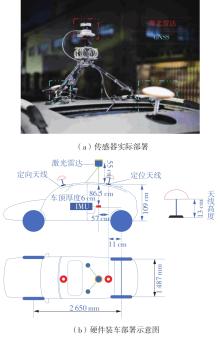
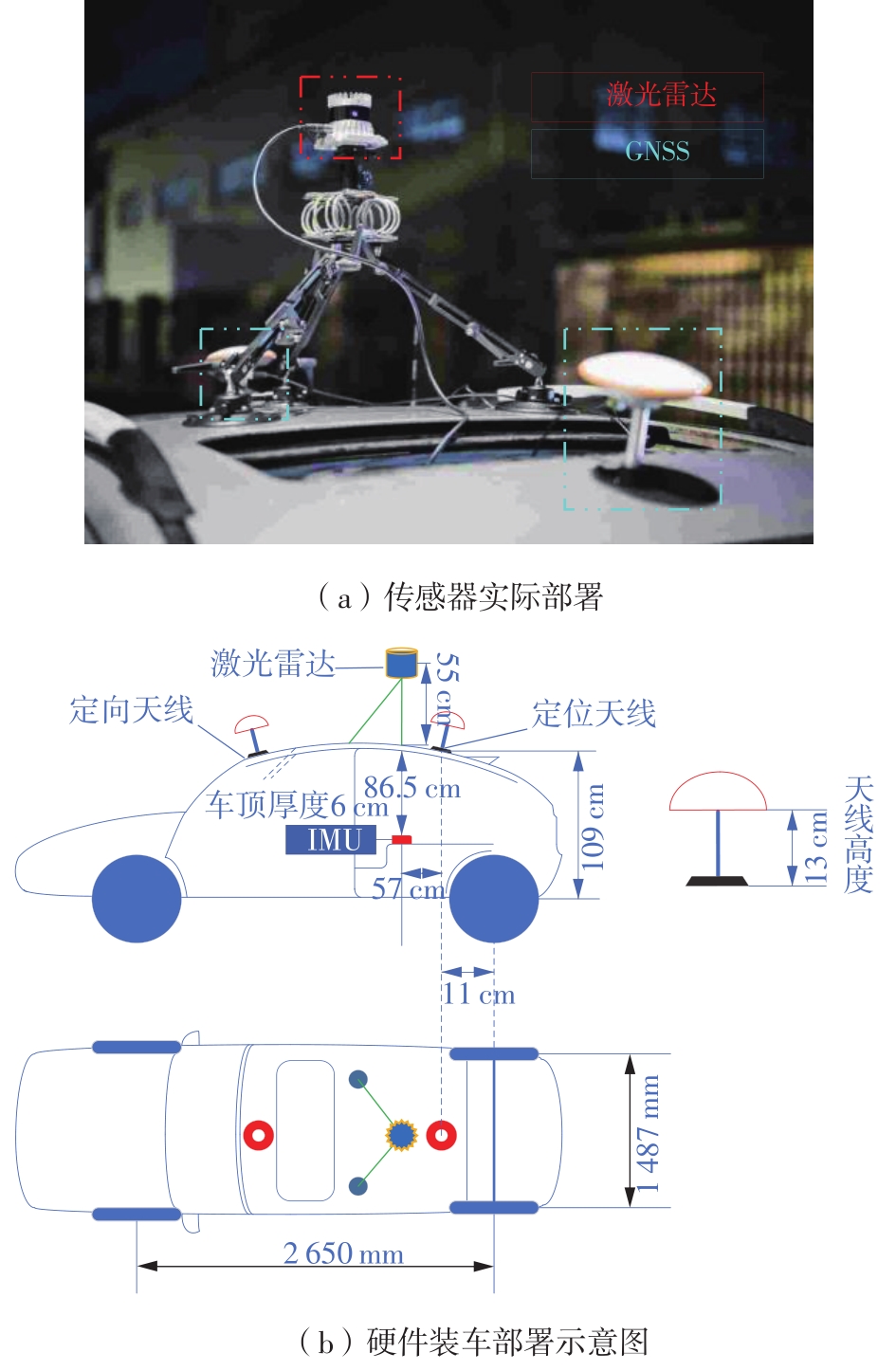
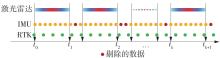
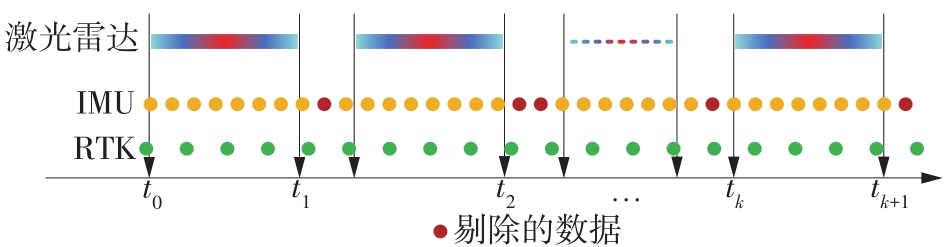
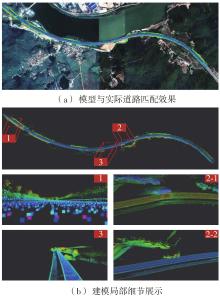
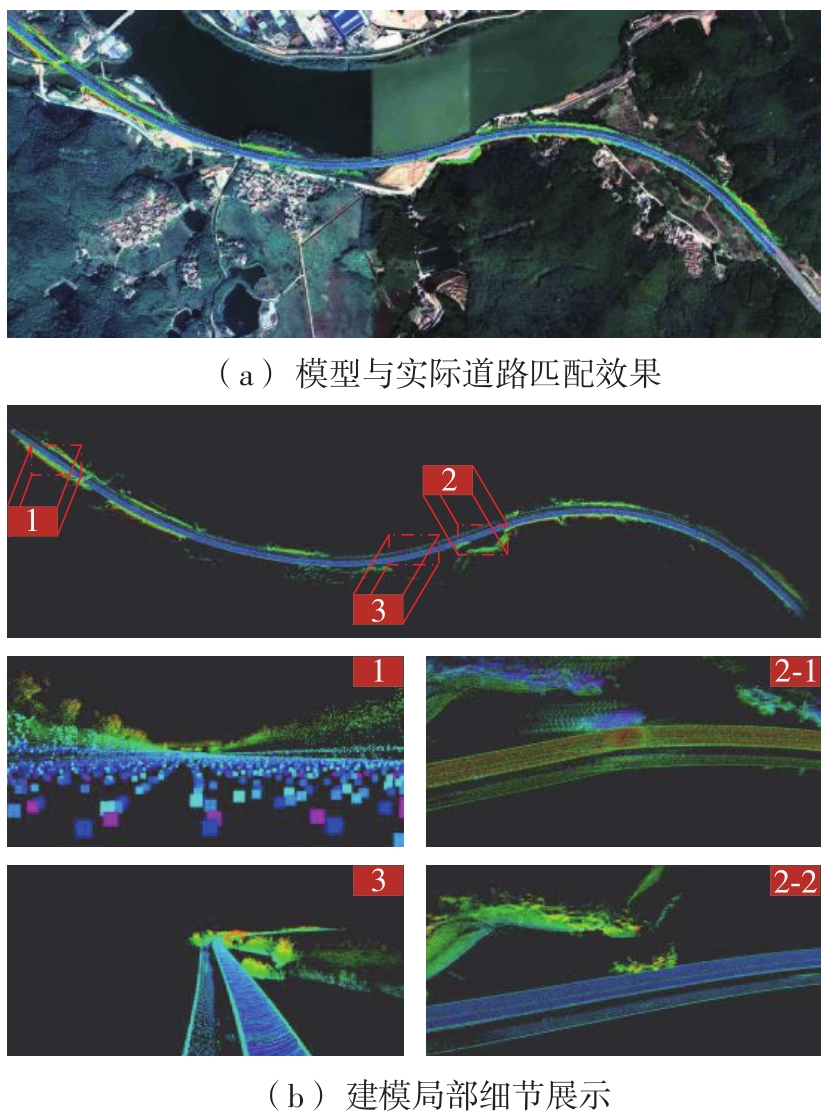
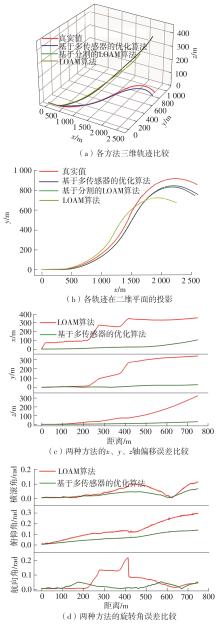
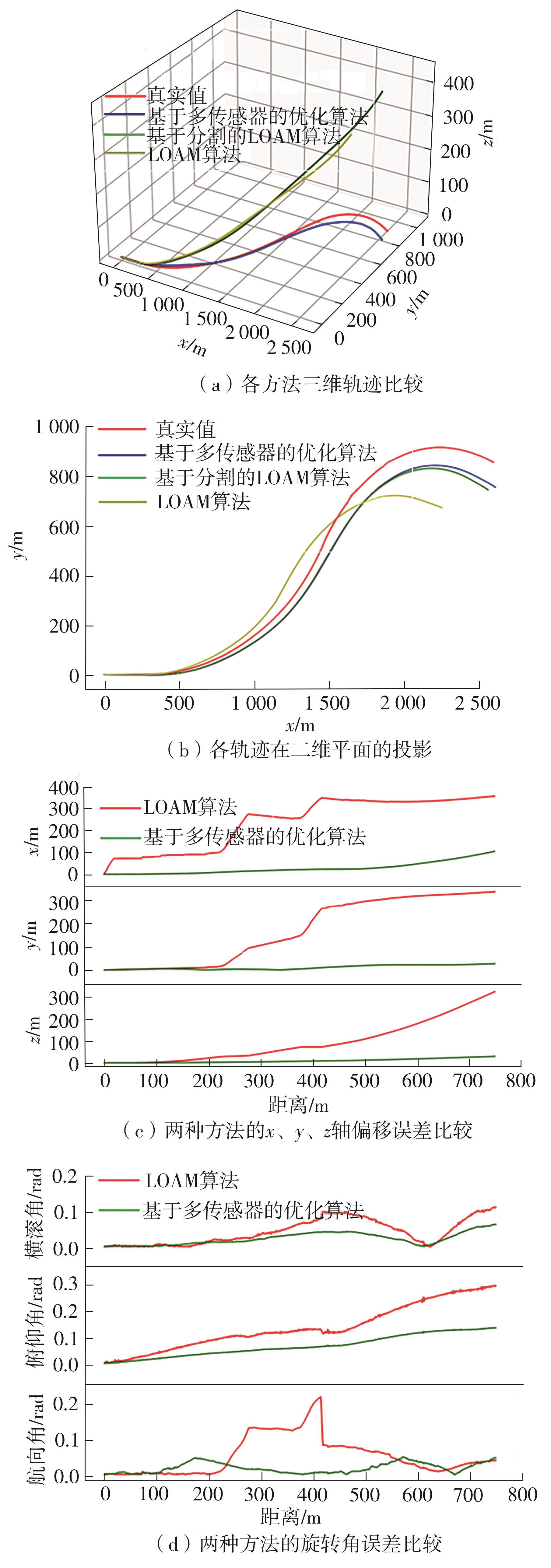
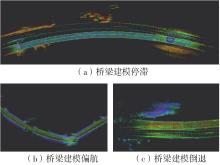
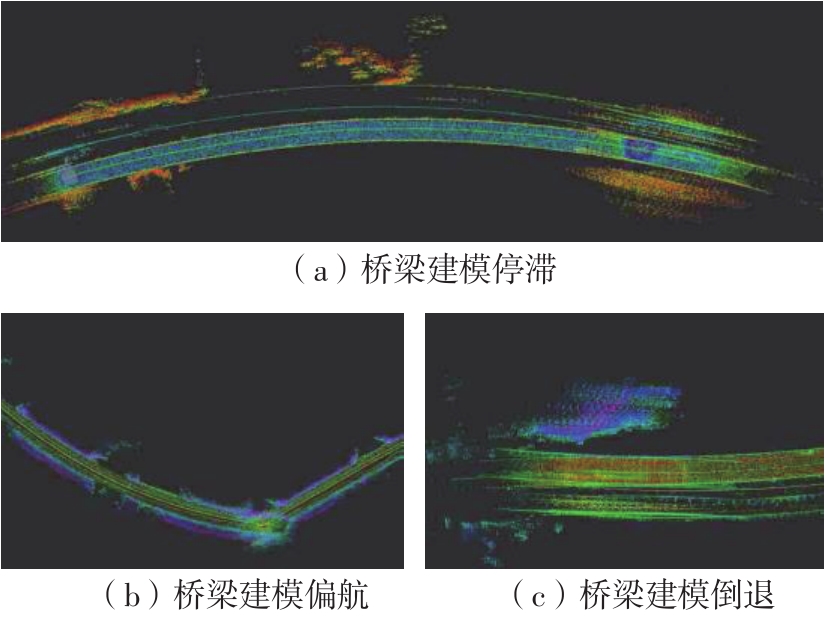
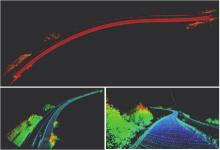
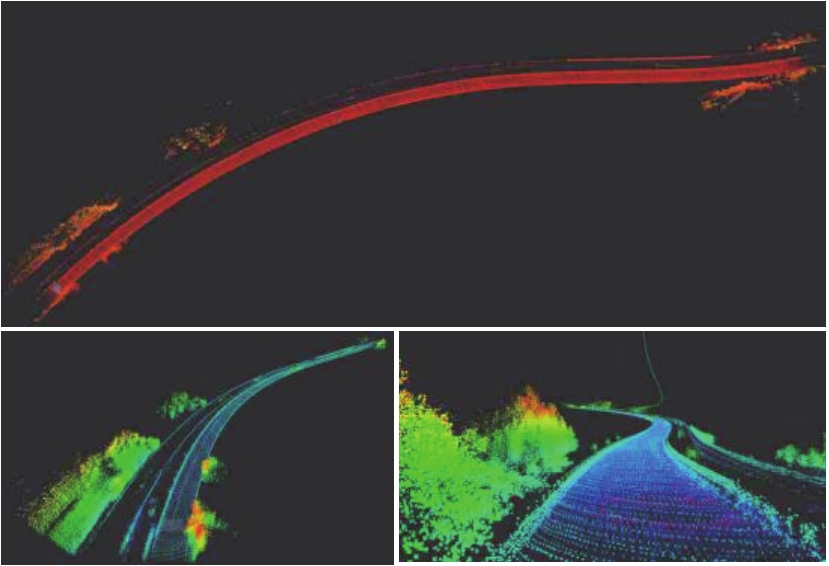
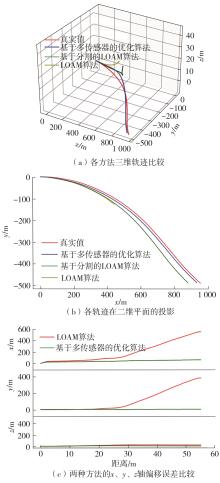
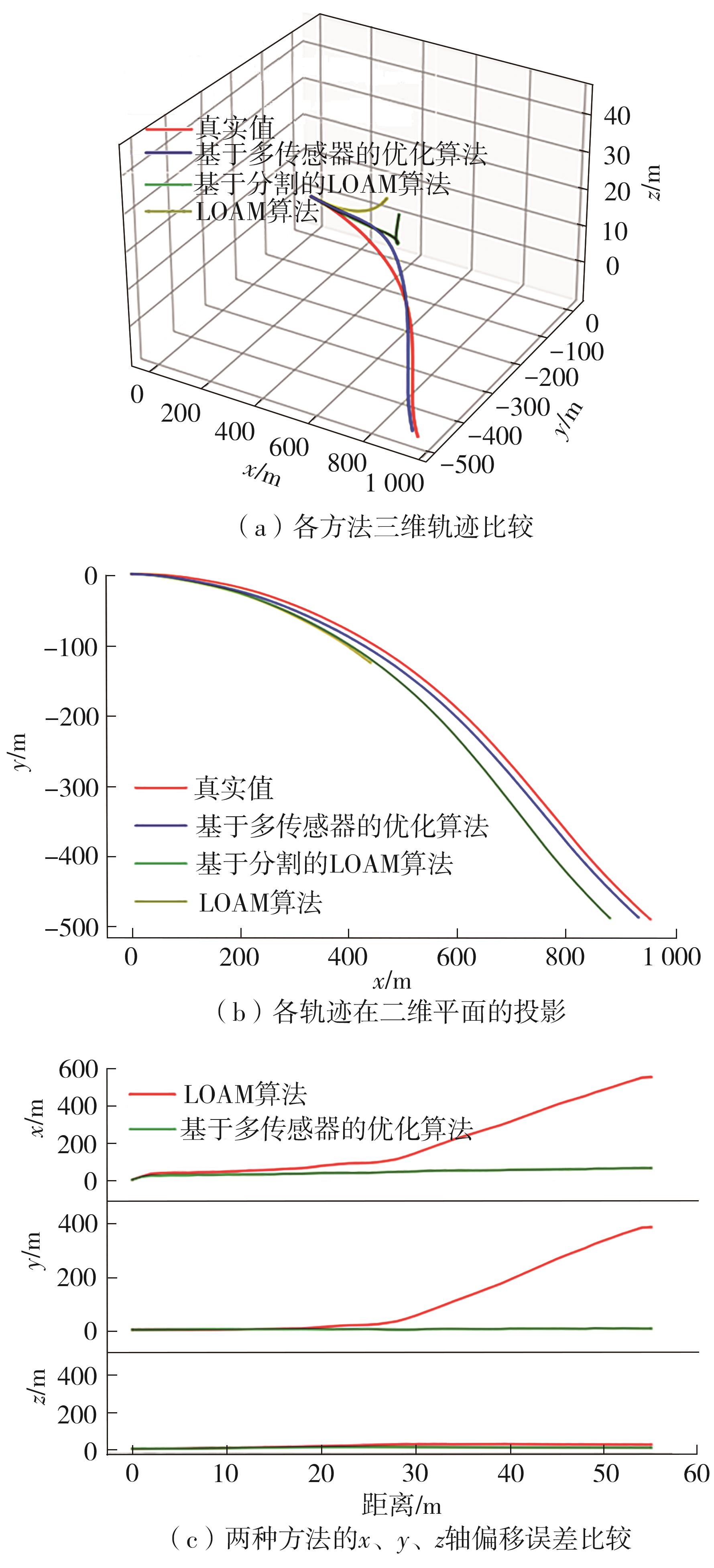
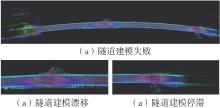
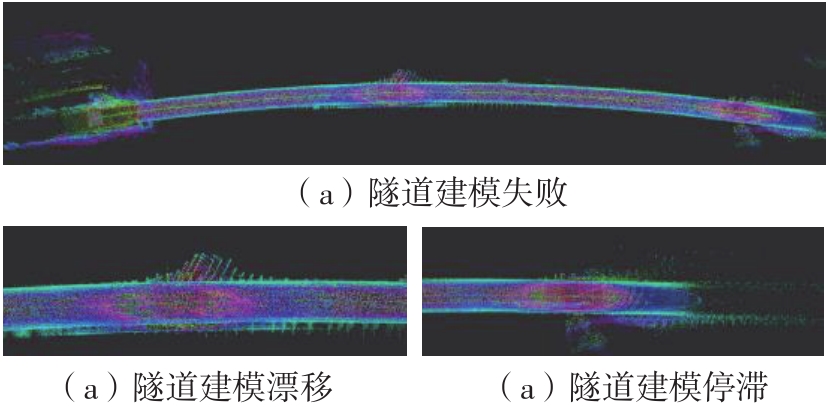
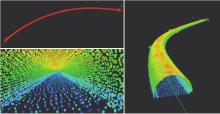
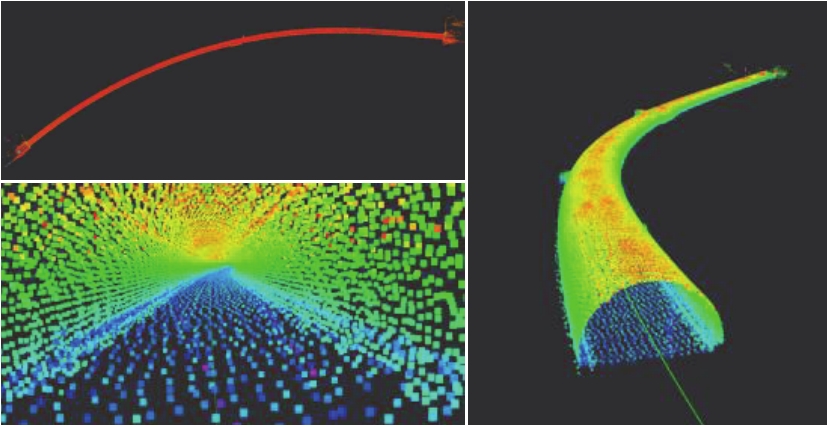
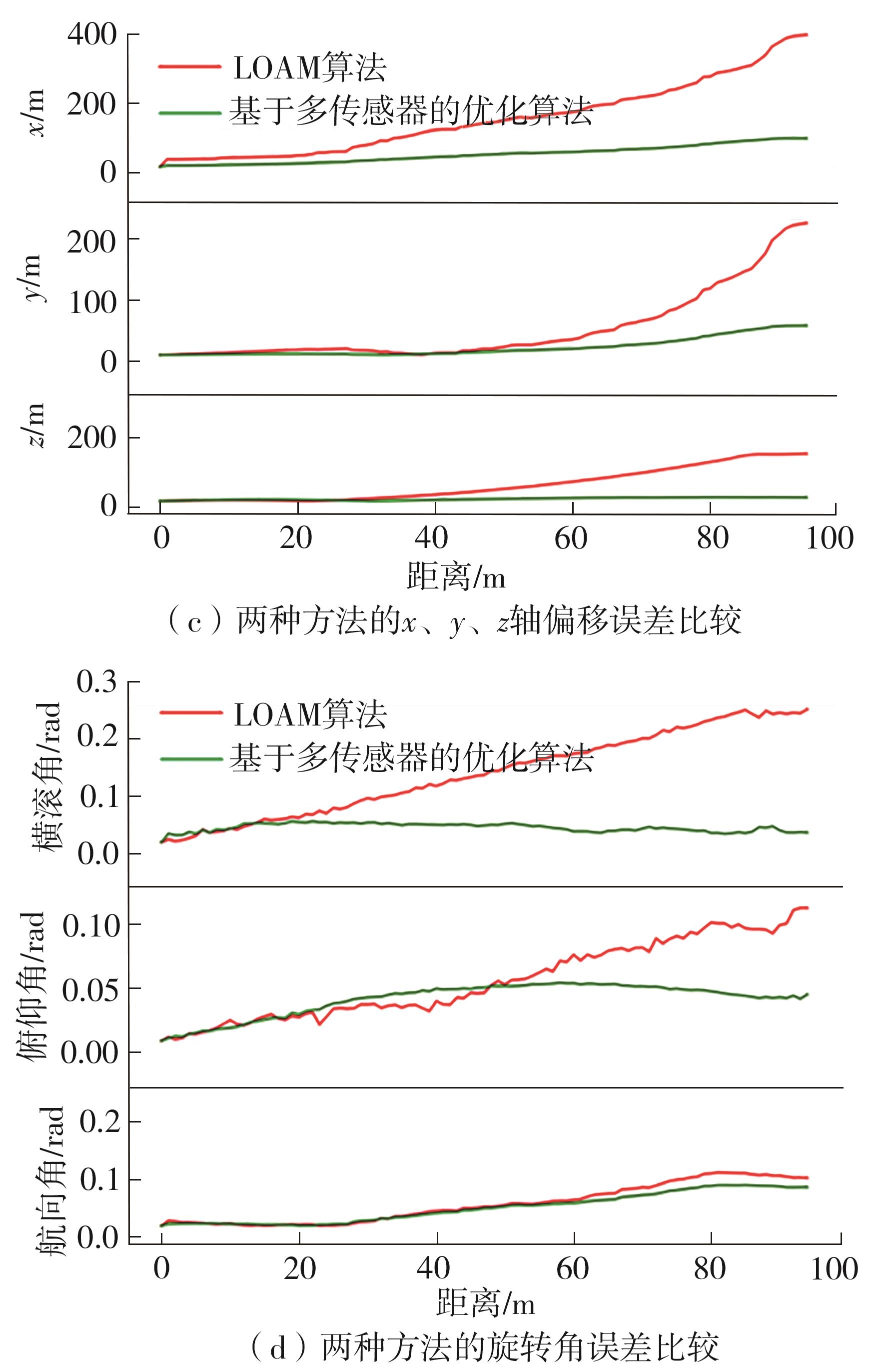
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (7): 129-138.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220583
Special Issue: 2023年交通运输工程
• Traffic & Transportation Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
3D Modeling Method of Highway Based on Lidar Odometer
