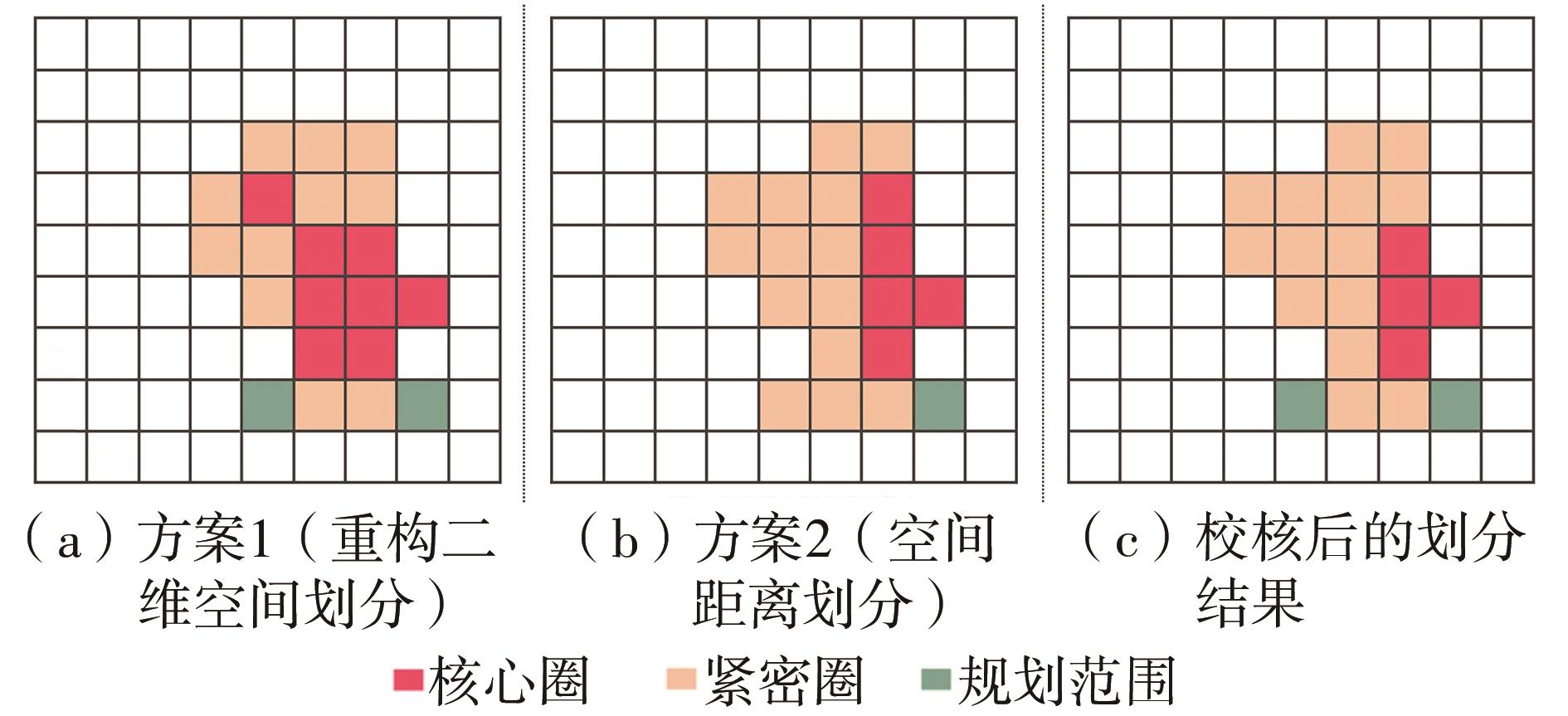
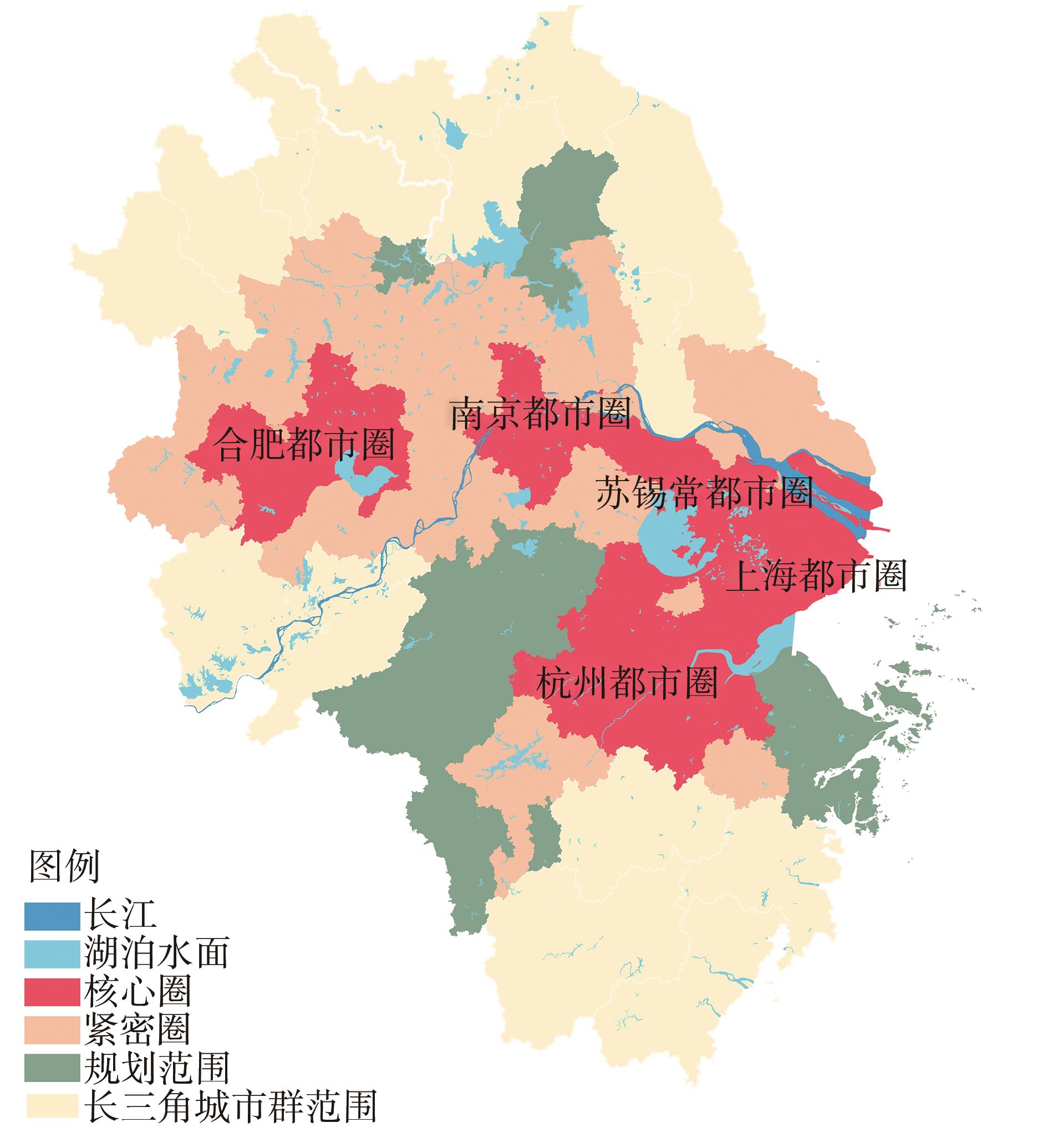
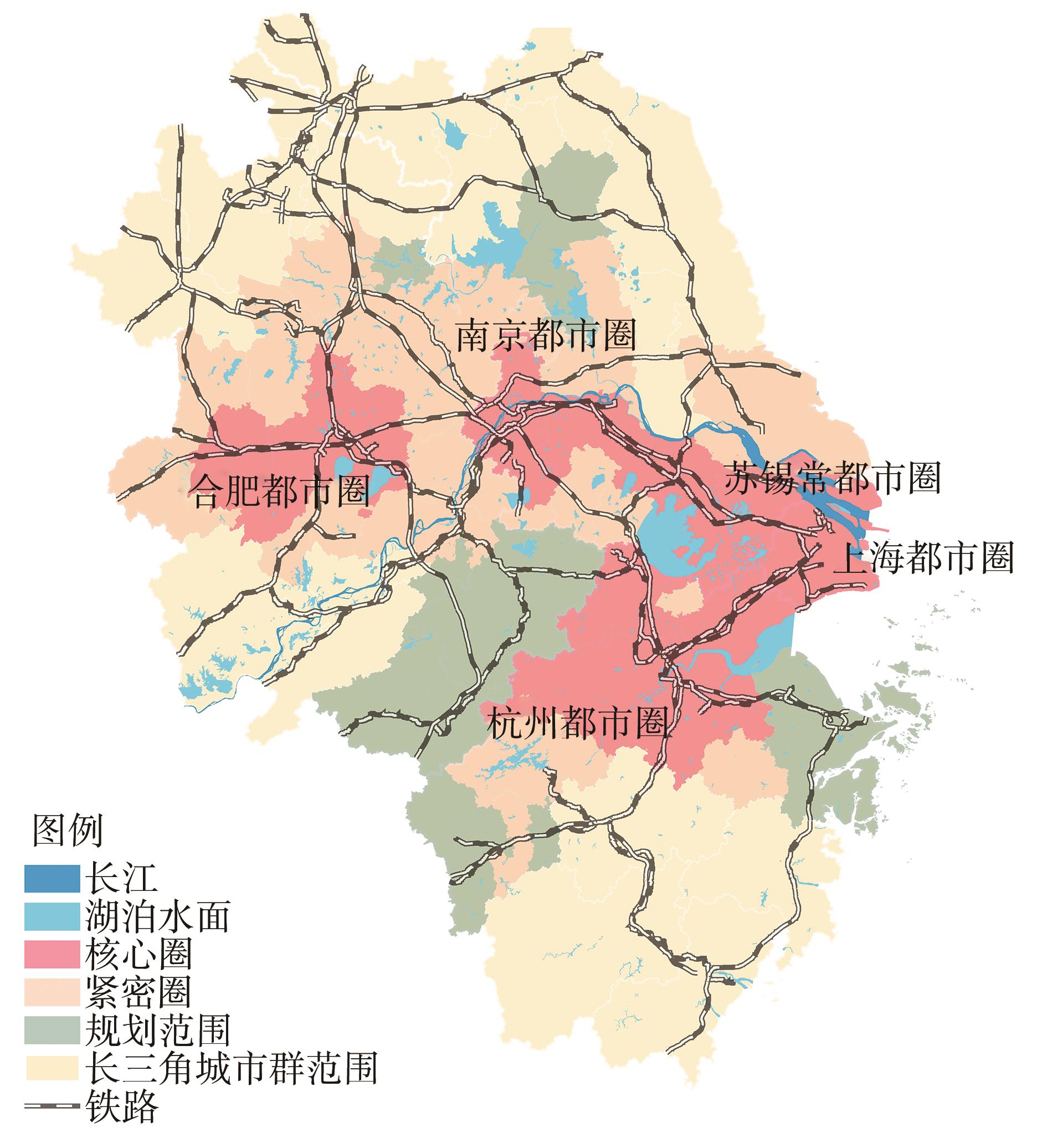
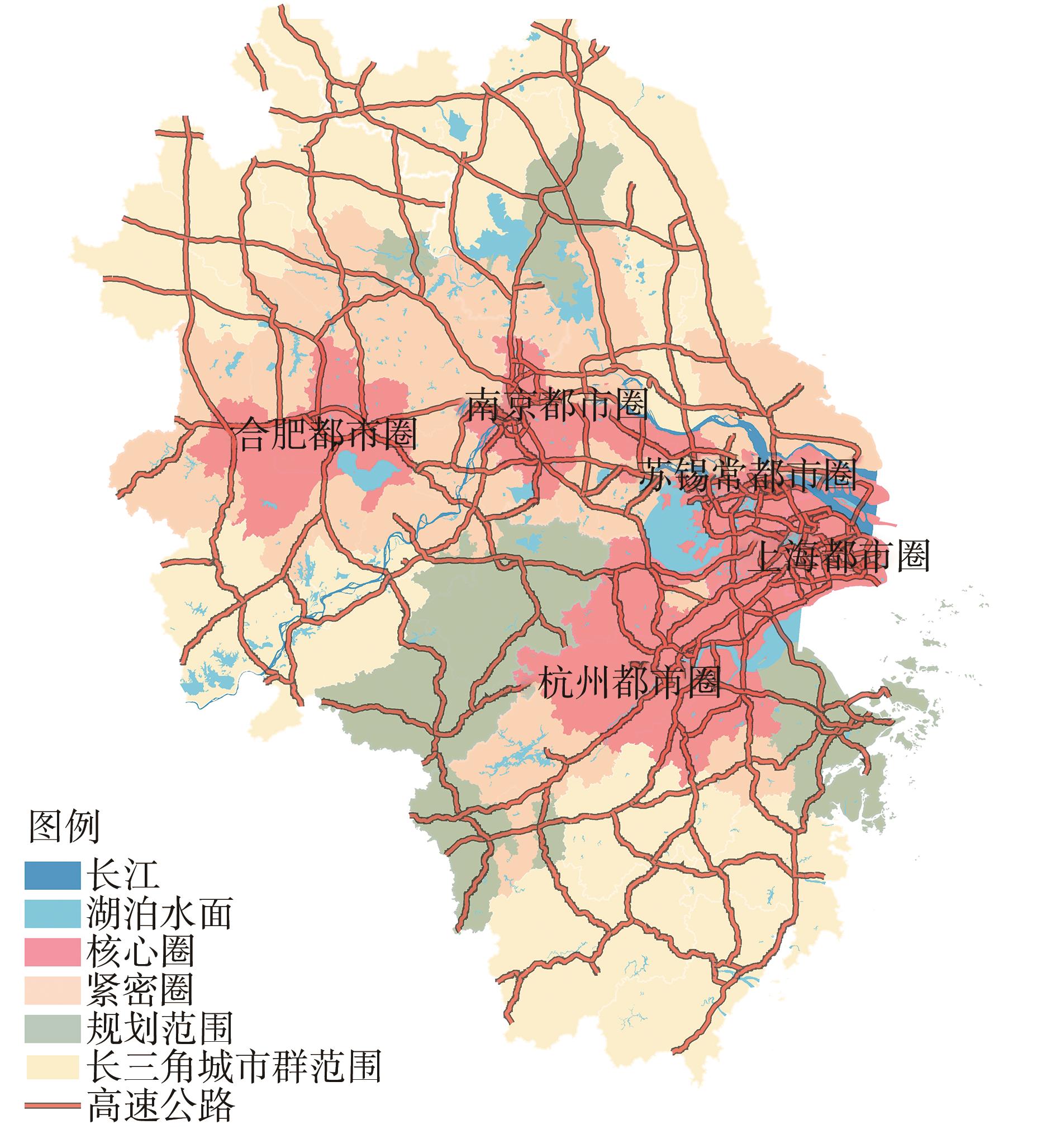
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 111-121.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220159
Special Issue: 2023年交通运输工程
• Traffic & Transportation Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Development Law of Traffic Network Density in the Spatial Structure of Metropolitan Area Hierarchy
WU Jiaorong1,2 HUANG Zhengwen1 DENG Yongqi2
- 1.Urban Mobility Institute,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering of the Ministry of Education,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
-
Received:2022-03-29Online:2023-02-25Published:2023-02-01 -
Contact:吴娇蓉(1973-),女,教授,工学博士,博士生导师,主要从事轨道交通与空间规划研究。 E-mail:wjrshtj@163.com -
About author:吴娇蓉(1973-),女,教授,工学博士,博士生导师,主要从事轨道交通与空间规划研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52072263)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WU Jiaorong, HUANG Zhengwen, DENG Yongqi . Development Law of Traffic Network Density in the Spatial Structure of Metropolitan Area Hierarchy[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(2): 111-121.
