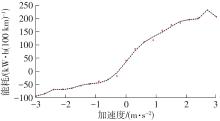
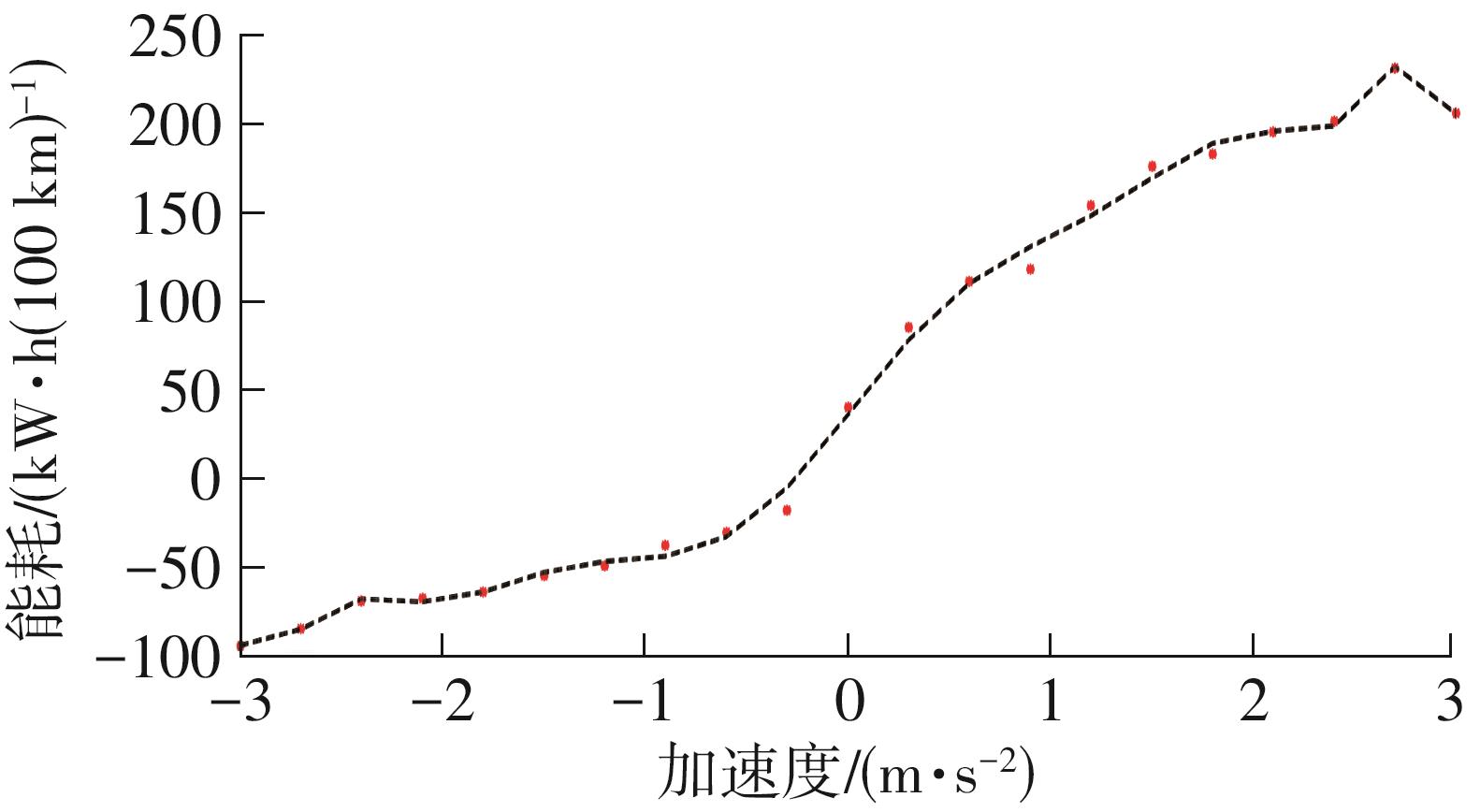
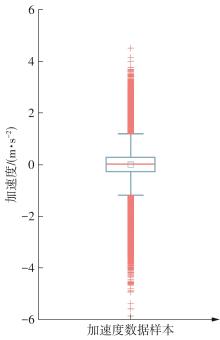
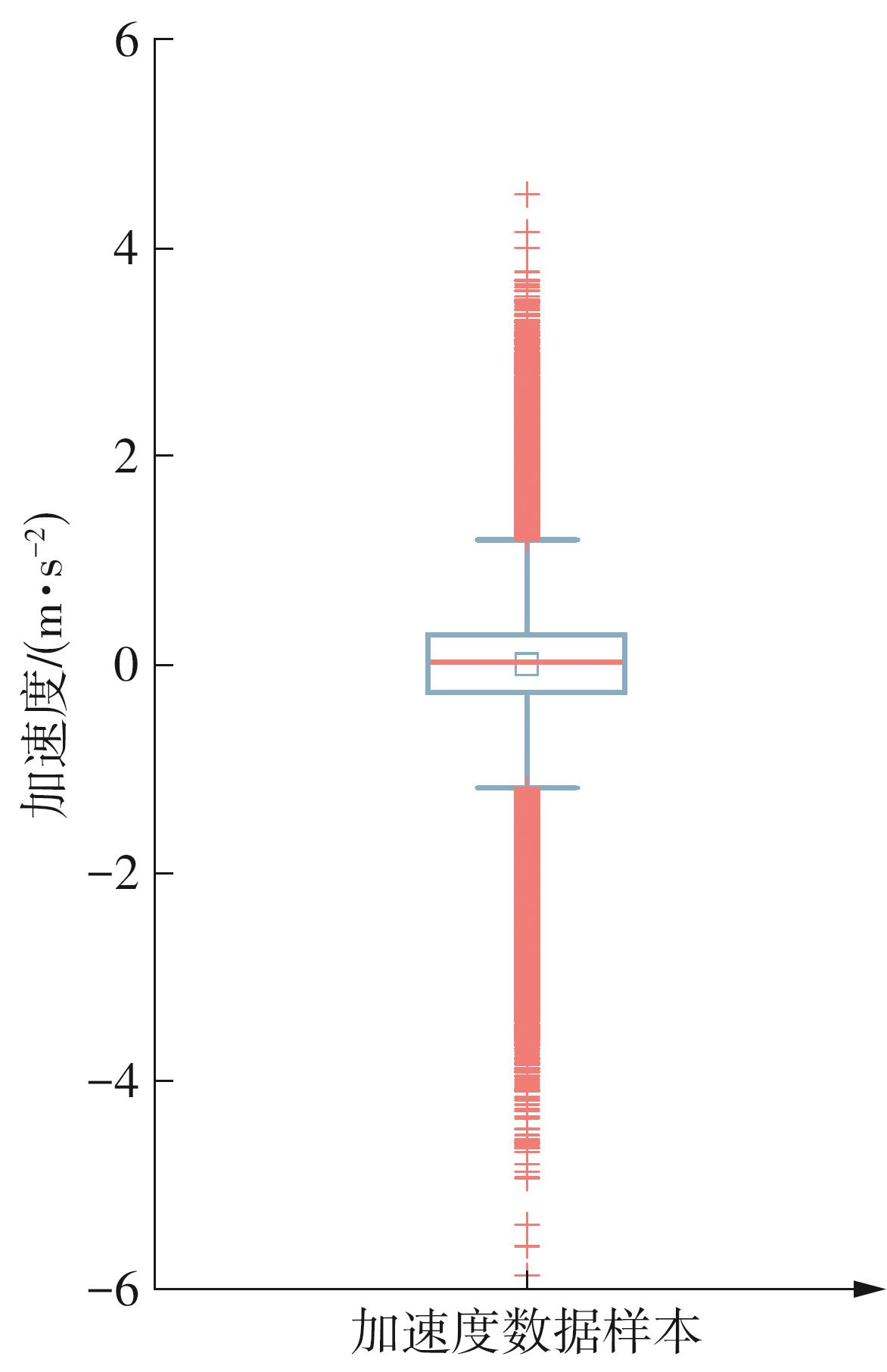
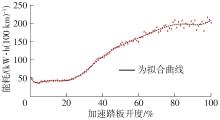
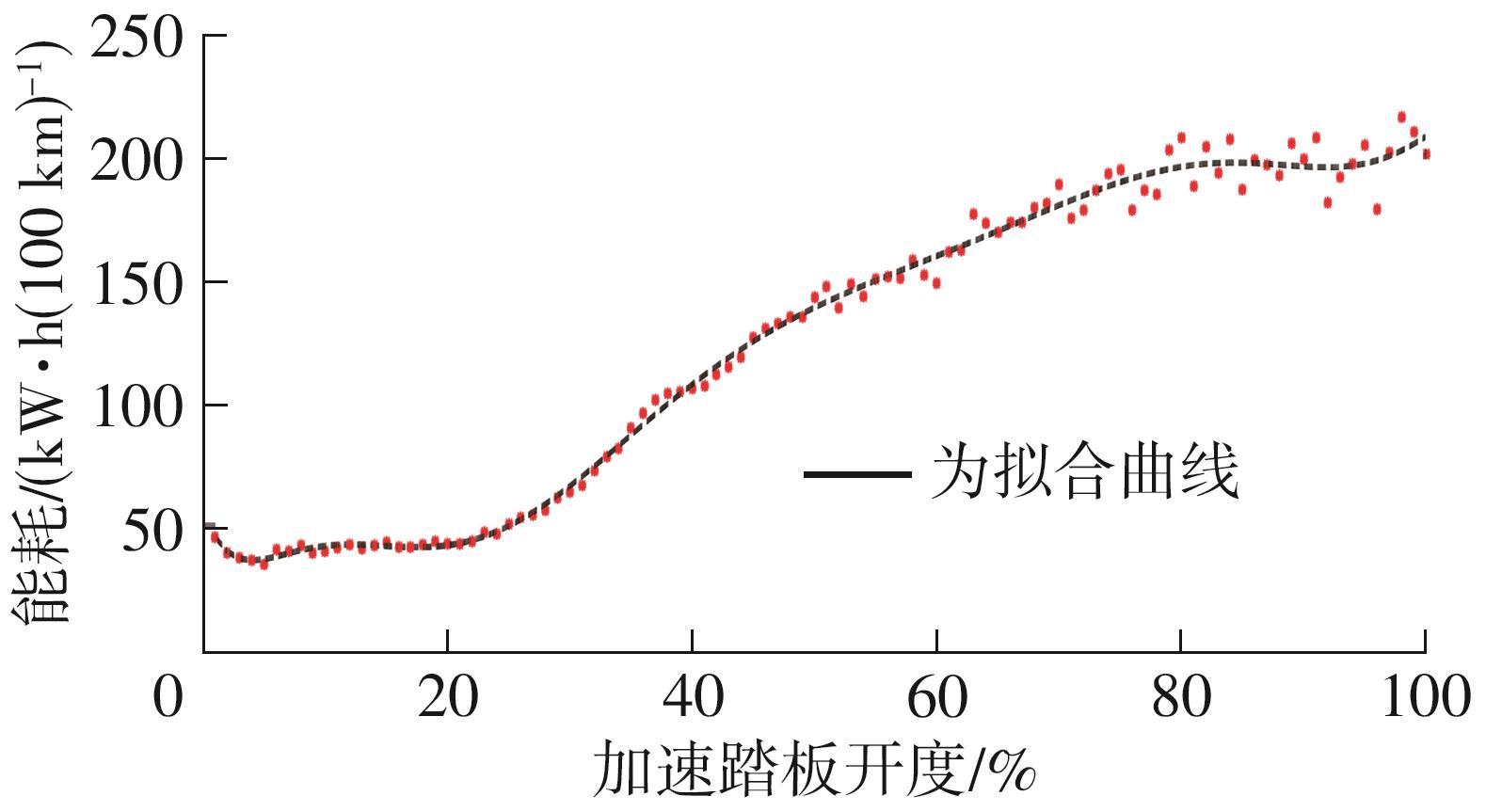
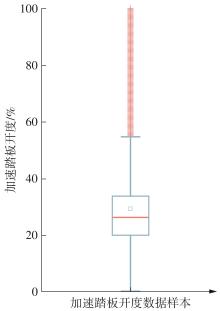
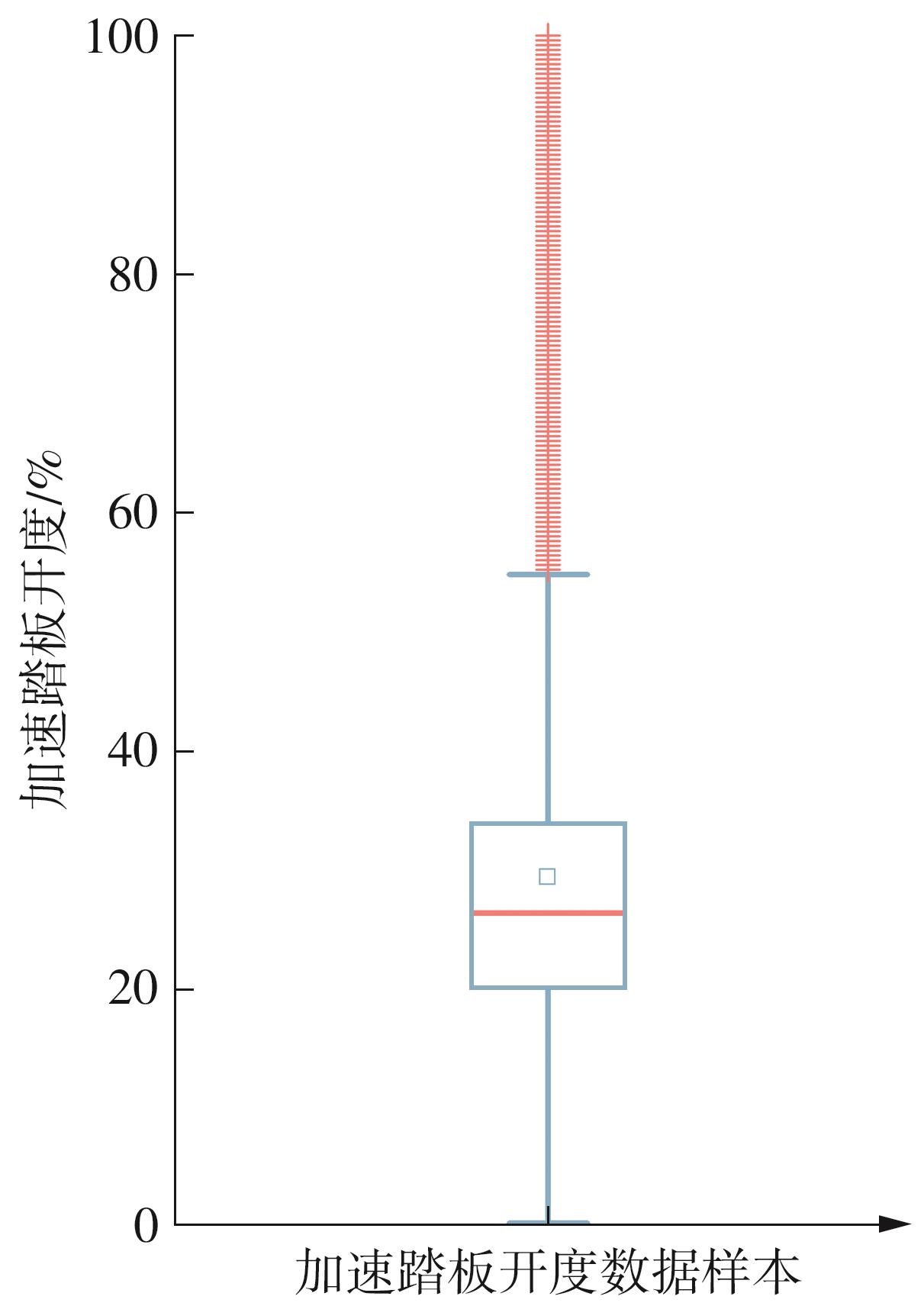
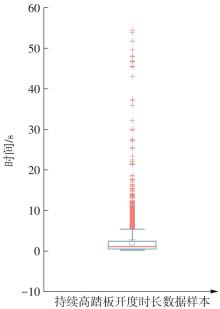
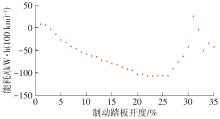
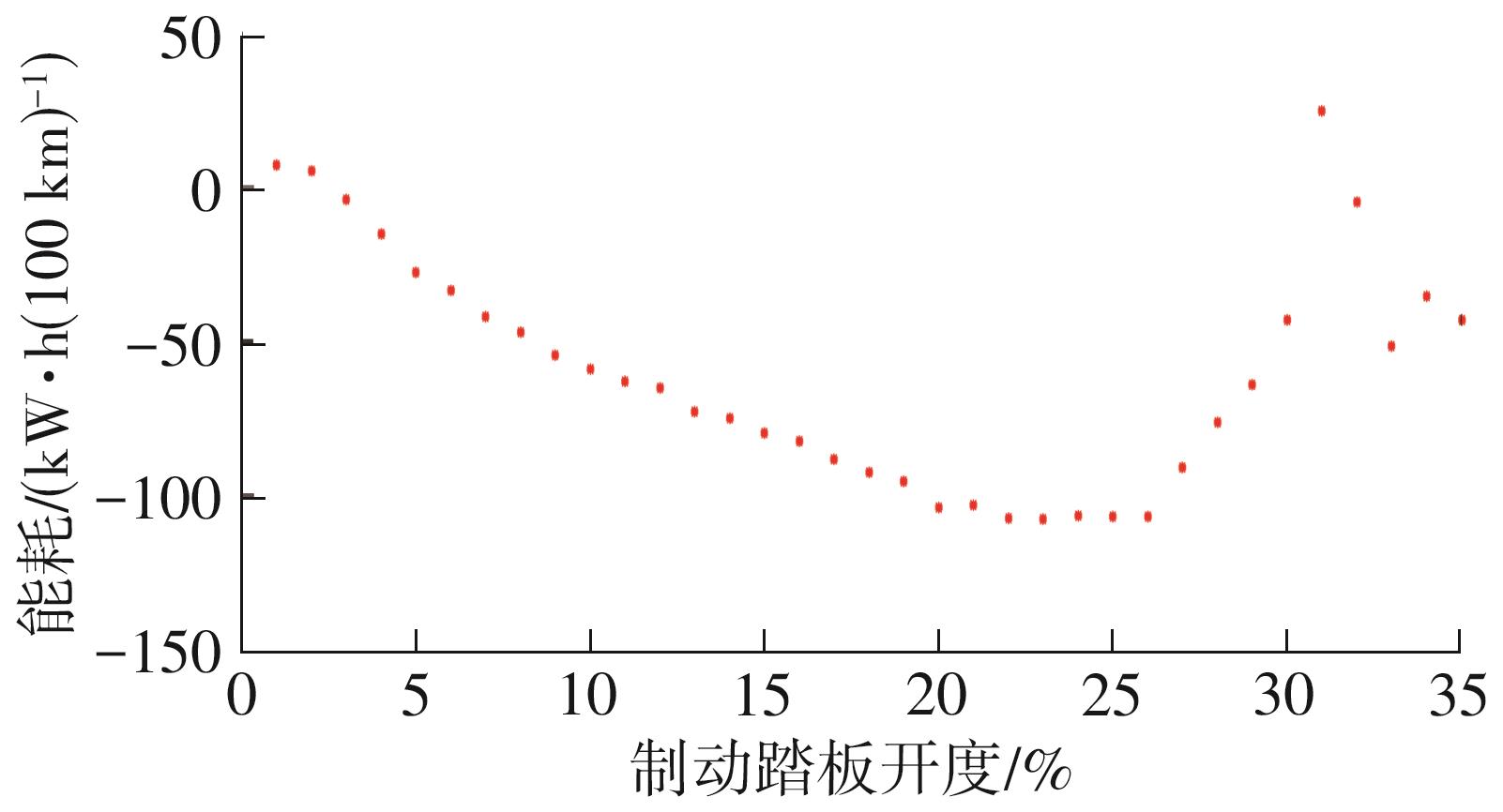
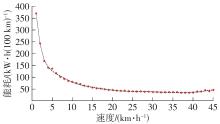
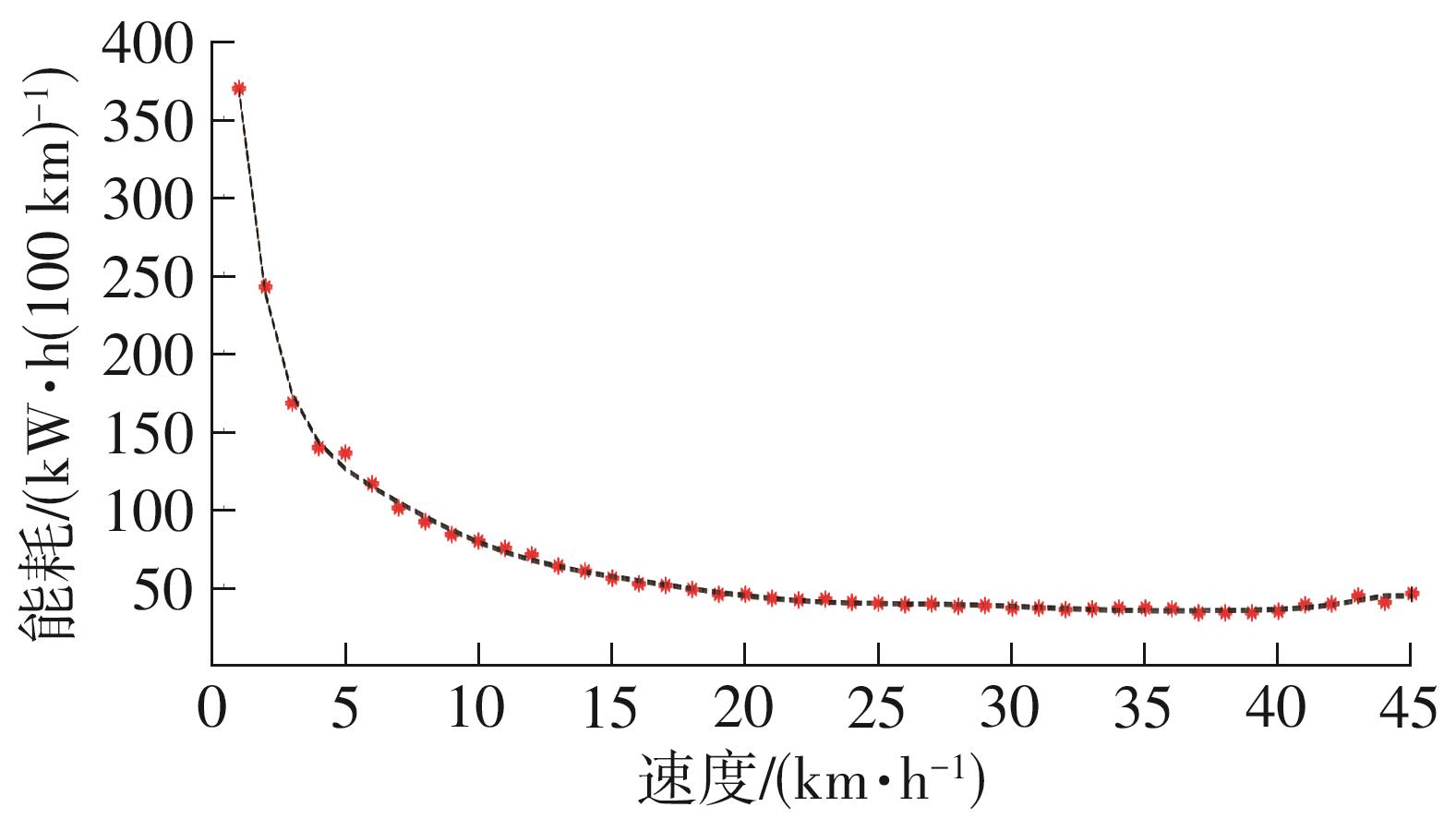
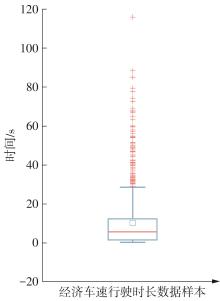
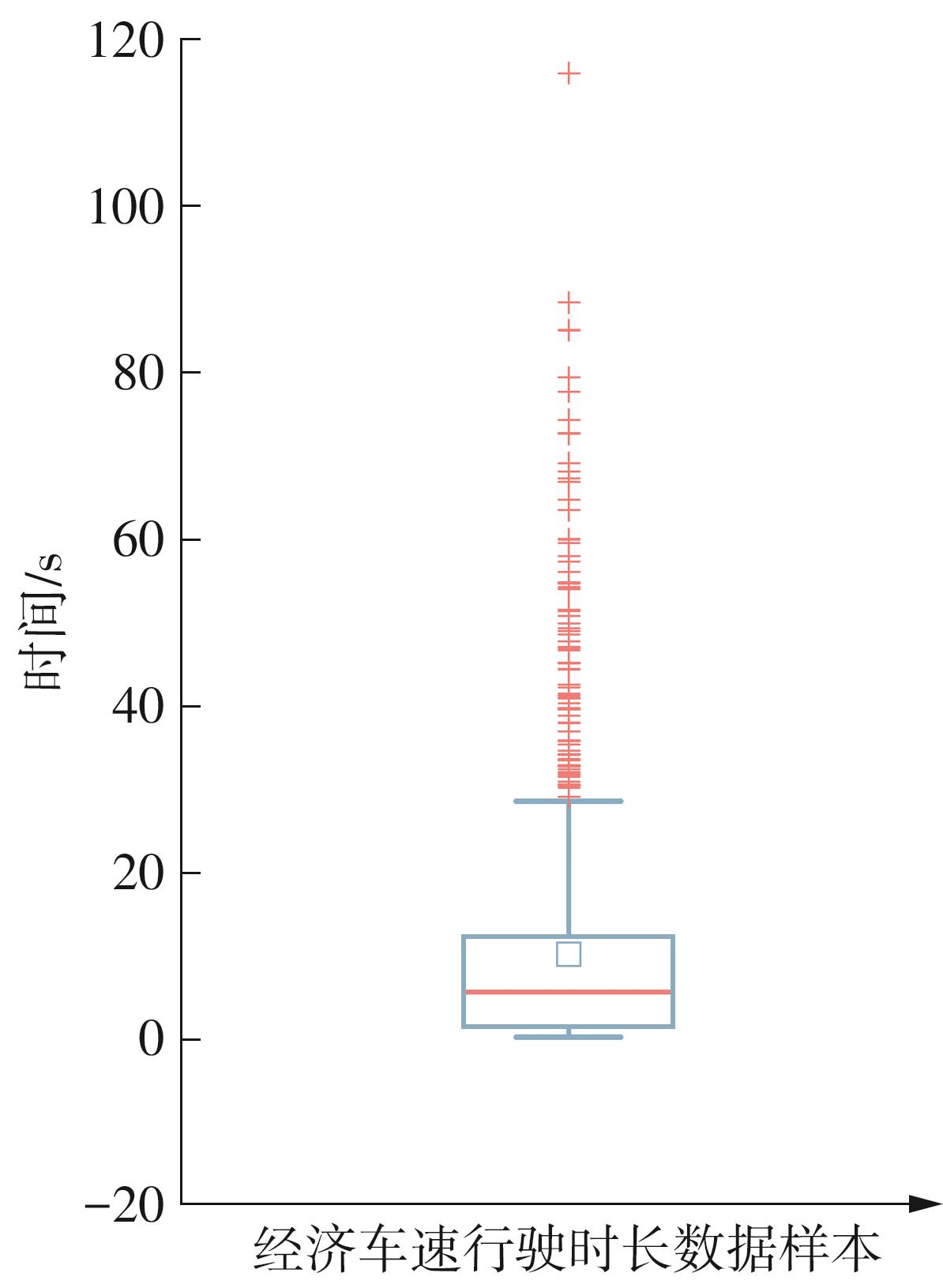
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 29-41.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240470
• Intelligent Transportation System • Previous Articles Next Articles
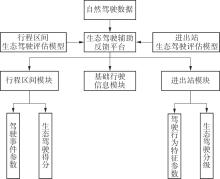
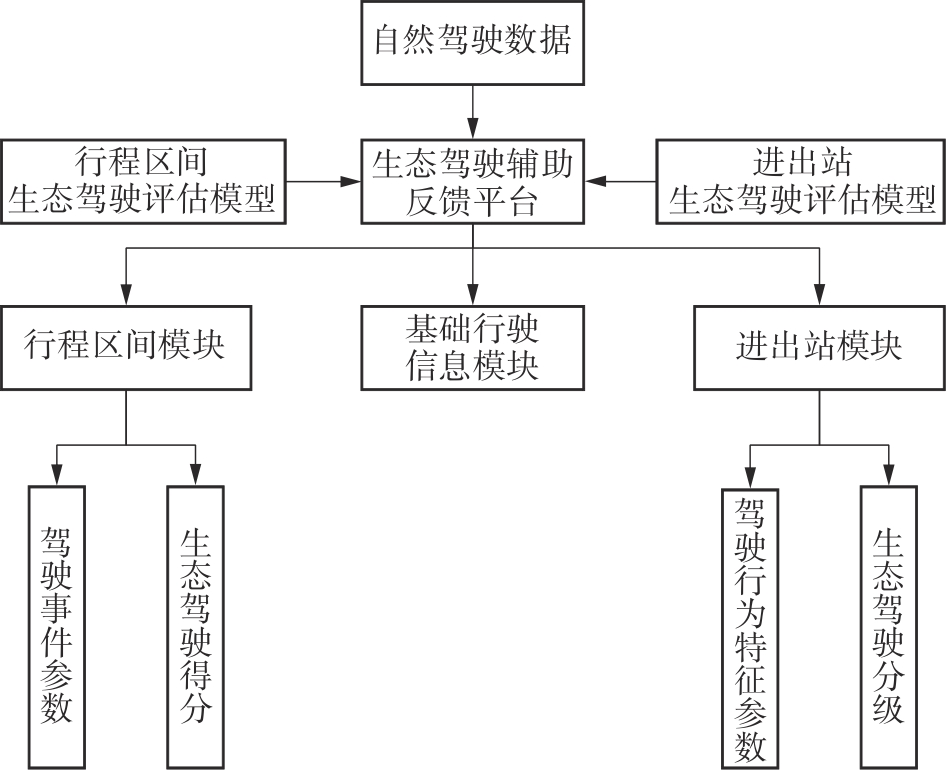
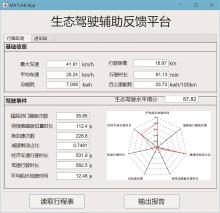
Evaluation Model for Eco-Driving Performance of Pure Electric Bus Drivers
ZHANG Yali, SHEN Yubo, YUAN Wei, ZHANG Kang, ZHANG Huiming
- School of Automobile,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710018,Shaanxi,China
-
Received:2024-09-20Online:2025-08-25Published:2025-01-17 -
Contact:袁伟(1975—),男,博士,教授,主要从事驾驶行为、智能驾驶和交通安全等研究。 E-mail:yuanwei@chd.edu.cn -
