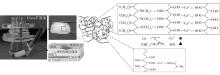
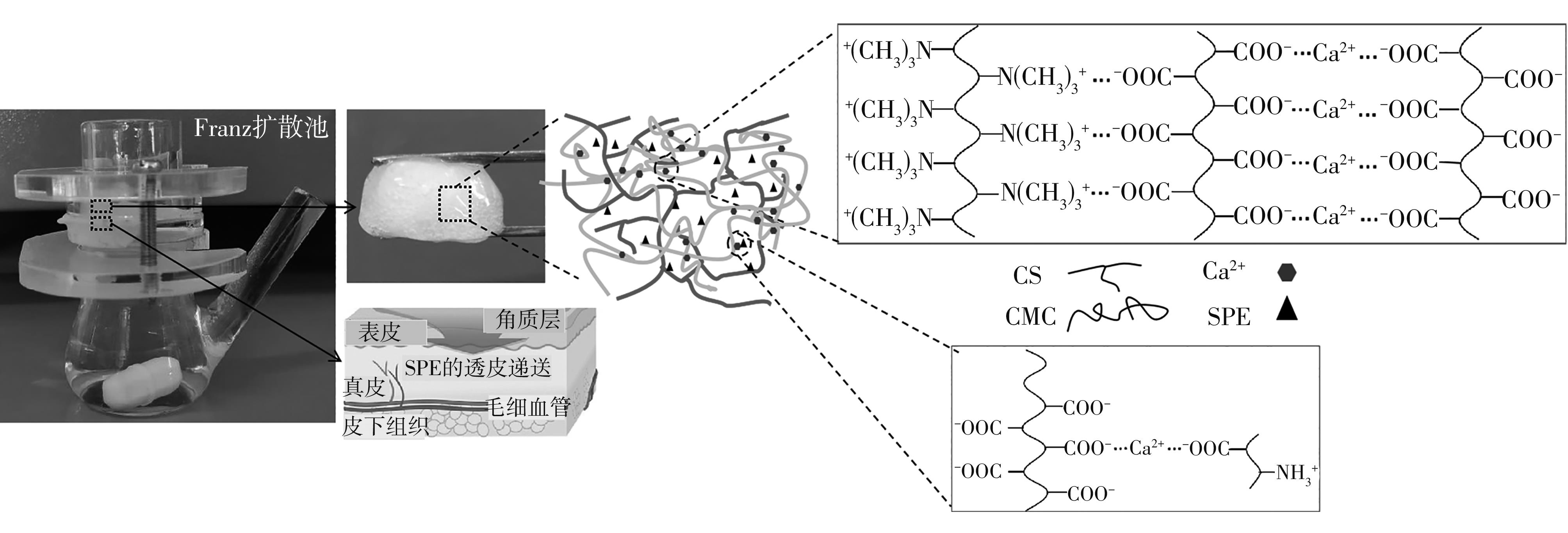
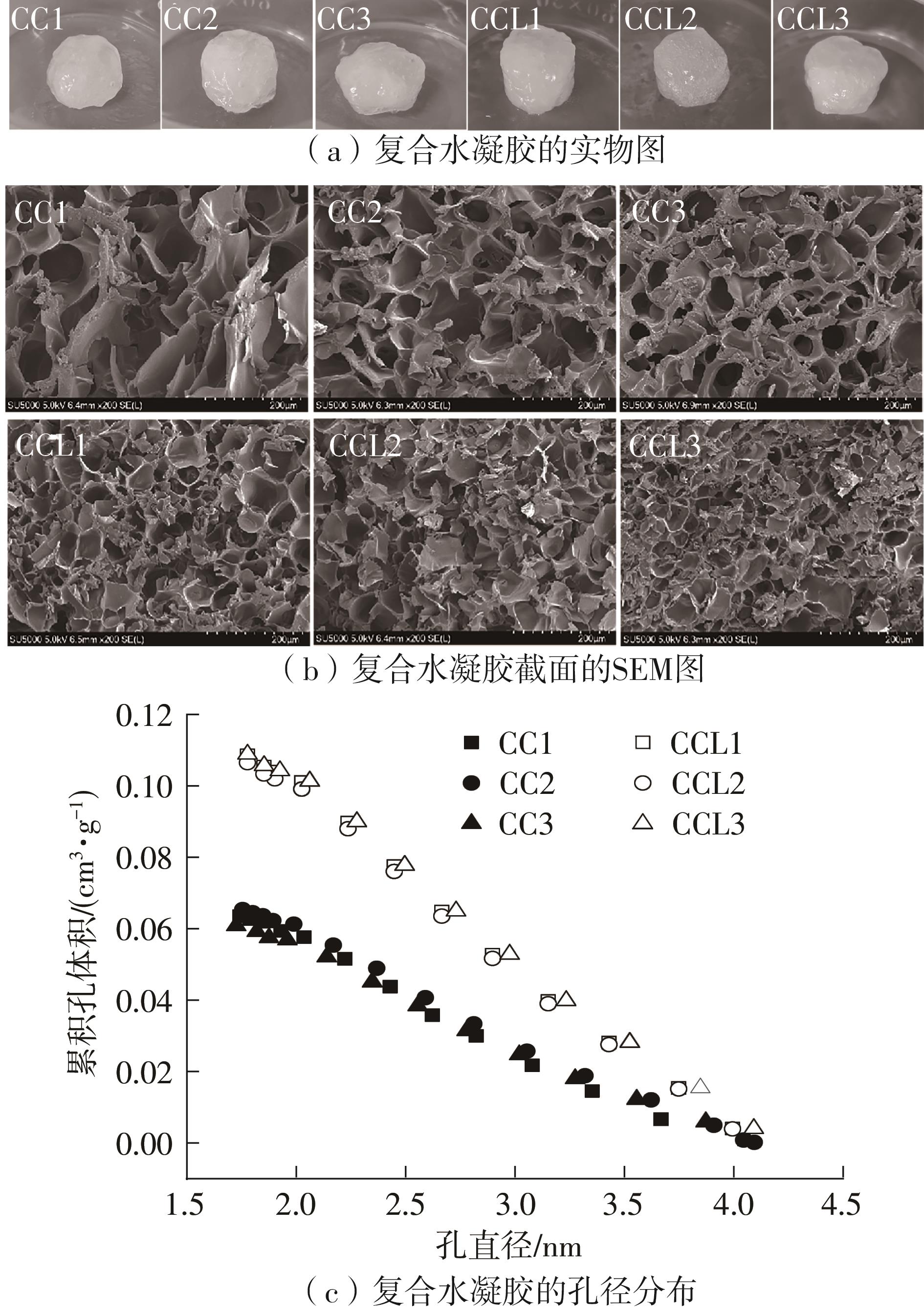
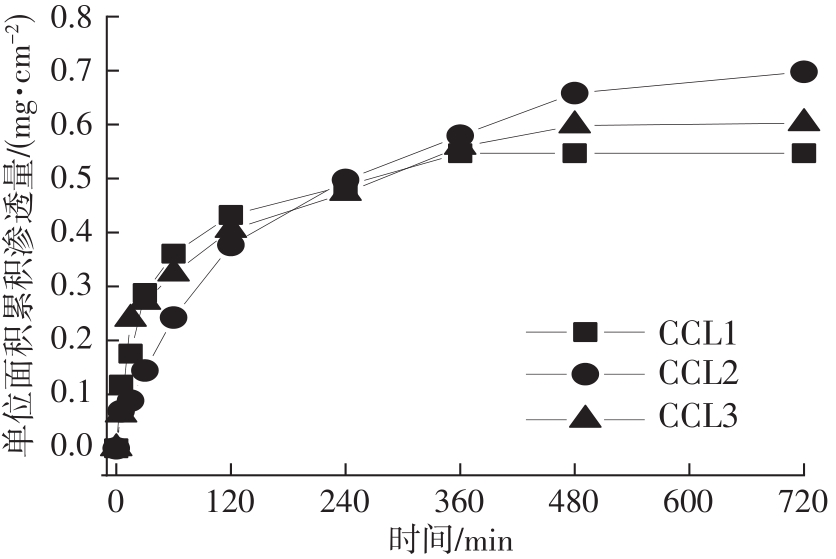
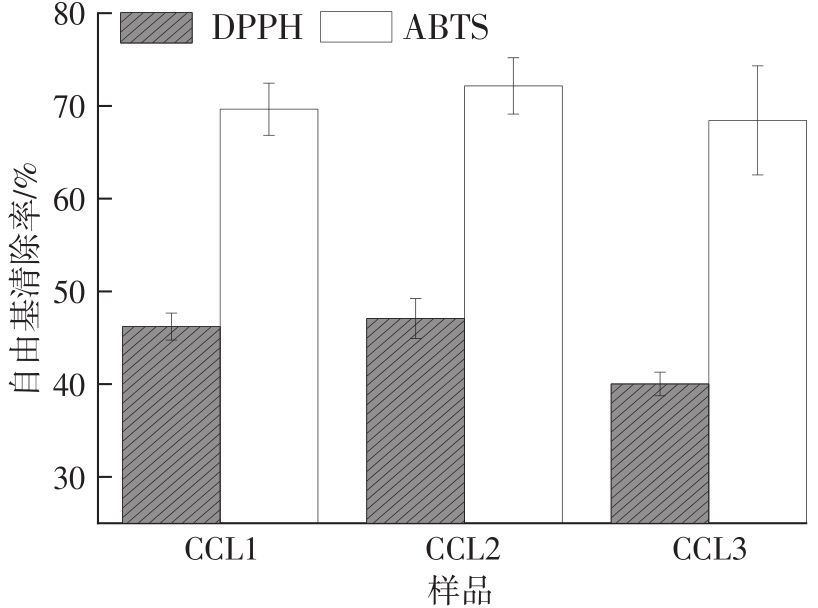
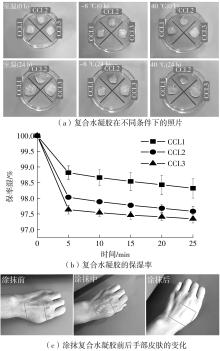
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 51-60.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220388
Special Issue: 2023年材料科学与技术