share this article
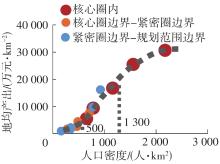
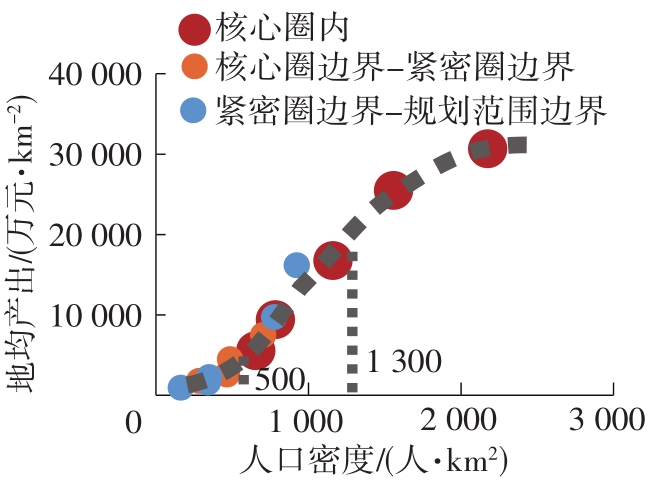
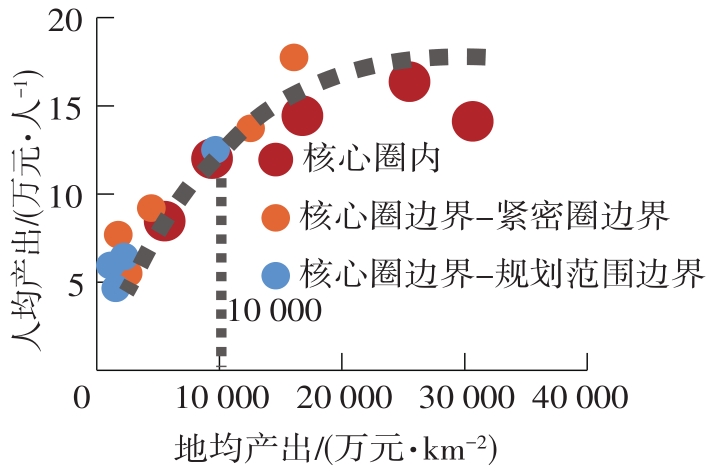
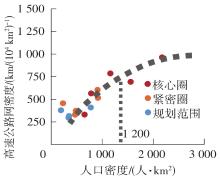
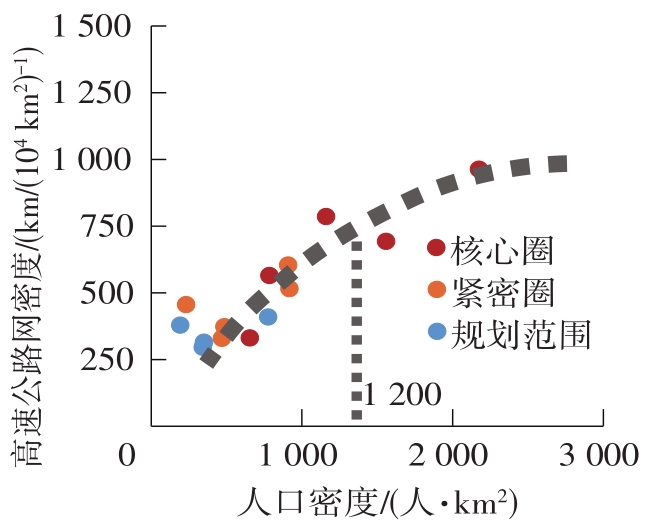
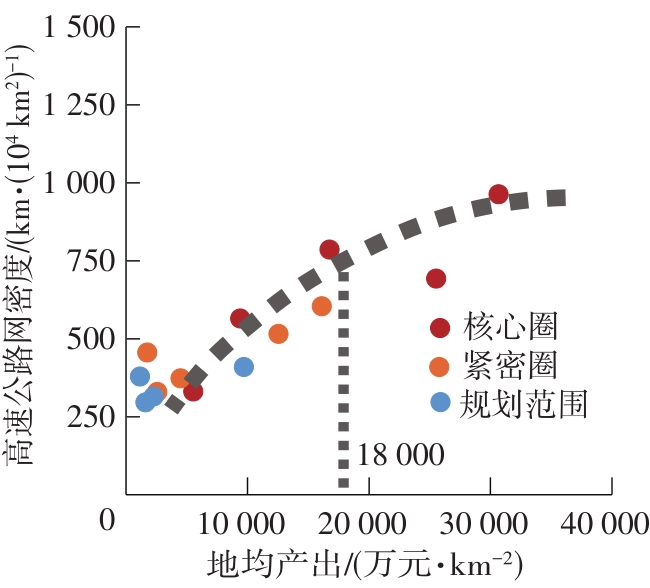
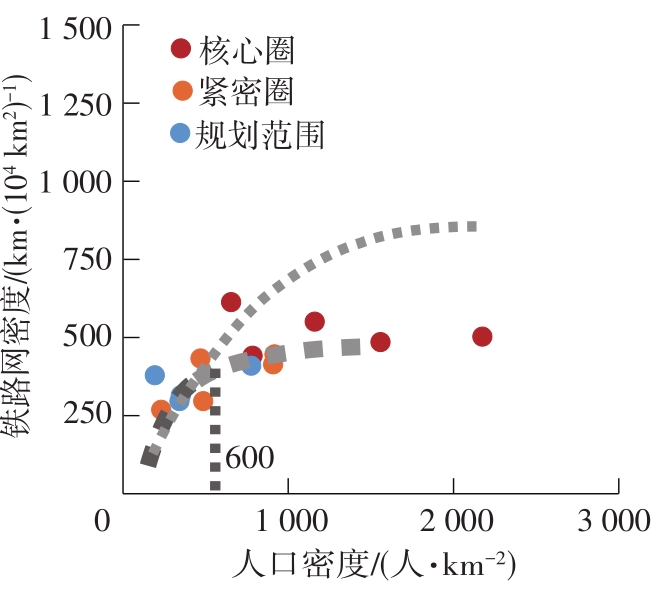
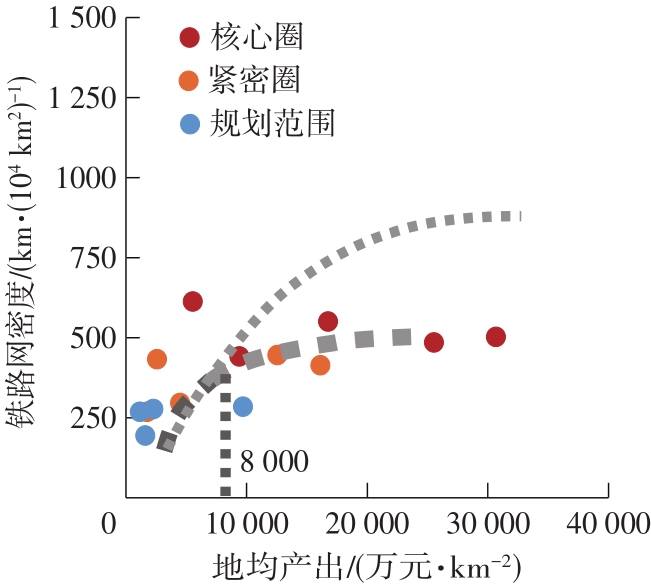
Table 4
Socioeconomic and traffic network indicators in each circling-layering metropolitan area"
| 名称 | 圈层 | 人口密度 | 人均产出 | 地均产出 | 铁路网密度 | 高速公路网密度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上海 | 核心圈 | 2 175(1) | 141 058(4) | 30 678(1) | 503 | 963 |
| 核心圈边界-紧密圈边界 | 916(4) | 137 127(5) | 12 554(5) | 446 | 516 | |
| 紧密圈边界-规划范围边界 | 777(7) | 124 800(6) | 9 693(6) | 285 | 410 | |
| 南京 | 核心圈 | 1 161(3) | 144 387(3) | 16 760(3) | 551 | 786 |
| 核心圈边界-紧密圈边界 | 486(9) | 91 893(8) | 4 470(9) | 297 | 374 | |
| 紧密圈边界-规划范围边界 | 350(11) | 64 385(11) | 2 254(11) | 277 | 315 | |
| 杭州 | 核心圈 | 784(6) | 120 042(7) | 9 410(7) | 442 | 566 |
| 核心圈边界-紧密圈边界 | 230(13) | 76 669(10) | 1 760(12) | 269 | 456 | |
| 紧密圈边界-规划范围边界 | 193(14) | 59 279(12) | 1 146(14) | 268 | 379 | |