About author:张雅丽(1991—),女,博士,讲师,主要从事电动汽车驾驶行为与生态驾驶研究。E-mail: zhangyali@chd.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province(2024JC-YBQN-0437);the Postdoctoral Research Project of Shaanxi Province(2023BSHEDZZ212);the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52402417)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Yali, SHEN Yubo, YUAN Wei, ZHANG Kang, ZHANG Huiming. Evaluation Model for Eco-Driving Performance of Pure Electric Bus Drivers[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(8): 29-41.
share this article
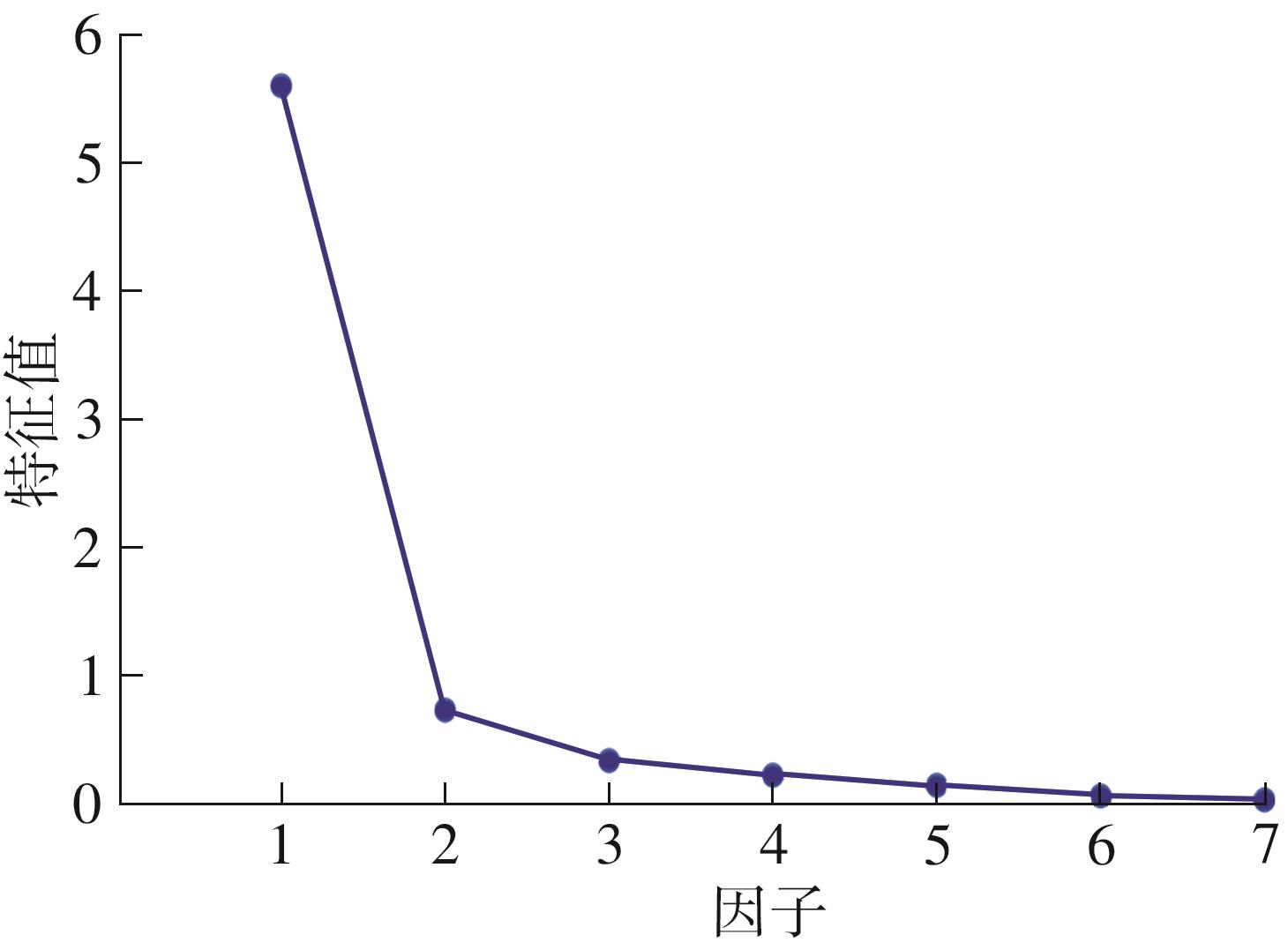
Table 3
Exploratory factor analysis variance explanation rate"
| 成分 | 旋转前 | 旋转后 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 特征根 | 方差解释率/% | 累积方差解释率/% | 特征根 | 方差解释率/% | 累积方差解释率/% | |||
| 1 | 5.584 | 79.774 | 79.774 | 346.284 | 49.469 | 49.469 | ||
| 2 | 0.713 | 10.182 | 89.955 | 167.949 | 23.993 | 73.462 | ||
| 3 | 0.319 | 4.555 | 94.511 | 147.342 | 21.049 | 94.511 | ||
| 4 | 0.204 | 2.916 | 97.427 | — | — | — | ||
| 5 | 0.126 | 1.795 | 99.222 | — | — | — | ||
| 6 | 0.043 | 0.616 | 99.838 | — | — | — | ||
| 7 | 0.011 | 0.162 | 100.000 | — | — | — | ||
| [1] | MINTSIS E, VLAHOGIANNI E I, MITSAKIS E. Dynamic eco-driving near signalized intersections:syste-matic review and future research directions[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering,Part A:Systems,2020,146(4):04020018/1-15. |
