Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 33-41.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230082
• Food Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
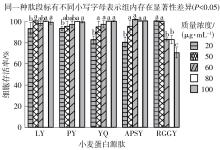
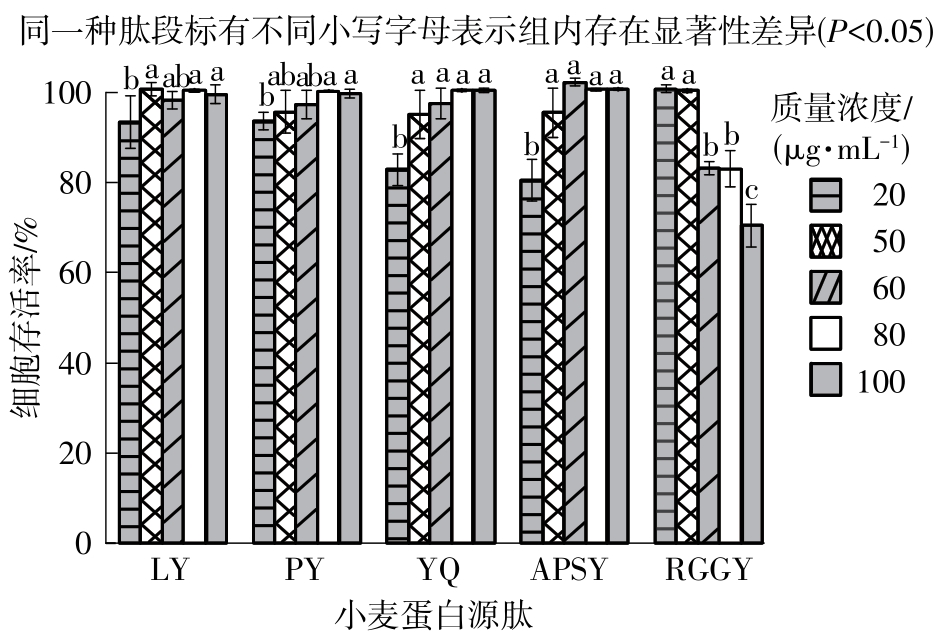
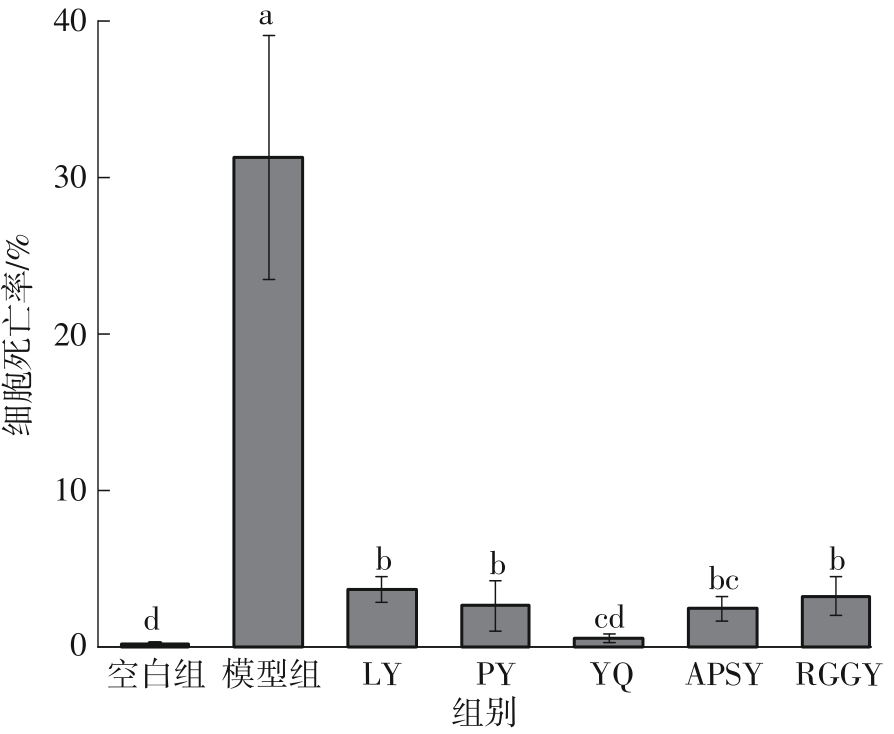
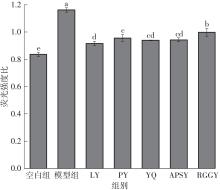
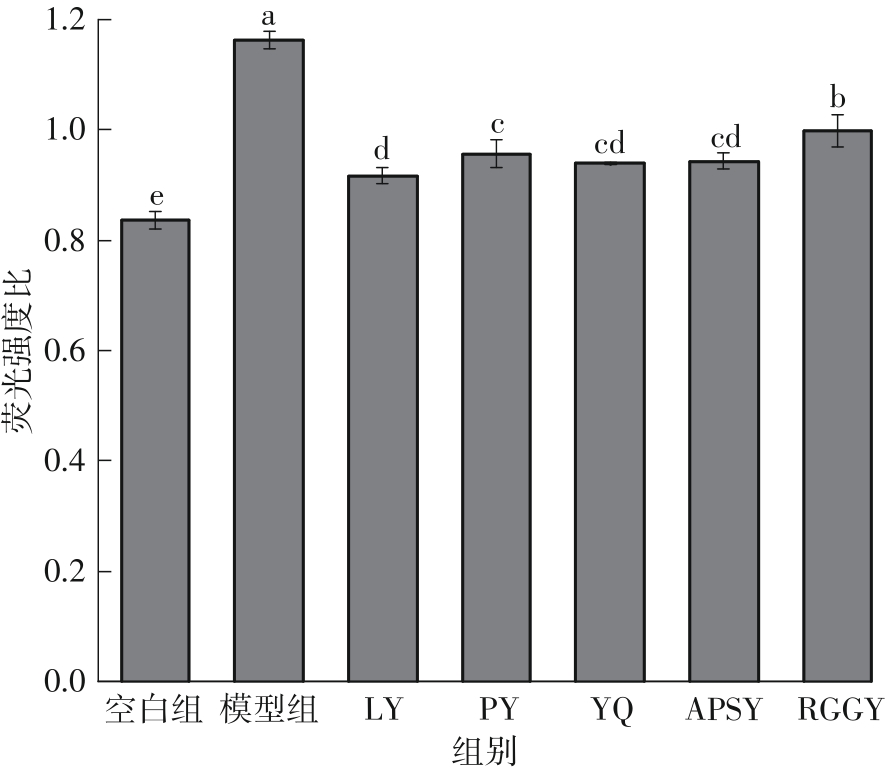
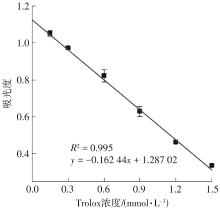
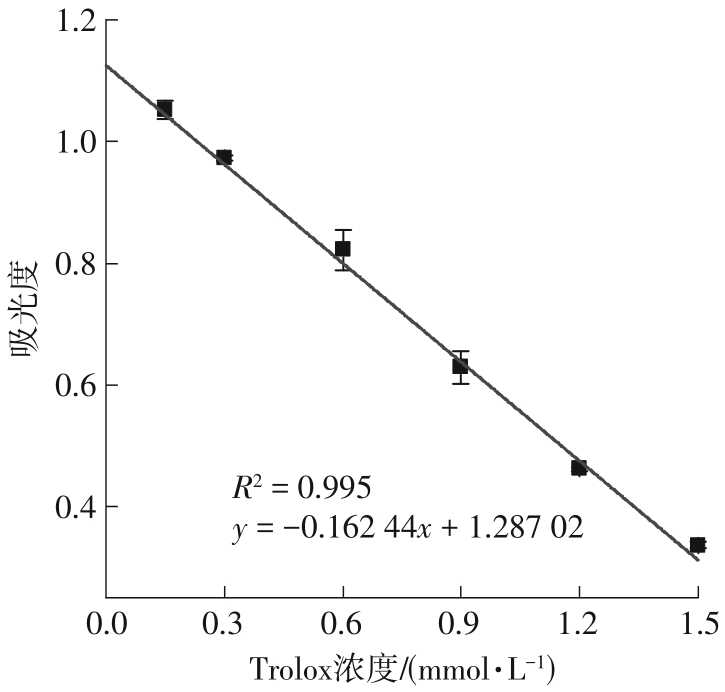
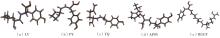
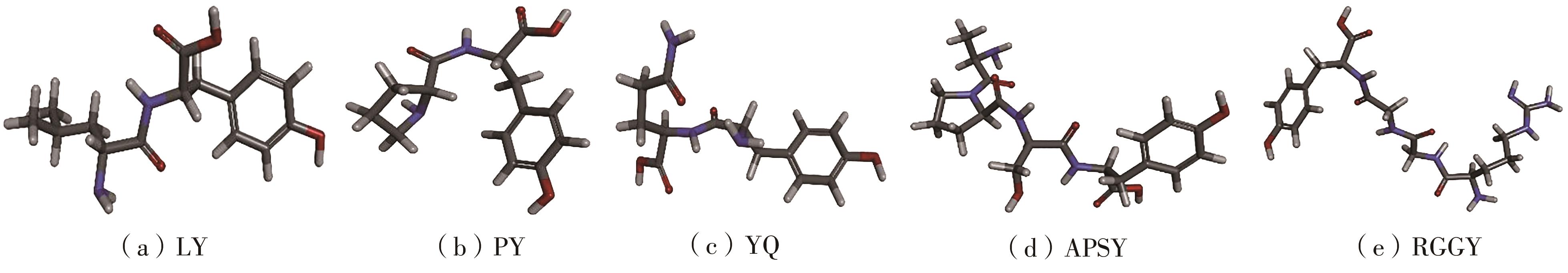
Inhibitory Effects and Molecular Mechanism of Wheat Antioxidant Peptides on Oxidative Stress Injury in Human Embryonic Kidney Cells
LIU Wenying1 REN Jie2 WU Hanshuo2 HAN Lujia1
- 1.College of Engineering,China Agricultural University,Beijing 100083,China
2.Beijing Engineering Research Center of Protein and Functional Peptides,China National Research Institute of Food and Fermentation Industries Co. ,Ltd. ,Beijing 100015,China
-
Received:2023-03-03Online:2024-04-25Published:2023-08-18 -
Contact:韩鲁佳(1964-),女,博士,教授,主要从事农产品加工工程研究。 E-mail:hanlj@cau.edu.cn -
About author:刘文颖(1984-),女,博士生,高级工程师,主要从事农产品加工工程研究。E-mail:wenyingliu888@126.com -
Supported by:the Key R&D Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region(2021BEG02027)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Wenying, REN Jie, WU Hanshuo, et al. Inhibitory Effects and Molecular Mechanism of Wheat Antioxidant Peptides on Oxidative Stress Injury in Human Embryonic Kidney Cells[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(4): 33-41.
share this article
| 1 | ZHAO X C, ZHANG L, YU H X,et al .Curcumin protects mouse neuroblastoma Neuro-2A cells against hydrogen-peroxide-induced oxidative stress[J].Food Chemistry,2011,129(2):387-394. |
| 2 | LUSHCHAK V I .Free radicals,reactive oxygen species,oxidative stress and its classification[J].Chemico-Biological Interactions,2014,224:164-175. |
| 3 | YI G F, DIN J U, ZHAO F,et al .Effect of soybean peptides against hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells via Nrf2 signaling[J].Food & Function,2020,11(3):2725-2737. |
| 4 | 刘文颖,冯晓文,程青丽,等 .大米低聚肽的制备和结构表征及体外抗氧化作用[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(11):47-56. |
| LIU Wenying, FENG Xiaowen, CHENG Qingli,et al .Preparation,structure characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity of rice oligopeptides[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(11):47-56. | |
