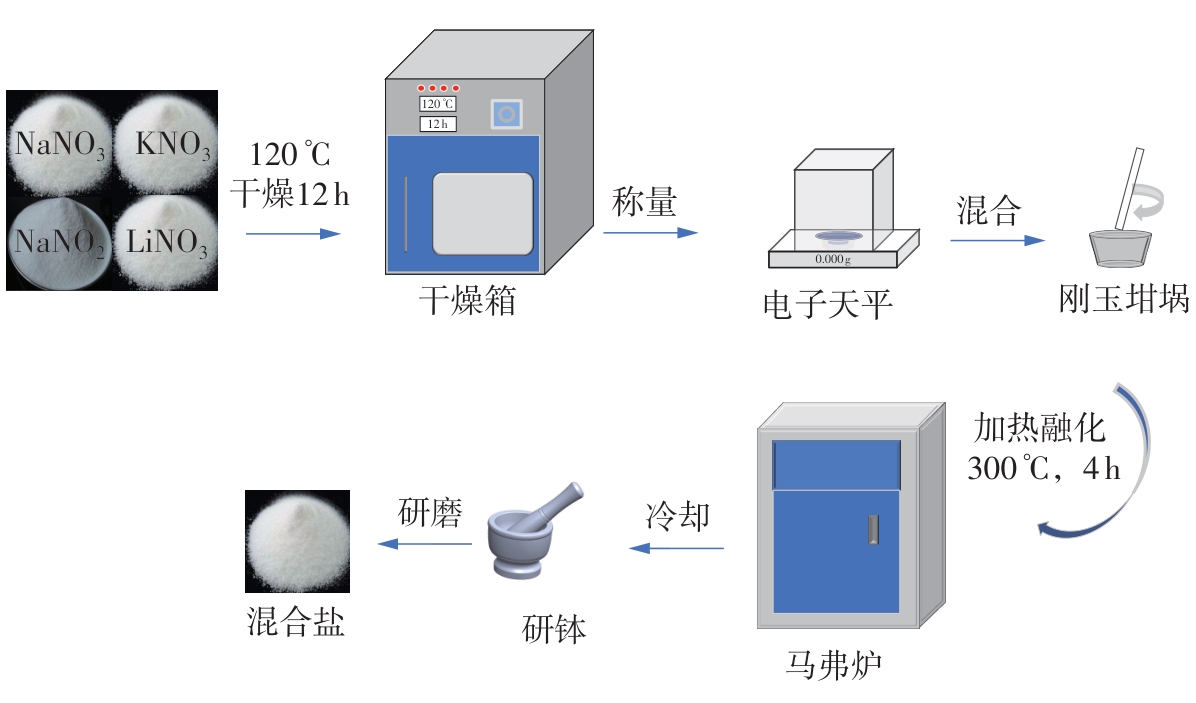
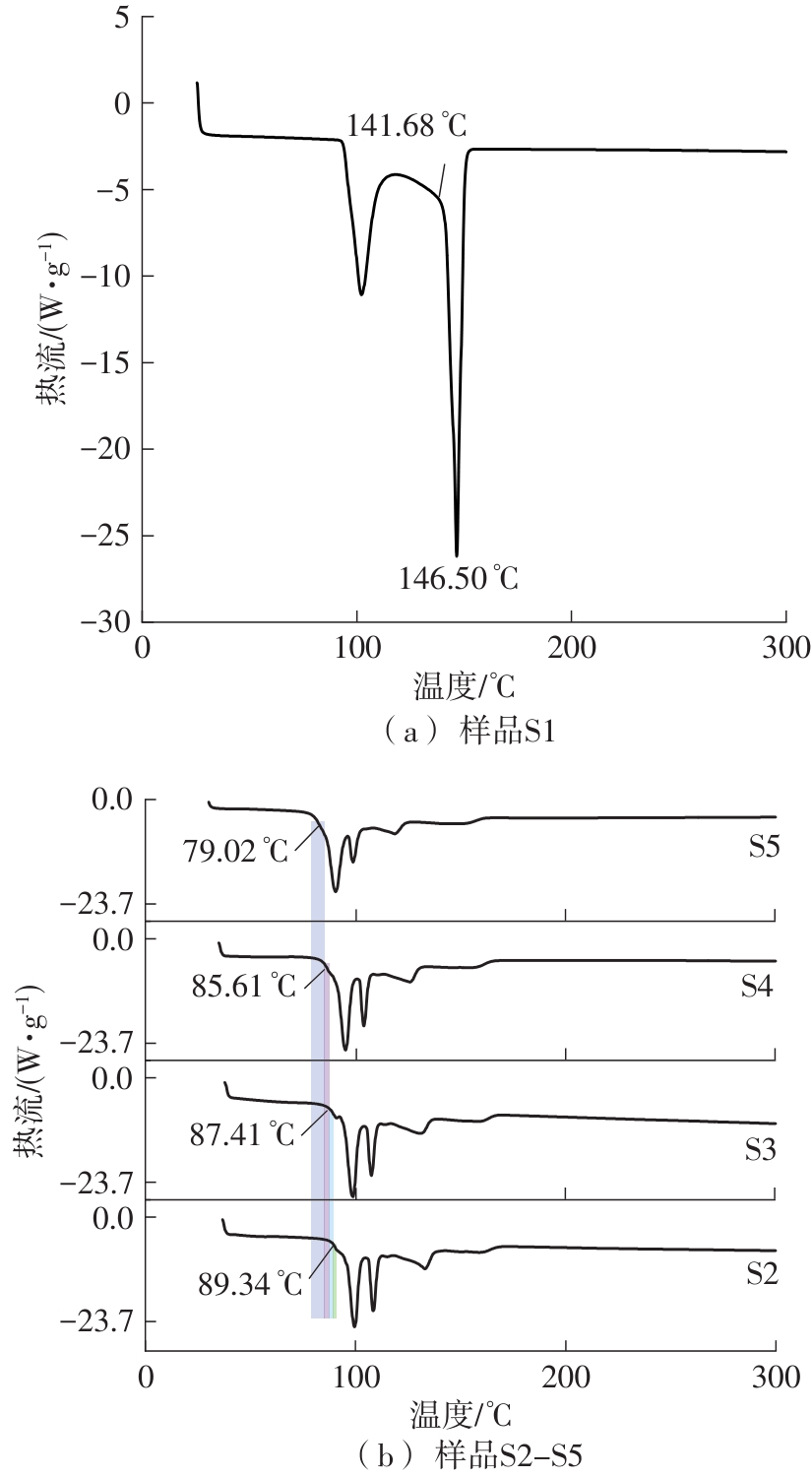
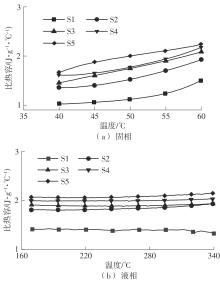
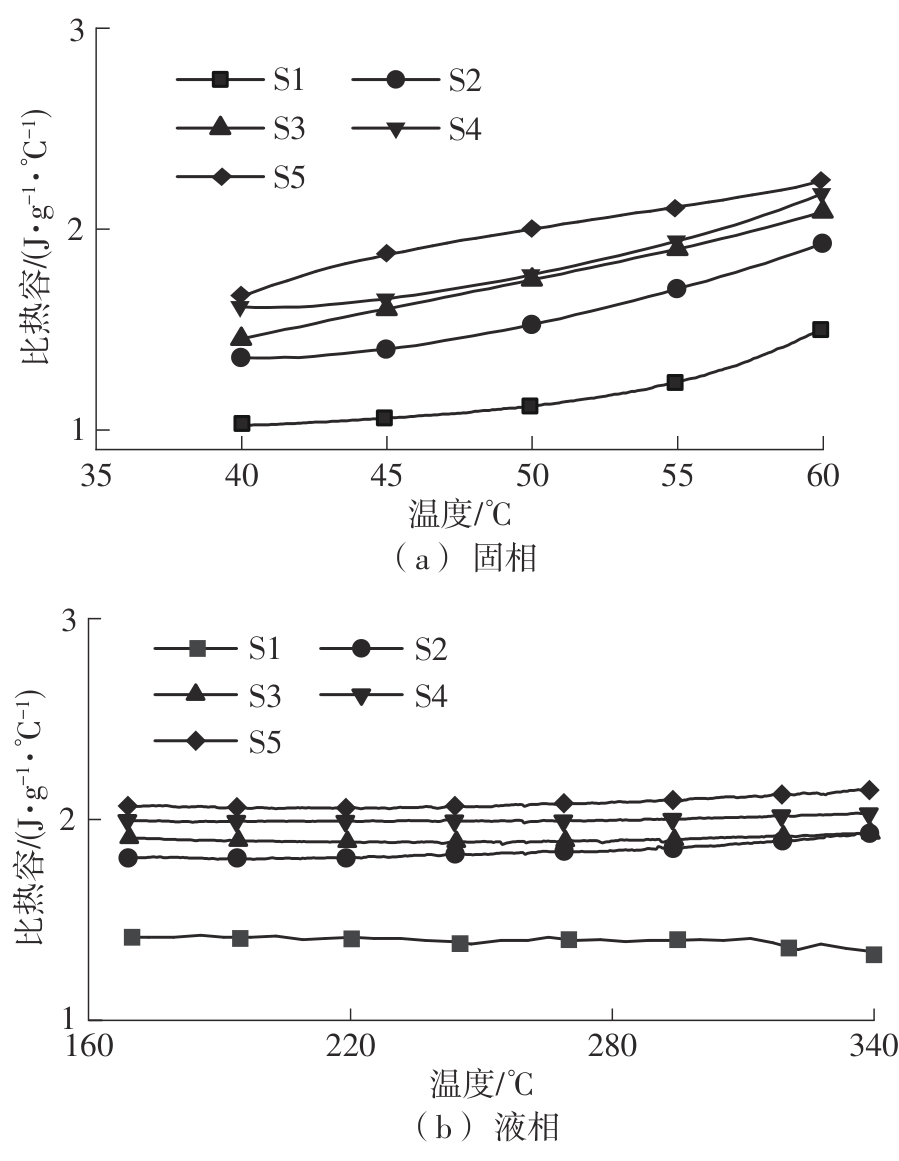
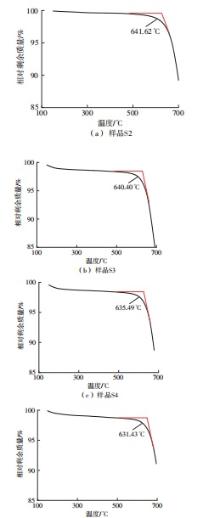
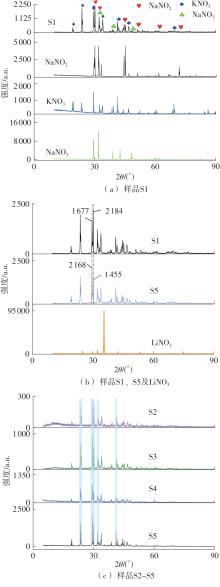
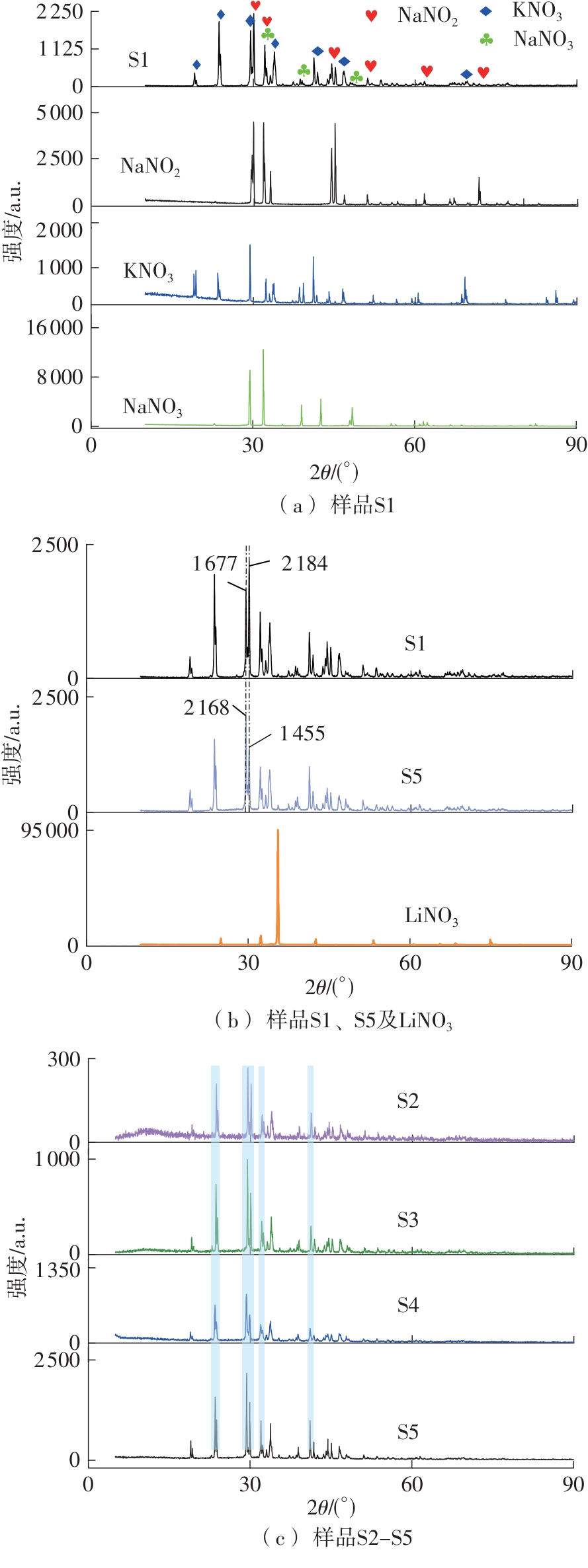
