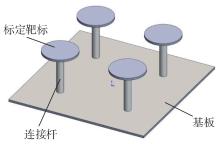
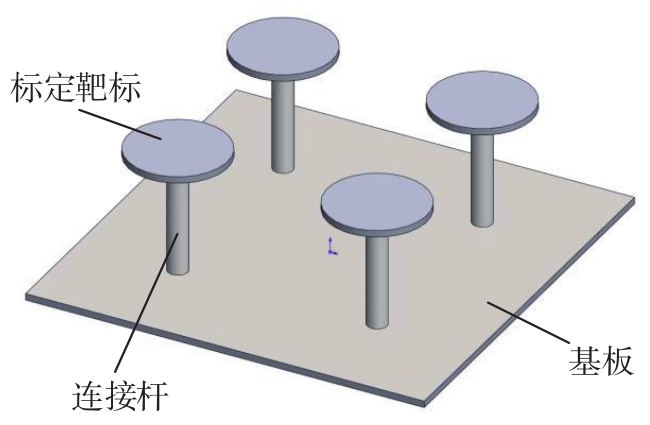
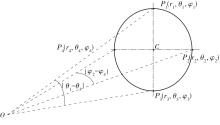
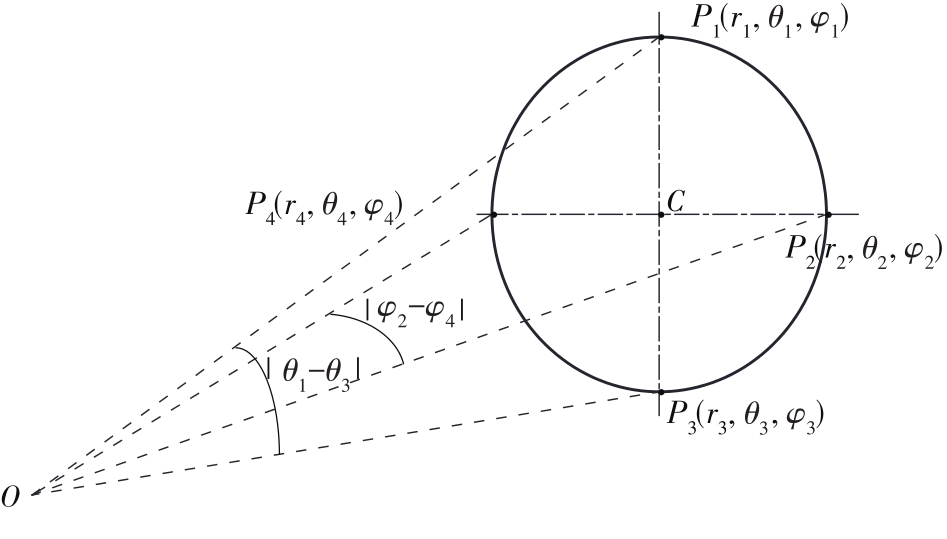
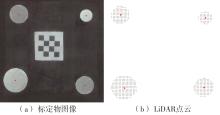
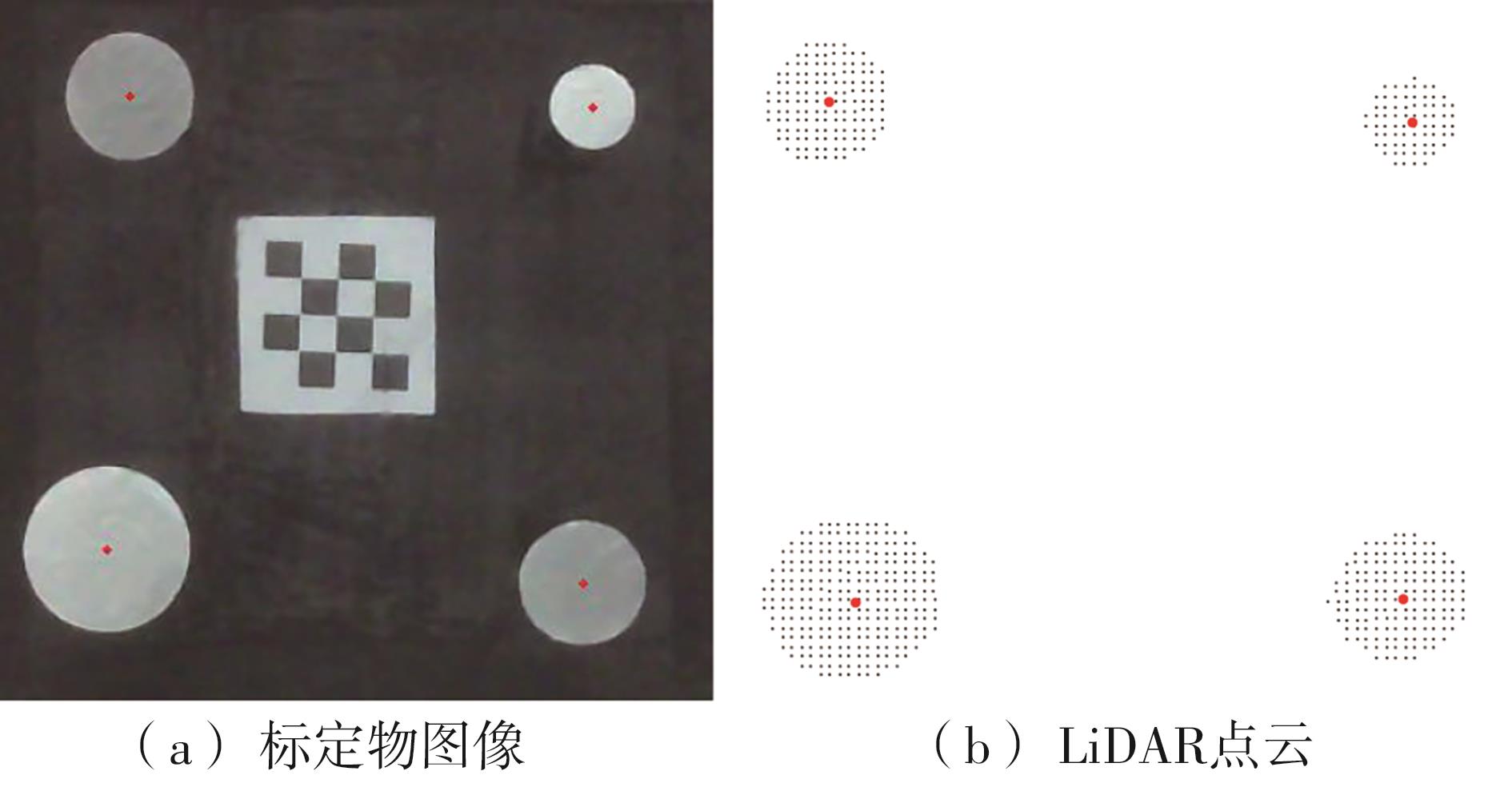
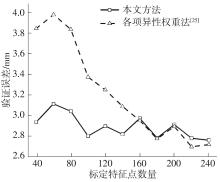
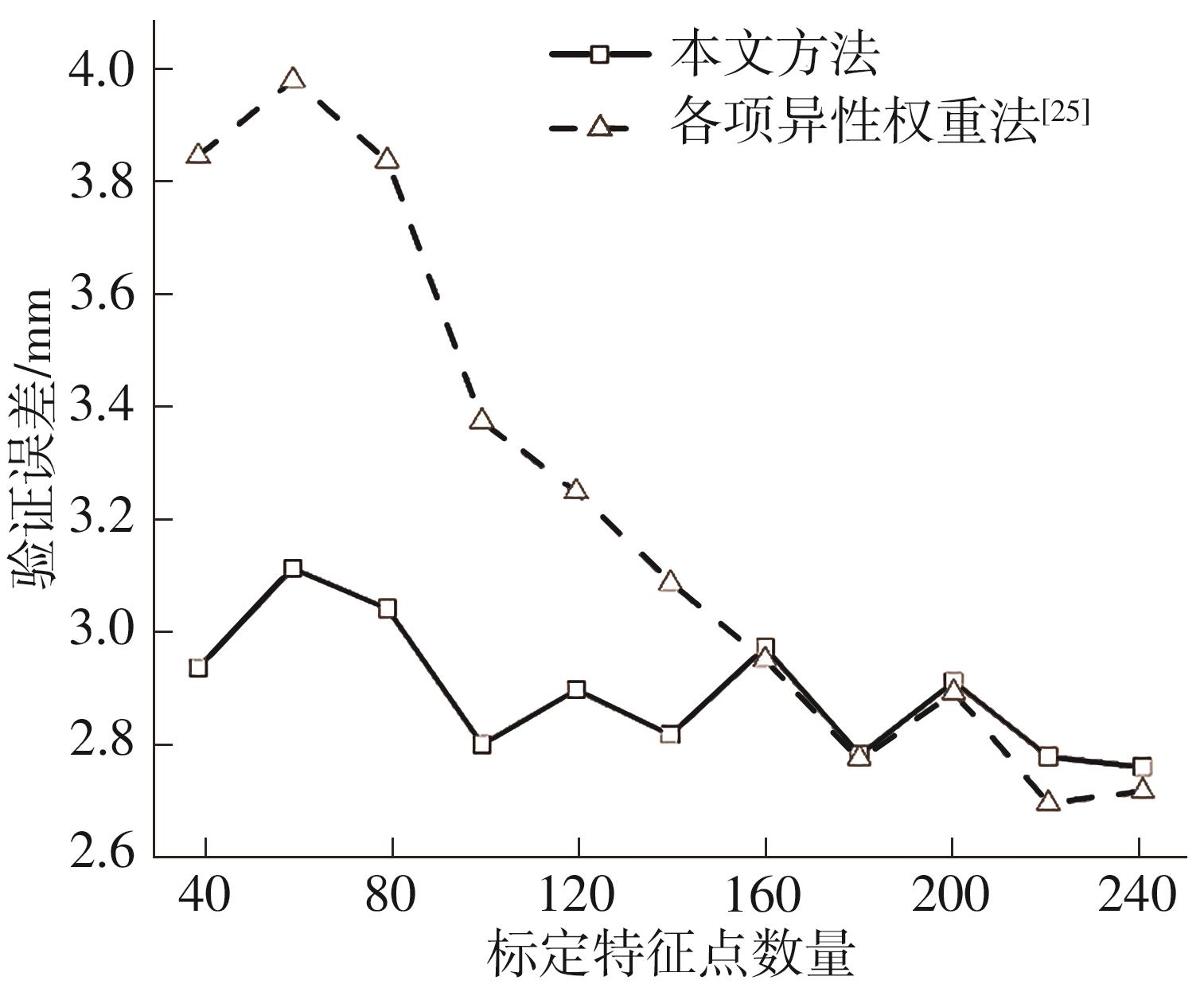
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 1-9.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220178
Special Issue: 2023年机械工程
