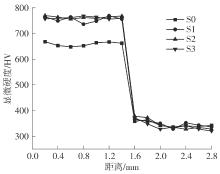
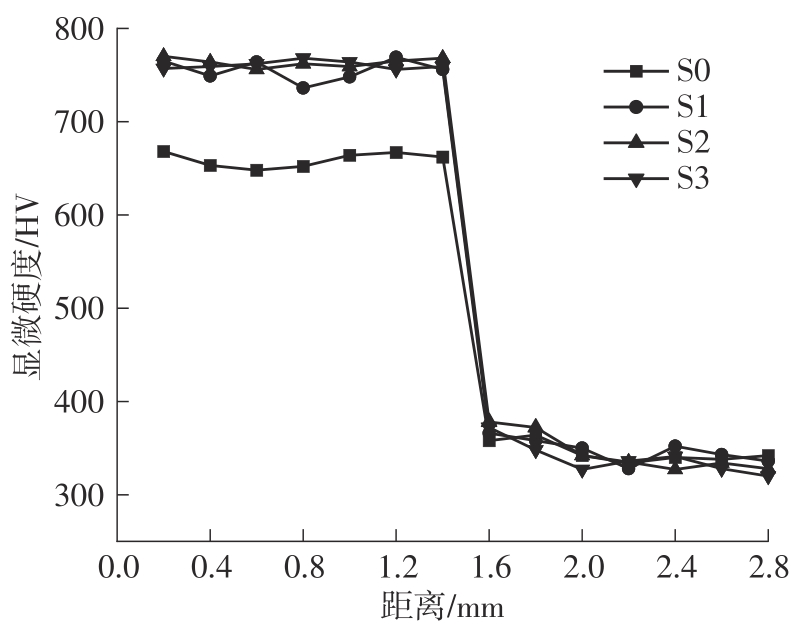
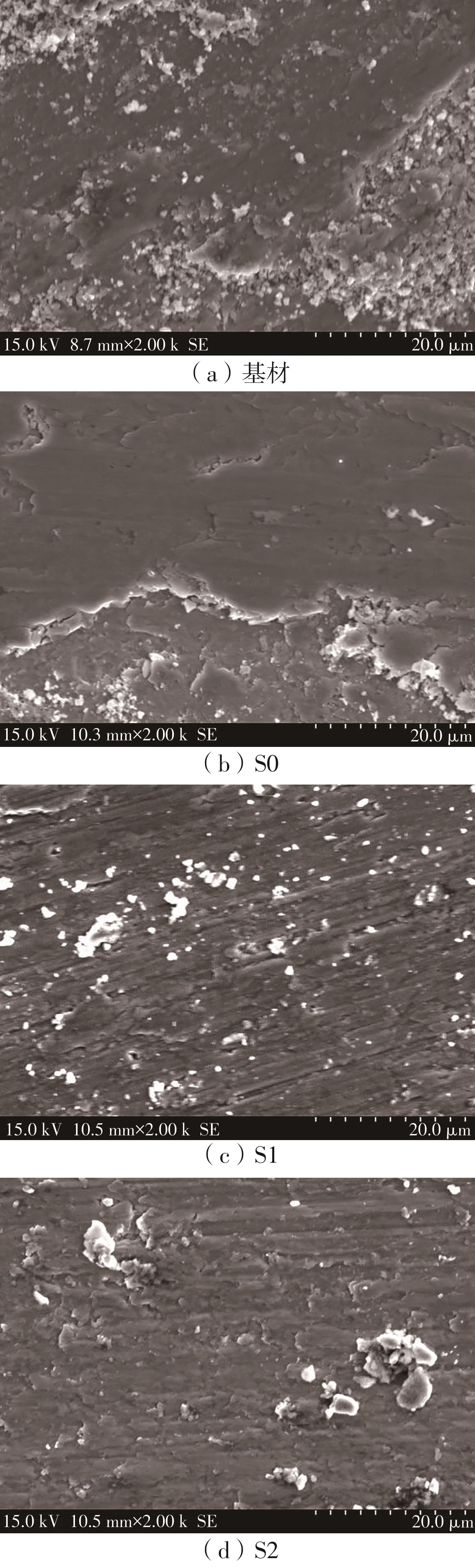
| 1 |
高敬,姚丽 .国内外钛合金研究发展动态[J].世界有色金属,2001(2):4-7.