| [2] | BERRY I M .The effects of driving style and vehicle performance on the real-world fuel consumption of US light-duty vehicles[D].Cambridge:Massachusetts Institute of Technology,2010. |
| [3] | HOLDSTOCK T, SORNIOTTI A, EVERITT M,et al .Energy consumption analysis of a novel four-speed dual motor drivetrain for electric vehicles[C]∥Proceeding of the 2012 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Confe-rence.Seoul:IEEE,2012:295-300. |
| [4] | KAMBLY K, BRADLEY T H .Geographical and temporal differences in electric vehicle range due to cabin conditioning energy consumption[J].Journal of Power Sources,2015,275:468-475. |
| [5] | AL-WREIKAT Y, SERRANO C, SODRE J R .Effects of ambient temperature and trip characteristics on the e-nergy consumption of an electric vehicle[J].Energy,2022,238:122028/1-9. |
| [6] | LAJUNEN A .Energy consumption and cost-benefit analysis of hybrid and electric city buses[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2014,38:1-15. |
| [7] | GONDER J, EARLEYWINE M, SPARKS W .Analy-zing vehicle fuel saving opportunities through intelligent driver feedback[J].SAE International Journal of Pa-ssenger Cars-Electronic and Electrical Systems,2012,5(2):450-461. |
| [8] | ZHANG Y, FU R, GUO Y,et al .Eco-driving stra-tegy for connected electric buses at the signalized intersection with a station[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment,2024,128:104076/1-21. |
