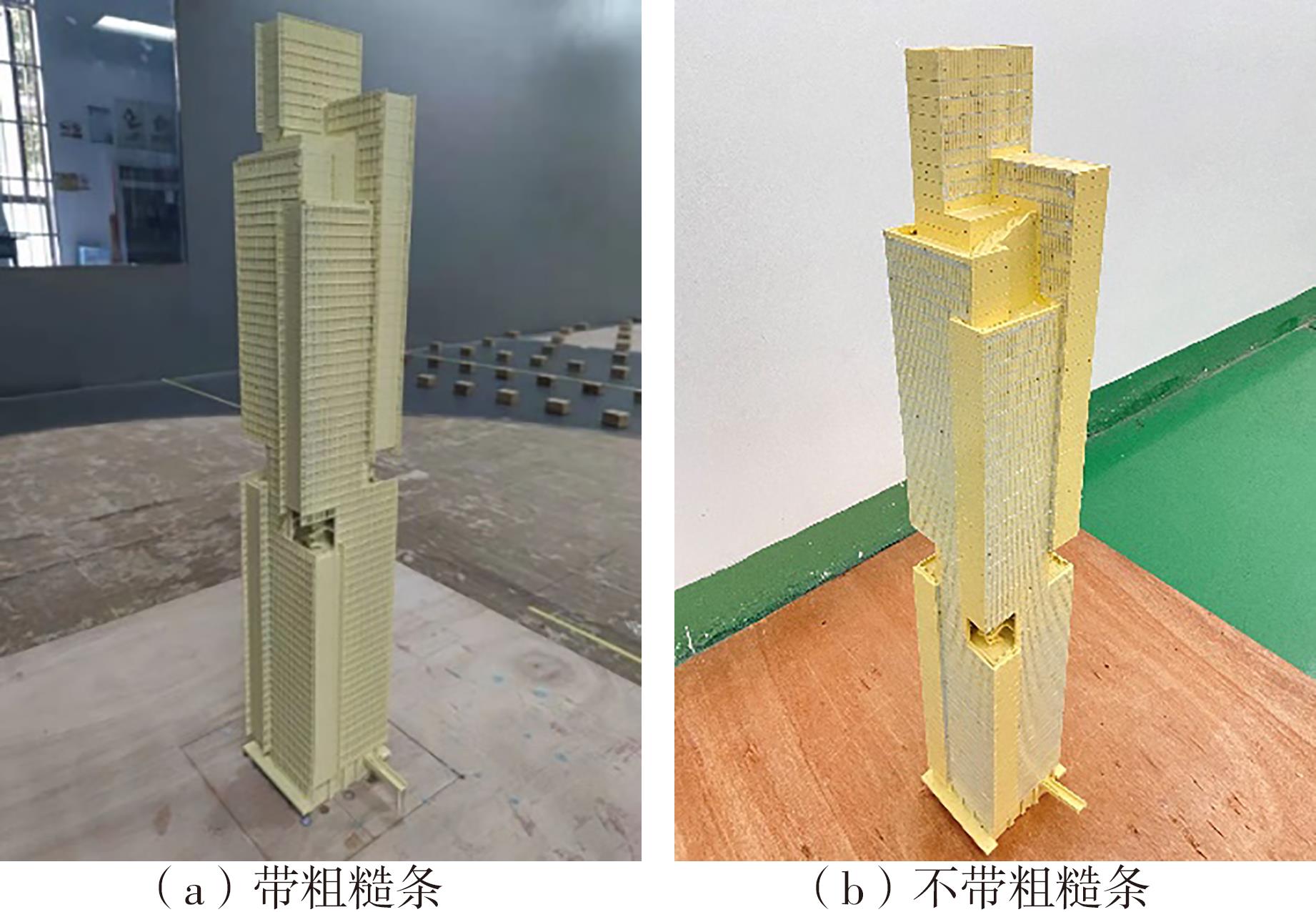
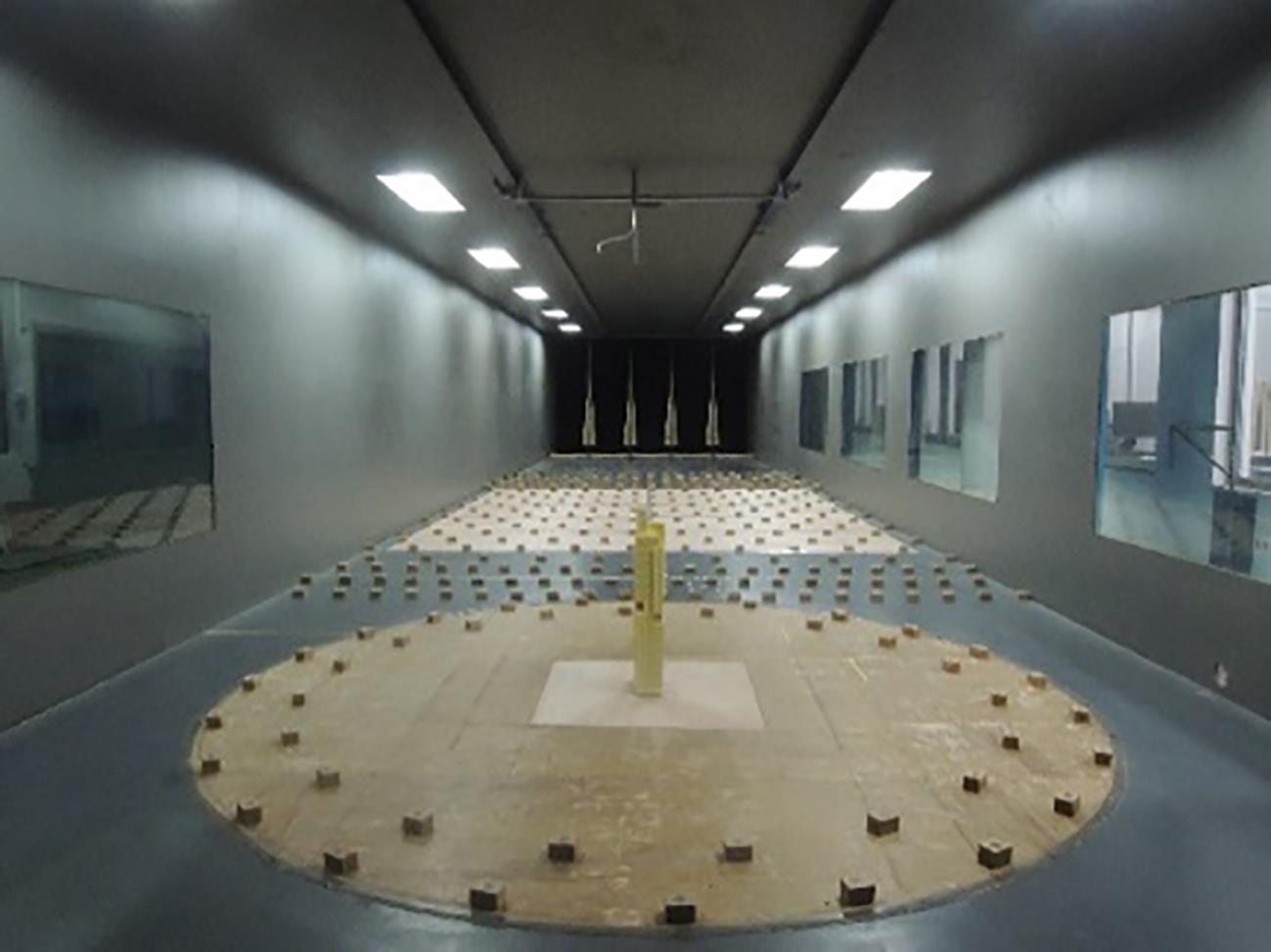
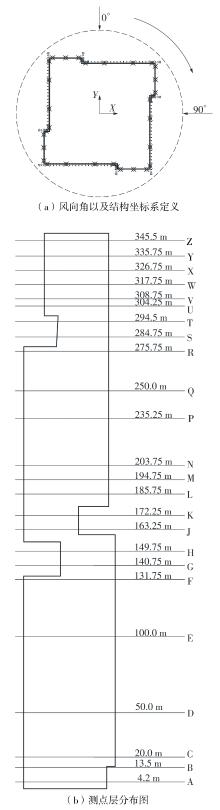
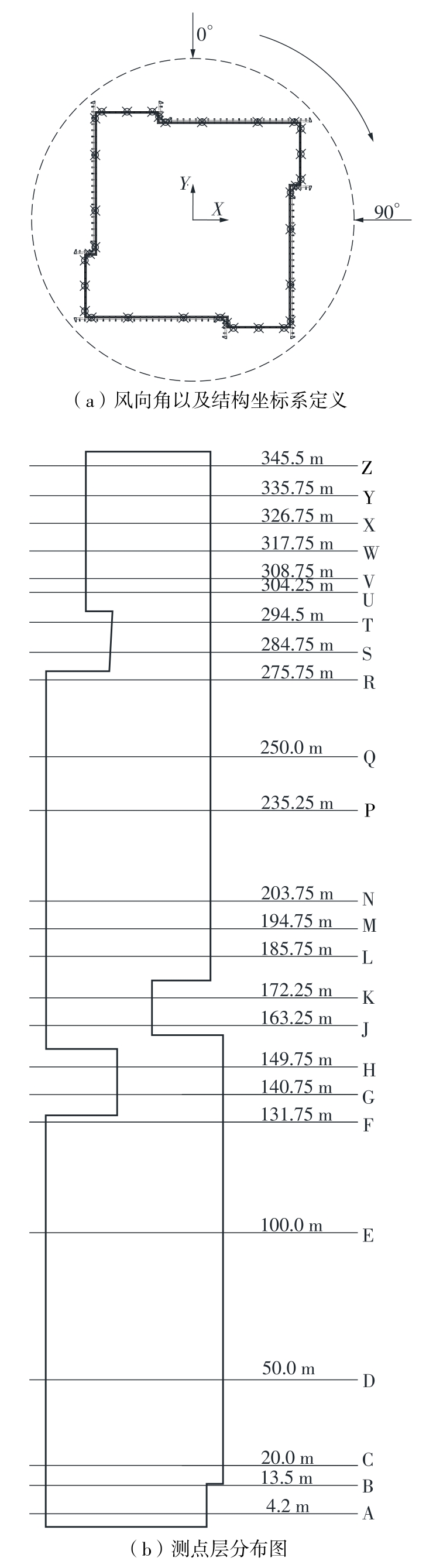
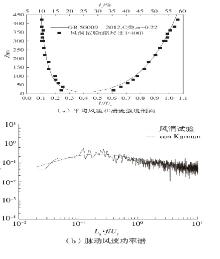
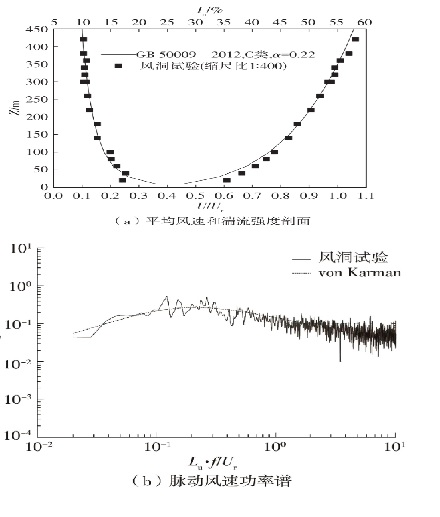
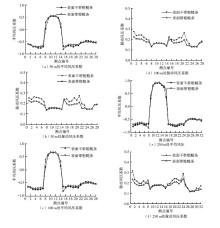