|
|
GAO Jing, YAO Li .Research and development of titanium alloy at home and abroad[J].World Non-Ferrous Metals,2001(2):4-7.
|
| 2 |
张海云,张金,朱磊,等 .WC含量对激光熔覆TC4涂层组织及性能的影响[J].热加工工艺,2022,51(8):83-87.
|
|
ZHANG Haiyun, ZHANG Jin, ZHU Lei,et al .Effects of WC content on microstructure and properties of TC4 compositePrepared by laser cladding[J].Hot Working Technology,2022,51(8):83-87.
|
| 3 |
赵永庆,葛鹏,辛社伟 .近五年钛合金材料研发进展[J].中国材料进展,2020,39(Z1):527-534.
|
|
ZHAO Yongqing, GE Peng, XIN Shewei .Progresses of R&D on Ti-Alloy materials in recent 5 years[J].Materials China,2020,39(Z1):527-534.
|
| 4 |
柯金,刘秀波,庄宿国,等 .Ti6Al4V合金激光熔覆NiMoSi复合涂层的高温抗氧化性能[J].中国表面工程,2018,31(6):109-117.
|
|
KE Jin, LIU Xiubo, ZHUANG Suguo,et al .High temperature oxidation resistance of NiMoSi composite coatings on Ti6Al4V Alloy by laser cladding[J].China Surface Engineering,2018,31(6):109-117.
|
| 5 |
谭金花,孙荣禄,牛伟,等 .TC4合金激光熔覆材料的研究现状[J].材料导报,2020,34(15):15132-15137.
|
|
TAN Jinhua, SUN Ronglu, NIU Wei,et al .Research status of TC4 alloy laser cladding Materials[J].Materials Reports,2020,34(15):15132-15137.
|
| 6 |
菅丽娜,张凌云,于荣莉,等 .钛合金表面激光熔敷Cr(13)Ni5Si2基金属硅化物涂层组织与耐磨性[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2005,34(6):936-939.
|
|
JIAN Lina, ZHANG Lingyun, YU Rongli,et al .Microstructure and wear resistance of laser clad Cr13Ni5Si2-Based metal silicide coating on titanium alloy[J].Race Metal Materials and Engineering,2005,34(6):936-939.
|
| 7 |
林熙 .TC4表面激光熔覆耐磨涂层组织结构及性能的研究[D].天津:天津工业大学,2018.
|
| 8 |
易家,彭如恕 .TC4钛合金表面激光合金化涂层的组织与耐磨性能[J].金属热处理,2020,45(2):225-230.
|
|
YI Jia, PENG Rushu .Microstructure and wear resistance of laser alloying coating on TC4 titanium alloy surface[J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2020,45(2):225-230.
|
| 9 |
孟祥军,沈颖,张少瑜,等 .Ti6Al4V合金激光熔覆Co-Ti3SiC2复合涂层的组织和摩擦学性能[J].金属热处理,2021,46(12):199-203.
|
|
MENG Xiangjun, SHEN Ying, ZHANG Shaoyu,et al .Microstructure and tribological properties of laser clad Co-Ti3SiC2 composite coating on Ti6A4V alloy[J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2021,46(12):199-203.
|
| 10 |
MORIDI A, HASSANI-GANGARAJ S M, GUAGLIANO M,et al .Cold spray coating:review of materialsystems and fu-tureperspectives[J].Surface Engineering,2014,30(6):369-395.
|
| 11 |
赵海涛,付洪宇 .激光熔覆数值模拟技术发展现状及应用[J].沈阳理工大学学报,2021,40(3):58-63,73.
|
|
ZHAO Haitao, FU Hongyu .The development and application of laser cladding numerical simulation technology[J].Journal of Shenyang Ligong University,2021,40(3):58-63,73.
|
| 12 |
李玉海,王震,赵晖,等 .铜合金激光表面强化研究进展[J].沈阳理工大学学报,2019,38(6):22-27.
|
|
LI Yuhai, WANG Zhen, ZHAO Hui,et al .Research progress on laser surface strengthening of copper alloy[J].Journal of Shenyang Ligong University,2019,38(6):22-27.
|
| 13 |
RAHMANI H, RASTEGARI S, MIRDAMADI S .Effective pa-rameters on microstructure and properties of EB-PVD NiCrAlY coating[J].Surface Engineering,2015,31(2):156-165.
|
| 14 |
TIAN Y S, CHEN C Z, WANG D Y,et al .Laser surface alloying of pure titanium with TiN-B-Si-Ni mixed powders[J].Applied Surface Science,2005,250(1):223-227.