| [9] | WANG J, RAKHA H A .Fuel consumption model for conventional diesel buses[J].Applied Energy,2016,170:394-402. |
| [10] | QIU C, WANG G .New evaluation methodology of regenerative braking contribution to energy efficiency improvement of electric vehicles[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2016,119:389-398. |
| [11] | 张红妮 .基于驾驶行为的纯电动公交车能耗规律与节能对策[D].西安:长安大学,2020. |
| [12] | 郭淼,赵晓华,姚莹,等 .基于驾驶行为和交通运行状态的事故风险研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(9):29-38. |
| GUO Miao, ZHAO Xiaohua, YAO Ying,et al .Study on accident risk based on driving behavior and traffic operating status[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(9):29-38. | |
| [13] | ZHANG Y, FU R, GUO Y,et al .Environmental screening model of driving behavior for an electric bus entering and leaving stops[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment,2022,112:103464/1-17. |
| [14] | ULLAH I, LIU K, YAMAMOTO T,et al .A comparative performance of machine learning algorithm to predict electric vehicles energy consumption:a path towards sustainability[J].Energy & Environment,2022,33(8):1583-1612. |
| [15] | ABDELATY H, AL-OBAIDI A, MOHAMED M,et al .Machine learning prediction models for battery-electric bus energy consumption in transit[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment,2021,96:102868/1-27. |