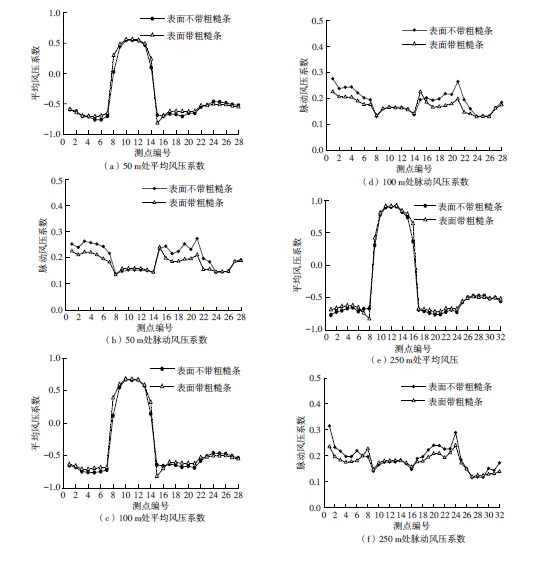
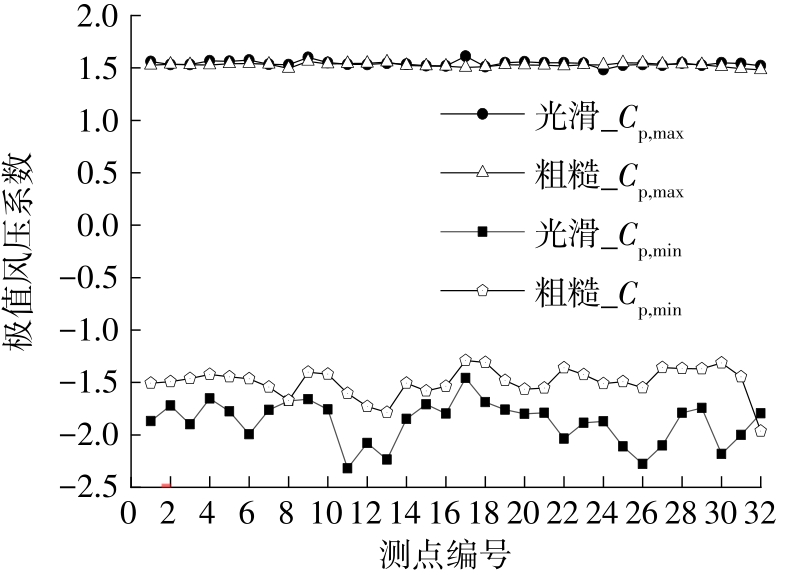
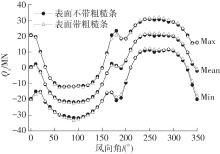
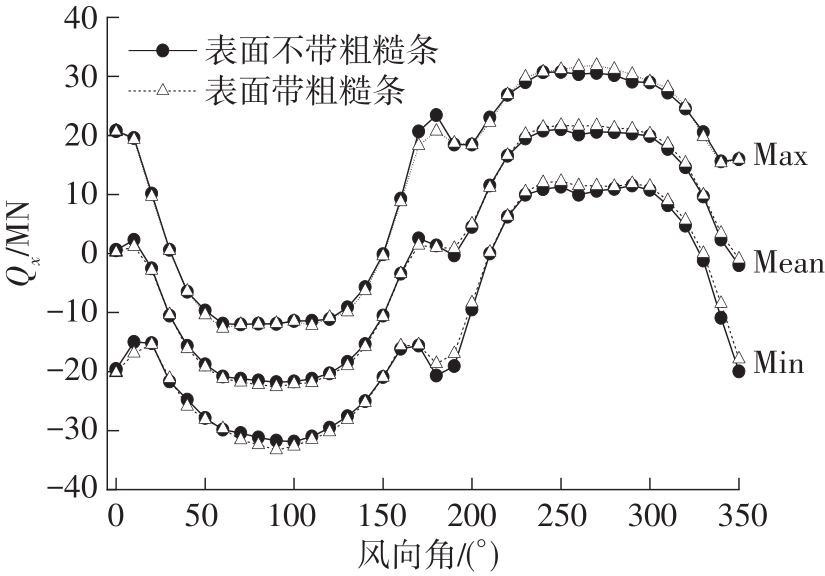
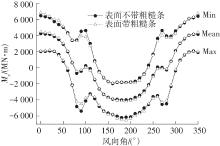
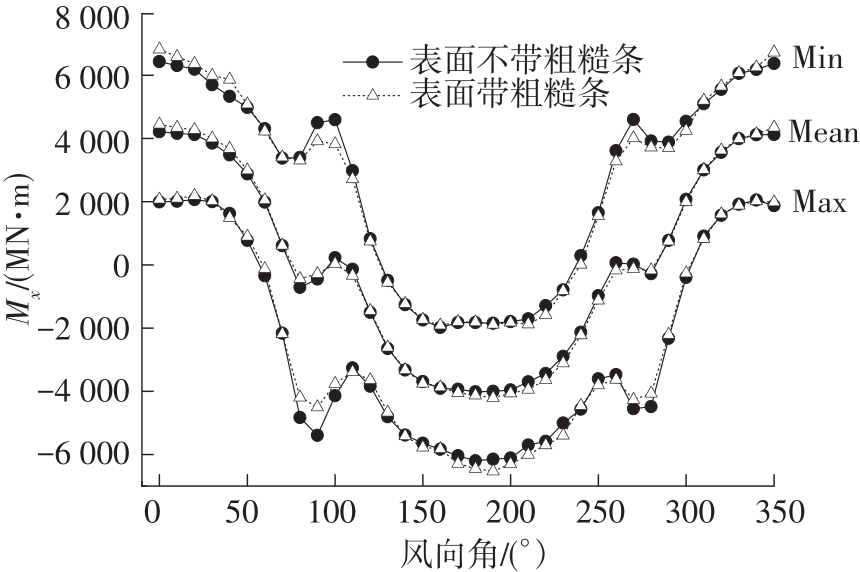
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1-8.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220290
Special Issue: 2023年土木建筑工程
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wind Tunnel Test Research on the Effect of Rough Strips on Wind Loads of A Super High-Rise Building
YANG Yi WANG Xin JI Changhui
- State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building Science,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-05-16Online:2023-04-25Published:2022-10-28 -
Contact:杨易(1975-),男,博士,研究员,主要从事风工程研究。 E-mail:ctyangyi@scut.edu.cn -
About author:杨易(1975-),男,博士,研究员,主要从事风工程研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52178480)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Yi, WANG Xin, JI Changhui. Wind Tunnel Test Research on the Effect of Rough Strips on Wind Loads of A Super High-Rise Building[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 1-8.
