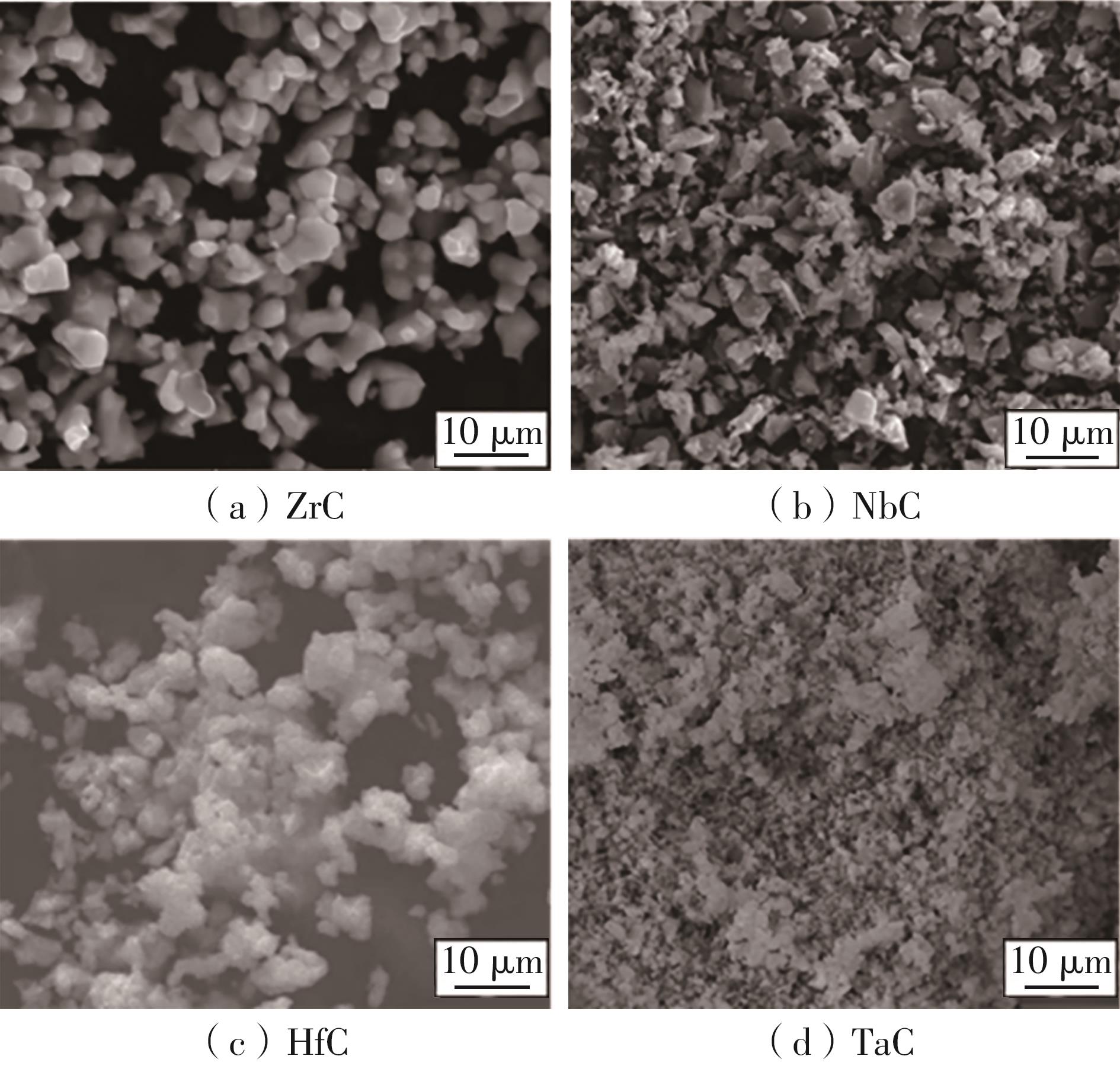
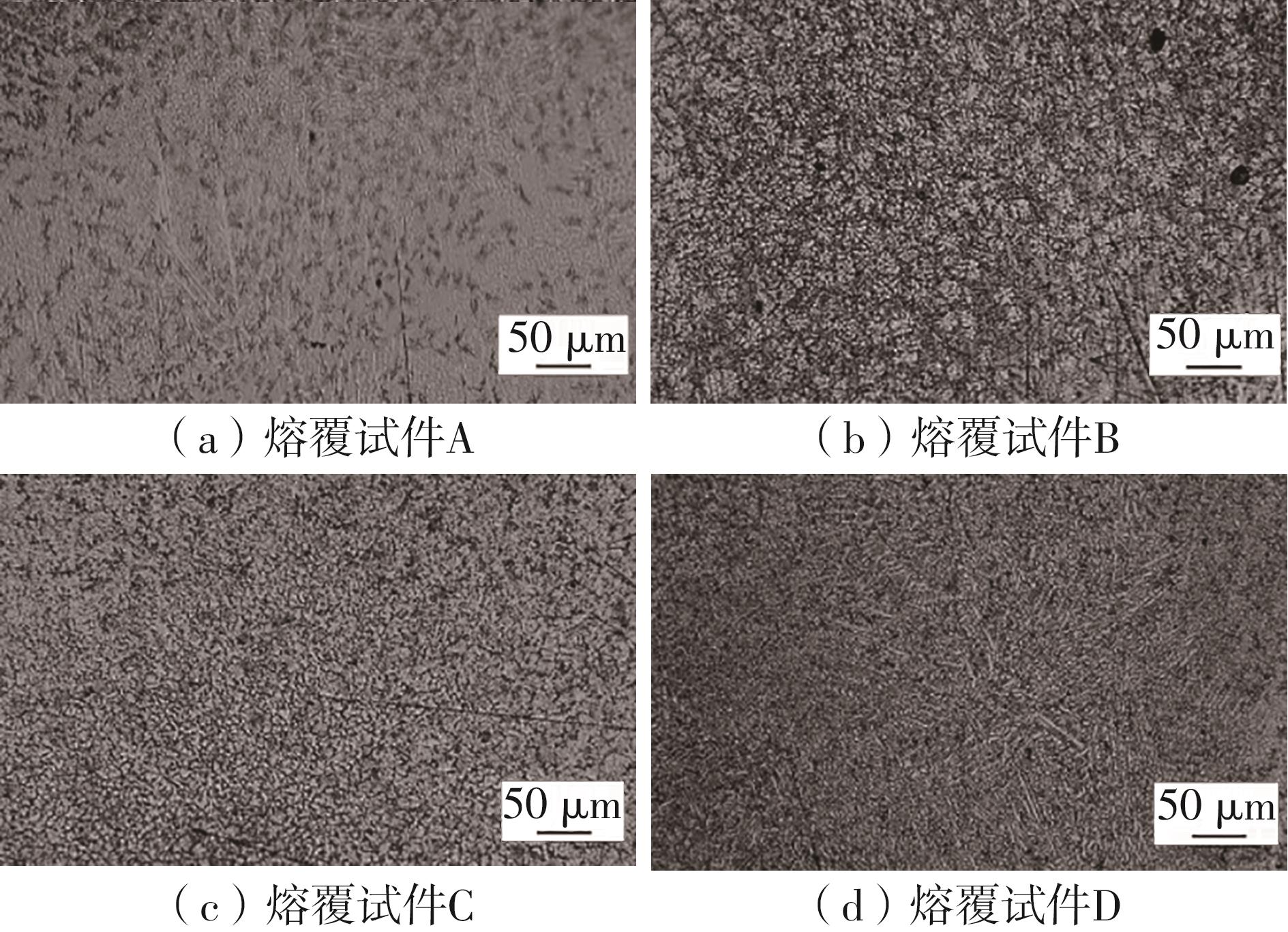
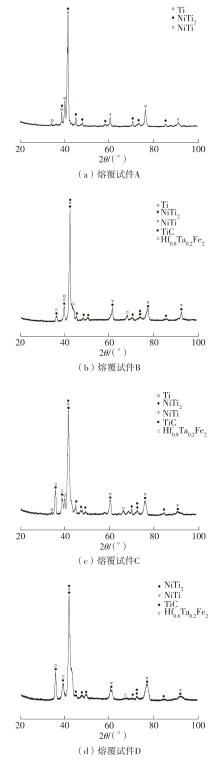
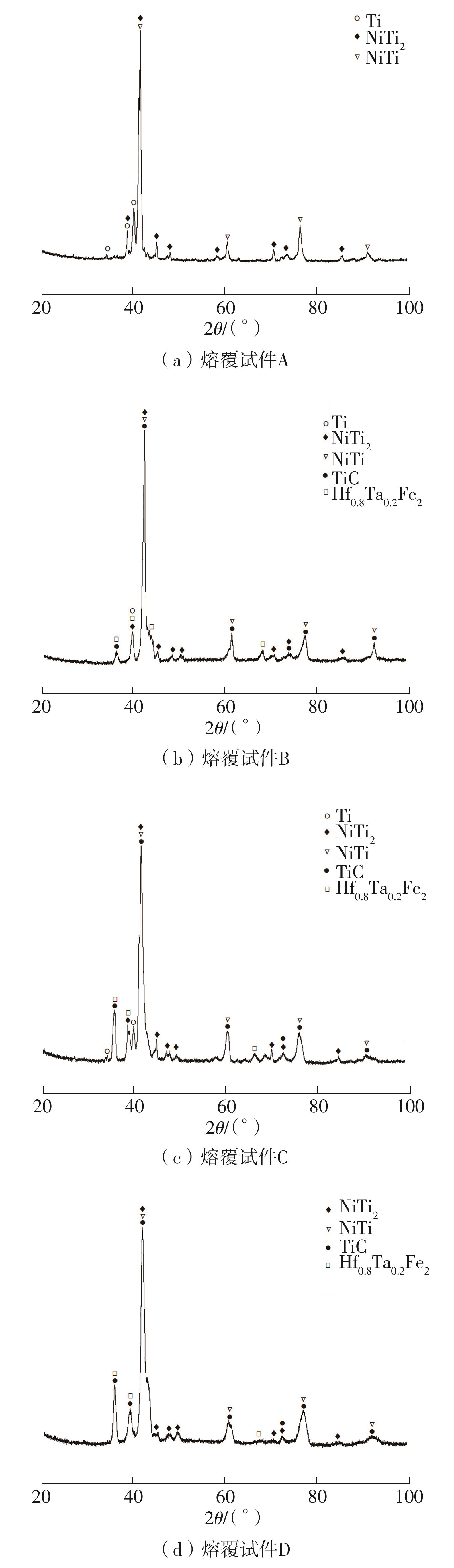
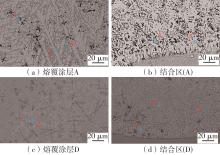
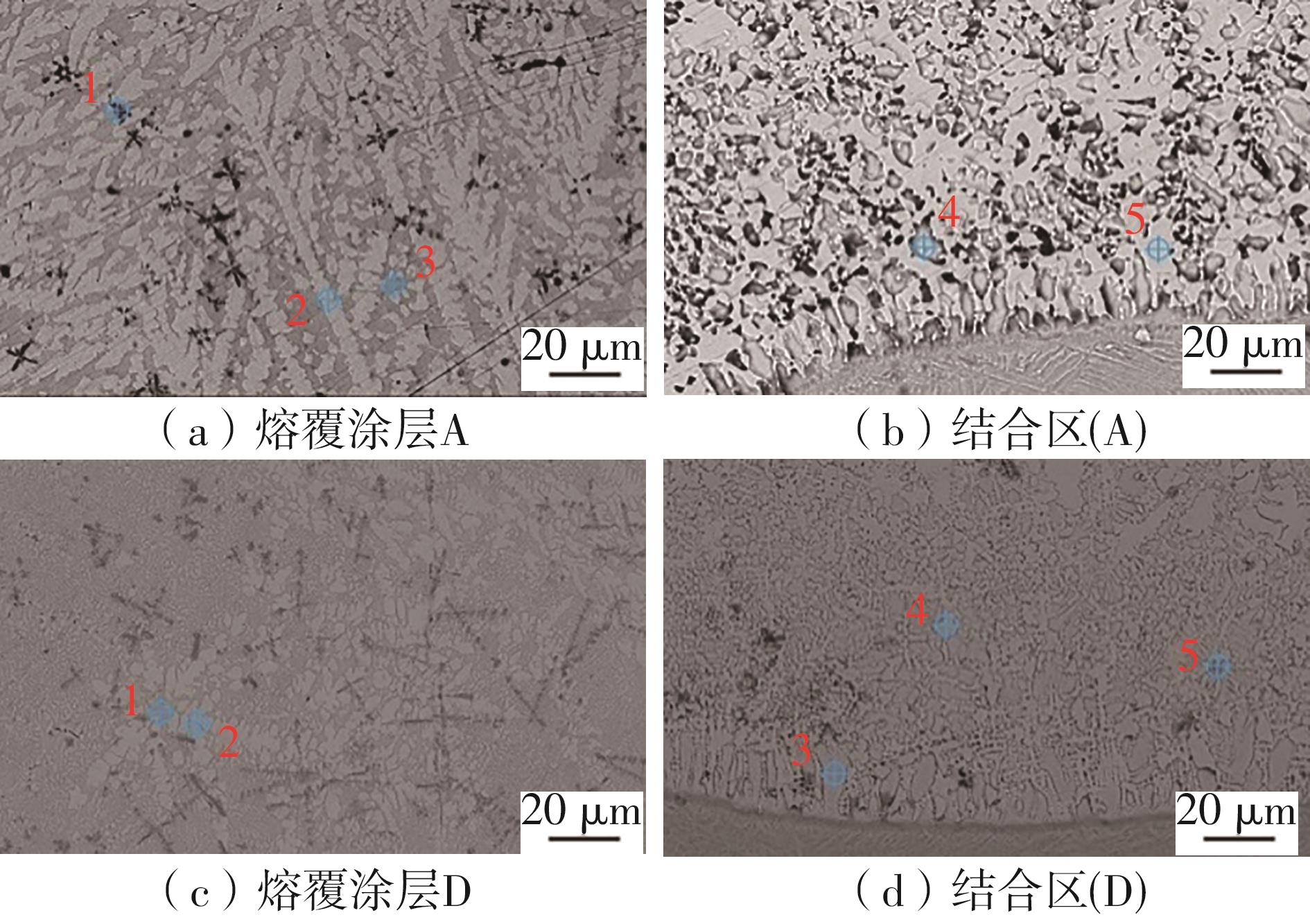
