华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 49-61.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240207
Mecanum轮全向AGV轨迹跟踪级联控制器设计
文生平1, 苏毅龙1, 瞿弘毅2
- 1.华南理工大学 广东省高分子先进制造技术及装备重点实验室/聚合物成型加工工程教育部重点实验室,广东 广州 510640
2.广东省科学院 智能制造研究所/广东省现代控制技术重点实验室,广东 广州 510070
Design of a Cascade Controller of Trajectory Tracking for Omnidirectional AGV Driven by Mecanum Wheels
WEN Shengping1, SU Yilong1, QU Hongyi2
- 1.Guangdong Advanced Polymer Manufacturing Technology and Equipment Key Laboratory/Key Laboratory of Polymer Processing Engineering of the Ministry of Education,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangdong Institute of Intelligent Manufacturing/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Modern Control Technology,Guangdong Academy of Sciences,Guangzhou 510070,Guangdong,China
摘要:
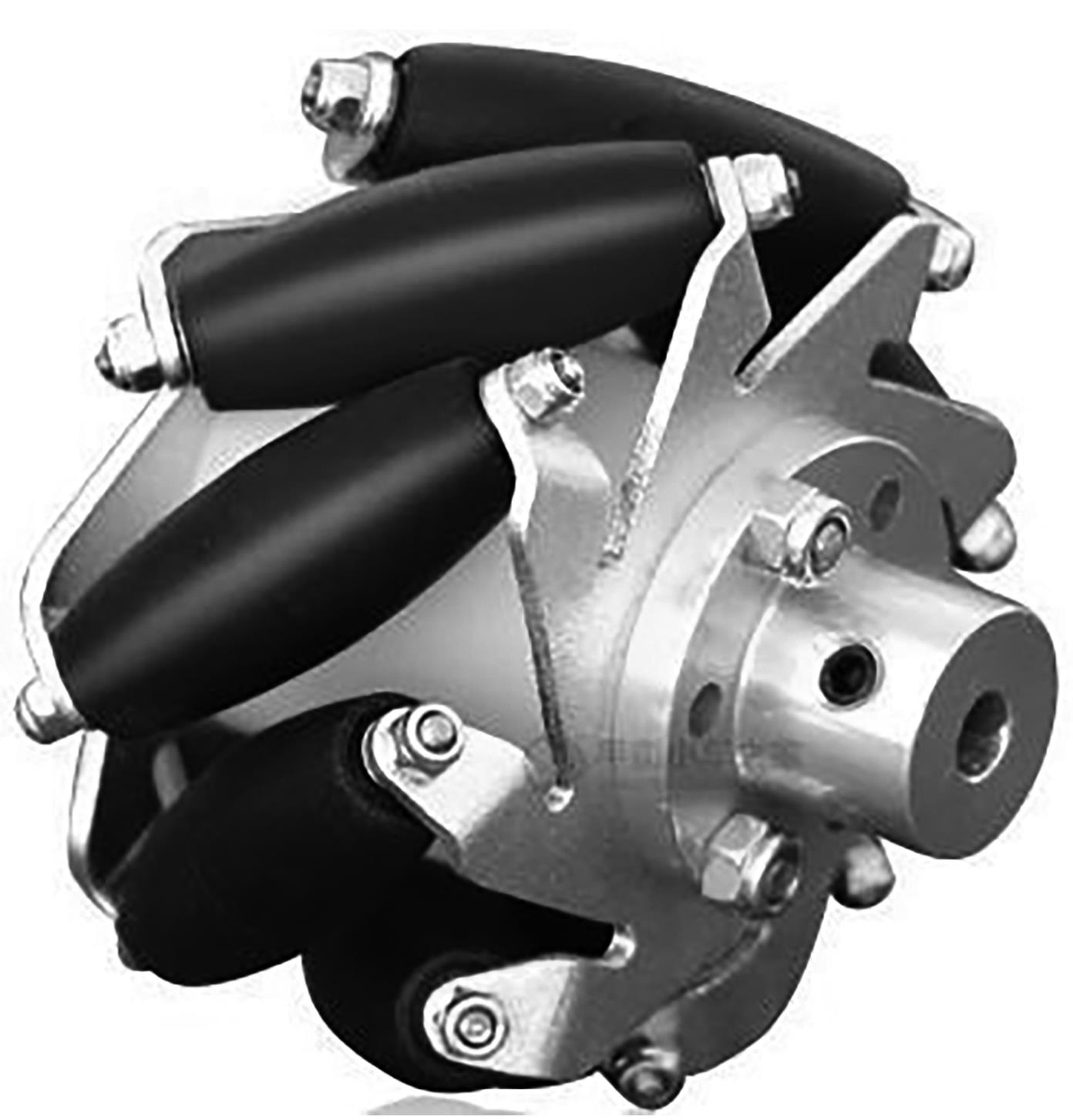
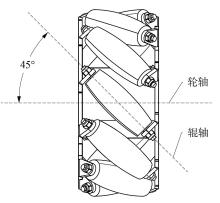
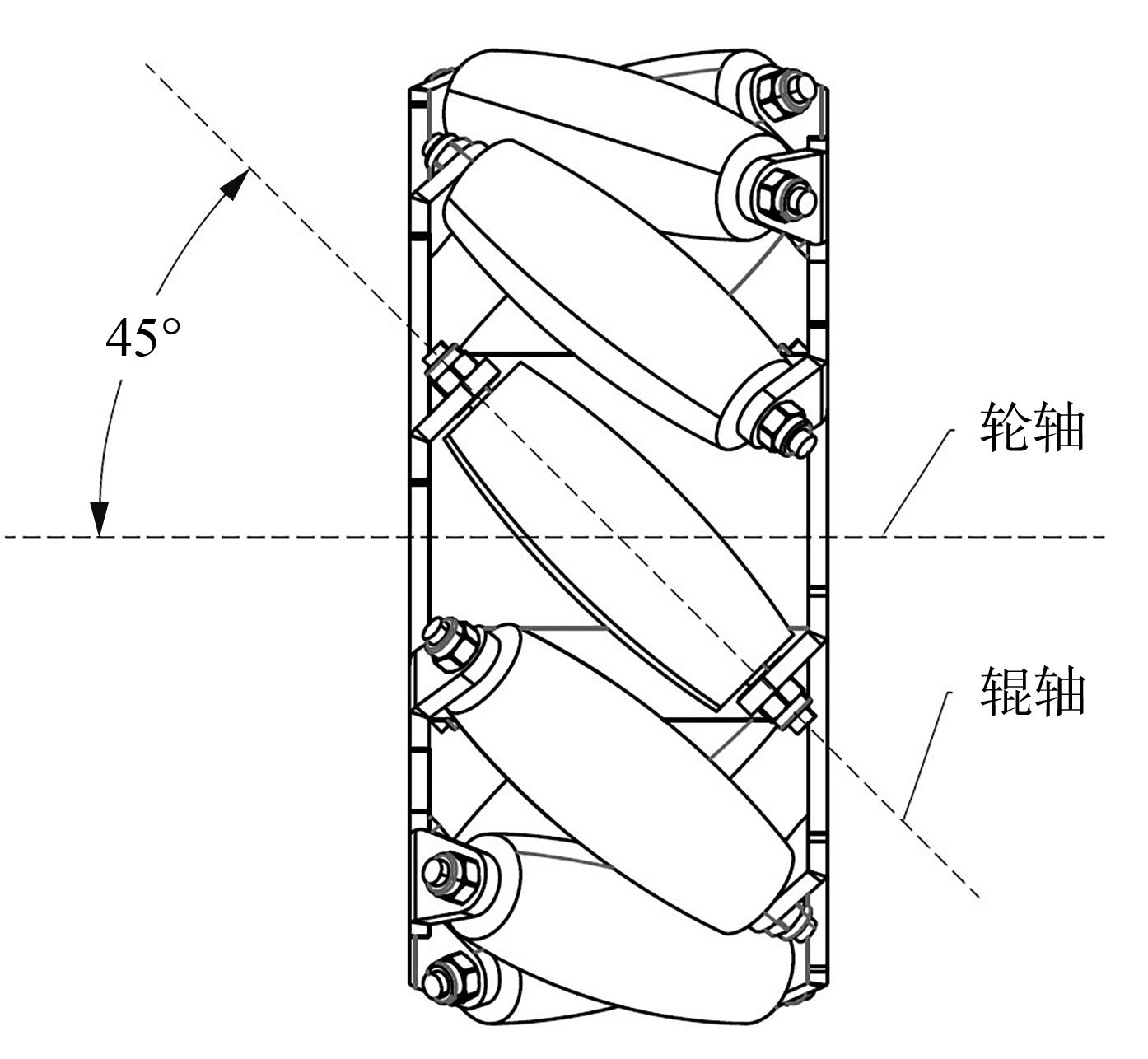
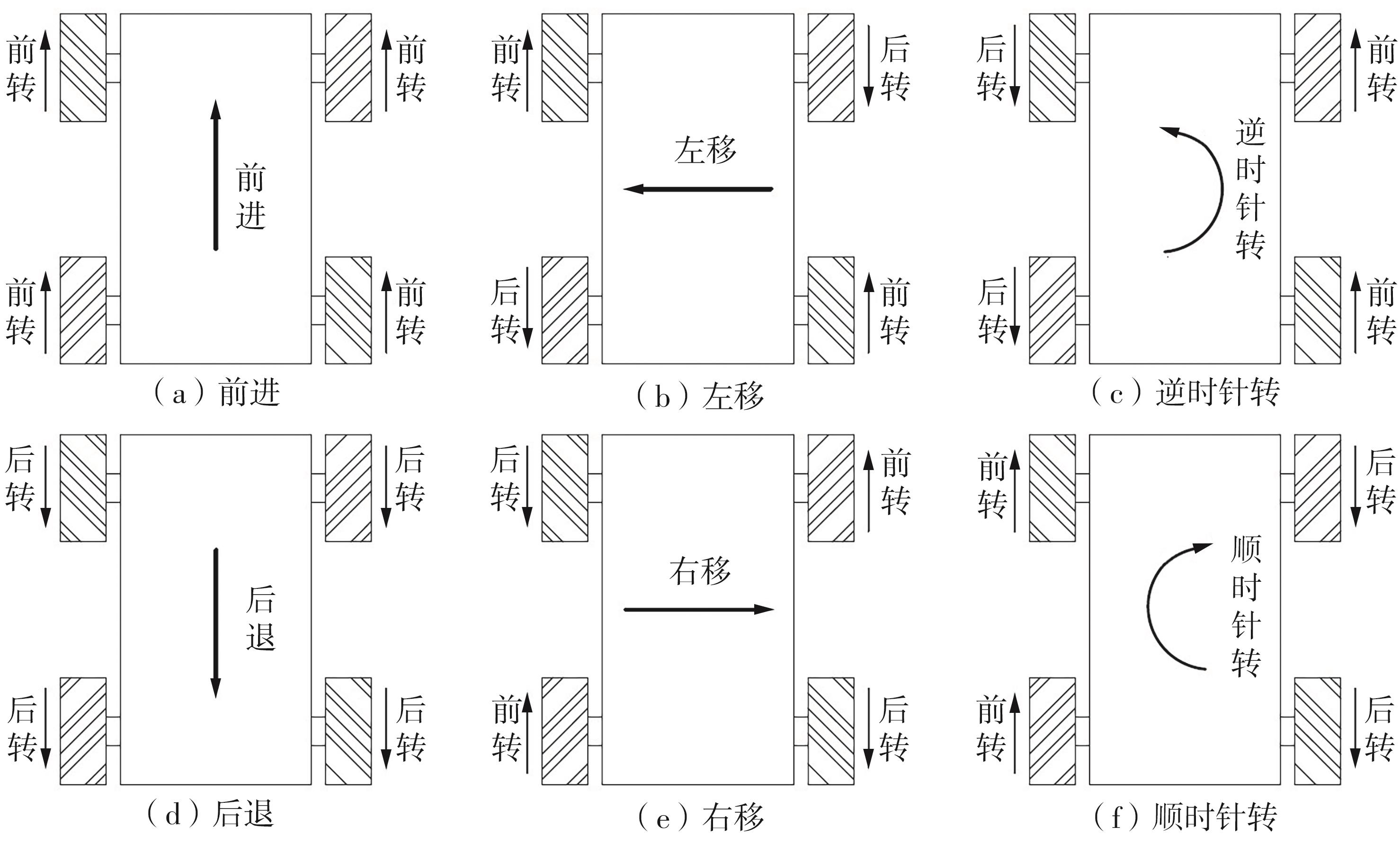
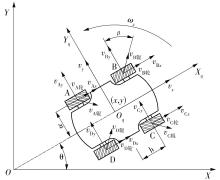
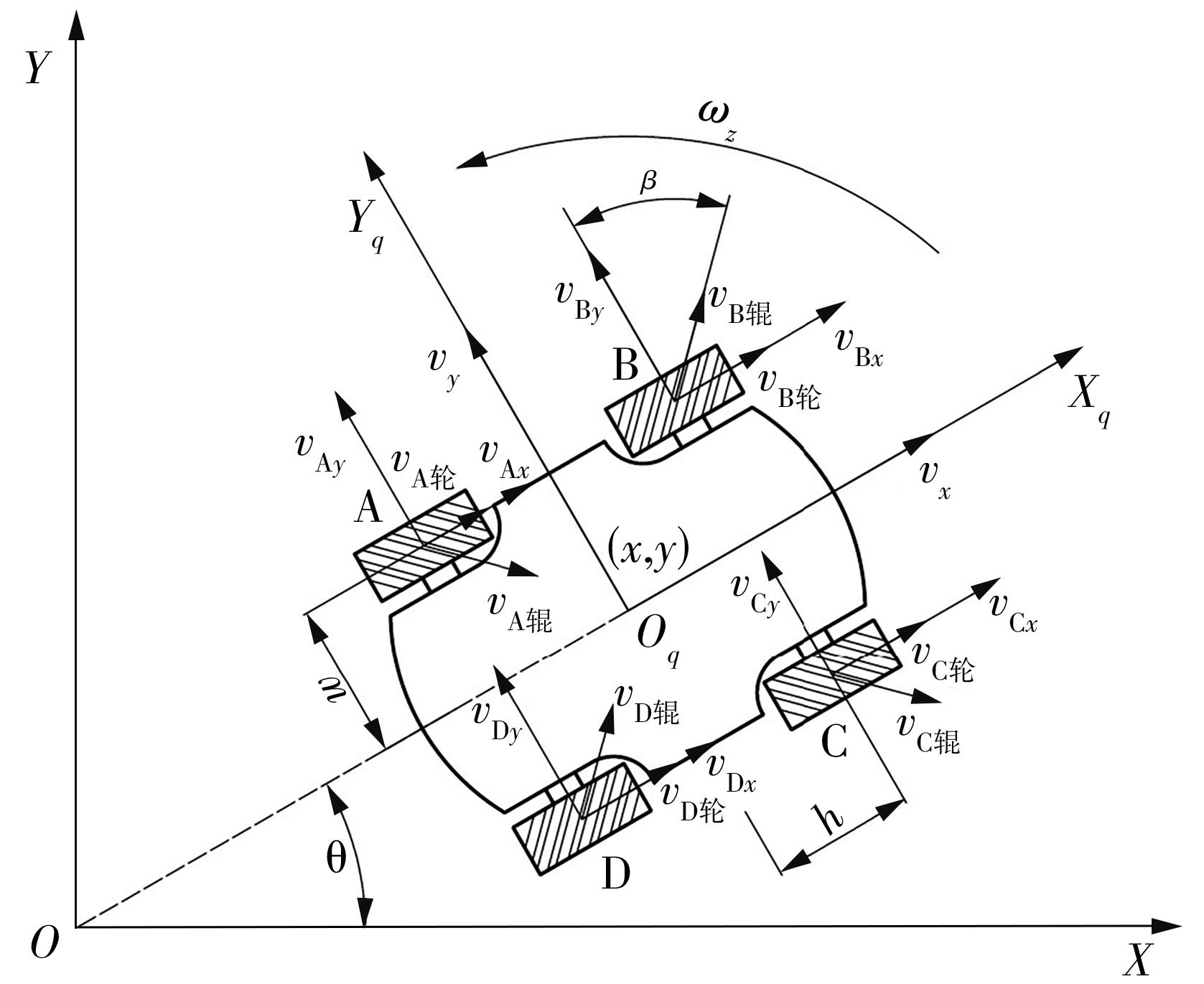