share this article
Table 3
Comparisons of the base overturning bending moments"
| 风向角/(°) | 工况 | 弯矩/(MN·m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | ||
| 0 | 光滑 | 6 433.55 | 1 988.89 | 4 211.22 |
| 粗糙 | 6 817.53 | 2 068.90 | 4 443.21 | |
| 180 | 光滑 | -1 828.78 | -6 202.29 | -4 015.44 |
| 粗糙 | -1 808.90 | -6 451.36 | -4 130.13 | |
| 190 | 光滑 | -1 852.56 | -6 151.95 | -4 002.25 |
| 粗糙 | -1 885.76 | -6 528.11 | -4 206.94 | |
| 350 | 光滑 | 6 373.42 | 1 870.28 | 4 121.85 |
| 粗糙 | 6 722.94 | 1 982.17 | 4 352.56 | |
| 1 | 建筑结构荷载规范: [S]. |
| 2 | JAFARI M, ALIPOUR A .Aerodynamic shape optimization of rectangular and elliptical double-skin facades to mitigate wind-induced effects on tall buildings[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2021,213:104586. |
| 3 | 杨肖悦,秦玮峰,柯延宇,等 .镂空双层幕墙对高层建筑结构风响应的影响[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报,2021,53(10):70-78. |
| YANG Xiaoyue, QIN Weifeng, KE Yanyu,et al .Effects of porous double skin façade system on structural wind responses of tall buildings[J].Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2021,53(10):70-78. | |
| 4 | 邹云峰,陈政清,牛华伟 .模型表面粗糙度对冷却塔风致响应及干扰的影响[J].空气动力学学报,2014,32(3):388-394. |
| ZOU Yunfeng, CHEN Zhengqing, NIU Huawei .Influence of model surface roughness on wind induced response and interference of cooling tower[J].Acta Aerodynamica Sinica,2014,32(3):388-394. | |
| 5 | 黄东梅,何世青,朱学,等 .表面粗糙度对超高层建筑风荷载与风振响应的影响[J].湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2017,44(9):41-51. |
| HUANG Dongmei, HE Shiqing, ZHU Xue,et al .Influence of surface roughness on wind load and wind induced response of super-tall building[J].Journal of Hunan University(Natural Science),2017,44(9):41-51. | |
| 6 | STATHOPOULOS T, ZHU X .Wind Pressures on buildings with mullions[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,1990,116(8):2272-2291. |
| 7 | QUAN Y, HOU F, GU M .Effects of vertical ribs protruding from facades on the wind loads of super high-rise buildings[J].Wind and Structures,2017,24(2):145-169. |
| 8 | 王磊,梁枢果,王泽康,等 .超高层建筑横风向风振局部气动外形优化[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2016,50(7):1239-1246,1265. |
| WANG Lei, LIANG Shu-guo, WANG Ze-kang,et al .Effect of aerodynamic optimization to across-wind response of super tall buildings[J].Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science),2016,50(7):1239-1246,1265. | |
| 9 | YUAN K, HUI Y, CHEN Z Q .Effects of façade appurtenances on the local pressure of high-rise building[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamic,2018,178:26-37. |
| 10 | 全涌,邱宏浩,张正维,等 .高层建筑水平悬挑遮阳板风荷载的风洞试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2022,43(3):92-97. |
| QUAN Yong, QIU Honghao, ZHANG Zhengwei,et al .Wind test study on wind load of overhanging horizontal sunshade of high-rise buildings[J].Journal of Building Structures,2022,43(3):92-97. | |
| 11 | MARUTA E, KANDA M, SATO J .Effects on surface roughness for wind pressure on glass and cladding of buildings[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1998,74/75/76:651-663. |
| 12 | MONTAZERI H, BLOCKEN B .CFD simulation of wind induced pressure coefficients on buildings with and without balconies:validation and sensitivity analysis[J].Building and Environment,2013,60:137-149. |
| 13 | CHAND I, BHARGAVA P K, KRISHAK N L V .Effect of balconies on ventilation inducing aeromotive force on low-rise buildings[J].Building and Environment,1998,33(6):385-396. |
| 14 | ZHENG X, MONTAZERI H, BLOCKEN B .CFD analysis of the impact of geometrical characteristics of building balconies on near-façade wind flow and surface pressure[J].Building and Environment,2021,200:107904. |
| 15 | 徐宗凯 .基于壁面带阳台的不同体型高层建筑风致响应研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2019. |
| 16 | 艾辉林,周志勇 .超高层建筑外表面复杂装饰条的风荷载特性研究[J].工程力学,2016,33(8):141-149. |
| AI Huilin, ZHOU Zhiyong .Research on wind load characteristics of complex decorative strips on the outer surface of high-rise building[J].Engineering Mechanics,2016,33(8):141-149. | |
| 17 | 艾辉林,周志勇 .一类复杂建筑外围装饰结构的风荷载参数研究[J].力学季刊,2014,35(3):513-521. |