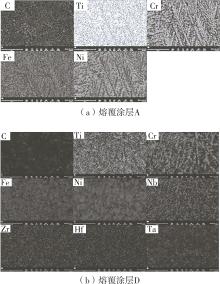
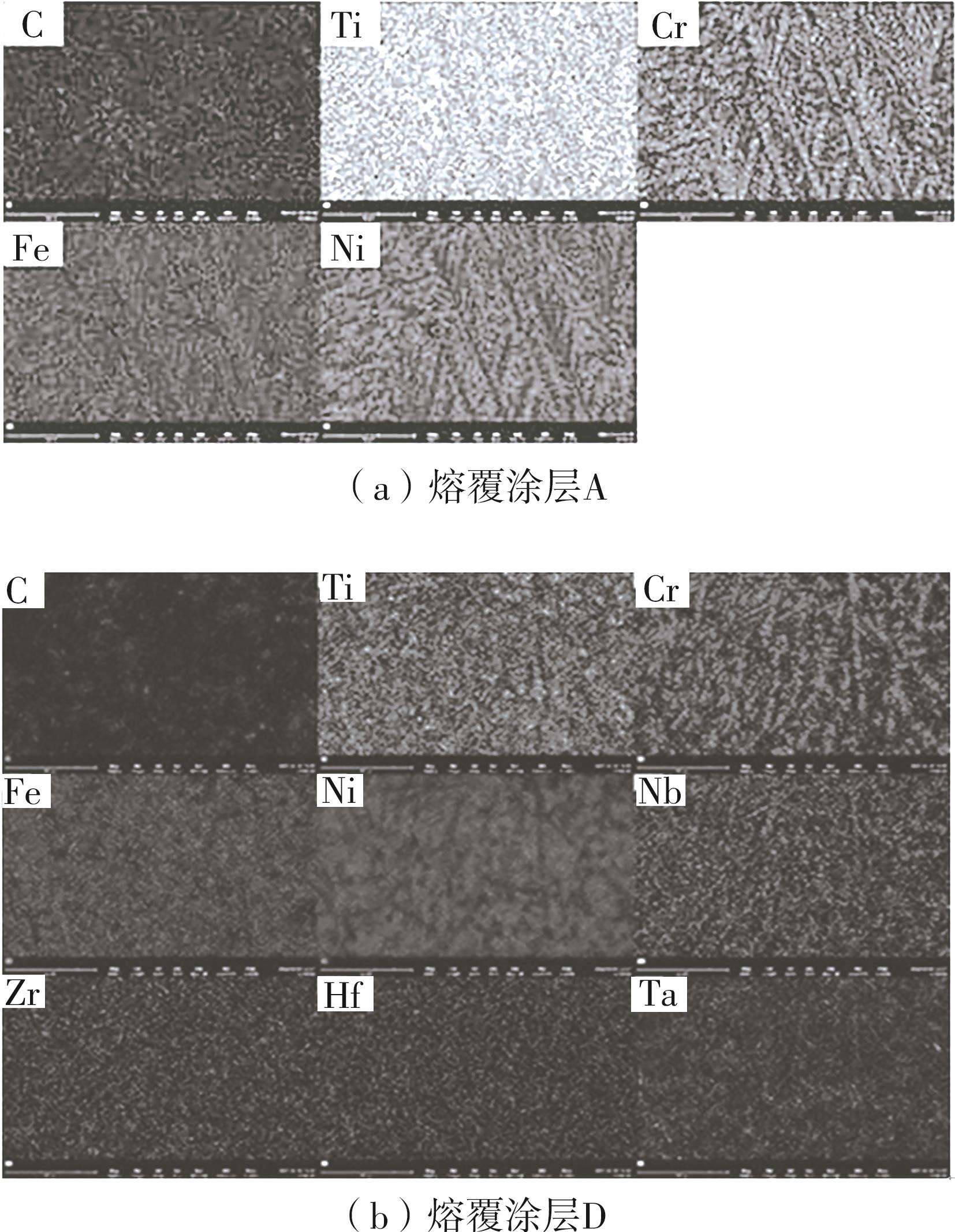
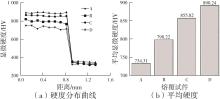
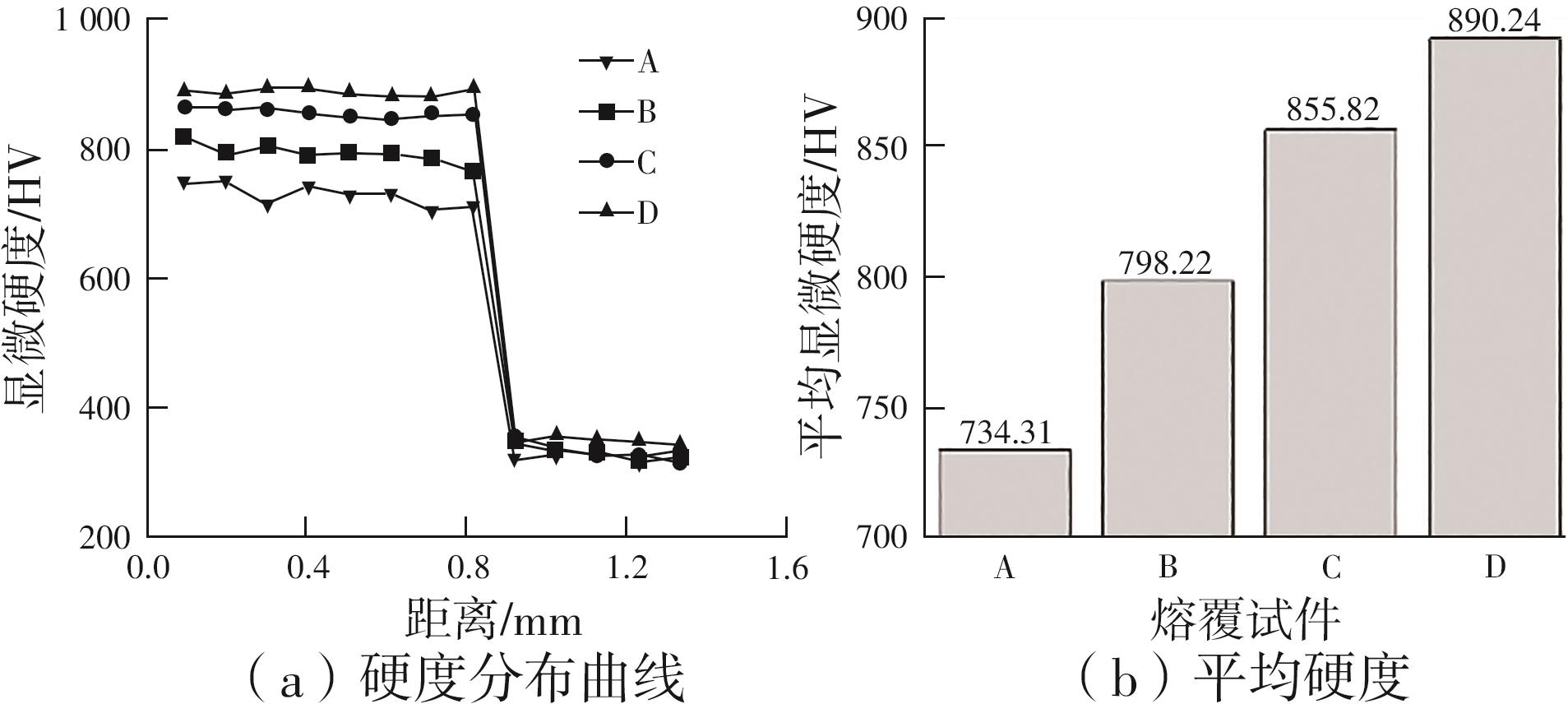
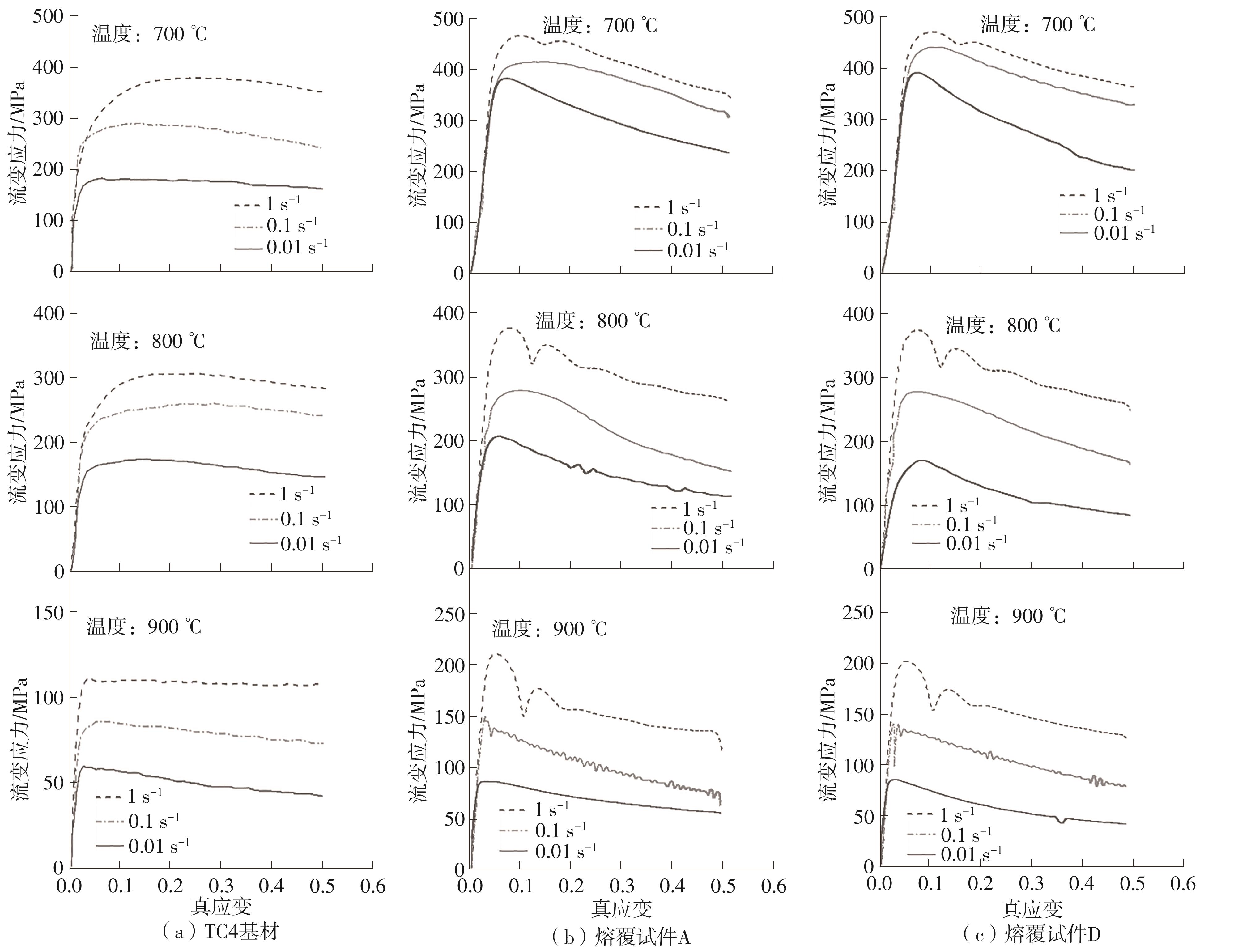
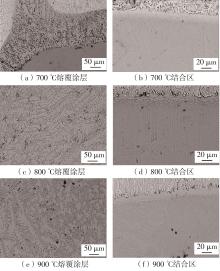
| 1 |