| 5 | NORDBERG J, ARNER E S J .Reactive oxygen species,antioxidants,and the mammalian thioredoxin system[J].Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2001,31(11):1287-1312. |
| 6 | 吉正梅,张晓春,彭钰迪,等 .鸭胚源抗氧化肽TD12对HepG2细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J].食品与发酵工业,2021,47(18):141-148. |
| JI Zhengmei, ZHANG Xiaochun, PENG Yudi,et al .Protective effect of duck embryo-derived antioxidant peptide TD12 on oxidative stress damage in HepG2 cells [J].Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(18):141-148. | |
| 7 | KARAMI Z, PEIGHAMBARDOUST S H, HESARI J,et al .Antioxidant,anticancer and ACE-inhibitory activities of bioactive peptides from wheat germ protein hydrolysates[J].Food Bioscience,2019,32:100450/1-12. |
| 8 | ZHANG J, WEN C, LI C,et al .Antioxidant peptide fractions isolated from wheat germ protein with subcritical water extraction and its transport across Caco-2 cells[J].Journal of Food Science,2019,84(8):2139-2146. |
| 9 | LIU W Y, ZHANG J T, TAKUYA MIYAKAWA,et al .Antioxidant properties and inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme by highly active peptides from wheat gluten[J].Scientific Reports,2021,11(1):5206/1-11. |
| 10 | 张燕,陈志飞,赵颂宁,等 .蛋清源抗氧化肽对HEK293细胞氧化应激损伤的抑制作用及机制[J].中国食品学报,2019,19(10):11-22. |
| ZHANG Yan, CHEN Zhifei, ZHAO Songning,et al .The anti-oxidative effects and mechanism of antioxidant peptides from egg white against oxidative stress injury in human embryonic kidney 293 cells[J].Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(10):11-22. | |
| 11 | ZHANG Q, CUI C, CHEN C Q,et al .Anti-proliferative and proapoptotic activities of Alpinia oxyphylla on HepG2 cells through ROS-mediated signaling pathway[J].Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2015,169:99-108. |
| 12 | LIU E Y, FANG L, FENG X W,et al . In vitro antioxidant and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of peptides derived from corn gluten meal [J].European Food Research and Technology,2020,246:2017-2027. |
| 13 | MINE Y, MA F P, LAURIAU S .Antimicrobial peptides released by enzymatic hydrolysis of hen egg white lysozyme[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2004,52(5):1088-1094. |
| 14 | WEN C, ZHANG J, ZHANG H,et al .Study on the structure-activity relationship of watermelon seed antioxidant peptides by using molecular simulations[J].Food Chemistry,2021,364:130432/1-7. |