• Materials Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
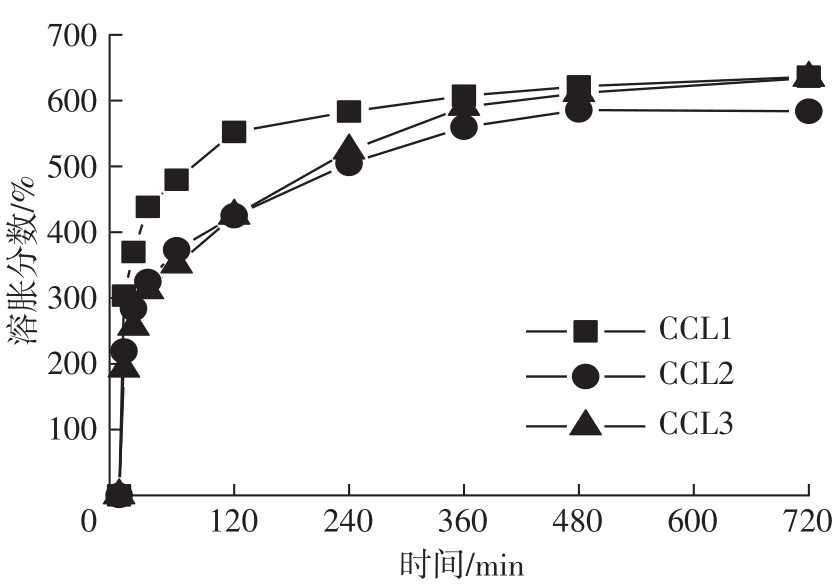
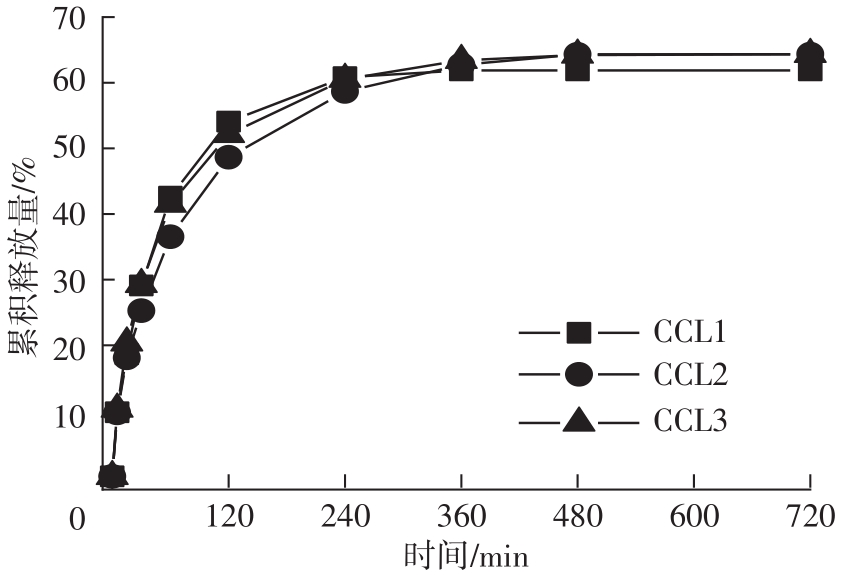
Study on CMC/CS/Ca2+ Composite Hydrogel for Transdermal Delivery of SPE in vitro and Its Antioxidant Activity
YE Jun1 LIU Luying1 HUANG Zhuosheng2 XIONG Jian3
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Pulp and Paper Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Yiruian Food Ingredients Co. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 201600,China
3.School of Food Science and Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-06-20Online:2023-01-25Published:2023-01-02 -
Contact:熊犍(1965-),男,博士,教授,主要从事纤维素及其他天然高分子结构与性能研究。 E-mail:lcjxiong@scut.edu.cn -
About author:叶君(1963-),女,博士,教授,主要从事植物资源化学研究。E-mail:jye@scut.edu.cn. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(22178128)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YE Jun, LIU Luying, HUANG Zhuosheng, et al. Study on CMC/CS/Ca2+ Composite Hydrogel for Transdermal Delivery of SPE in vitro and Its Antioxidant Activity[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(1): 51-60.
