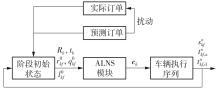
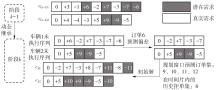
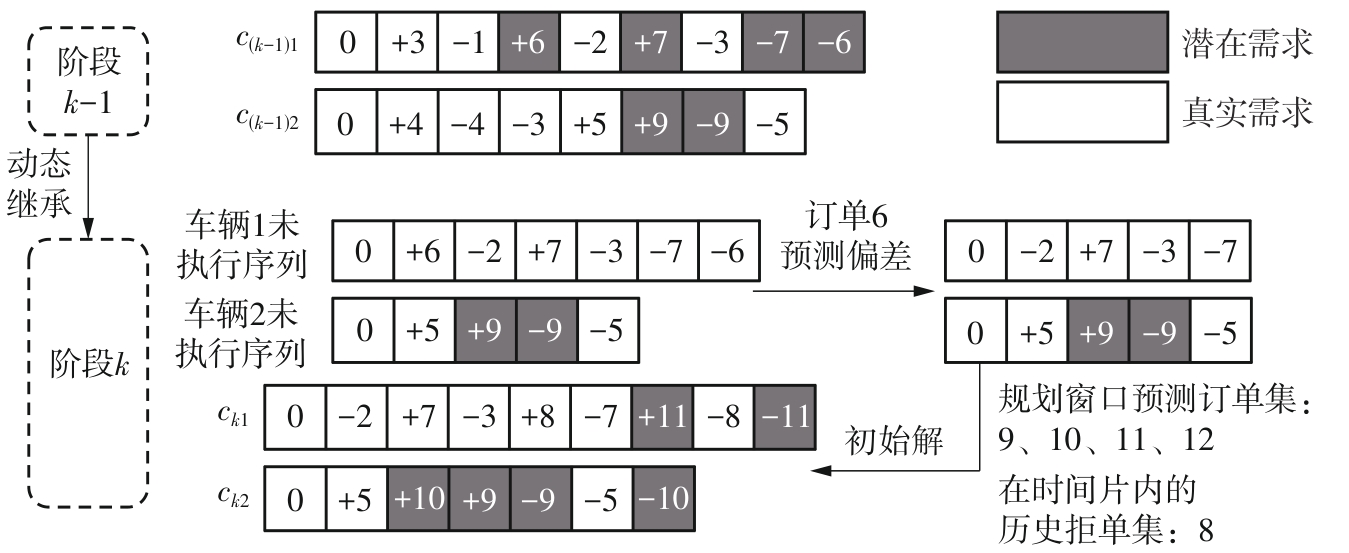
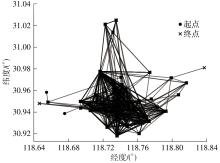
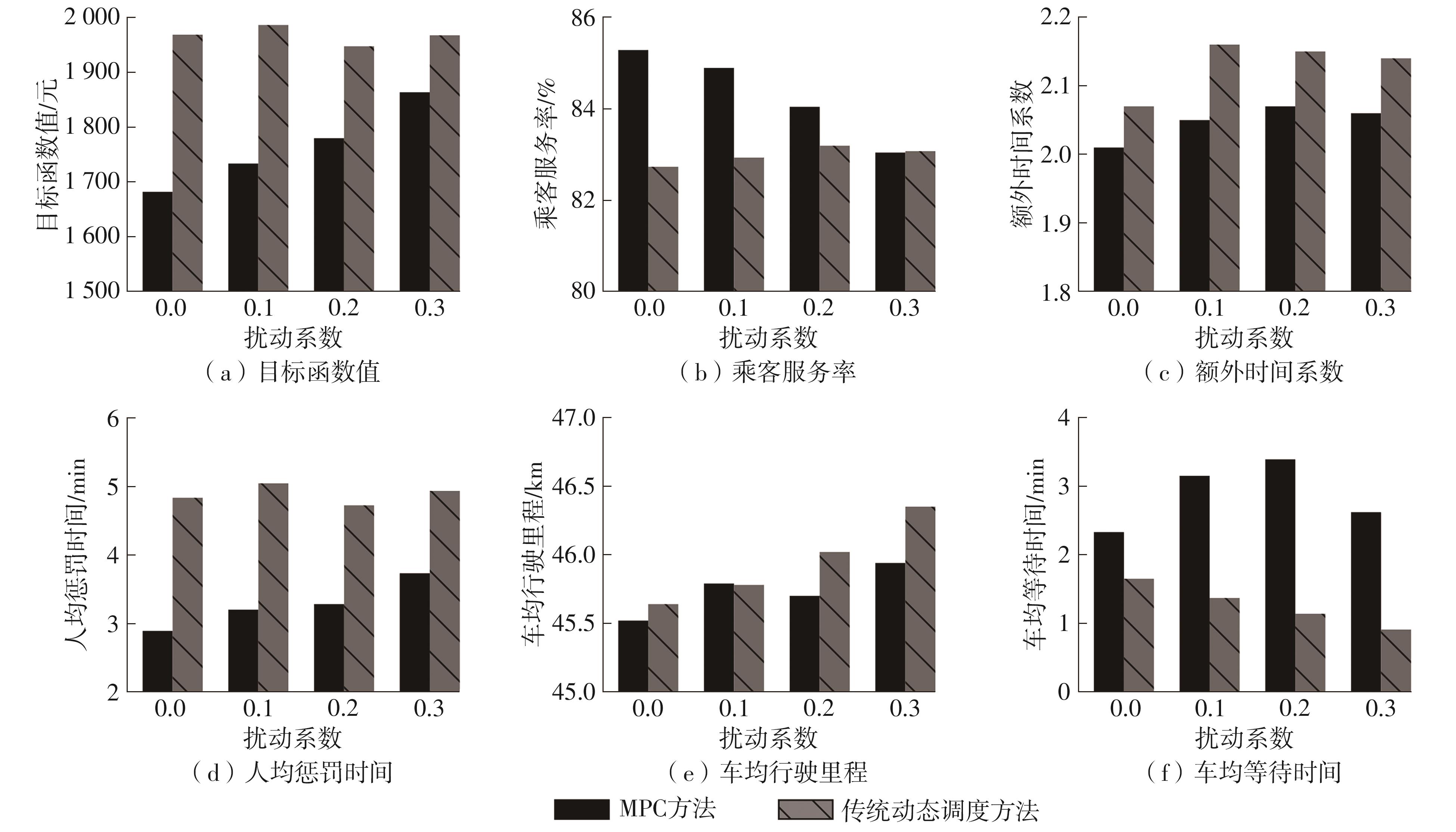
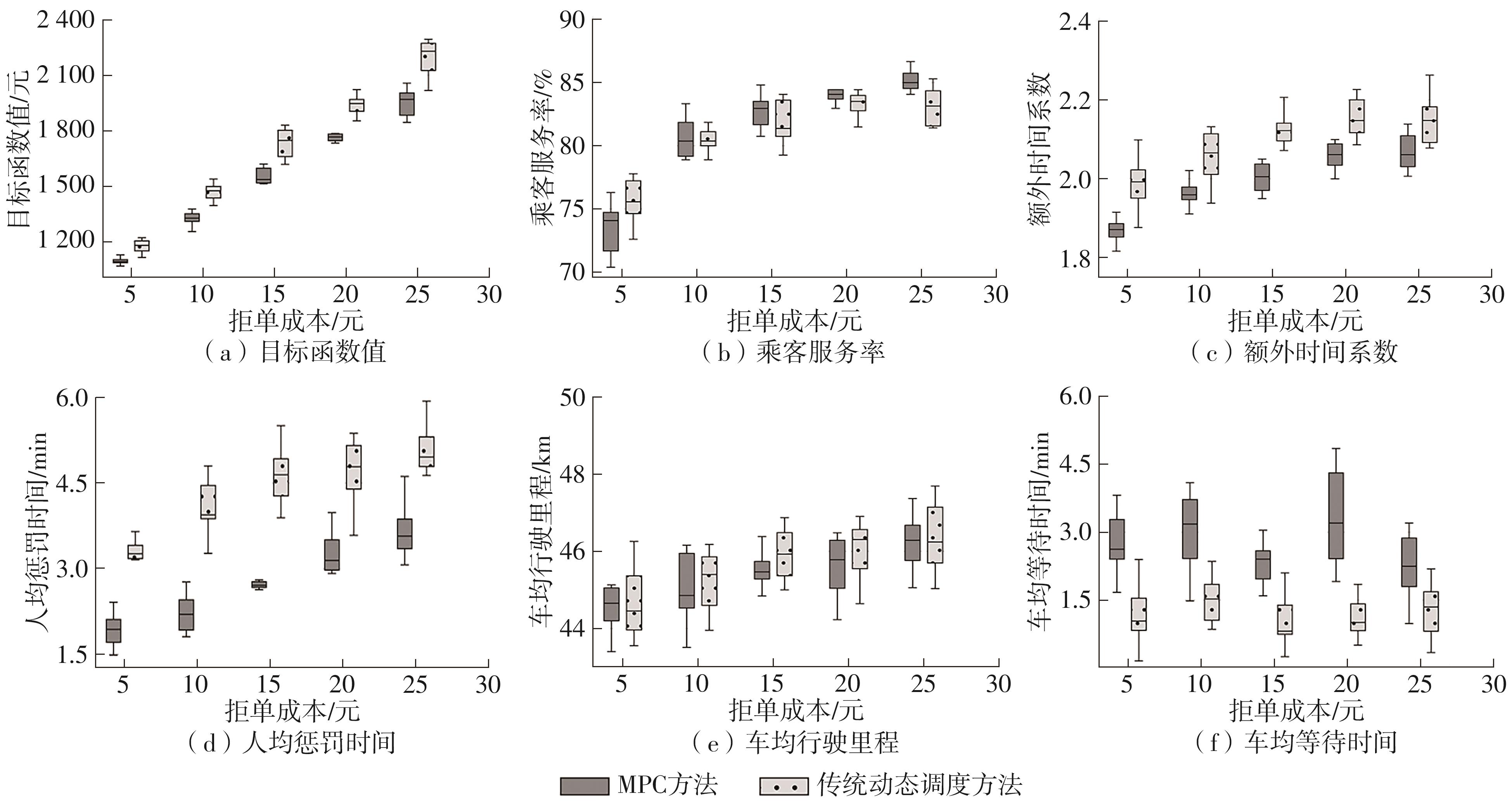
| 1 |
VANSTEENWEGEN P, MELIS L, AKTAS D,et al .A survey on demand-responsive public bus systems[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2022,137:103573/1-39.
|
| 2 |
宋翠颖,王鹤玲,田泽尚,等 .需求响应式公交车辆调度模型和算法研究综述[J].北京交通大学学报,2023,47(4):31-44.
|
|
SONG Cuiying, WANG Heling, TIAN Zeshang,et al .Review of demand-responsive transit vehicle scheduling models and algorithms[J].Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University,2023,47(4):31-44.
|
| 3 |
LIU Y N, OUYANG Y F .Mobility service design via joint optimization of transit networks and demand-responsive services[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2021,151:22-41.
|
| 4 |
靳文舟,胡为洋,邓嘉怡,等 .基于混合算法的需求响应公交灵活调度模型[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(1):123-133.
|
|
JIN Wenzhou, HU Weiyang, Deng Jiayi,et al .Fle-xible scheduling model of demand response transit based on hybrid algorithm[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(1):123-133.