| 15 | ZHANG J, LI M, ZHANG G,et al .Identification of novel antioxidant peptides from snakehead (Channa argus) soup generated during gastrointestinal digestion and insights into the anti-oxidation mechanisms[J].Food Chemistry,2021,337:127921/1-11. |
| 16 | LI C, ZHAN Y D, MA X Z,et al .B7-H4 facilitates proliferation and metastasis of colorectal carcinoma cell through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J].Clinical and Experimental Medicine,2020,20(1):79-86. |
| 17 | LIU L, QIU T X, SONG D W,et al .Inhibition of a novel coumarin on an aquatic rhabdovirus by targeting the early stage of viral infection demonstrates potential application in aquaculture[J].Antiviral Research,2020,174:104672/1-13. |
| 18 | LU Q B, LIN X Y, WU J,et al .Matrine attenuates cardiomyocyte ischemia-reperfusion injury through activating AMPK/Sirt3 signaling pathway[J].Journal of Receptors and Signal Transduction Research,2021,41(1):488-493. |
| 19 | LU J M, LIN P H, YAO Q Z,et al .Chemical and molecular mechanisms of antioxidants:experimental approaches and model systems[J].Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine,2010,14(4):840-860. |
| 20 | NEMOTO S, TAKEDA K, YU Z X,et al .Role for mitochondrial oxidants as regulators of cellular metabolism[J].Molecular and Cellular Biology,2000,20(19):7311-7318. |
| 21 | YU D L, ZHA Y Y, ZHONG Z,et al .Improved detection of reactive oxygen species by DCFH-DA:new insight into self-amplification of fluorescence signal by light irradiation[J].Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical,2021,339:129878/1-9. |
| 22 | LIU X, FU Q, XU P,et al .Rapid determination of monopersulfate with bromide ion-catalyzed oxidation of 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS)[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,433:133551/1-8. |
| 23 | QIN X Y, ZHANG J T, LIU G M,et al .Structure and composition of a potential antioxidant obtained from the chelation of pea oligopeptide and sodium selenite[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2019,64:103619/1-8. |
| 24 | CHANG O K, HA G E, HAN G S,et al .Novel antioxidant peptide derived from the ultrafiltrate of ovomucin hydrolysate[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61:7294-7300. |
| 25 | SUN J, HE H, XIE B J .Novel antioxidant peptides from fermented mushroom Ganoderma lucidum[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2004,52:6646-6652. |