• Mechanical Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
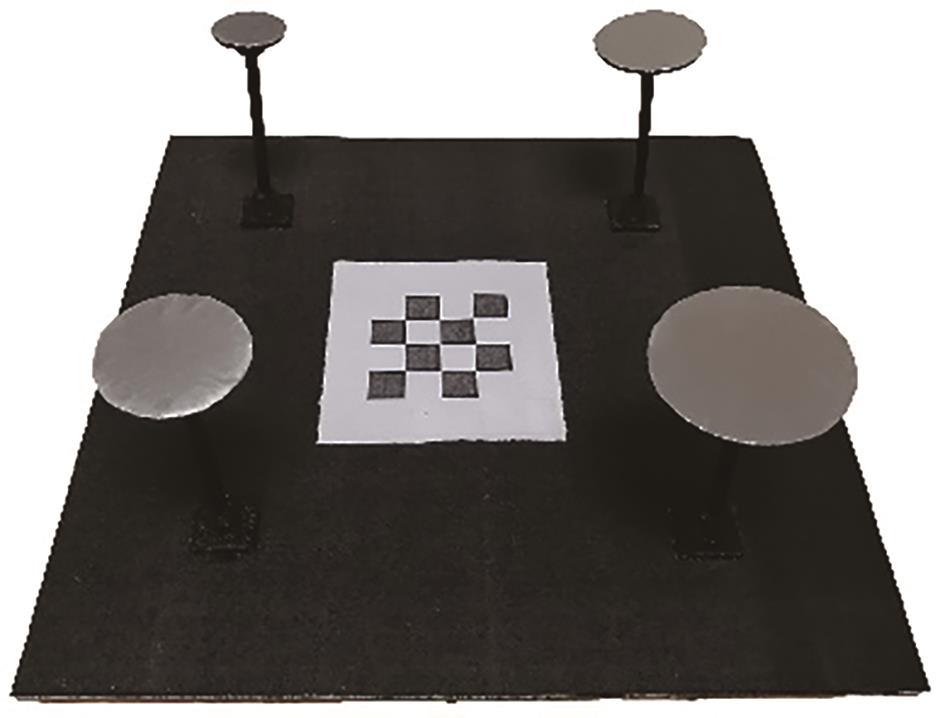
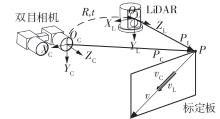
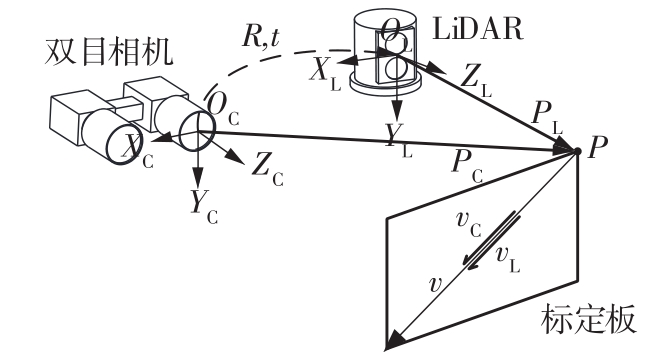
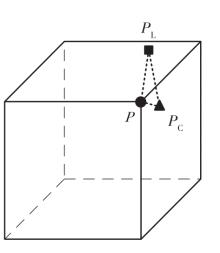
LiDAR-Binocular Camera Calibration by Minimizing LiDAR Isotropic Error
CHEN Zhong LIU Zichen ZHANG Xianmin
- School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-04-06Online:2023-02-25Published:2023-02-01 -
Contact:陈忠(1968-),男,博士,教授,主要从事柔顺机构动力、机器视觉机器及其应用、精密测量和故障诊断研究。 E-mail:mezhchen@scut.edu.cn -
About author:陈忠(1968-),男,博士,教授,主要从事柔顺机构动力、机器视觉机器及其应用、精密测量和故障诊断研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51875204);the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2020A1515011543)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
CHEN Zhong, LIU Zichen, ZHANG Xianmin. LiDAR-Binocular Camera Calibration by Minimizing LiDAR Isotropic Error[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(2): 1-9.
