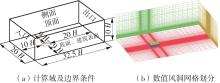
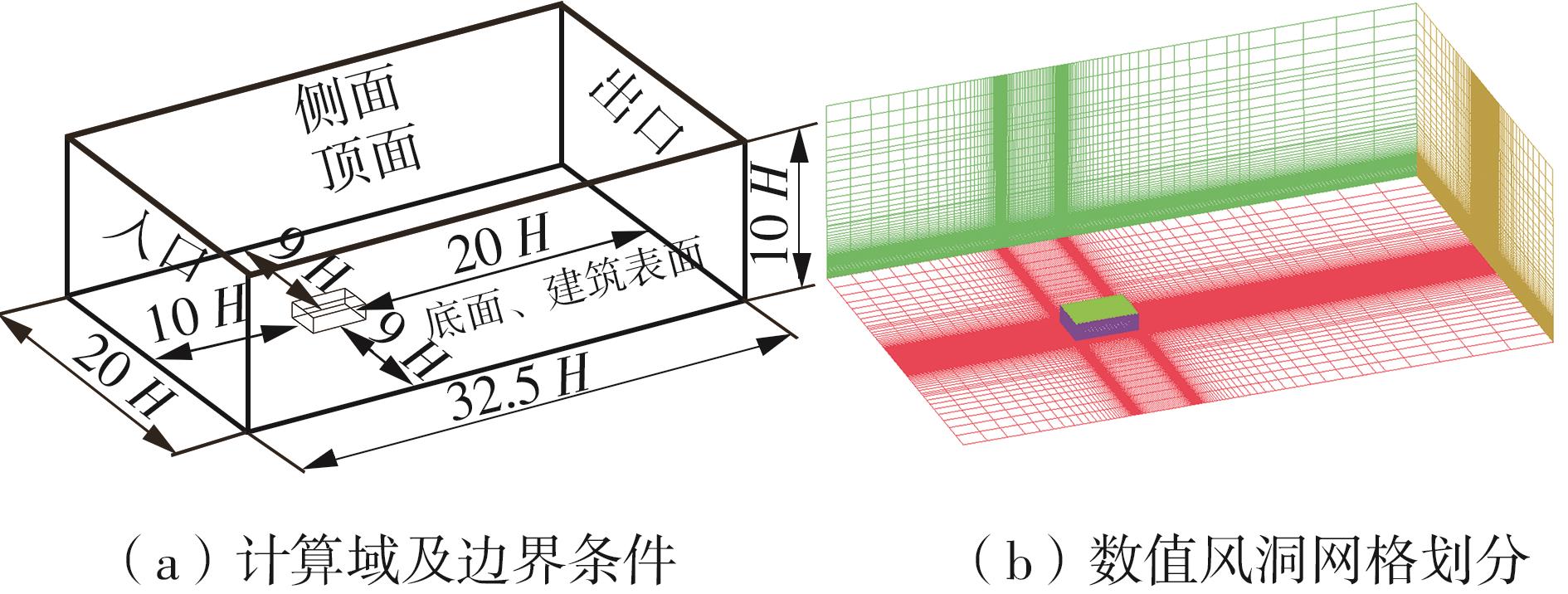
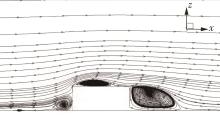
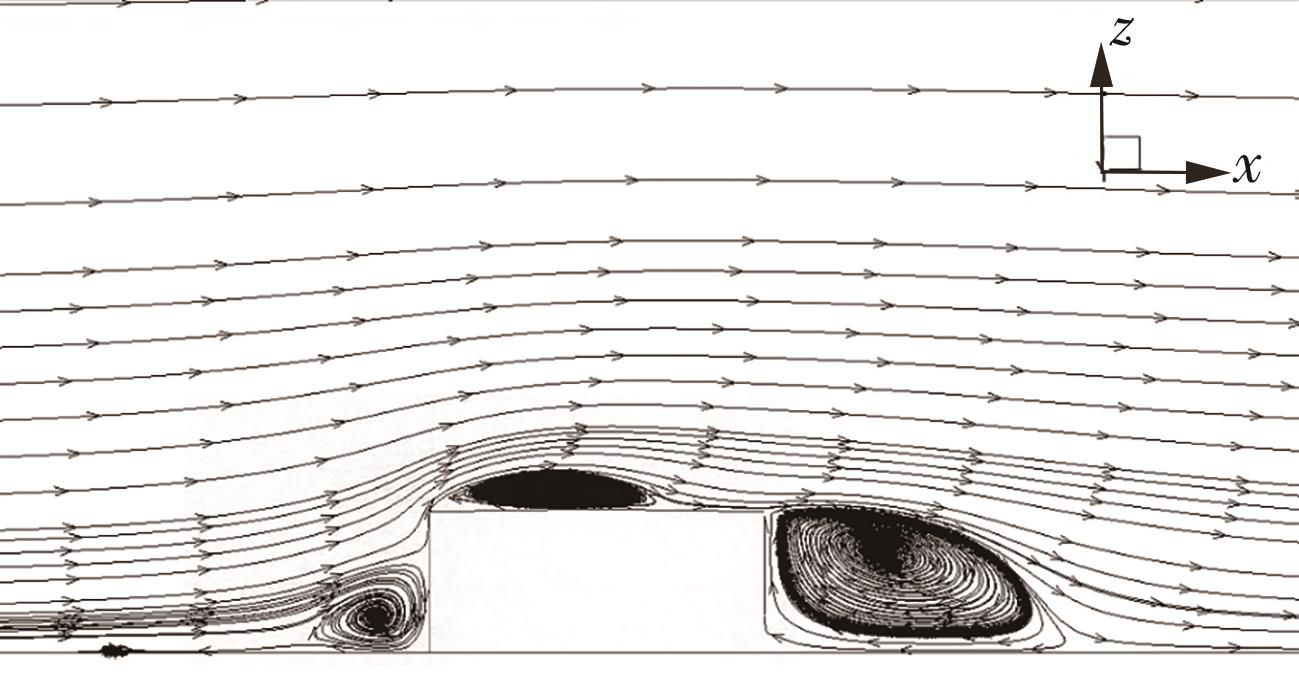
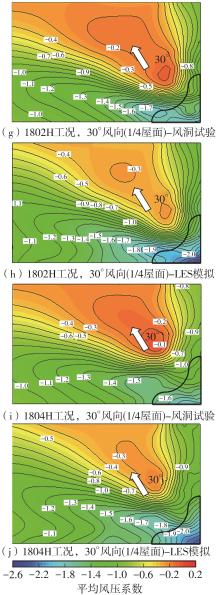
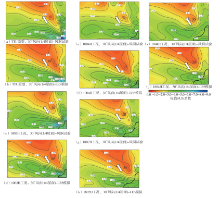
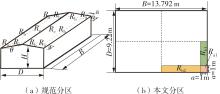