| 26 | CHEN H M, MURAMOTO K, YAMAUCHI F,et al .Structural analysis of antioxidative peptides from soybean beta-conglycinin[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1995,43:574-578. |
| 27 | SAITO K, JIN D H, OGAWA T,et al .Antioxidative properties of tripeptide libraries prepared by the combinatorial chemistry[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2003,51:3668-3674. |
| 28 | GU R Z, LIU W Y, LIN F,et al .Antioxidant and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of oligopeptides derived from black-bone silky fowl (Gallus gallus domesticus Brisson) muscle[J].Food Research International,2012,49:326-333. |
| 29 | ZHOU C, HU J, MA H,et al .Antioxidant peptides from corn gluten meal:orthogonal design evaluation [J].Food Chemistry,2015,187(15):270-278. |
| 30 | ZHU K X, ZHOU H M, QIAN H F .Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of wheat germ protein hydrolysates (WGPH) prepared with alcalase[J].Process Biochemistry,2006,41(6):1296-1302. |
| 31 | 张燕,魏汝君,潘风光,等 .蛋清源活性肽抗氧化及抗炎活性[J].食品科学,2018,39(13):153-158. |
| ZHANG Yan, WEI Rujun, PAN Fengguang,et al .Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of bioactive peptides derived from egg white proteins[J].Food Science,2018,39(13):153-158. | |
| 32 | WU R, HUANG J, HUAN R,et al .New insights into the structure-activity relationships of antioxidative peptide PMRGGGGYHY[J].Food Chemistry,2021,337:127678/1-8. |
| 33 | 文超婷 .西瓜籽肽的抗氧化构效关系及其分子机制研究[D].镇江:江苏大学,2021. |
| 34 | YANG Q, CAI X, YAN A,et al .A specific antioxidant peptide:its properties in controlling oxidation and possible action mechanism[J].Food Chemistry,2020,327:126984/1-9. |
| [1] | XU Xilin, PENG Yunyan, ZHOU Xiaoli, ZHONG Shuying, DUAN Longhui, LIU Dongmei. Study on Beneficial Characteristics inVitro of Enterococcus Faecalis EF-ZA1107-06 [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(12): 118-130. |
| [2] | YE Jun, LIU Luying, HUANG Zhuosheng, et al. Study on CMC/CS/Ca2+ Composite Hydrogel for Transdermal Delivery of SPE in vitro and Its Antioxidant Activity [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(1): 51-60. |
| [3] | ZHENG Bisheng, WEI Ruijing, GUO Chaowan, et al. Study on Purification of Kapok Flavonoids by Macroporous Resin and Its Anti-acne Efficacy [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(4): 119-128. |