| 合肥 | 核心圈 | 655(8) | 84 497(9) | 5 534(8) | 614 | 331 |
| 核心圈边界-紧密圈边界 | 467(10) | 54 786(13) | 2 560(10) | 433 | 330 | |
| 紧密圈边界-规划范围边界 | 341(12) | 46 290(14) | 1 578(13) | 194 | 296 | |
| 苏锡常 | 核心圈 | 1 559(2) | 163 661(2) | 25 513(2) | 503 | 963 |
| 核心圈边界-紧密圈边界 | 908(5) | 177 372(1) | 16 110(4) | 446 | 516 |
| 1 | 汪光焘,叶青,李芬,等 .培育现代化都市圈的若干思考[J].城市规划学刊,2019,67(5):14-23. |
| WANG Guang-tao, YE Qing, LI Fen,et al .Thoughts on cultivating modern metropolitan area[J].Urban Planning Forum,2019,67(5):14-23. | |
| 2 | 余慧敏,岳洋,曹卫东 .快速交通对我国区域可达性及经济空间关联的影响[J].地理与地理信息科学,2020,36(5):21-28. |
| YU Hui-min, YUE Yang, CAO Wei-dong .Impact of rapid traffic on China’s regional accessibility and economic spatial correlation[J].Geography and Geo-Information Science,2020,36(5):21-28. | |
| 3 | 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会,中华人民共和国交通运输部 .长江三角洲地区交通运输更高质量一体化发展规划[EB/OL],[2020-4-2].. |
| 4 | 马燕坤,肖金成 .都市区、都市圈与城市群的概念界定及其比较分析[J].经济与管理,2020,34(1):18-26. |
| MA Yan-kun,XIAO Jin-cheng,Definition and com- parative analysis of metropolitan areas,metropolitan circles and urban aggllomerations[J].Economy and Management,2020,34(1):18-26. | |
| 5 | 胡明远,龚璞,陈怀锦,等 .“十四五”时期我国城市群高质量发展的关键:培育现代化都市圈[J].行政管理改革,2020,136(12): 20-30. |