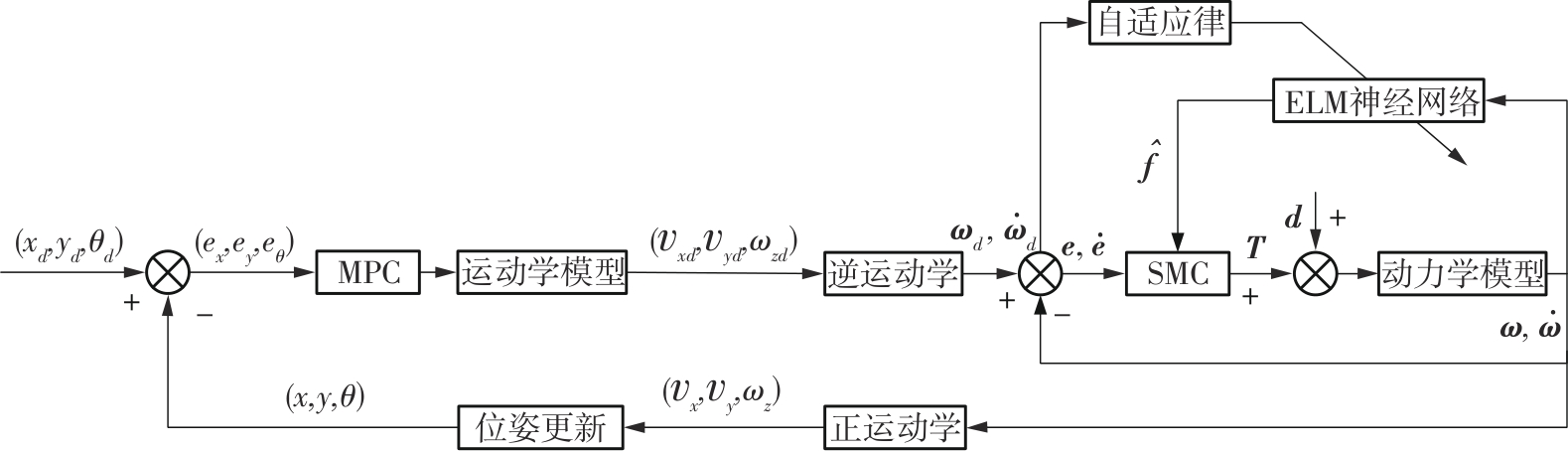
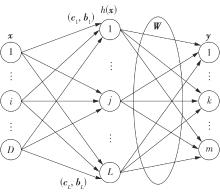
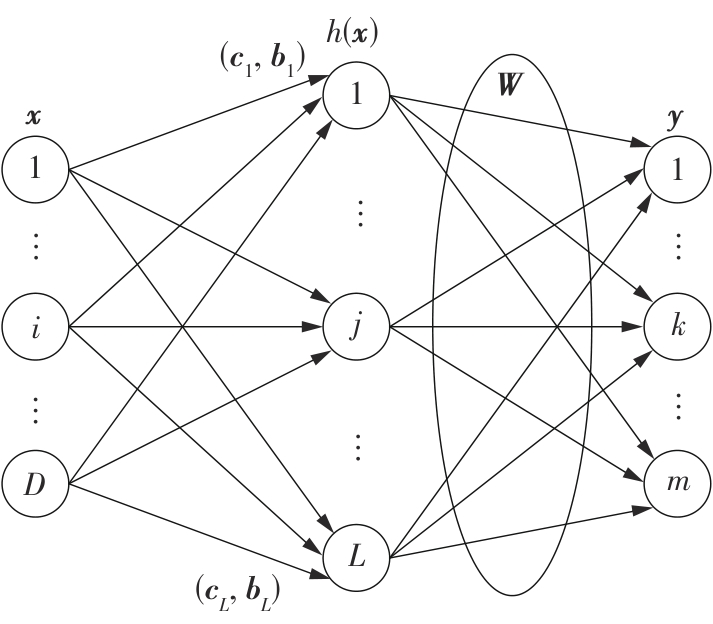
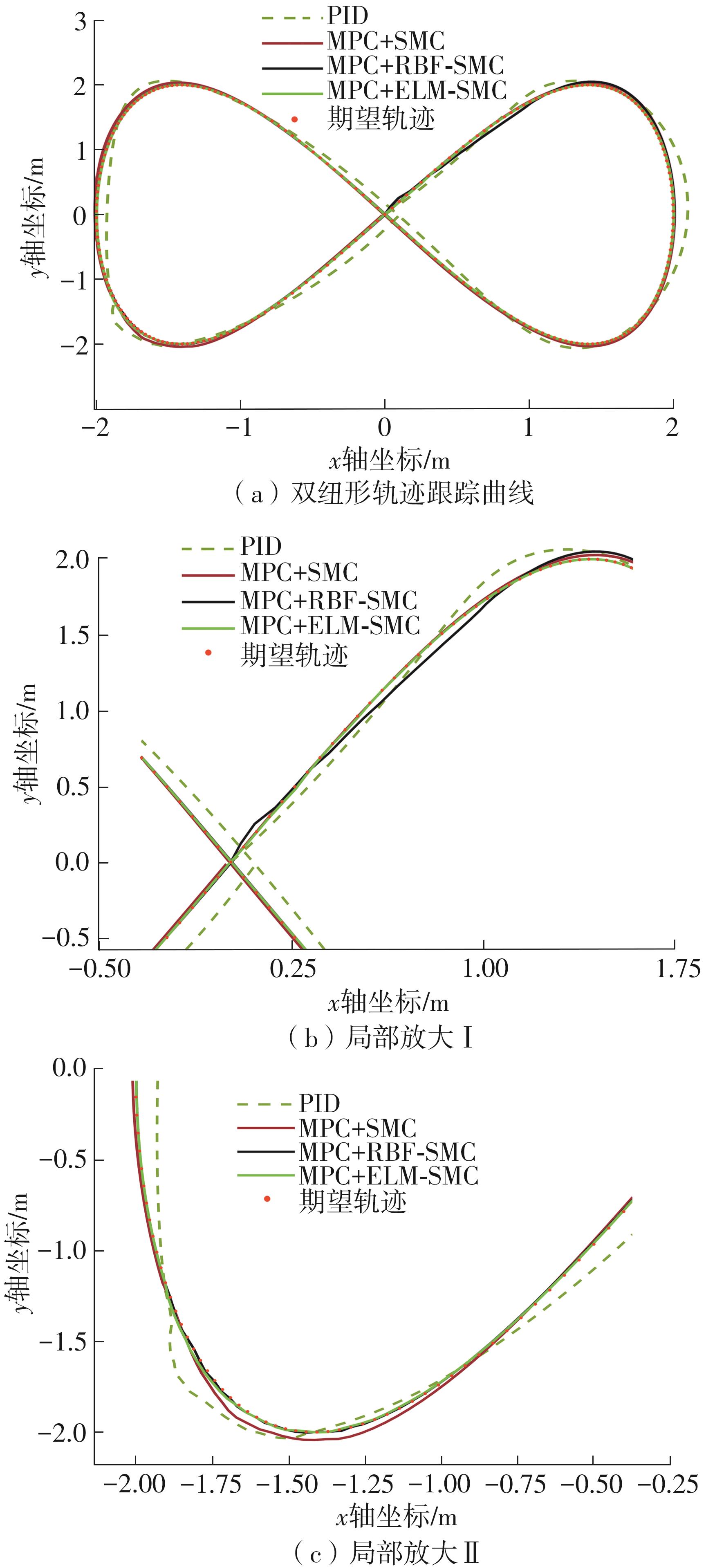
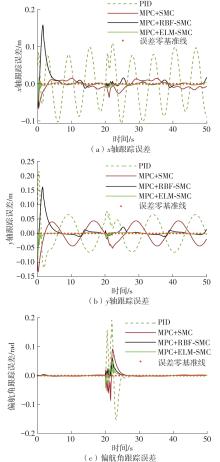
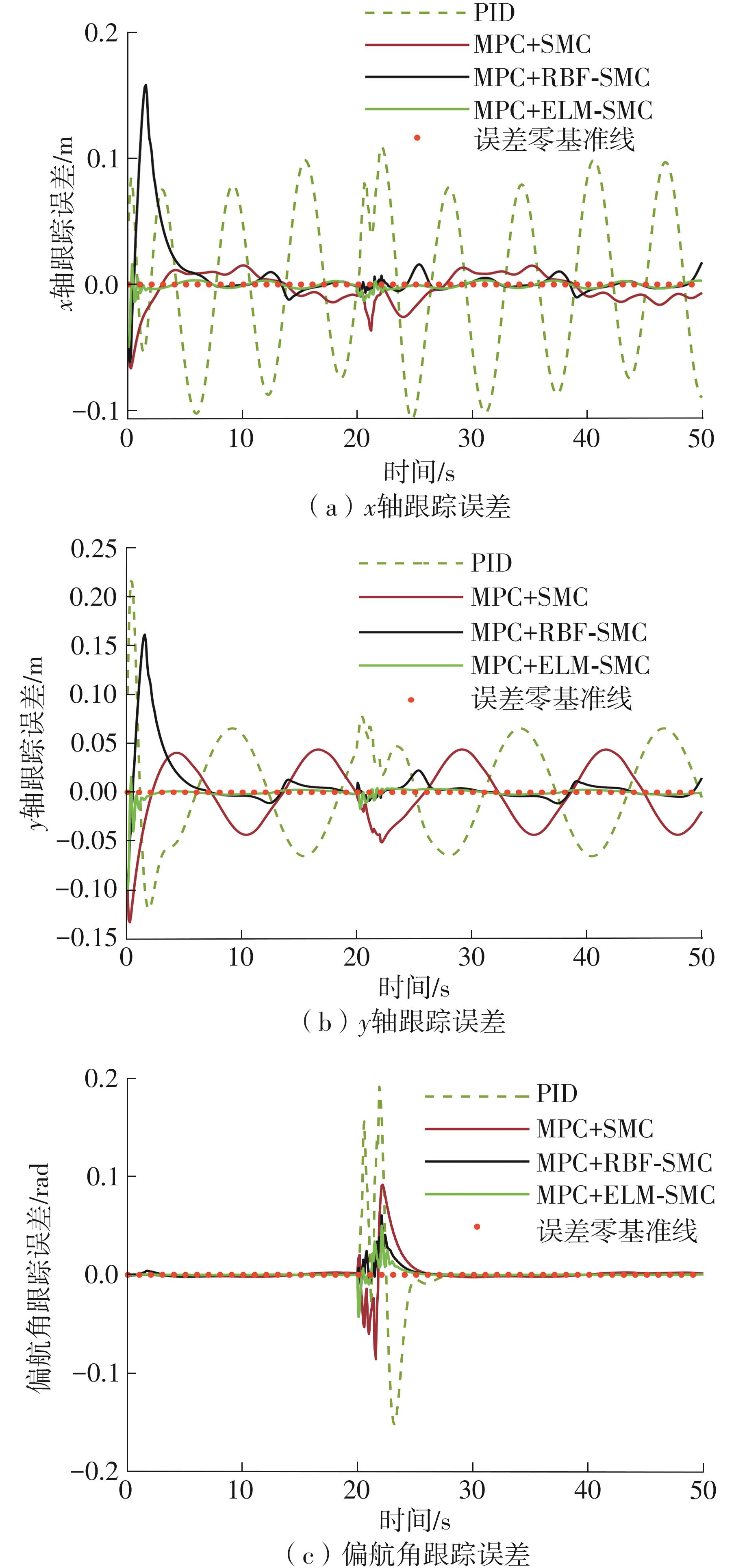