| AI Huilin, ZHOU Zhiyong .Wind Load Parameters Research about Class of Complex Peripheral Decorative Structure[J].Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics,2014,35(3):513-521. | |
| 18 | 张正维 .高层建筑立面装饰构件设计风荷载探讨[J].建筑结构,2019,49(22):46-52. |
| ZHANG Zhengwei .Discussion on design wind load of facade decorative fittings for high-rise buildings[J].Building Structure,2019,49(22):46-52. | |
| 19 | 严志威,全涌,涂楠坤,等 .外附网架对高层建筑立面围护结构风荷载影响研究[J].建筑结构,2015,45(2):75-79. |
| YAN Zhiwei, QUAN Yong, TU Nankun,et al .Effect research of attached grid on wind load of high-rise building facade envelope[J].Building Structure,2015,45(2):75-79. | |
| 20 | 程旭 .粗糙条围护结构对高层建筑风荷载影响的研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2020. |
| 21 | RIBEIRO J .Effect of surface roughness on the two- dimensional flow past circular cylinders,Part I:mean forces and pressures[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1991,37(3):311-326. |
| 22 | 高层建筑混凝土结构技术规程: [S]. |
| [1] | HUANG Si, ZHANG Guoran, TANG Zirui, et al. Fluid-Solid Coupling Analysis of Spherical Storage Tank under Wind Load [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(2): 67-75. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xiang YAN Quansheng JIA Buyu LIU Muguang YU Xiaolin. The Study of Wind Tunnel Test and Numerical Simulation of Aerodynamic Interference on Adjacent Three Separated Deck Bridges [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(12): 101-112. |
| [3] | YANG Chun, LI Penglin, XIONG Shuai, et al. Analysis of Monitoring Data of a Long-Span Steel Roof Based on BIM and BP Neural Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(9): 10-19. |
| [4] | YOU Yi YAN Zhitao LI Xinmin ZHONG Yongli HUANG Hanjie. Wind tunnel tests on drag coefficients of multiple-insulator strings [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 66-72. |
| [5] | HUANG Zundi LIANG Xifeng CHANG Ning YIN Zhichun HUANG Yuming ZHENG Jiongjie MO Guangxing. Optimization Research on Cross-section of Intercity EMU Body Based on LES [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 109-115. |
| [6] | DENG Meng-ren GUO Hao-xu XIONG Sheng-yang. Influence of Building Chambers on Internal Ventilation and Corresponding Simulation Analysis [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(5): 74-81. |
| [7] | Li Xiao-kang Xie Zhuang-ning Wang Zhan. Rapid Algorithm and Its Application of Wind-Induced Vibration Response of Super High-Rise Building Under the Control of Multiple Tuned Mass Dampers [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(4): 118-124. |
| [8] | Zhu Bing-hu Zhang Qi-lin. Monitoring and Analysis of Wind Effect on Membrane Roof of Expo Axis [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(2): 13-18. |
| [9] | Xie Zhuang-ning Liu Shuai Shi Bi-qing. Investigation into Wind Tunnel Test of Standard Low-Rise Building Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(6): 106-112. |
| [10] | Xie Zhuang-ning Zhu Jian-bo. Distribution Characteristics of Mean Wind Pressure on Tall Buildings [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(4): 128-134. |
| [11] | Xiao Zheng-zhi Li Zheng-liang Wang Zhi-song Yan Zhi-tao. Spatial Distribution Estimation of Wind Loads on Transmission Tower Based on High-Frequency Force Balance Tests [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(6): 147-152. |
| [12] | Hou Jia-jian Han Xiao-lei Xie Zhuang-ning . Wind Load Characteristics of Twin-Tower Corridor-Connected Tall Building with Complex Shape [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(3): 121-127. |
| [13] | Liu Yue-xing, Wang Fan, Wu Bo, et al. Wind Tunnel Test of Inclined Long-span Flat Roof in Complex Circumstance [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2004, 32(11): 75-80. |
| [14] | Fu J-i yang Gan Quan . Neural Network Models for Describing Characteristics of Wind Pressure Distribution on Large Span Flat Roof [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2003, 31(8): 62-66. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||