| HU Ming-yuan, GONG Pu, CHEN Huai-jin,et al .The key to high-quality development of China’s city clusters in the“14th Five-Year Plan”period:building the modem metropolitan areas[J].Administration Reform,2020,136(12):20-30. | |
| 6 | 郑德高,朱郁郁,陈阳,等 .上海大都市圈的圈层结构与功能网络研究[J].城市规划学刊,2017,65(S2):63-71. |
| ZHENG De-gao, ZHU Yu-yu, CHEN Yang,et al .Structure and functional network of shanghai metropolitan [J].Urban Planning Forum,2017,65(S2):63-71. | |
| 7 | 罗守贵,金芙蓉,黄融 .上海都市圈城市间经济流测度[J].经济地理,2010,30(1):80-85. |
| LUO Shou-gui, JIN Fu-rong, HUANG Rong .The measurement of economic flow of Shanghai metropolitan regions [J].Economic Geography,2010,30(1):80-85. | |
| 8 | 甄茂成,党安荣,阚长城 .基于大数据与网络分析的长三角城市群识别研究[J].上海城市规划,2019,29(6):16-24. |
| ZHEN Mao-cheng, DANG An-rong, KAN Chang-cheng .Study on the identification of urban agglomerations in the Yangtze river delta based on big data and network analysis[J].Shanghai Urban Planning Review,2019,29(6):16-24. | |
| 9 | 李俊峰,焦华富 .江淮城市群空间联系及整合模式 [J].地理研究,2010,29(3):535-544. |
| LI Jun-Feng, JIAO Hua-fu .Research on spatial combination and integrated patterns of Jianghuai urban agglomeration[J].Geographical Research,2010,29(3):535-544. | |
| 10 | 李治,连玉君,李培,等 .“圈层”结构、时空差异与能源强度——以十大城市群为例[J].城市发展研究,2015,22(1):56-65. |
| LI Zhi, LIAN Yu-jun, LI Pei,et al .Circling-layering economy,temporal and spatial differences and energy intensity-evidence from urban agglomerations(in Chinese)[J].Urban Development Studies,2015,22(1):56-65.. | |
| 11 | 张磊 .都市圈空间结构演变的制度逻辑与启示:以东京都市圈为例[J].城市规划学刊,2019,67(1):80-87. |
| ZHANG Lei .Institutional perspective on the change of metropolitan spatial structure and its implications:a case study of the Tokyo metropolitan area[J].Urban Planning Forum,2019,67(1):80-87. | |
| 12 | 周一星 .关于明确我国城镇概念和城镇人口统计口径的建议[J].城市规划,1986(3):10-15. |
| ZHOU Yi-xing,Suggestions on clarifying the concept of China’s towns and urban population statistics[J].City Planning Review,1986(3):10-15. | |
| 13 | 钮心毅,李凯克 .紧密一日交流圈视角下上海都市圈的跨城功能联系[J].上海城市规划,2019,29(3):16-22. |
| NIU Xin-yi, LI Kai-ke .Inter-city functional linkages in Shanghai metropolitan region from the perspective of close daily communication area[J].Shanghai Urban Planning Review,2019,29(3):16-22. | |
| 14 | 高鑫,修春亮,魏冶 .城市地理学的“流空间”视角及其中国化研究[J].人文地理,2012,27(4):32-36,160. |