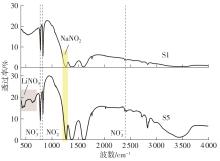
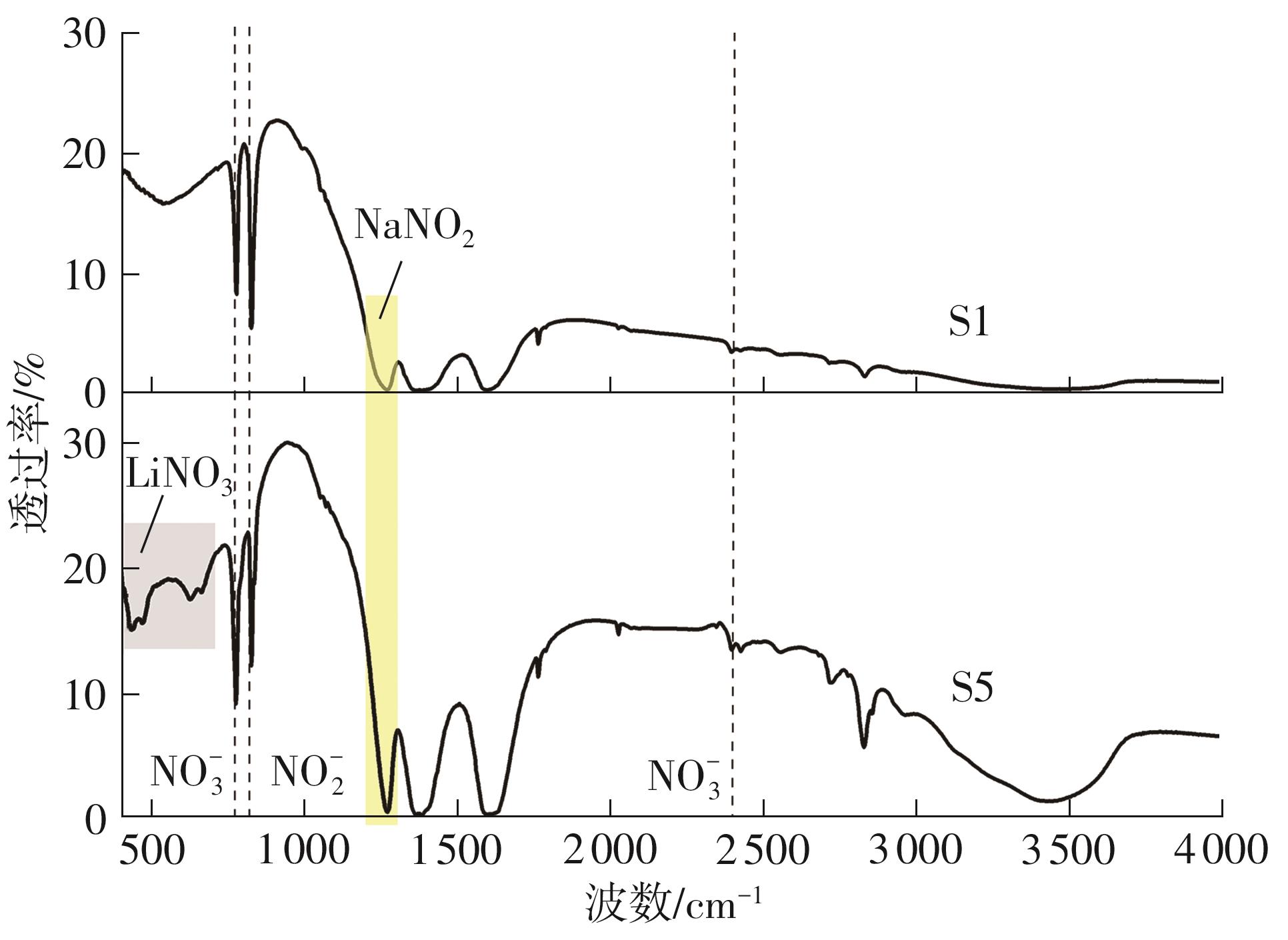
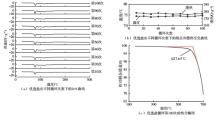
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 116-126.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240256
• Materials Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and Thermal Property Regulation of Nitrates Based Phase Change Material for Low and Medium Temperature Thermal Energy Storage
AN Zhoujian( ), LI Lu, MAO Shuai, LIU Ligong, DU Xiaoze, ZHANG Dong
), LI Lu, MAO Shuai, LIU Ligong, DU Xiaoze, ZHANG Dong
- School of Energy and Power Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,Gansu,China
-
Received:2024-05-27Online:2025-03-10Published:2024-08-23 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52206087);the Key R & D Program of Gansu Province(23YFGA0066);the Industrial Support Plan Project of Gansu Provincial Education;Department(2022CYZC-21)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
AN Zhoujian, LI Lu, MAO Shuai, LIU Ligong, DU Xiaoze, ZHANG Dong. Preparation and Thermal Property Regulation of Nitrates Based Phase Change Material for Low and Medium Temperature Thermal Energy Storage[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(3): 116-126.