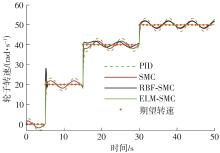
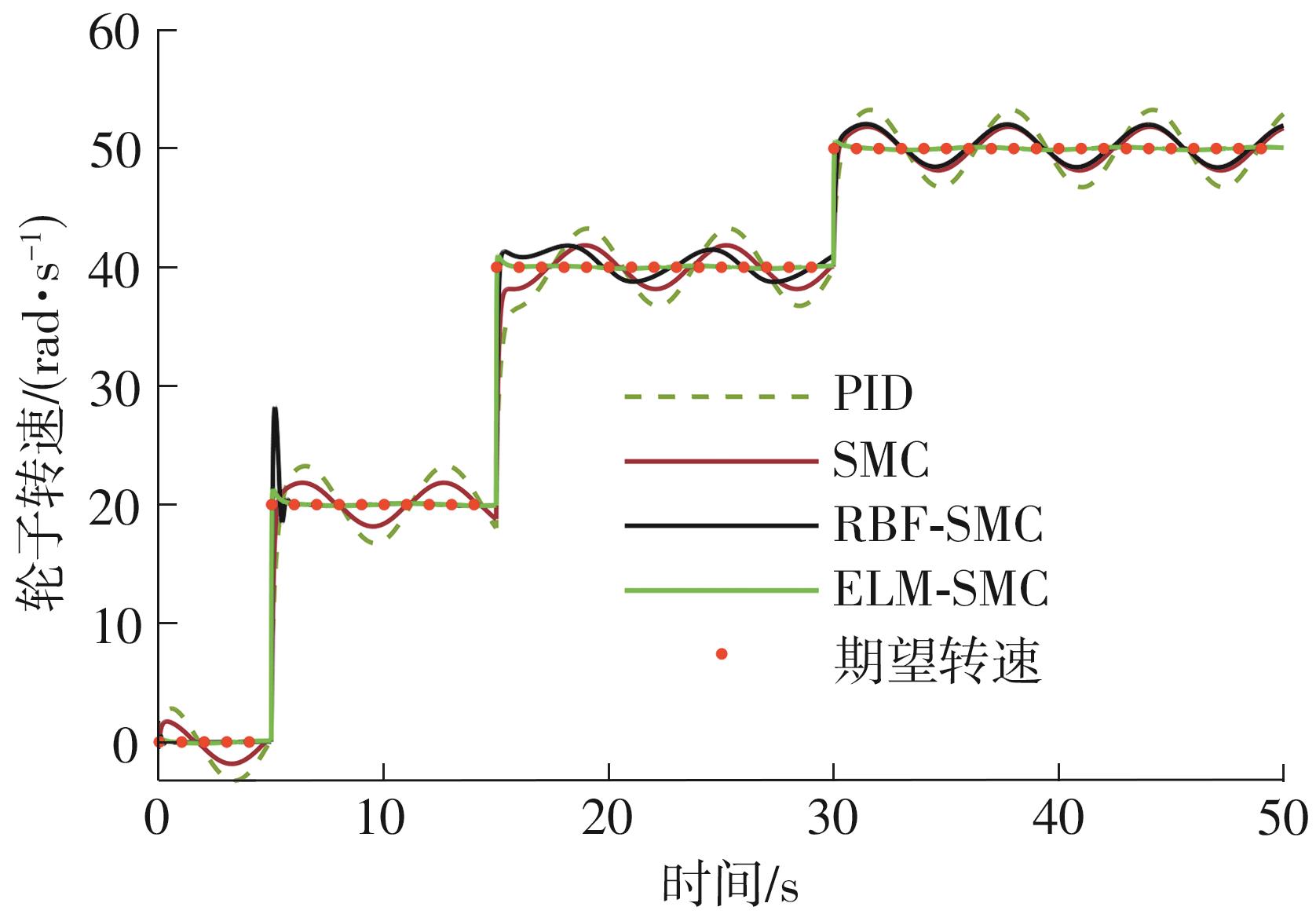
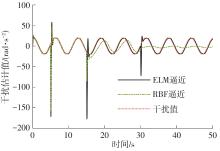
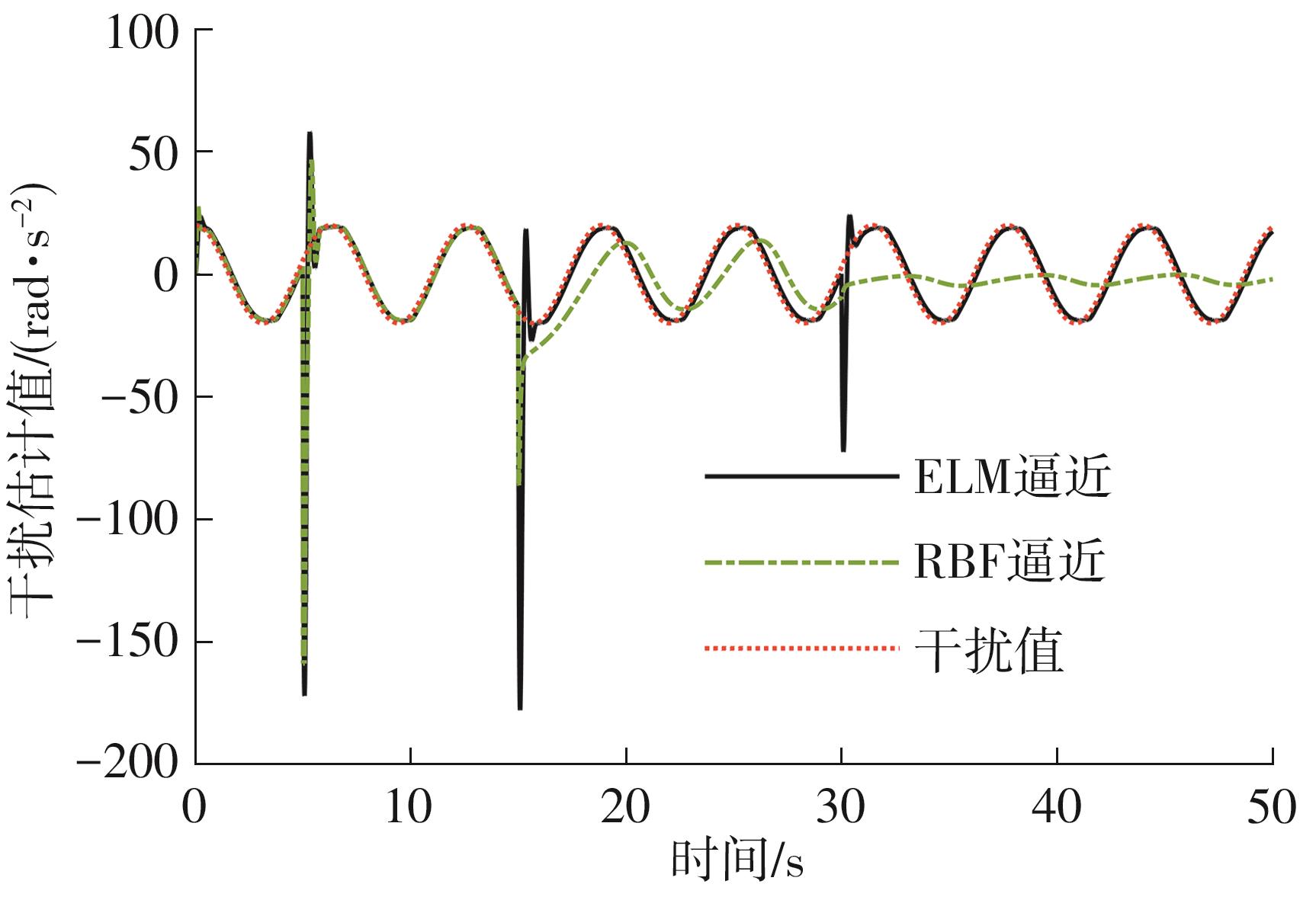
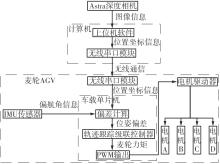
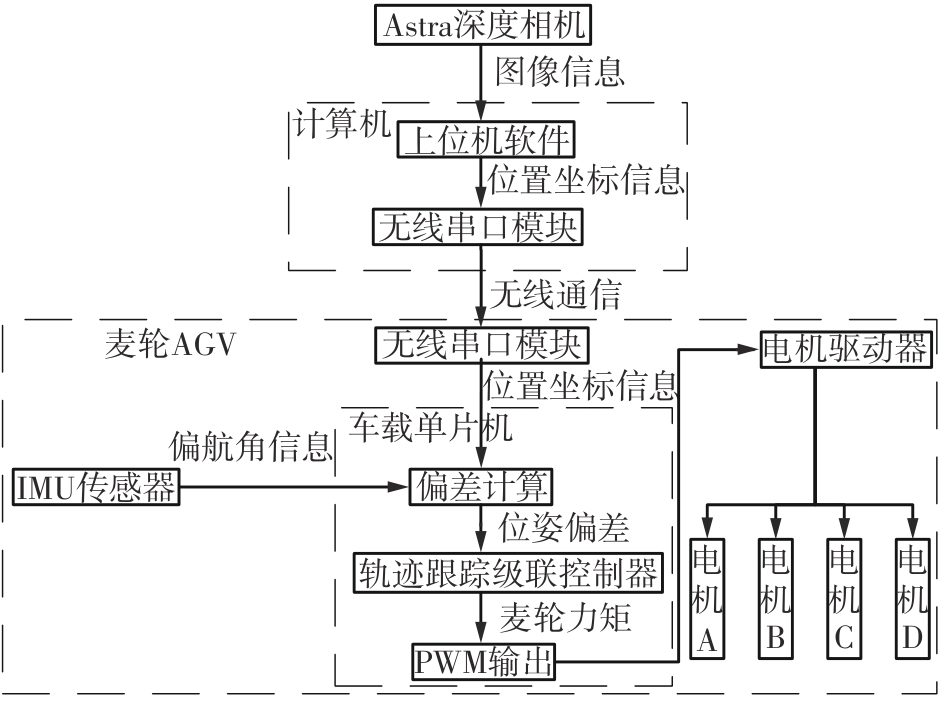
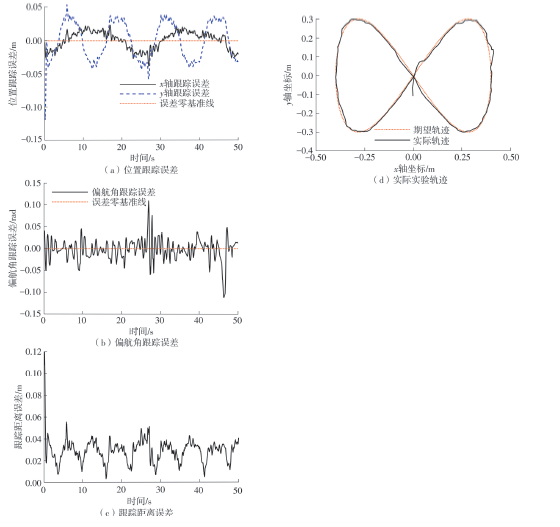