share this article
| 1 | LIN Y, JIANG M, CHEN W,et al .Cancer and ER stress:mutual crosstalk between autophagy,oxidative stress and inflammatory response[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2019,118:109249/1-10. |
| 2 | ZHENG Y-Z, DENG G, ZHANG Y-C .Multiple free radical scavenging reactions of flavonoids[J].Dyes and Pigments,2022,198:109877/1-8. |
| 3 | NDREPEPA G .Myeloperoxidase - a bridge linking inflammation and oxidative stress with cardiovascular disease[J].Clin Chim Acta,2019,493:36-51. |
| 4 | HEMMATI-DINARVAND M, SAEDI S, VALILO M,et al .Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease: conflict of oxidant-antioxidant systems[J].Neurosci Lett,2019,709:134296. |
| 5 | KHAMBU B, YAN S, HUDA N,et al .Autophagy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic liver disease[J].Liver Res,2018,2(3):112-119. |
| 6 | WANG X Q, WANG W, PENG M,et al .Free radicals for cancer theranostics[J].Biomaterials,2021,266:120474. |
| 7 | LIM H W, KOHLI I, RUVOLO E,et al .Impact of visible light on skin health: the role of antioxidants and free radical quenchers in skin protection[J].J Am Acad Dermatol,2022,86(3S):S27-S37. |
| 8 | ZHANG Q, TONG X, SUI X,et al .Antioxidant activity and protective effects of alcalase-hydrolyzed soybean hydrolysate in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells[J].Food Res Int,2018,111:256-264. |
| 9 | DHARADHAR S, MAJUMDAR A, DHOBLE S,et al .Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery:a systematic review[J].Drug Dev Ind Pharm,2019,45(2):188-201. |
| 10 | LIU T, CHEN M, FU J,et al .Recent advances in microneedles-mediated transdermal delivery of protein and peptide drugs[J].Acta Pharm Sin B,2021,11(8):2326-2343. |
| 11 | GHOSH B, BHATTACHARYA D, KOTAL A,et al .Cytocompatible,thermostable hydrogel with utility to release drug over skin[J].Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology,2019,94(3):616-627. |
| 12 | STASAID M, BOUTEMAK K, IBTISSEM L,et al .Synthesis of carboxymethyl xanthan/double-walled carbon nanotube hybrid hydrogel nanocomposite for transdermal release of drug[J].Soft Materials,2021,20(2):168-182. |
| 13 | LADENHEIM D, MARTIN G P, MARRIOTT C,et al .An in-vitro study of the effect of hydrocolloid patch occlusion on the penetration of triamcinolone acetonide through skin in man[J].J Pharm Pharmacol,1996,48(8):806-811. |
| 14 | PARK S H, SHIN H S, PARK S N .A novel pH-responsive hydrogel based on carboxymethyl cellulose/2-hydroxyethyl acrylate for transdermal delivery of naringenin[J].Carbohyd Polym,2018,200:341-352. |
| 15 | CARVALHO S M, MANSUR A A P, CAPANEMA N S V,et al .Synthesis and in vitro assessment of anticancer hydrogels composed by carboxymethylcellulose-doxorubicin as potential transdermal delivery systems for treatment of skin cancer[J].Journal of Molecular Liquids,2018,266:425-440. |
| 16 | XU S, CAO L, WU R,et al .Salt and pH responsive property of a starch-based amphoteric superabsorbent hydrogel with quaternary ammonium and carboxyl groups (Ⅱ)[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2006,101(3):1995-1999. |
| 17 | BERCEA M, BILIUTA G, AVADANEI M,et al .Self-healing hydrogels of oxidized pullulan and poly(vinyl alcohol)[J].Carbohyd Polym,2019,206:210-219. |
| 18 | SHU G, SHI X, CHEN L,et al .Antioxidant peptides from goat milk fermented by Lactobacillus casei L61:preparation,optimization,and stability evaluation in simulated gastrointestinal fluid[J].Nutrients,2018,10(6):797/1-13. |
| 19 | XU C, GUAN S, XU J,et al .Preparation,characterization and antioxidant activity of protocatechuic acid grafted carboxymethyl chitosan and its hydrogel[J].Carbohydr Polym,2021,252:117210. |
| 20 | PICHAYAKORN W, SUKSAEREE J, TAWEEPREDA W,et al .Polymer blended deproteinized natural rubber reservoirs for nicotine transdermal patches:in vitro drug release, permeation study,and stability test[J].Journal of Polymers and the Environment,2022,30(3):988-1000. |