share this article
| 1 | SCHENK T, CSATHÓ B .Fusion of LIDAR data and aerial imagery for a more complete surface description[J].International Archives of Photogrammetry Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences,2002,34(3/A):310-317. |
| 2 | PARK K, KIM S, SOHN K .High-precision depth estimation using uncalibrated LiDAR and stereo fusion[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2019,21(1):321-335. |
| 3 | YANG S, LI B, LIU M,et al .Heterofusion:dense scene reconstruction integrating multi-sensors[J].IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics,2019,26(11):3217-3230. |
| 4 | ALI M K, RAJPUT A, SHAHZAD M,et al .Multi-sensor depth fusion framework for real-time 3D reconstruction[J].IEEE Access,2019,7:136471-136480. |
| 5 | ZHEN W, HU Y, LIU J,et al .A joint optimization approach of lidar-camera fusion for accurate dense 3-d reconstructions[J].IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2019,4(4):3585-3592. |
| 6 | SNAVELY N, SEITZ S M, SZELISKI R .Photo tourism:exploring photo collections in 3D[J].Acm Transactions on Graphics,2006,25(3):835-846. |
| 7 | FURUKAWA Y, PONCE J .Accurate,dense,and robust multiview stereopsis[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2009,32(8):1362-1376. |
| 8 | ESTEBAN C H, SCHMITT F .Silhouette and stereo fusion for 3D object modeling[J].Computer Vision and Image Understanding,2004,96(3):367-392. |
| 9 | KADA M, MCKINLEY L .3D building reconstruction from LiDAR based on a cell decomposition approach[J].International Archives of Photogrammetry,Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences,2009,38(Part 3):W4. |
| 10 | YI C, ZHANG Y, WU Q,et al .Urban building reconstruction from raw LiDAR point data[J].Computer-Aided Design,2017,93:1-14. |
| 11 | UNNIKRISHNAN R, HEBERT M .Fast extrinsic calibration of a laser rangefinder to a camera[M].Pittsburgh,PA,USA:Robotics Institute,2005. |
| 12 | ZHOU L .A new minimal solution for the extrinsic calibration of a 2D LIDAR and a camera using three plane-line correspondences[J].IEEE Sensors Journal,2013,14(2):442-454. |
| 13 | FU B, WANG Y, DING X,et al .LiDAR-camera calibration under arbitrary configurations:observability and methods[J].IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement,2019,69(6):3089-3102. |
| 14 | ZHOU L, LI Z, KAESS M .Automatic extrinsic calibration of a camera and a 3d lidar using line and plane correspondences[C]∥2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).Madrid,Spain:IEEE,2018:5562-5569. |
| 15 | LI Y, RUICHEK Y, CAPPELLE C .Optimal extrinsic calibration between a stereoscopic system and a LIDAR[J].IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement,2013,62(8):2258-2269. |
| 16 | FREMONT V, BONNIFAIT P .Extrinsic calibration between a multi-layer lidar and a camera[C]∥2008 IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems.Seoul,Korea (South):IEEE,2008:214-219. |
| 17 | GUINDEL C, BELTRÁN J, MARTÍN D,et al .Automatic extrinsic calibration for lidar-stereo vehicle sensor setups[C]∥2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC).Yokohama,Japan:IEEE,2017:1-6. |
| 18 | PARK Y, YUN S, WON C S,et al .Calibration between color camera and 3D LIDAR instruments with a polygonal planar board[J].Sensors,2014,14(3):5333-5353. |
| 19 | CAI H, PANG W, CHEN X,et al .A novel calibration board and experiments for 3D LiDAR and camera calibration[J].Sensors,2020,20(4):1130. |
| 20 | HUANG J K, GRIZZLE J W .Improvements to target-based 3D LiDAR to camera calibration[J].IEEE Access,2020,8:134101-134110. |
| 21 | AN P, MA T, YU K,et al .Geometric calibration for LiDAR-camera system fusing 3D-2D and 3D-3D point correspondences[J].Optics Express,2020,28(2):2122-2141. |