| [16] | LEE C H, WU C H .A novel big data modeling method for improving driving range estimation of EVs[J].IEEE Access,2015,3:1980-1993. |
| [17] | 程颖,张佳乐,张少君,等 .大型货运车辆生态驾驶及节油潜力评估[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2020,20(6):253-258. |
| CHENG Ying, ZHANG Jiale, ZHANG Shaojun,et al .Evaluation of eco-dring behavior and fuel-saving potential of large freight vehicle[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering an Information Technology,2020,20(6):253-258. | |
| [18] | 朱江苏,王继磊,吕文芝,等 .基于多元回归的司机驾驶行为对油耗的影响[J].山东交通学院学报,2020,28(3):8-13. |
| ZHU Jiangsu, WANG Jilei, Wenzhi LÜ,et al .E-ffect of driver’s driving behavior on fuel consumption based on multiple regression[J].Journal of Shandong Jiaotong University,2020,28(3):8-13. | |
| [19] | 吴海东,臧力卓,肖百卉,等 .基于新能源公交大数据的驾驶行为经济性评估[J].中国公路学报,2022,35(3):177-190. |
| WU Haidong, ZANG Lizhuo, XIAO Baihui,et al .Evaluation of driving behavior economy based on big data of new energy bus[J].China Journal of Highway Transportation,2022,35(3):8-13. | |
| [20] | 陈晨 .城市道路驾驶员生态驾驶行为评估方法研究[D].北京:北京工业大学,2017. |
| [21] | 涂昊然 .基于驾驶行为的纯电动汽车能耗分析方法研究[D].北京:北京理工大学,2021. |
| [22] | 张雅丽,沈钰博,王伊 .纯电动公交车驾驶行为对能耗的影响研究[J].交通工程,2024,24(7):1-7,16. |
| ZHANG Yali, SHEN Yubo, WANG Yi .Research on the impact of driving behavior on energy consumption of electric buses[J].Journal of Transportation Enginee-ring,2024,24(7):1-7,16. | |