HUANG Yan1 FU Xinsha1 ZENG Yanjie2 LI Baijian1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangdong Provincial Transport Planning and Research Center,Guangzhou 510101,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2020-09-09Online:2023-07-25Published:2023-01-20 -
Contact:李百建(1987-),男,博士后,讲师,主要从事道路工程相关理论的研究。 E-mail:bjian_li@163.com -
About author:黄炎(1988-),男,博士生,主要从事智能交通系统研究。E-mail:yann_h0918@163.com -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51978283)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HUANG Yan, FU Xinsha, ZENG Yanjie, et al. 3D Modeling Method of Highway Based on Lidar Odometer[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 129-138.
share this article
| 1 | 王羽尘,于斌,陈晓阳,等 .基于激光雷达点云的道路几何信息提取与数字化建模研究[J].中国公路学报,2023,36(3):45-60. |
| WANG Yu-chen, YU Bin, CHEN Xiao-yang,et al .Extraction and digital modeling of road geometric information using LIDAR data points clouds[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2023,36(3):45-60. | |
| 2 | LONG N, YAN H, WANG L,et al .Unifying obstacle detection, recognition, and fusion based on the pola-rization color stereo camera and LiDAR for the ADAS[J].Sensors,2022,22(7):2453/1-20. |
| 3 | ALSADIK B .Ideal angular orientation of selected 64-channel multi beam Lidars for mobile mapping systems[J].Remote Sensing,2020,12(3):510/1-20. |
| 4 | BESL P J, MCKAY N D .A method for registration of 3-D shapes[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,1992,14(2):239-256. |
| 5 | ZHANG J, SINGH S .Low-drift and real-time lidar odometry and mapping[J].Autonomous Robots,2017,41(2):401-416. |
| 6 | YE H, CHEN Y, LIU M .Tightly coupled 3D lidar inertial odometry and mapping[C]∥Proceedings of 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA).Montreal:IEEE,2019:3144-3150. |
| 7 | ZHANG P, HANCOCK C M, LAU L,et al .Low-cost IMU and odometer tightly coupled integration with robust Kalman filter for underground 3-D pipeline mapping[J].Measurement,2019,137:454-463. |
| 8 | SHAN T, ENGLOT B, MEYERS D,et al .LIO-SAM:tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and mapping[C]∥Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).Las Vegas:IEEE,2020:5135-5142. |