郭鲤,何伟霞,周鹏,等 .我国钛及钛合金产品的研究现状及发展前景[J].热加工工艺,2020,49(22):22-28.
|
|
GUO Li, HE Weixia, ZHOU Peng,et al .Research status and development prospect of titanium and titanium alloy products in China[J].Hot Working Technology,2020,49(22):22-28.
|
| 2 |
李毅,赵永庆,曾卫东 .航空钛合金的应用及发展趋势[J].材料导报,2020,34(Z1):280-282.
|
|
LI Yi, ZHAO Yongqing, ZENG Weidong .Application and development of aerial titanium alloys[J].Materials Reports,2020,34(Z1):280-282.
|
| 3 |
张津超,石世宏,龚燕琪,等 .激光熔覆技术研究进展[J].表面技术,2020,49(10):1-11.
|
|
ZHANG Jin-chao, Shi Shi-hong, GONG Yan-qi,et al .Research progress of laser cladding technology[J].Surface Technology,2020,49(10):1-11.
|
| 4 |
杜学芸,许金宝,宋健 .激光熔覆再制造技术研究现状及发展趋势[J].金属加工(热加工),2020(3):15-19.
|
|
DU Xueyun, XU Jinbao, SONG Jian .Research status and development trend of laser cladding remanufacturing technology[J].MW Metal Forming,2020(3):15-19.
|
| 5 |
刘录录,孙荣禄 .激光熔覆技术及工业应用研究进展 [J].热加工工艺,2007,36(11):58-61.
|
|
LIU Lu-lu, SUN Rong-lu .Development of laser cladding technology and industrial application[J].Hot Working Technology,2007,36(11):58-61.
|
| 6 |
赵永庆,葛鹏,辛社伟 .近五年钛合金材料研发进展[J].中国材料进展,2020,39(7/8):527-534,557-558.
|
|
ZHAO Yongqing, GE Peng, XIN Shewei .Progresses of R&D on Ti-alloy materials in recent 5 years[J].Materials China,2020,39(7/8):527-534,557-558.
