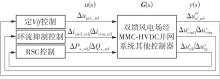
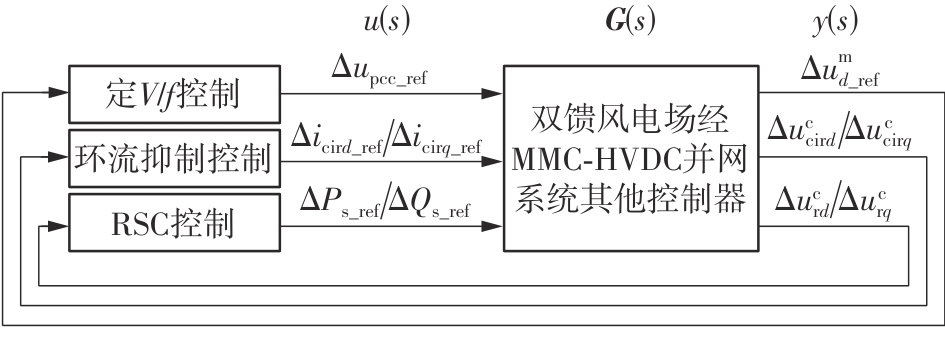
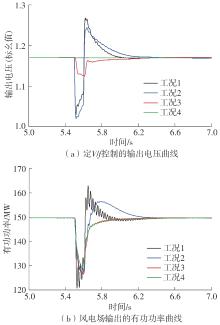
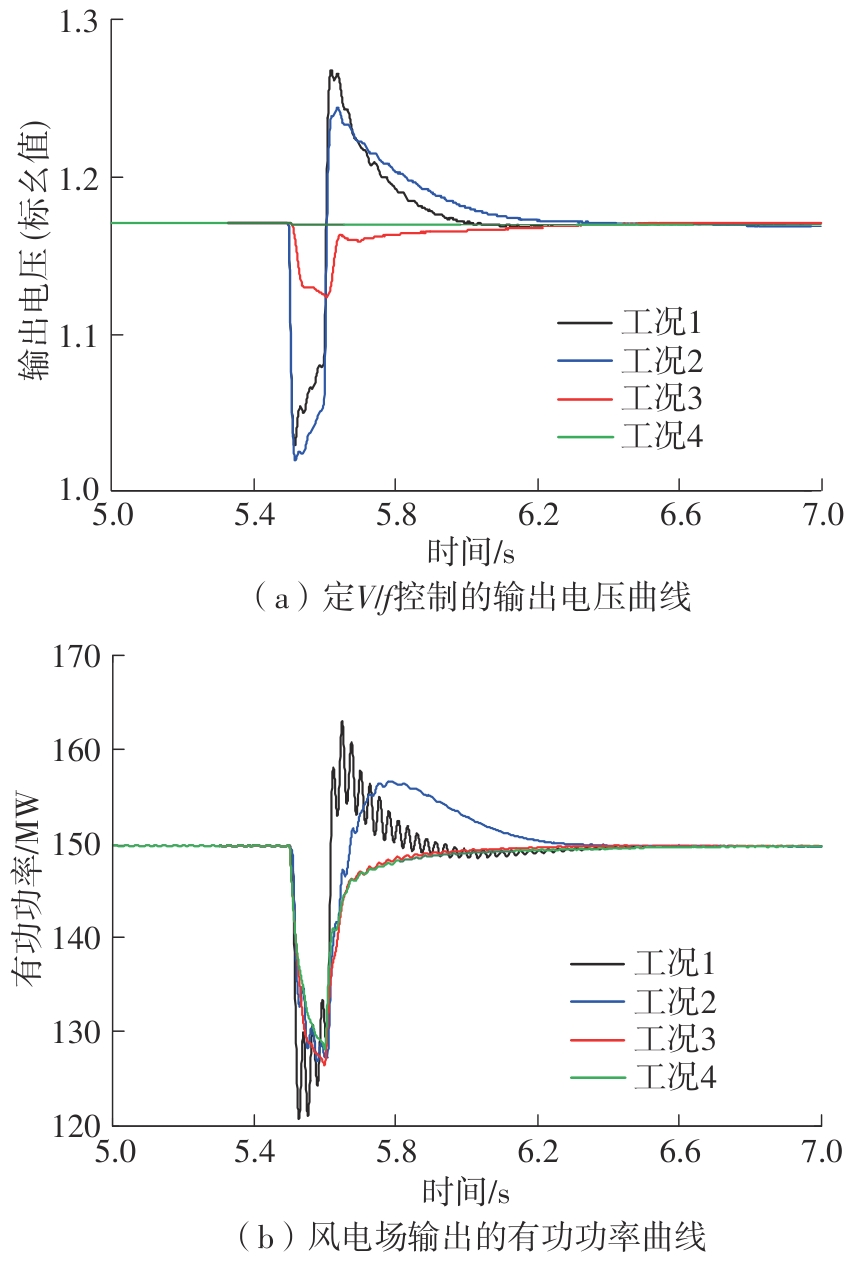
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 118-129.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240078
• Energy, Power & Electrical Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Quantitative Analysis of Interaction in Sub/Super-Synchronous Oscillation of Double-Fed Wind Farm Integrated into Grid Through MMC-HVDC System
ZHU Lin1, ZHAO Xinyue1,2, ZHONG Danting1, WU Zhigang1, GUAN Lin1
- 1.School of Electric Power Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.State Grid Hubei Technical Training Center (Wuhan Electric Power Technical College),Wuhan 430079,Hubei,China
-
Received:2024-02-20Online:2025-05-25Published:2024-07-22 -
About author:朱林(1979—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事新能源并网、电力系统稳定与控制研究。E-mail: zhul@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China(U22B6007);Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2024B1515250001)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHU Lin, ZHAO Xinyue, ZHONG Danting, WU Zhigang, GUAN Lin. Quantitative Analysis of Interaction in Sub/Super-Synchronous Oscillation of Double-Fed Wind Farm Integrated into Grid Through MMC-HVDC System[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(5): 118-129.
share this article
Table 2
Oscillation modes of the system"
| 模式 | 特征值 | 频率/Hz | 阻尼比 |
|---|---|---|---|
| λ1,2 | -1 523.6±j680.49 | 108.30 | 0.913 |
| λ3,4 | -8.24±j945.61 | 150.50 | 0.009 |
| λ5,6 | -17.59±j626.95 | 99.78 | 0.028 |
| λ7,8 | -418.26±j546.51 | 86.99 | 0.608 |
| λ9,10 | -234.86±j202.22 | 32.18 | 0.758 |
| λ11,12 | -62.38±j395.18 | 62.89 | 0.156 |
| λ13,14 | -10.36±j237.01 | 37.72 | 0.044 |
| λ15,16 | -118.5±j45.83 | 7.29 | 0.933 |
| λ17,18 | -15.12±j19.94 | 3.17 | 0.604 |
| λ19,20 | -19.25±j1.19 | 0.19 | 0.998 |
| λ21,22 | -3.9±j1.68 | 0.27 | 0.918 |
| 1 | 宋斯珩,赵书强,邵冰冰,等 .双馈风电场经柔直并网系统交互作用分析[J].太阳能学报,2021,42(4):409-416. |
| SONG Siheng, ZHAO Shuqiang, SHAO Bingbing,et al .Interaction analysis of a double-fed wind farm with a soft and direct grid-connection system[J].Journal of Solar Energy,2021,42(4):409-416. | |
| 2 | SUN K, WEN J, FANG J,et al .Impedance modeling and stability analysis of grid-connected DFIG-based wind farm with a VSC-HVDC[J].IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics,2020,8(2):1375-1390. |
| 3 | 洪潮,李鹏飞,陈雁,等 .MMC-HVDC提升交流电网频率稳定性的改进控制策略[J].南方电网技术,2019,13(10):8-14. |