| 9 | KAESS M, JOHANSSON H, ROBERTS R,et al .iSAM2: incremental smoothing and mapping using the Bayes tree[J].The International Journal of Robotics Research,2012,31(2):216-235. |
| 10 | SHAN T, ENGLOT B .LeGO-LOAM:lightweight and ground-optimized lidar odometry and mapping on variable terrain[C]∥Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).Madrid:IEEE,2018:4758-4765. |
| 11 | 安平,王国平,余佳东,等 .一种高效准确的视觉SLAM闭环检测算法[J].北京航空航天大学学报,2021,47(1):24-30. |
| AN Ping, WANG Guoping, YU Jiadong,et al .An efficient and accurate visual SLAM loop closure detection algorithm[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2021,47(1):24-30. | |
| 12 | GREJNER-BRZEZINSKA D A, TOTH C K, SUN H,et al .A robust solution to high-accuracy geolocation: quadruple integration of GPS,IMU,pseudolite,and terrestrial laser scanning[J].IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement,2011,60(11):3694-3708. |
| 13 | TEUNISSEN P J G, KHODABANDEH A .Review and principles of PPP-RTK methods[J].Journal of Geo-desy,2015,89(3):217-240. |
| 14 | DAM E B, KOCH M, LILLHOLM M .Quaternions,interpolation and animation[M].Copenhagen:Datalogisk Institut,Københavns Universitet,1998. |
| 15 | WU B, WAN A, YUE X,et al .Squeezeseg: convolutional neural nets with recurrent crf for real-time road-object segmentation from 3d lidar point cloud[C]∥Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA).Brisbane:IEEE,2018:1887-1893. |
| 16 | CARLEVARIS-BIANCO N, KAESS M, EUSTICE R M .Generic node removal for factor-graph SLAM[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics,2014,30(6):1371-1385. |
| 17 | CHANG L, NIU X, LIU T .GNSS/IMU/ODO/LiDAR-SLAM integrated navigation system using IMU/ODO pre-integration[J].Sensors,2020,20(17):4702/1-17. |
| 18 | QUIGLEY M, CONLEY K, GERKEY B,et al .ROS: an open-source robot operating system[C]∥Proceedings of ICRA Workshop on Open Source Software.Xi’an:[s. n.],2009. |
| 19 | ALVARRUIZ S A .A Ceres solver based bundle adjustment module[D].Barcelona:Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya,2014. |