| 21 | 面膜: [S]. |
| 22 | PENG Y, YAN B, LI Y,et al .Antifreeze and moisturizing high conductivity PEDOT/PVA hydrogels for wearable motion sensor[J].Journal of Materials Science,2020,55(3):1280-1291. |
| 23 | ELKENAWY N M, KARAM H M, ABOUL-MAGD D S .Development of gamma irradiated SSD-embedded hydrogel dyed with prodigiosin as a smart wound dressing:evaluation in a MDR infected burn rat model[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,211:170-182. |
| 24 | SALLAM M A, BOSCA M T M .Mechanistic analysis of human skin distribution and follicular targeting of adapalene-loaded biodegradable nanospheres with an insight into hydrogel matrix influence, in vitro skin irritation, and in vivo tolerability[J].Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2017,106(10):3140-3149. |
| 25 | 叶君,叶芳,熊犍 .含Eu3+的PVA/CMC荧光水凝胶的结构与性能[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(9):37-45. |
| YE Jun, YE Fang, XIONG Jian .Structure and properties of Eu3+-containing PVA/CMC fluorescent hydrogels[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(9):37-45. | |
| 26 | EABORN C .Compendium of chemical terminology:IUPAC recommendations[J].Journal of Organometallic Chemistry,1988,356(2):C76-C77. |
| 27 | SAPPIDI P, NATARAJAN U .Effect of salt valency and concentration on structure and thermodynamic behavior of anionic polyelectrolyte Na(+)-polyethacrylate aqueous solution[J].J Mol Model,2016,22(11):274. |
| 28 | BAO X L, LV Y, YANG B C,et al .A study of the soluble complexes formed during calcium binding by soybean protein hydrolysates[J].J Food Sci,2008,73(3):C117-C121. |
| 29 | SIMANAVICIUTE D, KLIMAVICIUTE R, RUTKAITE R .Equilibrium adsorption of caffeic,chlorogenic and rosmarinic acids on cationic cross-linked starch with quaternary ammonium groups[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,95:788-795. |
| 30 | POUR Z S, MAKVANDI P, GHAEMY M .Performance properties and antibacterial activity of crosslinked films of quaternary ammonium modified starch and poly(vinyl alcohol)[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,80:596-604. |
| 31 | XIONG J, LI Q Y, SHI Z X,et al .Interactions between wheat starch and cellulose derivatives in short-term retrogradation:rheology and FTIR study[J].Food Research International,2017,100:858-863. |
| 32 | JHA P, DHARMALINGAM K, NISHIZU T,et al .Effect of amylose-amylopectin ratios on physical,mechanical,and thermal properties of starch-based bionanocomposite films incorporated with CMC and nanoclay[J].Starch - Stärke,2020,72(1/2):1900121. |
| 33 | SHARRATT W N, LOPEZ C G, SARKIS M,et al .Ionotropic gelation fronts in sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for hydrogel particle formation[J].Gels,2021,7(2):44. |
| 34 | KIM A R, LEE S L, PARK S N .Properties and in vitro drug release of pH- and temperature-sensitive double cross-linked interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid/poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) for transdermal delivery of luteolin[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,118(Pt A):731-740. |
| 35 | WANG W, CHEN W, YANG H,et al .Textural and rheological properties of potato starch as affected by amino acids[J].International Journal of Food Properties,2017,20(Sup3):S3123-S3134. |
| 36 | KOUR P, AFZAL S, GANI A,et al .Effect of nanoemulsion-loaded hybrid biopolymeric hydrogel beads on the release kinetics,antioxidant potential and antibacterial activity of encapsulated curcumin[J].Food Chemistry,2022,376:131925. |
| 37 | ZHANG S, HOU J, YUAN Q,et al .Arginine derivatives assist dopamine-hyaluronic acid hybrid hydrogels to have enhanced antioxidant activity for wound healing[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2020, 392: 123775/1-10. |
| 38 | KIM B, KANG B, VALES T P,et al .Polyphenol-functionalized hydrogels using an interpenetrating chitosan network and investigation of their antioxidant activity[J].Macromolecular Research,2018,26(1):35-39. |