|
| 15 |
TIAN Y S, CHAN C Z, CHEN L X,et al .Microstructures and wear properties of composite coatings produced by laser alloying of Ti-6Al-4V with graphite and silicon mixed powders[J].Materials Letters,2006,60(1):109-113.
|
| 16 |
王东生,田宗军,沈理达,等 .钛合金激光表面改性技术研究现状[J].激光与光电子学进展,2008,45(6):24-32.
|
|
WANG Dongsheng, TIAN Zongjun, SHEN Lida,et al .Research states of laser surface modification technology on titanium alloys[J].Laser & Optoelectronics Progress,2008,45(6):24-32.
|
| 17 |
LI J N, CHEN C Z, ZONG L .Microstructure characteristics of Ti3Al/TiC ceramic layer deposited by laser cladding[J].International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2011,29(1):49-53.
|
| 18 |
LI J, CHEN C, SQUARTINI T,et al .A study on wear resistance and microcrack of the Ti3Al/TiAl+TiC ceramic layer deposited by laser cladding on Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J].Applied Surface Science,2010,257(5):1550-1555.
|
| 19 |
WANG H M, LIU Y F .Microstructure and wear resistance of laser clad Ti5Si3/NiTi2 intermetallic composite coating on titanium alloy[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A,2002,338(1):126-132.
|
| 20 |
SONG R, LI J, SHAO J Z,et al .Microstructural evolution and wear behaviors of laser cladding Ti2Ni/α(Ti) dual-phase coating reinforced by TiB and Ti C[J].Applied Surface Science,2015,355:298-309.
|
| 21 |
刘建弟,张述泉,王华明 .激光熔覆WC颗粒增强复合涂层的组织及耐磨性[J].中国有色金属学报,2012,22(9):2600-2607.
|
|
LIU Jian-di, ZHANG Shu-quan, WANG Hua-ming .Microstructure and wear resistance of laser cladding WC particles reinforced composite coatings[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2012,22(9):2600-2607.
|
| 22 |
王璐,胡树兵,单炜涛,等 .激光熔覆NiCrMn-WC复合涂层的组织与耐磨性[J].中国有色金属学报,2014,24(1):145-151.
|
|
WANG Lu, HU Shu-bing, SHAN Wei-tao,et al .Microstructure and wear resistance of laser cladding NiCrMn-WC composite coatings[J].The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2014,24(1):145-151.
|
| 23 |
ZHOU S, LEI J, DAI X,et al .A comparative study of the structure and wear resistance of NiCrBSi/50 wt% WC composite coatings by laser cladding and laser induction hybrid cladding[J].International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2016,60:17-27.
|
| 24 |
LUO X, LI J, LI G J .Effect of NiCrBSi content on microstructural evolution,cracking susceptibility and wear behaviors of laser cladding WC/Ni-NiCrBSi composite coatings[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2015,626:102-111.
|
| 25 |
冯进宇,肖华强,肖易,等 .TC4表面激光熔覆Ti-Al-(C,N)复合涂层的组织与力学性能[J].中国激光,2022,49(2):165-173.
|
|
FENG Jinyu, XIAO Huaqiang, XIAO Yi,et al .Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser cladded Ti-Al-(C,N) composite coating on TC4 surface[J].Chinese Journal of Lasers,2022,49(2):165-173.
|
| 26 |
秦阳,闫华,高秋实,等 .TC4表面激光熔覆原位合成Ti3SiC2/Ni基涂层的组织与耐磨性能[J].有色金属工程,2019,9(4):34-40.
|
|
QIN Yang, YAN Hua, GAO Qiushi,et al .Microstructure and wear resistance of in-situ synthesized Ti3SiC2/Ni-based coating by laser cladding on titanium alloy[J].Nonferrous Metals Engineering,2019,9(4):34-40.
|
| 27 |
覃鑫,祁文军,左小刚 .TC4钛合金表面激光熔覆NiCrCoAlY-Cr 3C2复合涂层的摩擦和高温抗氧化性能[J].材料工程,2021,49(12):107-114.
|
|
QIN Xin, QI Wen-jun, ZUO Xiao-gang .Friction and high temperature oxidation resistance of laser cladding NiCrCoAlY-Cr3C2 composite coating on TC4 titanium alloy[J].Journal of Materials Engineering,2021,49(12):107-114.
|