| GAO Xin, XIU Chun-liang, WEI Ye .Study on the sinicization of“space of flows”basing on the visual angle of urban geography[J].Human Geography,2012,27(4):32-36,160. | |
| 15 | 吴康,方创琳,赵渺希 .中国城市网络的空间组织及其复杂性结构特征[J].地理研究,2015,34(4):711-728. |
| WU Kang, FANG Chuang-lin, ZHAO Miao-xi .The spatial organization and structure complexity of Chinese intercity networks[J].Geographical Research,2015,34(4):711-728. | |
| 16 | 栾强,罗守贵,郭兵 .都市圈中心城市经济辐射力的分形测度及影响因素——基于北京、上海、广州的实证研究[J].地域研究与开发,2016(4):58-62. |
| LUAN Qiang, LUO Shou-gui, GUO Bing .Evaluating the economic radiation power of the central city in the metropolitan area based on the fractal model and its influencing factors analysis:cases study of Beijing,Shanghai and Guangzhou[J].Areal Research and Development,2016(4):58-62. | |
| 17 | 吴康,方创琳,赵渺希,等 .京津城际高速铁路影响下的跨城流动空间特征[J].地理学报,2013,68(2):159-174. |
| WU Kang, FANG Chuang-lin, ZHAO Miao-xi,et al .The intercity space of flow influenced by high-speed rail:A case study for the rail transit passenger behavior between Beijing and Tianjin[J].Acta Geographica Sinica,2013,68(2):159-174. | |
| 18 | 刘冰,许劼,张伊娜 .基于城际铁路的城市群空间网络重构——以沪宁,沪杭走廊为例[J].城市规划学刊,2020,68(2):40-48. |