| [23] | 付锐,张雅丽,袁伟 .生态驾驶研究现状及展望[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(3):1-12. |
| FU Rui, ZHANG Yali, YUAN Wei .Progress and prospect in research on eco-driving[J].China Journal of Highway Transportation,2019,32(3):1-12. | |
| [24] | 严利鑫,贾乐,刘清梅,等 .基于知识图谱的生态驾驶行为研究现状及热点分析[J].公路交通科技,2022,39(4):150-159. |
| YAN Lixin, JIA Le, LIU Qingmei,et al .Analysis on study status and hotspots of eco-driving behavior based on knowledge graph[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2022,39(4):150-159. | |
| [25] | BEUSEN B, BROEKX S, DENYS T,et al .Using on-board logging devices to study the longer-term impact of an eco-driving course[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment,2009,14(7):514-520. |
| [26] | GONDER J, EARLEYWINE M, SPARKS W .Final report on the fuel saving effectiveness of various driver feedback approaches[R].National Rene-wable Energy Lab.NREL). Golden,Colorado:[s.n.],2011. |
| [1] | REN Wenhao, ZHAO Xiaohua, CHEN Chen, FU Qiang. Impact of Connected Collision Warning Information System on Freeway Driving Behavior in Foggy Conditions [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(2): 27-37. |
| [2] | WU Biao, REN Hongze, ZHENG Lianqing, ZHU Xichan, MA Zhixiong. Complex Scenario Construction Method for Navigation Pilot Based on Natural Driving Behaviour [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(2): 38-47. |