|
| 7 |
覃鑫 .基于耐磨和耐高温氧化的TC4表面激光熔覆工艺研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2022.
|
| 8 |
张云龙 .Si的添加对TC4合金镍基涂层高温氧化及机械性能的影响[D].上海:上海工程技术大学,2021.
|
| 9 |
娄燕,李落星,彭大暑 .Ti3Al5Mo5V合金在热压缩变形状态下的组织和应力分析[J].金属热处理,2003,28(4):36-39.
|
|
LOU Yan, LI Luo-xing, PENG Da-shu .Analysis on microstructures and stress of Ti3Al5Mo5V alloy at hot compressing deformation state[J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2003,28(4):36-39.
|
| 10 |
WANG Z, WANG X, ZHU Z .Characterization of high-temperature deformation behavior and processing map of TB17 titanium alloy[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2017,692:149-154.
|
| 11 |
郭建亭 .高温合金材料与工程应用[M].北京:科学出版社,2010.
|
| 12 |
谢佳明,董合凤,张鹏鹏,等 .材料表面改性技术的发展研究[J].科技展望,2016,26(12):161.
|
|
XIE Jiaming, DONG Hefeng, ZHANG Pengpeng,et al .Research on the development of material surface modification technology[J].Science and Technology,2016,26(12):161.
|
| 13 |
SIMS C T .高温合金宇航和工业动力用的高温材料[M].大连:大连理工大学出版社,1992.
|
| 14 |
冯亮,曲恒磊,赵永庆,等 .TC21合金的高温变形行为[J].航空材料学报,2004,24(4):11-13.
|
|
FENG Liang, QU Heng-lei, ZHAO Yong-qing,et al .High temperature deformation behavior of TC21 alloy[J].Journal of Aeronautical Materials,2004,24(4):11-13.
|
| 15 |
李涵 .钛合金表面激光熔覆高熵合金涂层研究[D].大连:大连理工大学,2017.
|
| 16 |
宁永强,陈泳屹,张俊,等 .大功率半导体激光器发展及相关技术概述[J].光学学报,2021,41(1):0114001-1-0114001-10.
|
|
NING Yongqiang, CHEN Yongyi, ZHANG Jun,et al .Brief review of development and techniques for high power semiconductor lasers[J].Acta Optica Sinica,2021,41(1):0114001-1-0114001-10.
|
| 17 |
凌妍,钟娇丽,唐晓山,等 .扫描电子显微镜的工作原理及应用[J].山东化工,2018,47(9):78-79,83.
|
|
LING Yan, ZHONG Jiaoli, TANG Xiaoshan,et,al .The principle and application of scanning electron microscope[J].Shangdong Chemical Industry,2018,47(9):78-79,83.
|
| 18 |
陈向文,庄哲峰,孟素各 .激光熔覆不同TiC含量硬质合金层的组织与性能[J].机电技术,2015(6):115-118.
|
|
CHEN Xiangwen, ZHUANG Zhefeng, MENG Suge .Structure and properties of cemented carbide layers with different TiC contents by laser cladding[J].Mechanical & Electrical Technology,2015(6):115-118.
|
| 19 |
周军,曾卫东,舒滢,等 .热变形参数对Ti-17合金的片状α球化过程的影响[J].热加工工艺,2005(1):16-18,41.
|
|
ZHOU Jun, ZENG Wei-dong, SHU Ying,et al. Influence of hot processing parameters on globularization of lamellar α in Ti-17 alloy[J].Hot Working Technology,2005(1):16-18,41.
|
| 20 |
谭金花 .TC4合金表面激光熔覆钛基复合涂层组织及性能研究[D].天津:天津工业大学,2020.
|
| 21 |
种润,郭绍庆,张文扬,等 .GH4169合金激光增材制造过程热-力发展数值模拟[J].焊接,2021(3):13-21,61-62.
|
|
ZHONG Run, GUO Shaoqing, ZHANG Wenyang,et al .Numerical simulation of thermal-mechanical development of GH4169 alloy in laser additive manufacturing process[J].Welding & Joining,2021(3):13-21,61-62.
|