| 20 | DELLAERT F .Factor graphs and GTSAM: a hands-on introduction[R].Atlanta:Georgia Institute of Technology,2012. |
| [1] | YANG Yonghong, TANG Zude, WANG Chun, ZHU Guanru. Influence of Alignment Indexes of Highway Turning Section on Safety Performance of Concrete Guardrail [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 90-99. |
| [2] | ZHOU Chuhao, LIN Peiqun, YAN Mingyue. Traffic Data Imputation Based on Self-Supervised Learning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 101-114. |
| [3] | WU Yanxia, ZHOU Tong, HUANG Shuai, et al. Research on Roadside Environment Safety Based on Driver’s Attention Distribution Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 49-57. |
| [4] | WANG Xiaofei, LI Siyu, CHEN Mi, et al. Influence of the Combination Equilibrium of Horizontal and Crest Vertical Curves on Highway Safety [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 76-84. |
| [5] | FU Xinsha, ZENG Yanjie, MA Li, et al. Weather Recognition of Highway Surveillance Scenes Based on Light-Weight Deep Neural Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(3): 1-8. |
| [6] | HE Yongming, FENG Jia, QUAN Cong, et al. Braking Collision Avoidance System for Vehicles Driving on Superhighway Based on Co-simulation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(10): 19-28. |
| [7] | CHANG Xin, LI Haijian, RONG Jian, et al. Analysis of Capacity for Mixed Traffic Flow with Connected Vehicle Platoon on Freeway [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(4): 142-148. |
| [8] | ZHANG Chi ZHANG Hong QI Chen BAI Haochen GAO Jianrong HOU Yudi. Study of the Horizontal and Vertical Combination of the Split-end of the Exit Ramp [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 99-108. |
| [9] | WANG Yi-min GUO Ji-xing LI Lin-sheng HUANG Sheng-jun WANG Peng . Condition Evaluation of Subgrade in Highway Operation Period Based on Analytical Hierarchy Process [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(6): 37-43,51. |
| [10] | ZHAO Min MEI Deng SUN Di-hua. Monitoring Range Offset Detection Method of Highway Camera Based on Corner Set Feature [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(10): 100-107. |
| [11] | WANG Qiang SU Cheng. A Probe into Travel Spacing of Vehicles on Highway Bridges [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(3): 96-102. |
| [12] | Deng Ya-juan Wang Huan Du Ruo Hu Shao-rong. Division of Highway Network Hierarchy Based on Weighted Complex Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(4): 33-40. |
| [13] | Xu Lun- hui Hu San- gen Wu Shuai Luo Qiang . Overtaking Model for Two-Lane Highway Considering Vehicle Running Characteristics [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(4): 7-14 27. |
| [14] | Yang Yong-hong Hou Huang Chen Xing-guang Zhou Xiang-yang . Investigation into Minimum Vertical Curve Radius and Length of Highway in Mountainous Wind Farm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(12): 85-90. |
| [15] | Wang Qiang Su Cheng. Stationarity and Ergodicity of Random Motorcade on Highway Bridge [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(10): 8-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||