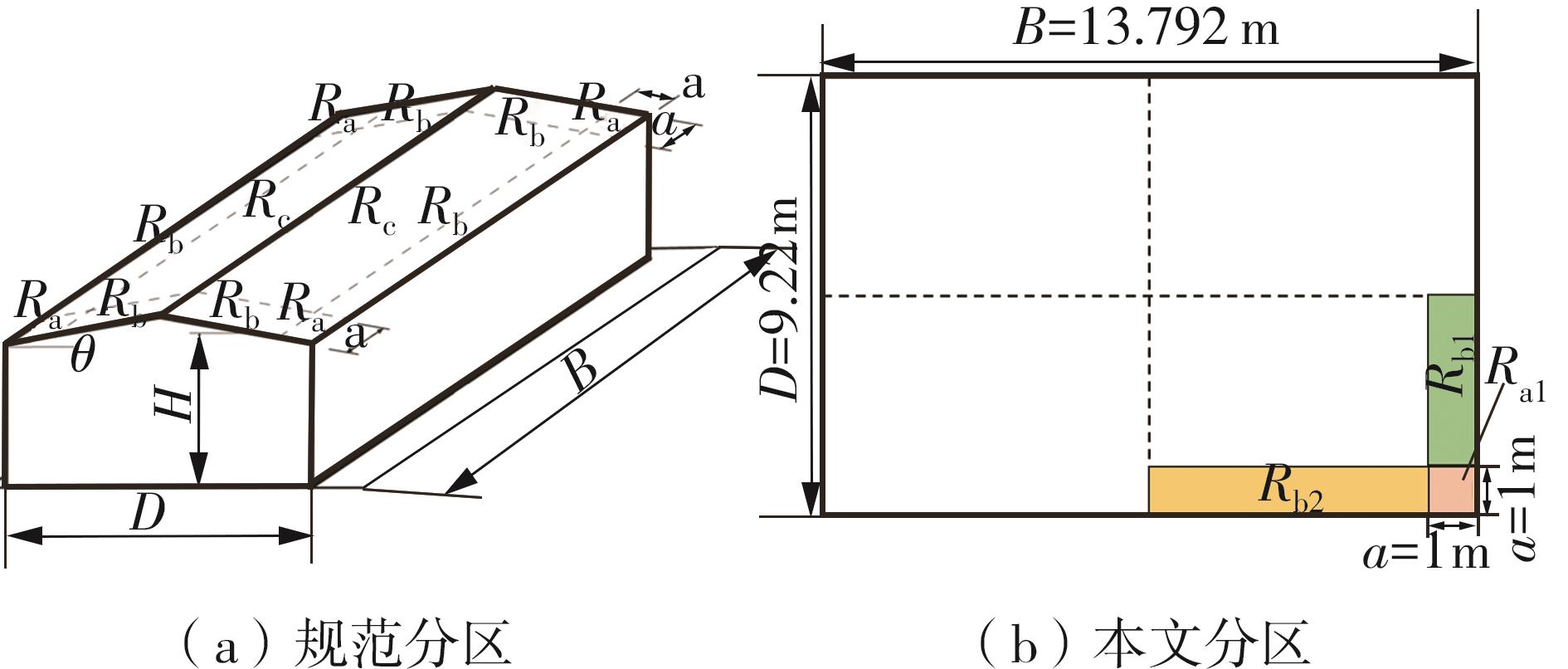
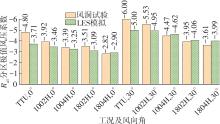
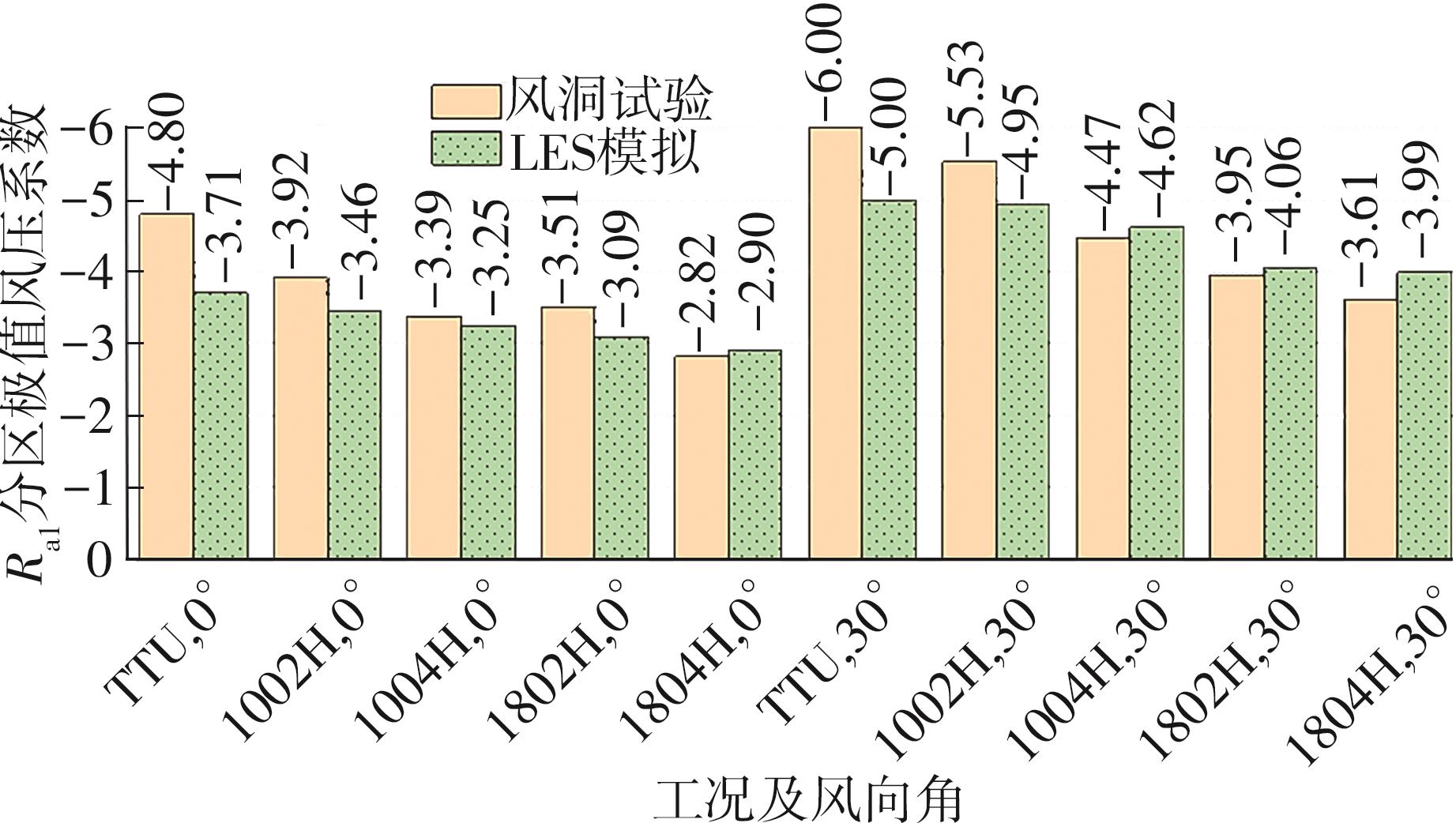
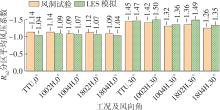
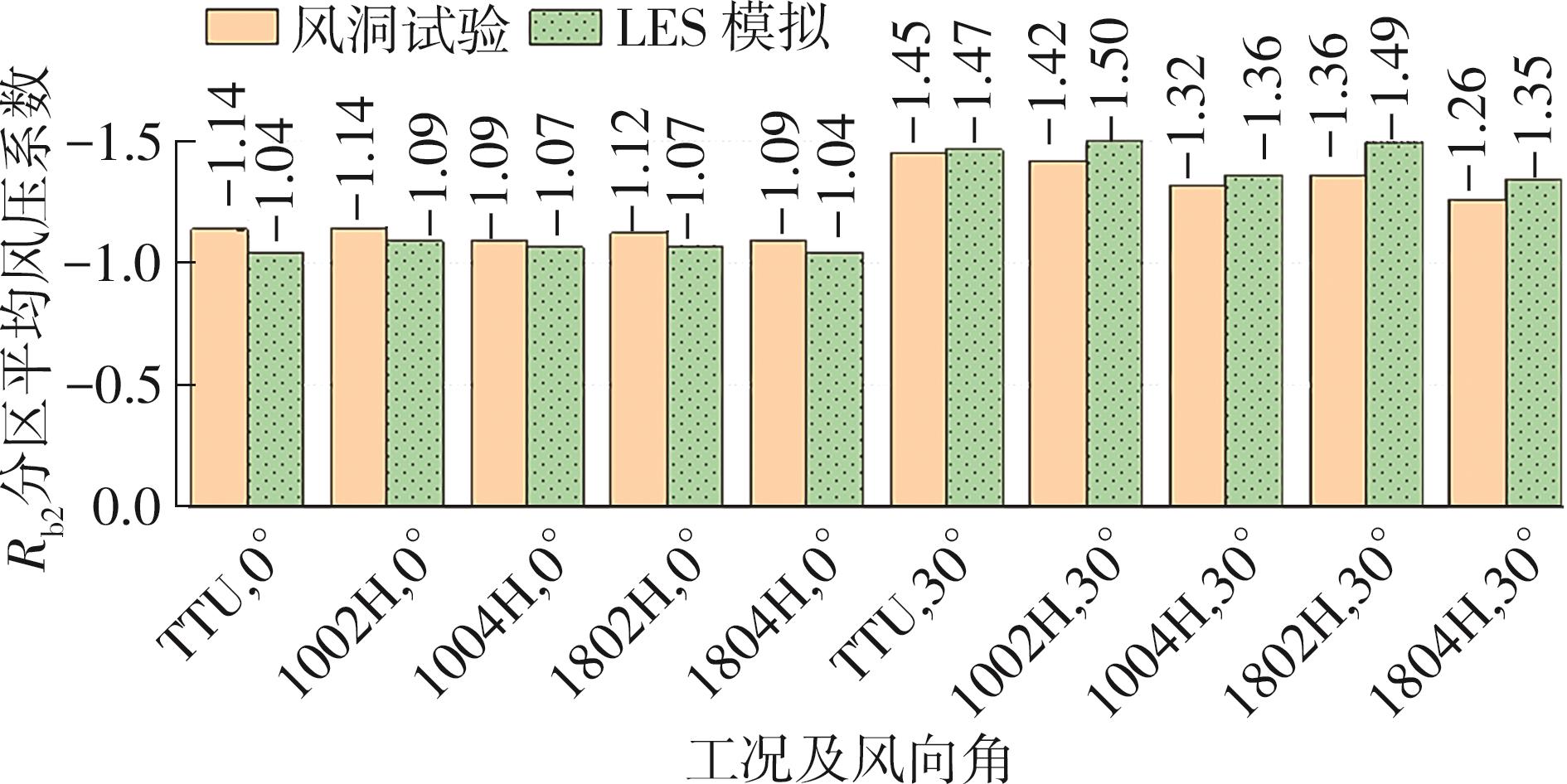
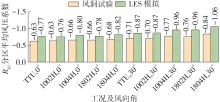
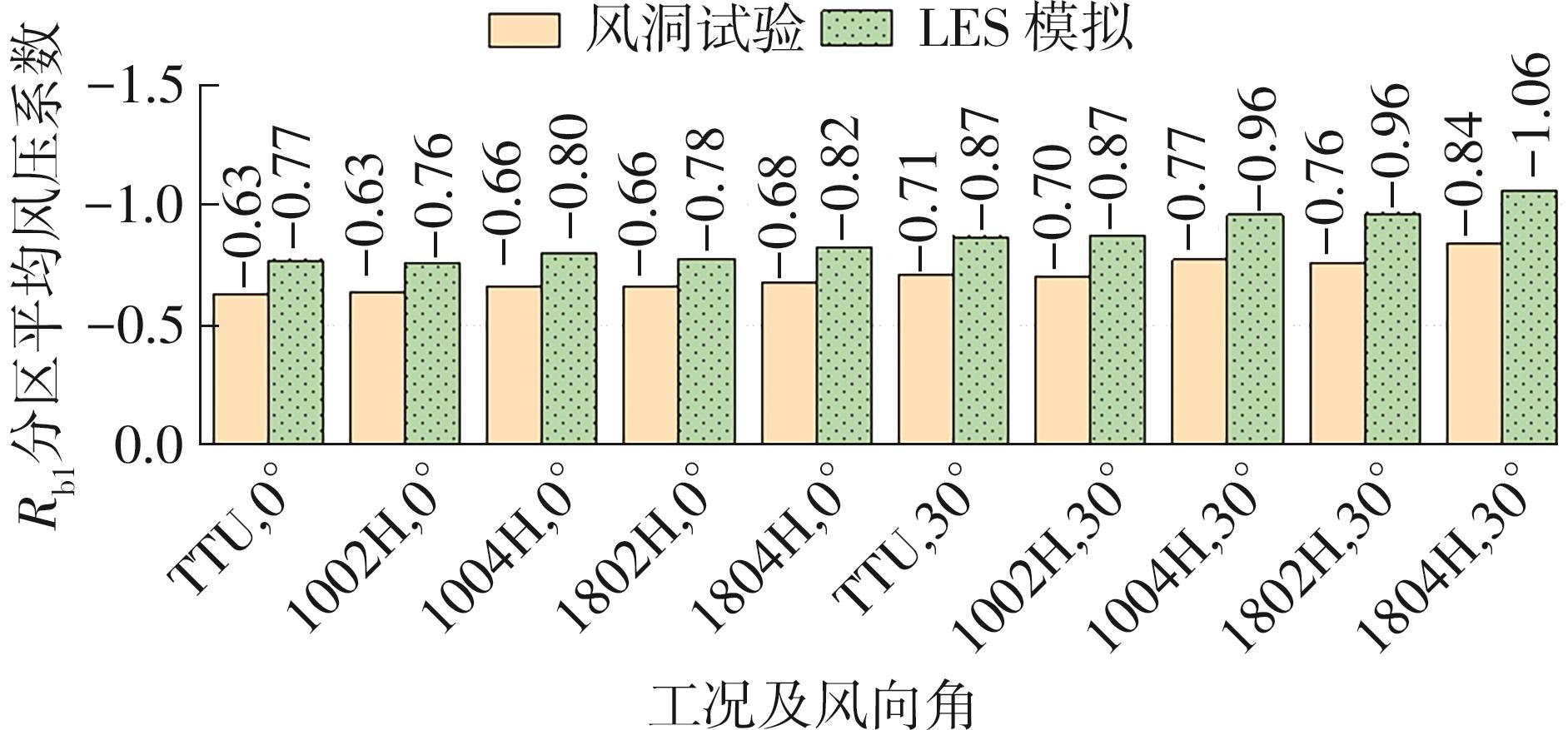
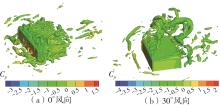
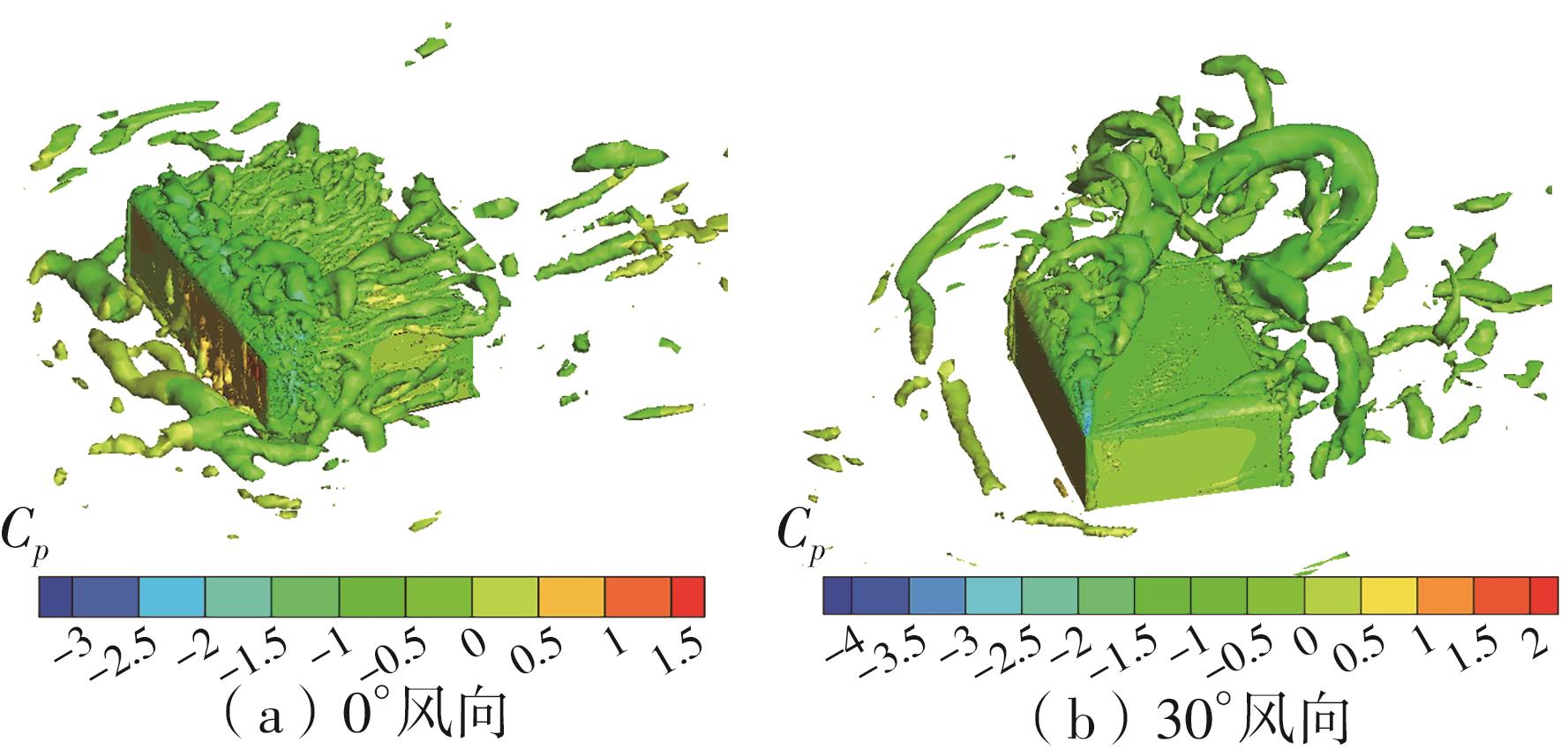
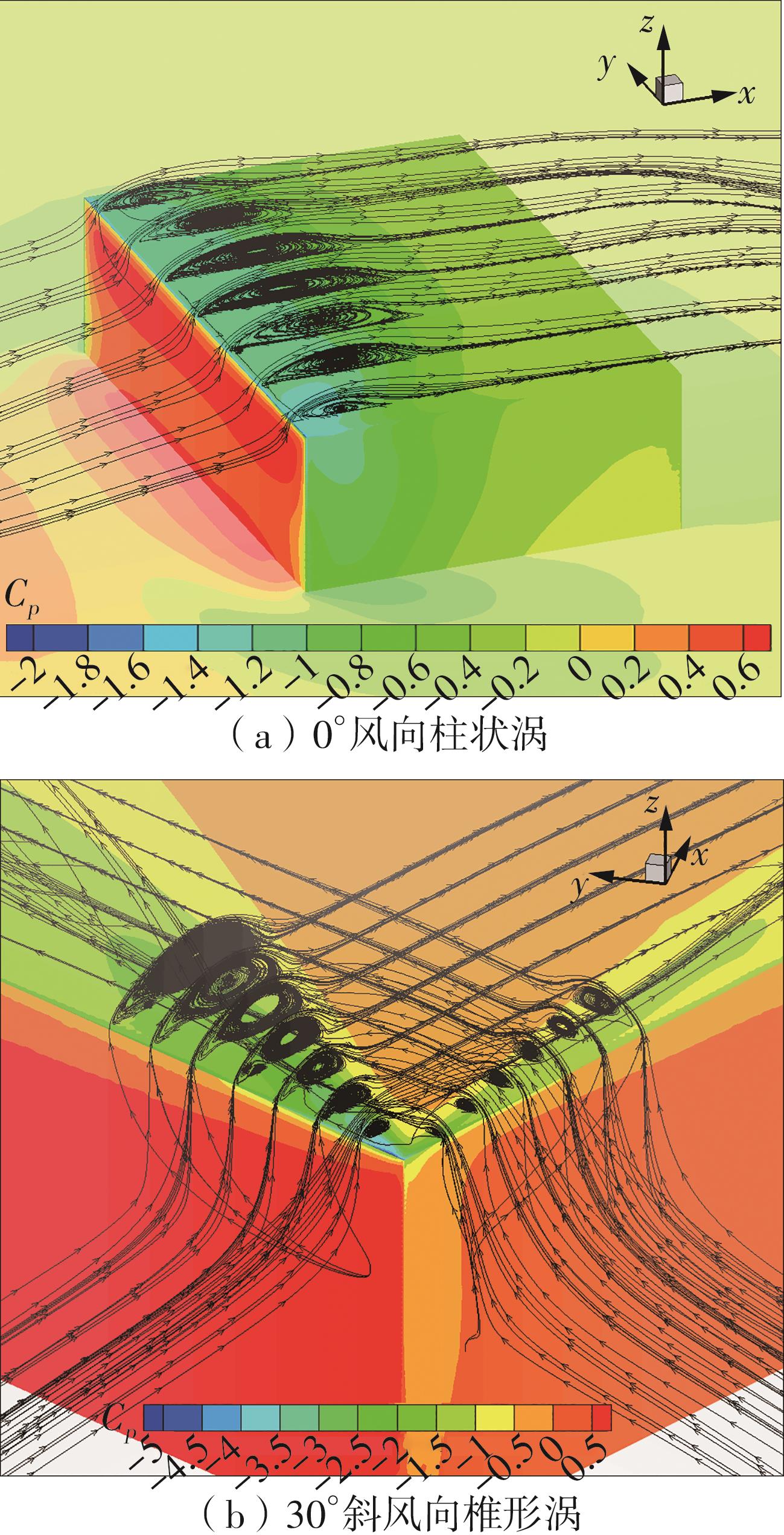
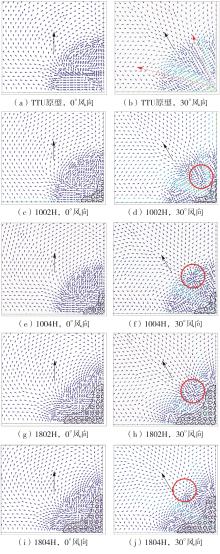
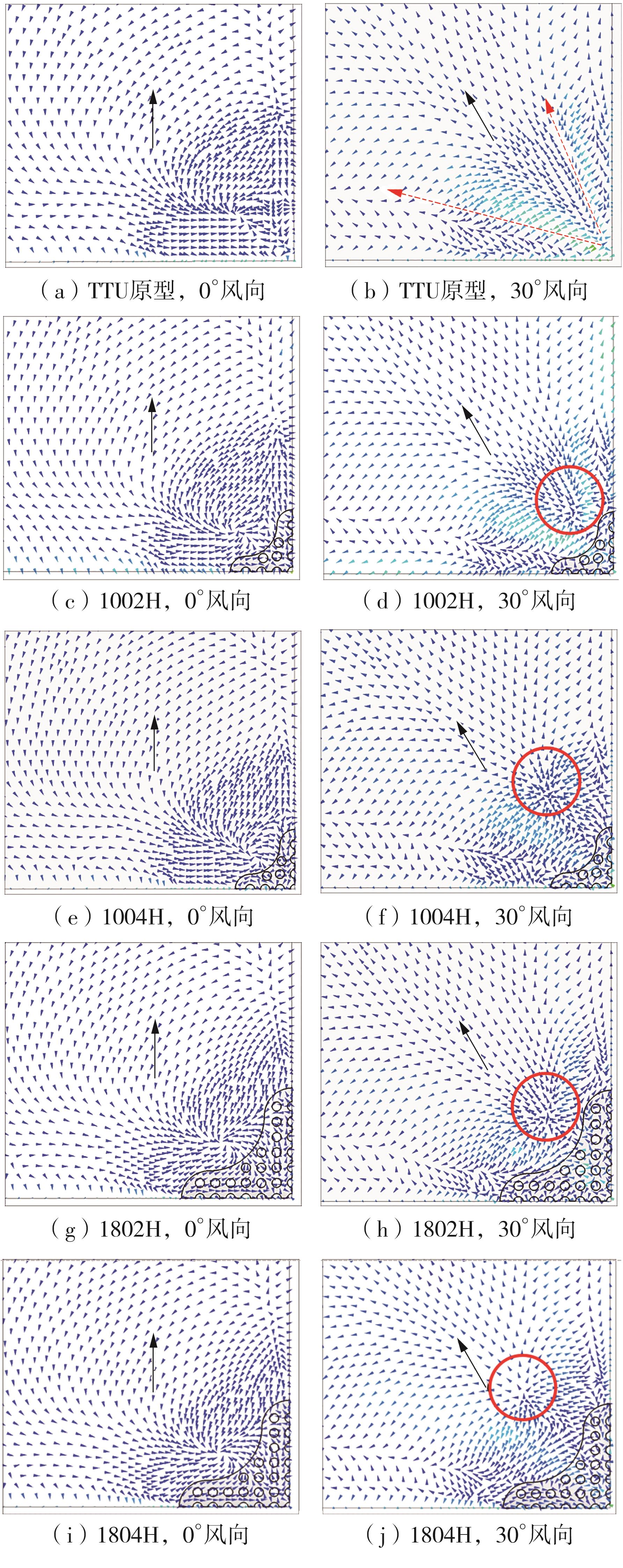
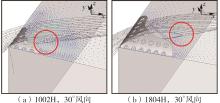
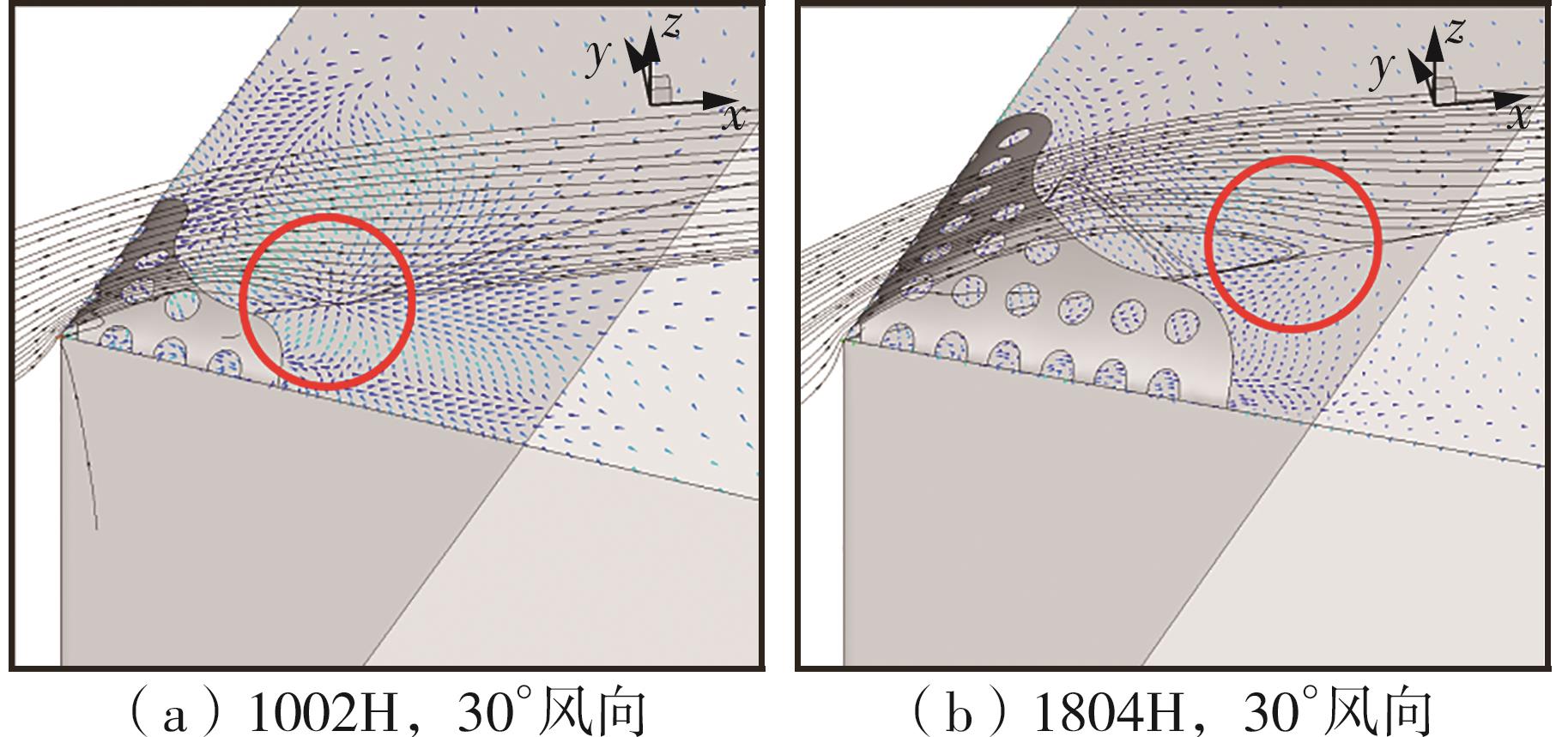