| HONG Chao, LI Pengfei, CHEN Yan,et al .Improved control strategy of MMC-HVDC to improve frequency stability of AC power grid[J].Southern Power Grid Technology,2019,13(10):8-14. | |
| 4 | 萧展辉,蔡微,黄剑文,等 .MMC型多端柔性直流配电系统协同控制与故障电流抑制策略[J].电力系统保护与控制,2019,47(11):103-110. |
| XIAO Zhanhui, CAI Wei, HUANG Jianwen,et al .Cooperative control and fault current suppression strategy of MMC multi-terminal flexible DC distribution system[J].Power System Protection and Control,2019,47(11):103-110. | |
| 5 | 王一凡,赵成勇,郭春义 .双馈风电场孤岛经模块化多电平换流器直流输电并网系统小信号稳定性分析与振荡抑制方法[J].电工技术学报,2019,34(10):2116-2129. |
| WANG Yifan, ZHAO Chengyong, GUO Chunyi .Stability analysis of small signal and oscillation suppression method for grid-connected DC transmission system with modular multilevel converter in doubly-fed wind farm[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2019,34(10):2116-2129. | |
| 6 | 马宁宁,谢小荣,贺静波,等 .高比例新能源和电力电子设备电力系统的宽频振荡研究综述[J].中国电机工程学报,2020,40(15):4720-4732. |
| MA Ningning, XIE Xiaorong, HE Jingbo,et al .A review of research on broadband oscillations in power systems of high proportion new energy and power electronic Equipment[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2020,40(15):4720-4732. | |
| 7 | 魏伟,许树楷,李岩,等 .南澳多端柔性直流输电示范工程系统调试[J].南方电网技术,2015,9(1):73-77. |
| WEI Wei, XU Shukai, LI Yan,et al .System debugging of Nan’ao multi-terminal flexible HVDC demonstration project[J].Southern Power Grid Technology,2015,9(1):73-77. | |
| 8 | 赵岩,郑斌毅,贺之渊 .南汇柔性直流输电示范工程的控制方式和运行性能[J].南方电网技术,2012,6(6):6-10. |
| ZHAO Yan, ZHENG Binyi, HE Zhiyuan .Control mode and operation performance of Nanhui flexible DC transmission demonstration project[J].Southern Power Grid Technology,2012,6(6):6-10. | |
| 9 | 尹聪琦,谢小荣,刘辉,等 .柔性直流输电系统振荡现象分析与控制方法综述[J].电网技术,2018,42(4):1117-1123. |
| YIN Congqi, XIE Xiaorong, LIU Hui,et al .Review of vibration analysis and control methods for flexible DC transmission systems[J].Power Grid Technology,2018,42(4):1117-1123. | |
| 10 | 杨秀,胡浩然,李增尧,等 .风电场交直流并网次/超同步振荡交互影响[J].电力建设,2022,43(1):49-62. |
| YANG Xiu, HU Haoran, LI Zengyao,et al .Interaction effect of AC-DC grid-connected sub-synchronous oscillation of wind farm[J].Electric Power Construction,2022,43(1):49-62. | |
| 11 | 孙焜,姚伟,文劲宇 .双馈风电场经柔直并网系统次同步振荡机理及特性分析[J].中国电机工程学报,2018,38(22):6520-6533. |
| SUN Kun, YAO Wei, WEN Jinyu .Mechanism and characteristic analysis of subsynchronous oscillation in a flexible and direct grid-connected system of a doubly-fed wind farm[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2018,38(22):6520-6533. | |
| 12 | SHAO B, ZHAO S, YANG Y,et al .Sub-synchronous oscillation characteristics and analysis of direct-drive wind farms with VSC-HVDC systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy,2021,12(2):1127-1140. |
| 13 | 任必兴,孙蓉,李强,等 .经柔性直流接入的大规模直驱风电场等效建模与小干扰稳定性分析[J].电力自动化设备,2022,42(5):142-152. |
| REN Bixing, SUN Rong, LI Qiang,et al .Equivalent modeling and small disturbance stability analysis of large-scale direct drive wind farm with flexible DC access[J].Electric Power Automation Equipment,2022,42(5):142-152. | |
| 14 | 邵冰冰,赵书强,高本锋,等 .多直驱风机经VSC-HVDC并网系统场内/场网次同步振荡特性分析[J].中国电机工程学报,2020,40(12):3835-3847. |
| SHAO Bingbing, ZHAO Shuqiang, GAO Benfeng,et al .Analysis of in-field/in-field synchronous oscillation characteristics of multi-direct drive fan in VSC-HVDC grid-connected system[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2020,40(12):3835-3847. | |
| 15 | 尹睿,孙媛媛,王姗姗,等 .直驱风机经柔直送出系统多控制环节间交互机理研究[J].中国电机工程学报,2022,42(10):3627-3642. |
| YIN Rui, SUN Yuanyuan, WANG Shanshan,et al .Research on interaction mechanism of multiple control links of direct drive fan in flexible direct feed system[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2022,42(10):3627-3642. | |
| 16 | 王一凡,赵成勇,郭春义 .直驱风电场与柔直互联系统的传递函数模型及其低频振荡稳定性分析[J].中国电机工程学报,2020,40(5):1485-1498. |
| WANG Yifan, ZHAO Chengyong, GUO Chunyi .Transfer function model and low frequency oscillation stability analysis of direct drive wind farm and flexible direct interconnection system[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2020,40(5):1485-1498. | |
| 17 | 高本锋,刘毅,宋瑞华,等 .双馈风电场经LCC-HVDC送出的次同步振荡特性研究[J].中国电机工程学报,2020,40(11):3477-3489. |
| GAO Benfeng, LIU Yi, SONG Ruihua,et al .Study on sub-synchronous oscillation characteristics of doubly-fed wind farm sent by LCC-HVDC[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2020,40(11):3477-3489. | |
| 18 | 高本锋,刘毅,李蕴红,等 .直驱风电场与LCC-HVDC次同步交互作用的扰动传递路径及阻尼特性分析[J].中国电机工程学报,2021,41(5):1713-1729. |
| GAO Benfeng, LIU Yi, LI Yunhong,et al .Disturbance transfer path and damping characteristics analysis of direct drive wind farm and LCC-HVDC subsynchronous interaction[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2021,41(5):1713-1729. | |
| 19 | 郭春义,刘晓颖,吕乃航,等 .风火打捆传统直流外送系统中控制环节对轴系-控制交互模式的影响机理研究[J].中国电机工程学报,2023,44(9):3463- 3475. |
| GUO Chunyi, LIU Xiaoying, Naihang LYU,et al .Study on the influence mechanism of control link on shaft-control interaction mode in wind-fire baling traditional DC delivery system[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2023,44(9):3463-3475. | |
| 20 | 张芳,杨中尧 .混合双馈入直流输电系统控制回路间交互影响定量分析[J].电力自动化设备,2021,41(3):78-84. |
| ZHANG Fang, YANG Zhongyao .Quantitative analysis of interaction between control loops of hybrid doubly-fed HVDC transmission system[J].Electric Power Automation Equipment,2019,41(3):78-84. | |
| 21 | 朱林,田政鳞,王正宇,等 .基于相对增益矩阵的惯量响应空间耦合特征分析[J].电力建设,2022,43(9):125-131. |
| ZHU Lin, TIAN Zhenglin, WANG Zhengyu,et al .Spatial coupling characteristics analysis of inertia response based on relative gain matrix[J].Electric Power Construction,2022,43(9):125-131. | |
| 22 | 庞博,郭春义,王潇,等 .风电接入对柔性直流电网站间耦合振荡模式的影响及站间交互作用的定量评估[J].电网技术,2023,47(8):3206-3220. |
| PANG Bo, GUO Chunyi, WANG Xiao,et al .Influence of wind power access on coupling oscillation modes of flexible DC Sites and quantitative evaluation of interaction between sites[J].Power Grid Technology,2019,47(8):3206-3220. | |
| 23 | 韩平平,汪龙建,窦盛,等 .基于RGA和αβ坐标系的直驱风场内机组间谐波交互分析[J].电力系统保护与控制,2020,48(7):29-40. |
| HAN Pingping, WANG Longjian, DOU Sheng,et al .Analysis of harmonic interaction between units in direct drive wind field based on RGA and αβ coordinate system[J].Power System Protection and Control,2020,48(7):29-40. | |
| 24 | 王一凡,赵成勇 .混合型风电场经MMC-HVDC送出系统的振荡模式分析[J].电力系统保护与控制,2020,48(9):18-26. |
| WANG Yifan, ZHAO Chengyong .Analysis of oscillation mode of hybrid wind farm delivery system through MMC-HVDC[J].Power System Protection and Control,2019,48(9):18-26. | |
| 25 | LYU J, CAI X, MOLINAS M .Frequency domain stability analysis of MMC-based HVdc for wind farm integration[J].IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics,2016,4(1):141-151. |
| 26 | 倪以信,陈寿孙,张宝霖 .动态电力系统的理论和分析[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2002. |
| 27 | BRISTOL E .On a new measure of interaction for multivariable process control[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,1966,11(1):133-134. |
| [1] | FU Qiang, ZHAO Xiaohua, LI Haijian, et al. Operational Characteristics and Eco-Safe Influence of Connected Mixed Platoon in Car-Following Event [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(8): 65-75. |
| [2] | ZHENG Zhi, GUO Naisheng, YOU Zhanping. Molecular Simulation of Interaction Behavior Between Asphalt Components and Waste Wood Oil [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(12): 79-86. |
| [3] | LI Peizhen, XIAO Jiaqu, YANG Jinping, et al.. Dynamic Response of Frame Structure System Considering SSI Effect [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(9): 139-148. |
| [4] | MO Haijun, ZHAO Hang, CHENG Yu, et al. Normal Contact Stiffness Model of Fine Particle Shot Peening Gear [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 90-98. |
| [5] | Li Lin, Yu An-ling, Wu Zhi, et al. Investigation into Interaction Mechanism and Antioxidant Activity of Resveratrol and Modified Pectin [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(9): 1-10. |
| [6] | TONG Fang, LAN Fengchong, CHEN Jiqing, et al. Dynamic Response of Aortic Valve of Occupant to Blunt Thoracic Impact in Traffic Accident [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(1): 113-122,152. |
| [7] | IKA Novita Dewi, CAI Xiaoling, et al. Drug-Drug Interaction Extraction Model Combining Category Keywords with Attention Mechanism [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(1): 10-17. |
| [8] | LI Lin, WU Ming, LI Bing, et al. Study on Interaction between Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Bovine Serum Albumin [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(11): 123-130. |
| [9] | MENG Yuhuan, BAI Yunmeng, CUI Ying, et al. Coexpression Analysis of Gene Pairs with Protein-Protein Interaction in Cancers [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(11): 78-88. |
| [10] | DAI Gonglian GE Hao ZHENG Rongrong CHEN Guorong. Stress Analysis of Continuously Welded Rail of Ballastless Tracks on Simply Supported Girder Bridges with Different Spans [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(10): 81-92. |
| [11] |
LI Peizhen SHU Xin YANG Jinping .
Parametric Analysis of Structure with Additional Viscoelastic Dampers Considering Soil-Structure Dynamic Interaction
|
| [12] | XIONG Jian XIE Liping ZHANG Ting LIANG Min YUAN Erdong REN Jiaoyan. Interaction Between Memory-Enhancing Chinese Herbal Medicine and Walnut Peptides#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(11): 1-8. |
| [13] | SHEN Aiqin SONG Pan GUO Yinchuan LI Peng. Numerical Simulation Analysis of Transient Hydrodynamic Pressure on the Road Surface Based on COMSOL Multiphysics [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(11): 92-101. |
| [14] | PANG Yu-xia CAI Meng LOU Hong-ming . Preparation and Pb2+ Removal Capacity of Phosphorylated Lignin [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(6): 96-102. |
| [15] | SU Lin-wang CAI Jian LIU Pei-ge CHEN Qing-jun WEI Mu-yang RONG Liang-wan. Experimental Investigation into RC Beam Under the Action of Alternating Load in Salt-Spray Environment [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(5): 97-104. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||