| 22 | HORAUD R, HANSARD M, EVANGELIDIS G,et al .An overview of depth cameras and range scanners based on time-of-flight technologies[J].Machine Vision and Applications,2016,27(7):1005-1020. |
| 23 | MAIER-HEIN L, FRANZ A M, DOS SANTOS T R,et al .Convergent iterative closest-point algorithm to accomodate anisotropic and inhomogenous localization error[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2011,34(8):1520-1532. |
| 24 | BALACHANDRAN R, FITZPATRICK J M .Iterative solution for rigid-body point-based registration with anisotropic weighting[C]∥Medical Imaging 2009:Visualization,Image-Guided Procedures,and Modeling.Florida,United States:SPIE Medical Imaging,2009:1051-1060. |
| 25 | WANG W, LIU Y, CHEN R,et al .A calibration method with anisotropic weighting for LiDAR and stereo camera system[C]∥2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO).Dali,China:IEEE,2019:422-426. |
| [1] | BI Xin, WENG Caien, WANG Yu, et al. An Autonomous Extrinsic Calibration Method for 4D Millimeter-Wave Radar Point Clouds and Visual Images [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(1): 74-83. |
| [2] | HUANG Yan, FU Xinsha, ZENG Yanjie, et al. 3D Modeling Method of Highway Based on Lidar Odometer [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 129-138. |
| [3] | YAO Bin, ZHANG Zihao, DAI Yu, et al. Research on Dynamic Characteristics of Force Sensor Based on VFF-RLS [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(5): 86-94. |
| [4] | YU Bin, ZHANG Yuqin, WANG Yuchen, et al. Automated Extraction of Road Geometry Information Using Mobile LiDAR Point Cloud [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(2): 88-99. |
| [5] | LUO Dongyu, WANG Jiangfeng, CHEN Jingya, et al. Operating Speed Prediction Based on Dynamic Visual Field in Three-Dimensional Point Cloud Environment [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(7): 17-25. |
| [6] | CHEN Zhijian, WANG Yuchen, HUANG Pengcheng, et al. Design of Ultra-Wideband Active Magnetic Field Probe for Near-Field Measurement [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(6): 131-140. |
| [7] | ZHANG Libin WU Dao SHAN Hongying LIU Qifeng. Dynamic Measurement Method for Vehicle Contour Dimensions Based on Laser Point Cloud [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(3): 61-69. |
| [8] | WANG Hongwei YANG Yajie ZHANG Long. Calibration Technology of Three-Dimension Sound Intensity Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(7): 123-127,136. |
| [9] |
.
Evaluation of Flow Field Simulation of Turbine in Water-Medium Hydrodynamic Coupling Based on PIV Experiment
|
| [10] |
KUANG Yongcong LI Jiayu LIANG Jinglun OUYANG Gaofei.
Precise Positioning Method of Electronic-Component Leads Based on Rotational Stereo Vision
|
| [11] | ZHANG Xian-min ZENG Lei. Kinematic Calibration of 3-RRR Parallel Mechanism Considering Reducer Backlash [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(7): 47-54. |
| [12] | BAI Pu-jun XUE Na LIU Song-tao SONG Tao LI Jin-he. Angular Calibration Method of Precision Rotating Platform Based on Laser Tracker [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(1): 100-107. |
| [13] | KUANG Yong-cong CUI Liang-chun. A New Calibration Method for Line-Structured Light Vision Sensor Based on Linear Scale [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(1): 71-77. |
| [14] | Zhang Xian-min Liu Han. A Clearance Approach of Kinematic Calibration and Error Compensation for 3-RRR Parallel Robot [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(7): 97-103. |
| [15] | Li Jing Liang Ju Zeng Cheng Li Xue- mei Li Hua. Transient Heat Transfer Analysis of Calibration and Cooling System for Extruded Plastic Pipe [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(7): 81-86. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||