| [4] | HUANG Yanbo, SUN Weizheng, HOU Yi, et al. Protective Mechanism of Yeast Hydrolysates Against the Oxidative Injury on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(1): 23-29. |
| [5] | Li Lin, Yu An-ling, Wu Zhi, et al. Investigation into Interaction Mechanism and Antioxidant Activity of Resveratrol and Modified Pectin [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(9): 1-10. |
| [6] | XU Xilin, ZHOU Xiaoli, ZHENG Liuqing, et al. Antioxidant Activity of Lactobacillus rhamnosus LR ZB1107-01 in Vitro [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(3): 88-94. |
| [7] | LIU Wenying, FENG Xiaowen, CHENG Qingli, et al. Preparation,Structure Characterization and in vitro Antioxidant Activity of Rice Oligopeptides [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(11): 47-56. |
| [8] | SU Jianyu HU Han WU Ping MENG Xiaofeng XU Zhenbo ZHENG Huade. Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities of Myricetin In Vitro [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(3): 101-108,152. |
| [9] | . Copper(II)-coordinating Force and Antioxidant Activity of Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(12): 126-132. |
| [10] |
LIU Hongsheng FENG Mingyue CHEN Xia.
Preparation and Characterization of Starch Functional Film
|
| [11] |
LIU Hongsheng FENG Mingyue CHEN Xia.
Preparation and Characterization of Starch Functional Film
|
| [12] | YOU Lijun HUANG Shiming ZHENG Guiqing ZHAO Zhengang HAN Rui MENG Hecheng. Structural,Antioxidant Activity and Immunomodulatory Activity of Polysaccharides Isolated from Undaria pinnatifida#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(11): 29-38. |
| [13] | SUN Wei-zheng YANG Kun LIN Lian-zhu ZOU Ying ZHAO Mou-ming. Investigation into Identification,Antioxidant Activity and Anti-Hemolysis Activity of Phenolics Compounds in High Acid Apple [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(3): 146-152. |
| [14] | REN Jiao-yan SHANG Shuai-ming LIANG Ming ZHANG Ting ZHOU Yong LI Hai-long YUAN Er-dong. Protective Effect of Corbicula Fluminea Hydrolyzates on Ethanol-Induced LO2 Cells Injury [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(12): 20-26. |
| [15] | Zhao Qiang-zhong Feng Meng-ying Lin Lian-zhu Zhao Mou-ming. Separation,Identification and Antioxidant Activity of Glycoproteins from Millettia Speciosa Champ. [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(11): 8-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||