| [3] | HE Qingling, PEI Yulong, DONG Chuntong, et al. Classification and Identification of Risky Driving Behavior Based on Hybrid Strategy Improved ASO-LSSVM [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(9): 131-141. |
| [4] | CHEN Bingshuo, LI Yang, ZHAO Xiaohua, et al. Study on Evaluation and Influencing Factors of Cognitive Driving Ability in Elderly Drivers [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(9): 142-152. |
| [5] | FU Qiang, ZHAO Xiaohua, LI Haijian, et al. Operational Characteristics and Eco-Safe Influence of Connected Mixed Platoon in Car-Following Event [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(8): 65-75. |
| [6] | GAO Longkai, ZHAO Xiaohua, OU Jushang, et al. Optimization Design of the Stereoscopic Compound Expressway Sign System Based on Unity3D [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 20-30. |
| [7] | DING Xiaobin, YANG Huitai, SHI Yu. Formation Factor Analysis and Evaluation Model Construction of Mud Cake on EPB Cutterhead [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 71-83. |
| [8] | ZHANG Ting, CHEN Feng, LI Huang, et al. Evaluation of the Effect of Self-Luminous Road Marking in Expressway Weaving Section Based on Driving Behavior [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(11): 106-117. |
| [9] | ZHAO Xiaohua, DONG Wenhui, LI Jia, et al. Influence Characteristics and Action Mechanism of Tunnel Traffic Signs Based on Driving Behavior [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 88-100. |
| [10] | ZHANG Wenhui, SU Jiaqi, HA Zihong, et al. Location and Capacity Optimization Model of Battery-Swapped Electric Bus Charging Station [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 126-134. |
| [11] | GUO Miao, ZHAO Xiaohua, YAO Ying, et al. Study on Accident Risk Based on Driving Behavior and Traffic Operating Status [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 29-38. |
| [12] | BIAN Yang, YU Jie ZHAO, Xiaohua, et al. Research on the Comprehensive Influence of Navigation BroadcastWording on Driving Behavior [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(11): 30-37,54. |
| [13] | FU Xinsha DU Jintao HE Shijian. Effects of Guide Distance and Initial Speed on Driving Behavior at Expressway Exit [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(11): 1-9. |
| [14] | Chen Gang Liu Yu-sha Wen Ai He Bei-hai. Characteristic Analysis and Evaluation Model of Thermal Aging of Paper Based on Thermogravimetry [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(1): 19-23,29. |
| [15] | Feng Yu-qin Leng Jun-qiang Zhang Ya-ping Li Han-wu Zhang Chun-ping. Evaluation Model of Fuel Economy of Urban Road Section [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(8): 104-108. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||