| 39 | ADEPU S, KHANDELWAL M .Ex-situ modification of bacterial cellulose for immediate and sustained drug release with insights into release mechanism[J].Carbohyd Polym,2020,249:116816/1-11. |
| 40 | GANJI F, VASHEGHANI-FARAHANI S, VASHEGHANI- FARAHANI E .Theoretical description of hydrogel swelling:a review[J].Iranian Polymer Journal,2010,19(5):375-398. |
| 41 | BRAZEL C S, PEPPAS N A .Dimensionless analysis of swelling of hydrophilic glassy polymers with subsequent drug release from relaxing structures[J].Biomaterials,1999,20(8):721-732. |
| 42 | RAMADON D, MCCRUDDEN M T C, COURTENAY A J,et al .Enhancement strategies for transdermal drug delivery systems:current trends and applications[J].Drug Deliv Transl Res,2022,12(4):758-791. |
| [1] | HUANG Yanbo, SUN Weizheng, HOU Yi, et al. Protective Mechanism of Yeast Hydrolysates Against the Oxidative Injury on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(1): 23-29. |
| [2] | Li Lin, Yu An-ling, Wu Zhi, et al. Investigation into Interaction Mechanism and Antioxidant Activity of Resveratrol and Modified Pectin [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(9): 1-10. |
| [3] | YE Jun YE Fang XIONG Jian. Structure and Properties of Eu3+-Containing PVA/CMC Fluorescent Hydrogels [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(9): 37-45. |
| [4] | XU Xilin, ZHOU Xiaoli, ZHENG Liuqing, et al. Antioxidant Activity of Lactobacillus rhamnosus LR ZB1107-01 in Vitro [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(3): 88-94. |
| [5] | LIU Wenying, FENG Xiaowen, CHENG Qingli, et al. Preparation,Structure Characterization and in vitro Antioxidant Activity of Rice Oligopeptides [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(11): 47-56. |
| [6] | SU Jianyu HU Han WU Ping MENG Xiaofeng XU Zhenbo ZHENG Huade. Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities of Myricetin In Vitro [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(3): 101-108,152. |
| [7] | . Copper(II)-coordinating Force and Antioxidant Activity of Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(12): 126-132. |
| [8] | YOU Lijun HUANG Shiming ZHENG Guiqing ZHAO Zhengang HAN Rui MENG Hecheng. Structural,Antioxidant Activity and Immunomodulatory Activity of Polysaccharides Isolated from Undaria pinnatifida#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(11): 29-38. |
| [9] | SUN Wei-zheng YANG Kun LIN Lian-zhu ZOU Ying ZHAO Mou-ming. Investigation into Identification,Antioxidant Activity and Anti-Hemolysis Activity of Phenolics Compounds in High Acid Apple [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(3): 146-152. |
| [10] | REN Jiao-yan SHANG Shuai-ming LIANG Ming ZHANG Ting ZHOU Yong LI Hai-long YUAN Er-dong. Protective Effect of Corbicula Fluminea Hydrolyzates on Ethanol-Induced LO2 Cells Injury [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(12): 20-26. |
| [11] | Li Li Luo Xian- Hui Zhang Jing. Effects of In- Vitro Digestion on Properties and ACE Inhibitory Activities of Soybean Peptides [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(3): 125-130. |
| [12] | Ye Jun Li Wen- hao Xiong Jian. Synthesis,Structure and Thermal Property of Dialdehyde Carboxymethyl Cellulose Prepared at Low pH Value [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(6): 127-132. |
| [13] | Zhao Mou-ming Zou Lin-wu You Li-jun. Effects of Extraction Methods on Lentinan Properties [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(10): 26-33. |
| [14] | Zhao Mou-ming Zhang Yuan-hong Cui Chun Yuan Bo-en. Effect of Pepsin Pretreatment on Hydrolysis Characteristics of Soy Protein [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(8): 110-115. |
| [15] | Ye Jun Zhang Yan-xingXiong Jian. UV-Based Rapid Determination of Degree of Substitution of CMC with High Substitution [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(1): 58-62. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||