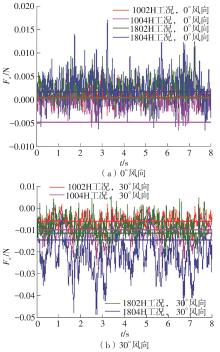
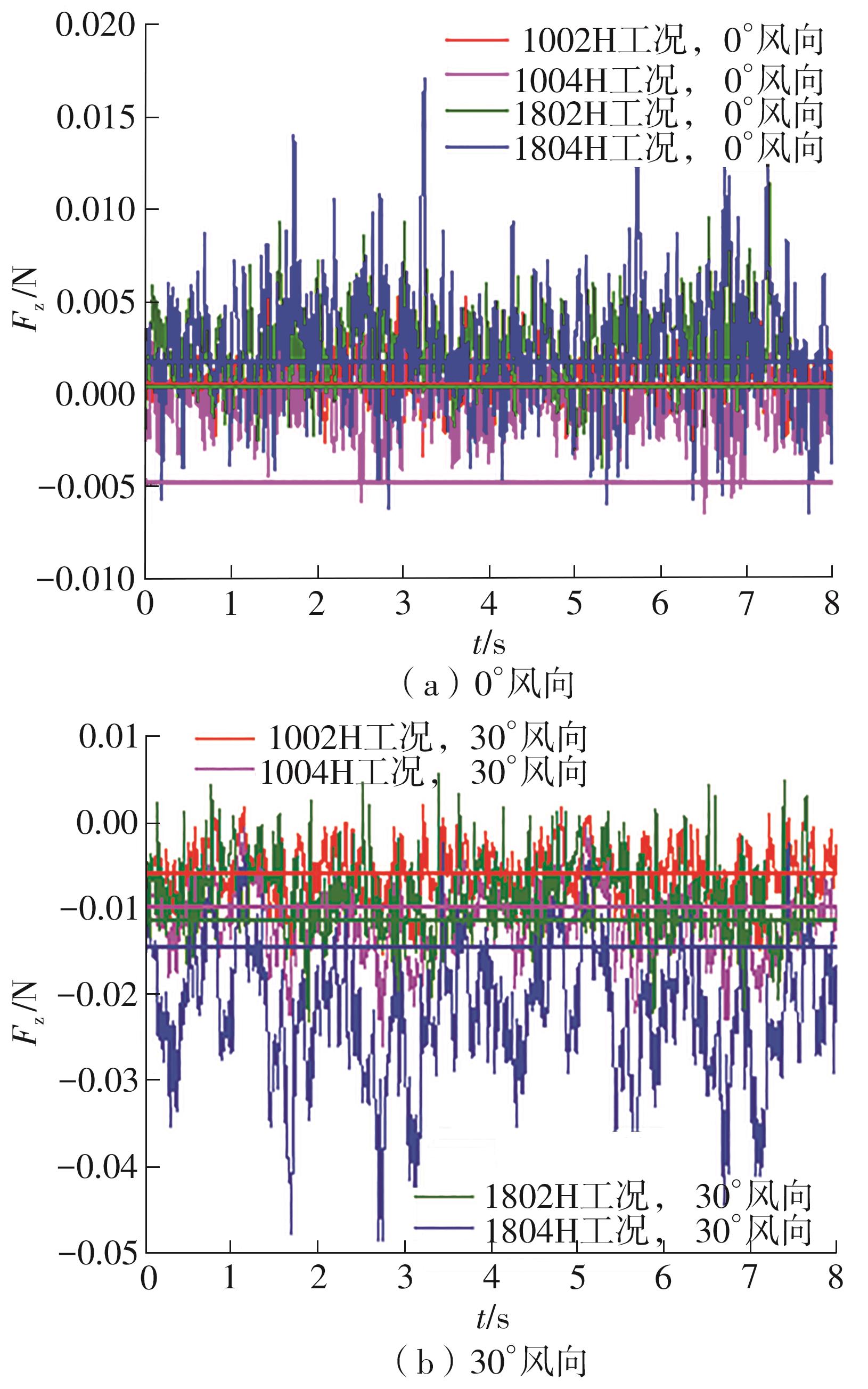
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 136-148.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240266
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles
LES Study on the Influence of Streamlined Accessories on the Wind Loads of TTU Model
YANG Yi1, WANG Zhe1, ZHANG Zhiyuan2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building and Urban Science,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Central & Southern China Municipal Engineering Design and Research Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Wuhan 430010,Hubei,China
-
Received:2024-05-28Online:2025-02-25Published:2025-02-03 -
About author:杨易(1975—),男,博士,教授,主要从事风工程研究。E-mail: ctyangyi@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52178480);the Guangdong Province Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund Project(2022A1515010350)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Yi, WANG Zhe, ZHANG Zhiyuan. LES Study on the Influence of Streamlined Accessories on the Wind Loads of TTU Model[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(2): 136-148.