针对四Mecanum轮驱动的自动导引车(AGV)的轨迹跟踪控制问题,设计了一种模型预测控制(MPC)和自适应滑模控制(SMC)级联的控制器,来改善控制精度和稳定性,提高控制过程的层次性、针对性和有效性。在运动学层面,建立了AGV轨迹跟踪误差模型,将其转化为二次规划问题,并加入约束条件,配合模型预测控制的滚动优化来在线求解二次规划的最优解,将AGV位姿误差转化为轮子转速的期望输出;在动力学层面,采用滑模控制得到轮子的输出力矩,实现轮子对期望转速的跟踪,引入具有快速准确逼近能力的极限学习机(ELM)神经网络对模型不确定性和未知干扰进行在线观测,并与滑模控制相结合自适应抵消干扰,进一步提高控制器的鲁棒性。在余弦扰动和脉冲干扰下对控制器进行仿真验证,并将结果与PID控制结果进行对比,发现MPC+SMC级联控制器的跟踪效果具有明显优势;与采用径向基函数(RBF)神经网络观测的级联控制器的对比表明,采用ELM观测器的控制器对干扰的鲁棒性更强,在各转速条件下与干扰曲线的拟合度均超过95%,其跟踪误差在多项指标上相比其他方法小1个数量级,最大位置偏差仅为毫米级。轨迹跟踪样机实验结果验证了该控制器的实用性和可行性。
中图分类号: