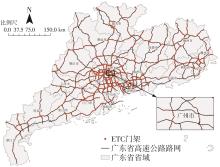
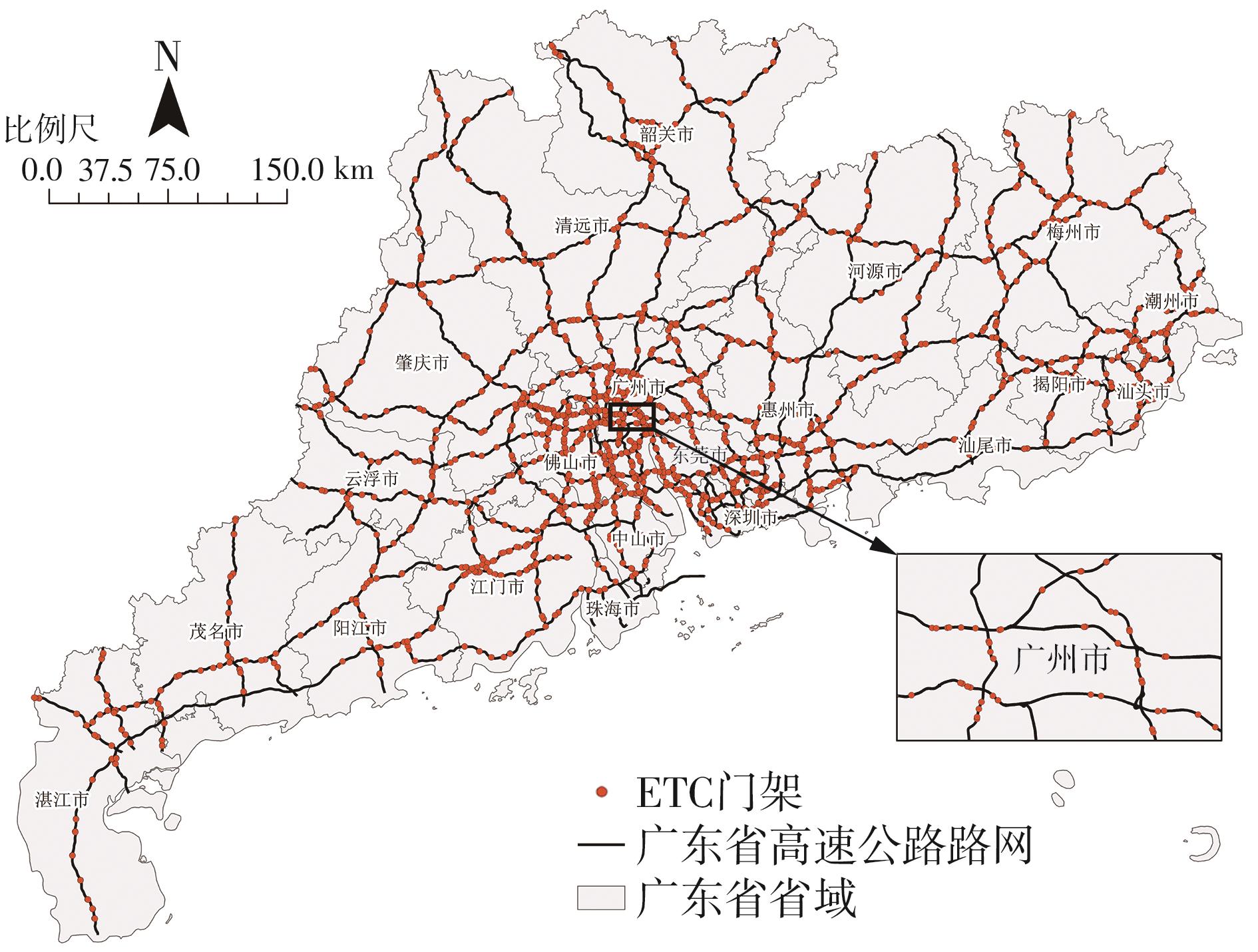
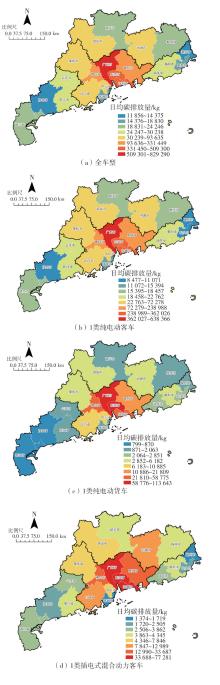
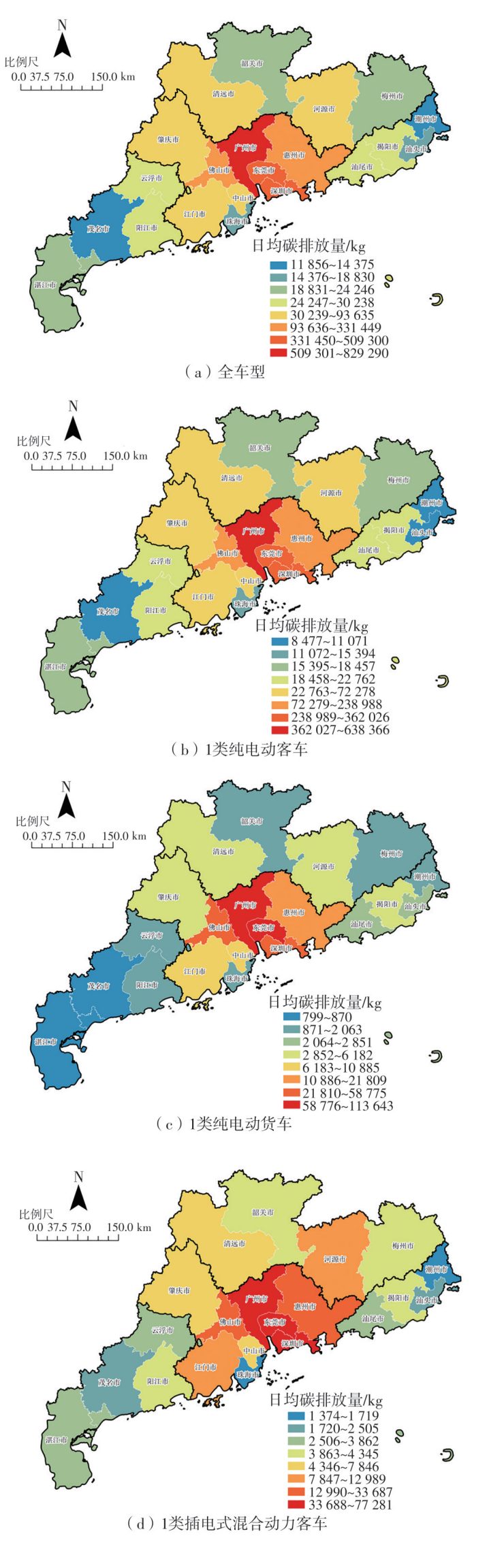
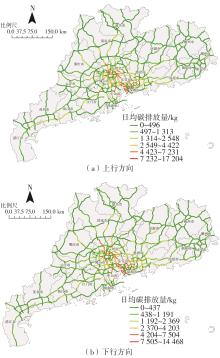
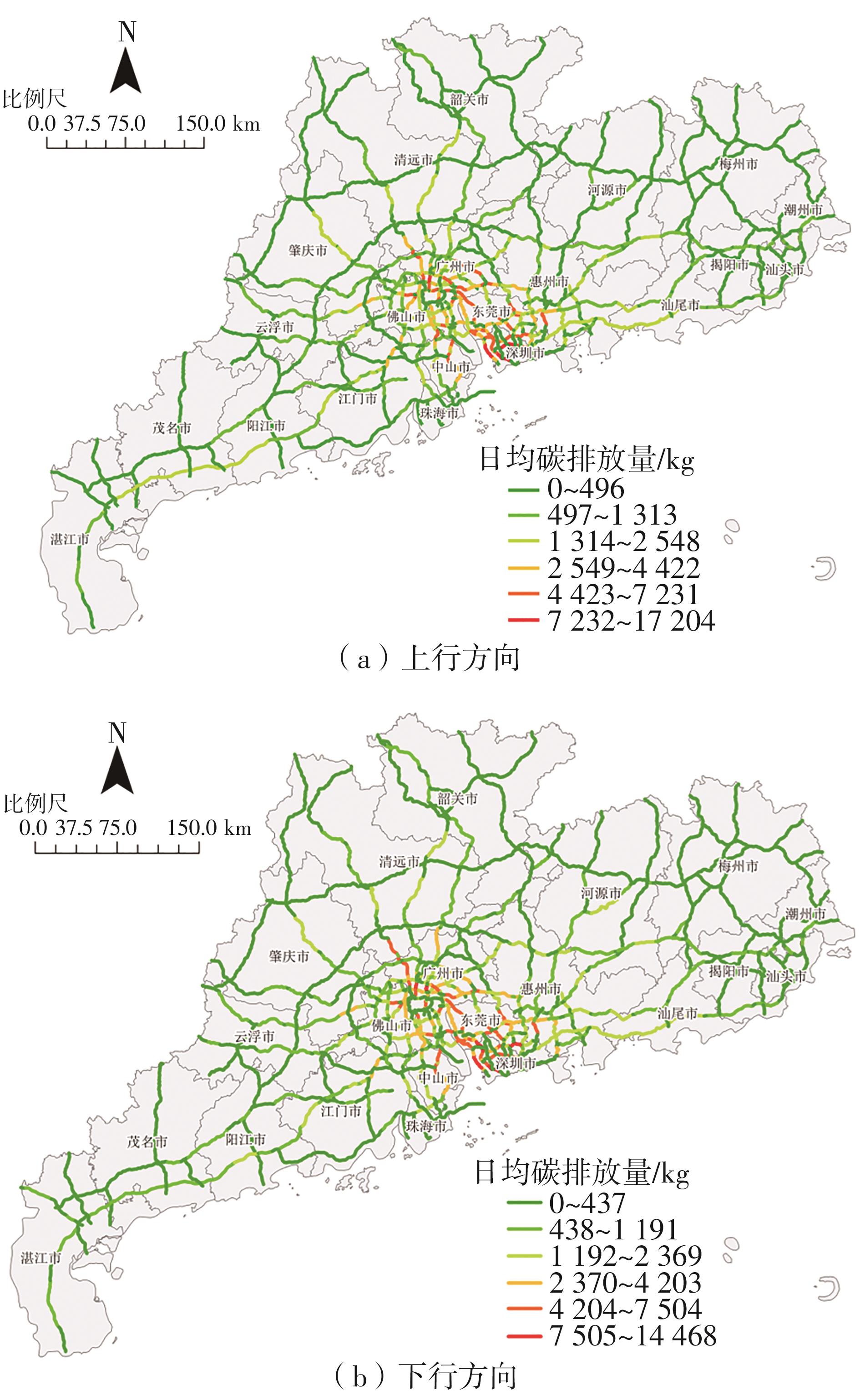
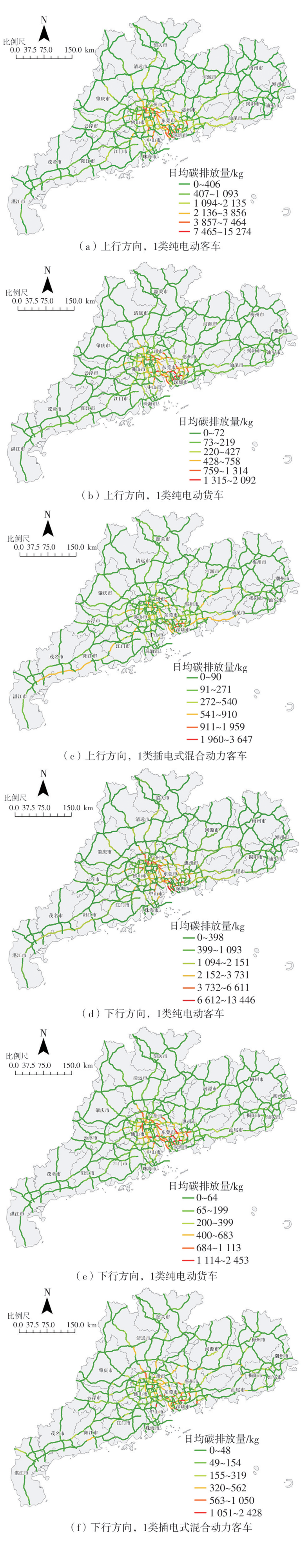
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 1-13.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230293
• Traffic & Transportation Engineering • Next Articles
Calculation and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Carbon Emissions from New Energy Vehicles on Expressways
WEN Huiying1( ), HE Ziqi1, HU Yuqing2, HUANG Junda1(
), HE Ziqi1, HU Yuqing2, HUANG Junda1( )
)
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangdong E-Serve United Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510620,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-05-04Online:2024-08-25Published:2024-03-08 -
Contact:黄俊达(1995—),男,博士,主要从事交通规划、交通仿真研究。 E-mail:cthuangjunda@mail.scut.edu.cn -
About author:温惠英(1965—),女,教授,博士生导师,主要从事交通规划、交通安全研究。E-mail:hywen@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52072131);the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2023A1515011322)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WEN Huiying, HE Ziqi, HU Yuqing, et al. Calculation and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Carbon Emissions from New Energy Vehicles on Expressways[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(8): 1-13.
share this article
Table 3
Average electricity consumption per 100 km of different types of battery electric vehicles"
1类客车 品牌编号 | 车流量/辆 | 车流量占比/% | 平均100 km电耗/(kW·h) | 100 km电耗均值/(kW·h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 814 | 24.47 | 16.00 | 15.76 |
| 2 | 15 331 | 14.53 | 16.50 | |
| 3 | 13 221 | 12.53 | 15.80 | |
| 4 | 10 598 | 10.05 | 15.10 | |
| 5 | 7 528 | 7.14 | 15.40 | |
1类货车 品牌编号 | 车流量/辆 | 车流量占比/% | 平均100 km电耗/(kW·h) | 100 km电耗均值/(kW·h) |
| 1 | 709 | 14.52 | 23.90 | 24.64 |
| 2 | 651 | 13.33 | 26.00 | |
| 3 | 531 | 10.87 | 22.10 | |
| 4 | 281 | 5.75 | 24.50 | |
| 5 | 247 | 5.06 | 26.70 |
| 1 | 赵芳敏,蔡志洲,彭令发 .公路碳评价指标体系初探[J].交通节能与环保,2021,17(6):1-4,9. |
| ZHAO Fangmin, CAI Zhizhou, PENG Lingfa .Study on highway carbon evaluation index system[J].Transport Energy Conservation & Environmental Protection,2021,17(6):1-4,9. | |
| 2 | HULSHOF D, MULDER M .Willingness to pay for CO2 emission reductions in passenger car transport[J].Environmental and Resource Economics,2020,75(4):899-929. |
| 3 | YANG T, XING C, LI X .Evaluation and analysis of new-energy vehicle industry policies in the context of technical innovation in China[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,281:125126/1-18. |
| 4 | 王芳,邱彬 .2023年新能源汽车发展形势研判[J].智能网联汽车,2023(2):64-68. |
| WANG Fang, QIU Bin .Analysis of the development situation of new energy vehicles in 2023[J].Intelligent Connected Vehicles,2023(2):64-68. | |
| 5 | SELENA M S, VISWANATH A S, BASIL S,et al .Well-to-wheel analysis of greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption for electric vehicles:a comparative study in Oceania[J].Energy Policy,2021,158:112552/1-14. |
| 6 | 严军华,王舒笑,袁浩然,等 .电动汽车能耗与气体排放分析及环境影响评价[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(6):137-144. |
| YAN Junhua, WANG Shuxiao, YUAN Haoran,et al .Life cycle assessment of energy consumption with emi-ssion and environmental impact of electric vehicle[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2018,46(6):137-144. | |
| 7 | YANG Z, WANG B, JIAO K .Life cycle assessment of fuel cell,electric and internal combustion engine vehicles under different fuel scenarios and driving mileages in China[J].Energy,2020,198:117365/1-9. |
| 8 | 奚悦,马同涛,刘明光,等 .面向汽车电动化替代的公路交通碳排放影响因素分析[J].现代电力,2023,40(6):985-994. |
| XI Yue, MA Tongtao, LIU Mingguang,et al .Analysis on influencing factors of road traffic carbon emission oriented to vehicle electrification substitution[J].Modern Electric Power,2023,40(6):985-994. | |
| 9 | 付佩,兰利波,陈颖,等 .面向2035的节能与新能源汽车全生命周期碳排放预测评价[J].环境科学,2023,44(4):2365-2374. |
| FU Pei, LAN Li-bo, CHEN Ying,et al .Life cycle prediction assessment of energy saving and new energy vehicles for 2035[J].Environmental Science,2023,44(4):2365-2374. | |
| 10 | YU A, WEI Y, CHEN W,et al .Life cycle environmental impacts and carbon emissions:a case study of electric and gasoline vehicles in China[J].Transportation Research Part D,2018,65:409-420. |
| 11 | 詹炜鹏,王震坡,邓钧君,等 .基于大数据的电动汽车行驶阶段碳减排影响因素分析[J].汽车工程,2022,44(10):1581-1590. |
| ZHAN Weipeng, WANG Zhenpo, DENG Junjun,et al .Analysis of influencing factors of carbon emission reduction in the driving stage of electric vehicles based on big data[J].Automotive Engineering,2022,44(10):1581-1590. | |
| 12 | 广东省统计局,国家统计局广东调查总队 .2022年广东省国民经济和社会发展统计公报[N].南方日报,2023-03-31(A6). |
| 13 | HELMERS E, MARX P .Electric cars:technical characteristics and environmental impacts[J].Environmental Sciences Europe,2012,24(1):1-15. |
| 14 | 中国电力企业联合会 .中国电力行业年度发展报告2021[EB/OL].(2021-07-09)[2023-11-15].. |
| 15 | YAN X, SUN S .Impact of electric vehicle development on China’s energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions[J].Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy,2021,23:2909-2925. |
| 16 | 综合能耗计算通则: [S]. |
| 17 | 车用汽油:)[S]. |
| 18 | 车用柴油:)[S]. |
| [1] | HE Qingling, PEI Yulong, DONG Chuntong, et al. Classification and Identification of Risky Driving Behavior Based on Hybrid Strategy Improved ASO-LSSVM [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(9): 131-141. |
| [2] | SU Yuejiang, WEN Huiying, YUAN Minxian, WU Dexin, ZHOU Lulu, QI Weiwei. Travel Carbon Emission Prediction Model Based on Resident Attribute Data [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(8): 23-33. |
| [3] | WANG Jiangfeng, LI Xiudong, SONG Zhifan, et al. Differentiated Highway Toll Pricing Model Considering Carbon Emission Reduction Benefits [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(8): 14-22. |
| [4] | GAO Longkai, ZHAO Xiaohua, OU Jushang, et al. Optimization Design of the Stereoscopic Compound Expressway Sign System Based on Unity3D [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 20-30. |
| [5] | LIN Peiqun, ZHANG Yang, LUO Zhiqing, et al. Precise Calculation Method of Traffic Carbon Emission in Expressway Segment Integrating Multi-Source Data [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 100-108. |
| [6] | WANG Linhong, LI Hongtao, LI Ruonan. Design of Speed Limit at Expressway in Rainy Day Considering Drivers’ Visual Search Ability [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(6): 20-29. |
| [7] | WU Jiaorong, HUANG Zhengwen, DENG Yongqi . Development Law of Traffic Network Density in the Spatial Structure of Metropolitan Area Hierarchy [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(2): 111-121. |
| [8] | JIANG Yu, WANG Yasha, XUE Qingwen, et al. Research on Space-Time Taxiing Optimization of Aircraft Based on Carbon Emission [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 152-159. |
| [9] | HU Xinghua, CHEN Xinghui, WANG Ran, et al. Optimization Model of Bus Priority Control Considering Carbon Emissions with Stochastic Characteristics [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 160-170. |
| [10] | LIN Xukun, ZHANG Yang, LUO Zhiqing, et al. Study on Measuring Method of Vehicle Carbon Emission in Expressway Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 22-28. |
| [11] | ZHOU Xuan, WANG Xinyao, YAN Junwei, et al. Anomaly Detection of Complex Building Energy Consumption System Based on Machine Learning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 144-154. |
| [12] | WEN Huiying, LI Qiuling, ZHAO Sheng. Research on Spatiotemporal Characteristic and Risk of Lane-Changing Behaviors of Large Vehicles in Expressway Merging Area [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 11-21. |
| [13] | JI Tianyao WANG Tingshao. Building Energy Consumption Prediction Based on Word Embedding and Convolutional Neural Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(6): 40-48. |
| [14] | XIE Jiehui, NIU Fujun, PENG Zhiyu, et al. Deformation Law and Settlement Prediction Application of Soft Soil Subgrade in Coastal Expressway [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(4): 97-107. |
| [15] | ZHOU Xuan LEI Shangpeng YAN Junwei. Multi-Step Forecasting for Lighting and Equipment Energy Consumption in Office Building Based on Deep Learning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(10): 19-29. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||