share this article
| 1 | YANG Q, YIN J, LIU M, et al .Post-disaster investigations of damage feature of buildings and structures due to several local strong winds in China during 2021-2024[J].Advances in Wind Engineering,2024(1):100011. |
| 2 | 杨易,谢壮宁,石碧青 .屋顶构造形式对传统民居风荷载特性的影响[J].建筑结构学报,2017,38(2):143-150. |
| YANG Yi, XIE Zhuangning, SHI Biqing .Influence of roof members on wind load characteristics of traditional low-rise residence buildings[J].Journal of Building Structures,2017,38(2):143-150. | |
| 3 | 董欣,叶继红,丁洁民 .低矮建筑表面破坏性旋涡及其诱导的风压特性研究综述[J].建筑结构学报,2018,39(1):1-10. |
| DONG Xin, YE Jihong, DING Jiemin .Review of destructive vortices and vortex-induced wind pressures on low-rise buildings[J].Journal of Building Structures,2018,39(1):1-10. | |
| 4 | PRATT R N, KOPP G A .Velocity field measurements above the roof of a low-rise building during peak suctions[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2014,133(1): 234-241. |
| 5 | WU F, SARKAR P P, MEHTA K C .Full-scale study of conical vortices and roof corner pressures[J].Wind and Structures,2001,4(2):131-146. |
| 6 | 黄强 .低层建筑表面风荷载数值模拟研究[D].上海:同济大学,2007. |
| 7 | HUANG P, PENG X, GU M .Wind tunnel study on effects of various parapets on wind load of a flat-roofed low-rise building[J].Advances in Structural Engineering. 2017,20(12):1907-1919. |
| 8 | 甘石 .扰流板抗风装置性能分析及其在低矮建筑上的应用研究[D].大连:大连理工大学,2020. |
| 9 | 胡晓兵,杨易 .高层建筑标准模型脉动风压特性大涡模拟适用方法研究[J].建筑结构学报,2022,43(10):95-103. |
| HU Xiaobing, YANG Yi .Study on suitable method to simulate fluctuating wind pressure characteristics of standard high-rise building model based on LES[J].Journal of Building Structures,2022,43(10):95-103. | |
| 10 | 建筑结构荷载规范: [S]. |
| 11 | MENTER F R .Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications[J].AIAA Journal,1994,32(8):1598-1599. |
| 12 | YANG Y, XIE Z, GU M .Consistent inflow boundary conditions for modelling the neutral equilibrium atmospheric boundary layer for the SST k-ω model[J].Wind and Structures,2017,24(5):465-466. |
| 13 | LEVIAN M L, MEHTA K C, VANN W P .Field measurements of pressures on the Texas Tech Building[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodyna-mics,1991,38(1):227-234. |
| 14 | 孙虎跃 .基于CFD和PIV技术的大跨屋盖表面流动结构研究[D].南京:东南大学,2017. |
| 15 | SUARIS W, IRWIN P. Effect of roof-edge parapets on mitigating extreme roof suctions[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2010,98(1): 483-491. |
| 16 | AZZI Z, HABTE F, ELAWADY A,et al .Aerodynamic mitigation of wind uplift on low-rise building roof using large-scale testing[J].Frontiers in Built Environment,2020,5(1): 149-150. |
| 17 | RICHARDS P J, ROBINSON M .Wind loads on porous structures[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1999,83(1/2/3):455-465. |
| 18 | Engineering science data unit:Item 72009—2007 [S]. |
| 19 | YU Y, YANG Y, XIE Z .A new inflow turbulence generator for large eddy simulation evaluation of wind effects on a standard high-rise building[J].Building and Environment,2018,138:300-313. |
| 20 | ZHOU L, TSE K T, HU G .Aerodynamic correlation and flow pattern of high-rise building with side ratio of 3∶1 under twisted wind profile:a computational study[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2022,228(2):105087-105088. |
| 21 | 胡晓兵,杨易 .基于NSRFG方法的标准地貌风场大涡模拟研究[J].工程力学,2020,37(9):112-122. |
| HU Xiaobing, YANG Yi .Research on NSRFG-based LES simulation for standard[J].Engineering Mecha-nics,2020,37(9):112-122. | |
| 22 | LEVITAN M L, MEHTA K C .Texas tech field experiments for wind loads part I:building and pressure measuring system[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1992,44(3):1565-1576. |
| 23 | MEHTA K C, Levitan M L, Iverson R E,et al .Roof corner pressures measured in the field on a low building[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1992,41(1/2/3): 181-192. |
| 24 | HAM H J, BIENKIEWICZ B .Wind tunnel simulation of TTU flow and building roof pressure[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1998,77(98):119-133. |
| 25 | 杨庆山,田玉基,陈波,等 .行业标准《屋盖结构风荷载标准》的主要内容[J].工程力学,2018,35(7):1-6. |
| YANG Qingshan, TIAN Yüji, CHEN Bo,et al .Main contents of the standard for wind loads on roof structures[J].Engineering Mechanics,2018,35(7):1-6. |
| [1] | ZHANG Binyu, WANG Yigang, YU Wuzhou, et al. Experimental Study on the Noise and Transmission of Automobile Door Sealing Cavity [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(9): 104-114. |
| [2] | WANG Ningzhen, QIN Kangjie, TANG Liang, SHANGGUAN Lijian, ZHOU Fupeng, SHANGGUAN Wenbin. Optimization Design of Battery Box of Electric Vehicles Based on Response Surface Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(12): 43-51. |
| [3] | CHEN Zhong, QIU Yuliang, ZHANG Xianmin. Optimization Design and Experiment of XY Compliant Platform with Local Resonance Damping [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(12): 1-13. |
| [4] | YANG Yi, WANG Xin, JI Changhui. Wind Tunnel Test Research on the Effect of Rough Strips on Wind Loads of A Super High-Rise Building [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 1-8. |
| [5] | CHAI Bosen, WANG Guangyi, ZHU Guoren, et al. Large Eddy Simulation Flow Field Analysis and Visualization Test Verification of Hydraulic Torque Converter Under Braking Condition [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(3): 95-105. |
| [6] | HUANG Si, ZHANG Guoran, TANG Zirui, et al. Fluid-Solid Coupling Analysis of Spherical Storage Tank under Wind Load [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(2): 67-75. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xiang YAN Quansheng JIA Buyu LIU Muguang YU Xiaolin. The Study of Wind Tunnel Test and Numerical Simulation of Aerodynamic Interference on Adjacent Three Separated Deck Bridges [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(12): 101-112. |
| [8] | YANG Chun, LI Penglin, XIONG Shuai, et al. Analysis of Monitoring Data of a Long-Span Steel Roof Based on BIM and BP Neural Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(9): 10-19. |
| [9] | YOU Yi YAN Zhitao LI Xinmin ZHONG Yongli HUANG Hanjie. Wind tunnel tests on drag coefficients of multiple-insulator strings [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 66-72. |
| [10] | HUANG Zundi LIANG Xifeng CHANG Ning YIN Zhichun HUANG Yuming ZHENG Jiongjie MO Guangxing. Optimization Research on Cross-section of Intercity EMU Body Based on LES [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 109-115. |
| [11] | SHI Bai-jun LIU De-hui LI Zhen-yan. Parameterized Analysis and Optimization of Vehicle Anti-Roll Bar [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(6): 98-104,112. |
| [12] | Li Xiao-kang Xie Zhuang-ning Wang Zhan. Rapid Algorithm and Its Application of Wind-Induced Vibration Response of Super High-Rise Building Under the Control of Multiple Tuned Mass Dampers [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(4): 118-124. |
| [13] | Zhu Bing-hu Zhang Qi-lin. Monitoring and Analysis of Wind Effect on Membrane Roof of Expo Axis [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(2): 13-18. |
| [14] | Xie Zhuang-ning Liu Shuai Shi Bi-qing. Investigation into Wind Tunnel Test of Standard Low-Rise Building Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(6): 106-112. |
| [15] | Xie Zhuang-ning Zhu Jian-bo. Distribution Characteristics of Mean Wind Pressure on Tall Buildings [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(4): 128-134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||