| LIU Bing, XU Jie, ZHANG Yi-na .The spatial network reconstruction of mega-region based on intercity high-speed-rail——the case study of Hu-Ning and Hu-Hang Corridor[J].Urban Planning Forum,2020,68(2):40-48. | |
| 19 | 龚朴一,杨家文 .基于微博大数据的中国城市群空间结构研究[J].城市发展研究,2020,27(6):1-8. |
| GONG Pu-yi, YANG Jia-wen .Spatial structure study of urban agglomerations in China based on weibo big data[J].Urban Development Studies,2020,27(6):1-8. | |
| 20 | 韩童茜,王立梅,许鑫 .长三角城市群科研合作网络演化研究——基于SCIE和SSCI论文的实证分析[J].情报理论与实践,2020,43(10):151-156. |
| HAN Tong-qian, WANG Li-mei, XU Xin .Evolution of scientific research cooperation network in the Yangtze river delta city group:empirical analysis based on SCIE and SSCI papers[J].Information Studies: Theory & Application,2020,43(10):151-156. | |
| 21 | 赵鹏军,胡昊宇,海晓东,等 .基于手机信令数据的城市群地区都市圈空间范围多维识别——以京津冀为例[J].城市发展研究,2019,6(9):2,75-85. |
| ZHAO Peng-jun, HU Hao-yu, Xiao-dong HAI,et al .Identifying metropolitan edge in city clusters region using mobile phone data:a case study of Jing-Jin-Ji[J].Urban Development Studies,2019,6(9):2,75-85. | |
| 22 | 杨勇,高汝熹,罗守贵 .都市圈中心城市及其经济势能[J].安徽农业科学,2007,35(13):4062-4063. |
| YANG Yong, GAO Ru-xi, LUO Shou-gui .Central cities and their economic potential of metropolitan areas[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2007,35(13):4062-4063. | |