|
| 5 |
胡迪,靳文舟 .基于站点优化的需求响应公交调度研究[J].深圳大学学报理工版,2022,39(2):209-215.
|
|
HU Di, JIN Wenzhou .Flex-route demand response transit scheduling based on station optimization[J].Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering,2022,39(2):209-215.
|
| 6 |
LI X, WANG T Q, XU W H,et al .A novel model and algorithm for designing an eco-oriented demand responsive transit (DRT) system[J].Transportation Research Part E:Logistics and Transportation Review,2022,157:102556/1-33.
|
| 7 |
靳文舟,杜昊,巫威眺 .基于ALNS-TS算法的半灵活型需求响应公交调度问题[J].深圳大学学报理工版,2023,40(4):425-434.
|
|
JIN Wenzhou, DU Hao, WU Weitiao .Semi-flexible demand responsive transit scheduling based on ALNS-TS algorithm[J].Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering,2023,40(4):425-434.
|
| 8 |
郭梅雪,靳文舟,巫威眺 .考虑充换电的模块化需求响应公交路径优化[J].交通运输工程与信息学报,2024,22(3):34-51.
|
|
GUO Meixue, JIN Wenzhou, WU Weitiao .Optimization of modular demand-responsive transit routes consi-dering charging and battery swapping[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information,2024,22(3):34-51.
|
| 9 |
韩博文 .考虑实时需求的需求响应式公交调度方法研究[J].广西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2019,37(3):9-20.
|
|
HAN Bowen .Demand responsive transit scheduling method considering real-time demand[J].Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2019,37(3):9-20.
|
| 10 |
HUANG D, GU Y, WANG S,et al .A two-phase optimization model for the demand-responsive customized bus network design[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2020,111:1-21.
|
| 11 |
巫威眺,周霄,朱彦辰,等 .考虑乘客时空灵活性的需求响应客货联运动态调度[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2023,23(4):211-227.
|
|
WU Wei-tiao, ZHOU Xiao, ZHU Yan-chen,et al .Demand-responsive dynamic scheduling considering passengers’ spatio temporal flexibility for passenger and freight transportation[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2023,23(4):211-227.
|
| 12 |
ALBAREDA-SAMBOLA M, FERNÁNDEZ E, LAPORTE G .The dynamic multiperiod vehicle routing problem with probabilistic information[J].Computers & Operations Research,2014,48:31-39.
|
| 13 |
NÚÑEZ A, CORTÉS C E, SÁEZ D,et al .Multiobjective model predictive control for dynamic pickup and delivery problems[J].Control Engineering Practice,2014,32:73-86.
|
| 14 |
刘亚杰,吴志永 .灾后动态环境下基于MPC的应急运输实时调度[J].控制与决策,2018,33(12):2131-2141.
|
|
LIU Ya-jie, WU Zhi-yong .Real-time relief transportation planning based on MPC in post-disaster dynamic environment[J].Control and Decision,2018,33(12):2131-2141.
|
| 15 |
石建力,谢丽蓉 .近似动态规划求解随机需求分批配送车辆路径问题[J].运筹与管理,2023,32(5):16-22.
|
|
SHI Jianli, XIE Lirong .Approximate dynamic programming for the split delivery vehicle routing problem with stochastic demands[J].Operations Research and Management Science,2023,32(5):16-22.
|
| 16 |
LI G L, CHEN Y X, WANG Y M,et al .City-scale synthetic individual-level vehicle trip data[J].Scientific Data,2023,10(1):96/1-18.
|
| 17 |
刘小寒,马晓磊,刘钲可 .面向公共交通的电动自动驾驶模块车调度优化[J].中国公路学报,2022,35(3):240-248.
|
|
LIU Xiao-han, MA Xiao-lei, LIU Zheng-ke .Dispatch optimization of electric autonomous modular vehicles for public transport[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2022,35(3):240-248.
|
 ), ZHANG Yong, SUN Jie
), ZHANG Yong, SUN Jie