| 23 | 李振波 .宁波都市圈空间范围界定及经济联系比较研究[D].宁波:宁波大学,2017. |
| 24 | 张小东,韩昊英,唐拥军,等 .基于百度迁徙数据的中国城市网络结构特征研究[J].地球信息科学学报,2021,23(10):1798-1808. |
| ZHANG Xiao-dong, HAN Hao-ying, TANG Yong-jun,et al .Research on the characteristics of urban network structure in China based on baidu migration data[J].Journal of Geo-information Science,2021,23(10):1798-1808. | |
| 25 | HOLLAND S M .Non-metric multidimensional scaling (mds)[EB/OL].[2008-5-31].. |
| 26 | 王钊,杨山,龚富华,等 .基于城市流空间的城市群变形结构识别——以长江三角洲城市群为例[J].地理科学,2017,37(9):52-59. |
| WANG Zhao, YANG Shan, GONG Fu-hua,et al .Identification of urban agglomerations deformation structure based on urban-flow space:a case study of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration[J].Scientia Geographica Sinica,2017,37(9):52-59. | |
| 27 | 燕霞 .基于多维标度技术的中国地区社会经济发展分析[D].广州:华南理工大学,2010. |
| 28 | 路青,蔡震,吴昊天 .中国都市圈全景扫描及其发展规律研判[J].规划师,2021,37(10):5-11. |
| LU Qing, CAI Zhen, WU Hao-tian,et al .A study on the spectrum and development law of metropolitan areas in China[J].Plannems,2021,37(10):5-11. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||