share this article
| 1 | 黄晟,王静宇,郭沛,等 .碳中和目标下能源结构优化的近期策略与远期展望[J].化工进展,2022,41(11):5695-5708. |
| HUANG Sheng, WANG Jingyu, GUO Pei,et al .Short-term strategy and long-term prospect of energy structure optimization under carbon neutrality target[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2022,41(11):5695-5708. | |
| 2 | ALVA G, LIU L, HUANG X,et al .Thermal energy storage materials and systems for solar energy applications[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2017,68:693-706. |
| 3 | 魏小兰,林国庆,丁静,等 .硝酸熔盐纳米流体比热容提高的模拟与实验研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(9):46-55. |
| WEI Xiaolan, LIN Guoqing, DING Jing,et al .Simulation and experiment investigation into specific heat capacity enhancement of nitrate molten salt nanofluid[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2021,49(9):46-55. | |
| 4 | ZHOU Y, LI J, WANG G,et al .Assessing the short-to medium-term supply risks of clean energy minerals for China[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,215:217-225. |
| 5 | ZHANG Z, DING T, ZHOU Q,et al .A review of technologies and applications on versatile energy storage systems[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2021,148:111263/1-31. |
| 6 | DELOVATO N, SUNDARNATH K, CVIJOVIC L,et al .A review of heat recovery applications for solar and geothermal power plants[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2019,114:109329/1-19. |
| 7 | WOOLLEY E, LUO Y, SIMEONE A .Industrial waste heat recovery:a systematic approach[J].Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments,2018,29:50-59. |
| 8 | DADI D, INTRONA V, BENEDETTI M .Decarbonization of heat through low-temperature waste heat recovery:proposal of a tool for the preliminary evaluation of technologies in the industrial sector[J].Sustainability,2022,14(19):12626/1-28. |
| 9 | GIORDANO L, BENEDETTI M .A methodology for the identification and characterization of low-temperature waste heat sources and sinks in industrial processes:application in the Italian dairy sector[J].Energies,2022,15:155/1-33. |
| 10 | 吴玉庭,任楠,马重芳 .熔融盐显热蓄热技术的研究与应用进展[J].储能科学与技术,2013,2(6):586-592. |
| WU Yuting, REN Nan, MA Chongfang .Research and application of molten salts for sensible heat storage[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2013,2(6):586-592. | |
| 11 | MAGENDRAN S S, KHAN F S A, Mubarak N M,et al .Synthesis of organic phase change materials (PCM) for energy storage applications:a review[J].Nano-Structures and Nano-Objects,2019,20:100399/1-18. |
| 12 | 何媚质,杨鲁伟,张振涛 .有机-无机复合相变材料的研究进展[J].化工进展,2018,37(12):4709-4718. |
| HE Meizhi, YANG Luwei, ZHANG Zhentao .Research progress of organic-inorganic composite phase change materials[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2018,37(12):4709-4718. | |
| 13 | KALIDASAN B, PANDEY A K, SAIDUR R,et al .Nano additive enhanced salt hydrate phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J].International Materials Reviews,2023,68(2):140-183. |
| 14 | LIN Y, ALVA G, FANG G .Review on thermal performances and applications of thermal energy storage systems with inorganic phase change materials[J].Energy,2018,165:685-708. |
| 15 | PAN G, WEI X, YU C,et al .Thermal performance of a binary carbonate molten eutectic salt for high-temperature energy storage applications[J].Applied Energy,2020,262:114418/1-12. |
| 16 | HUA H, YASUDA K, KONISHI H,et al .Electrochemical formation of Nd-Ni alloys in molten CaCl2-NdCl3 [J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2021,168(3):032506/1-6. |
| 17 | 左芳菲,韩伟,姚明宇 .熔盐储能在新型电力系统中应用现状与发展趋势[J].热力发电,2023,52(2):1-9. |
| ZUO Fangfei, HAN Wei, YAO Mingyu .Application status and development trend of molten salt energy sto-rage in novel power systems[J].Thermal Power Ge-neration,2023,52(2):1-9. | |
| 18 | NAZIR H, BATOOL M, OSORIO F J B,et al .Recent developments in phase change materials for energy storage applications:a review[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2019,129:491-523. |
| 19 | HAMEED G, GHAFOOR M A, YOUSAF M,et al .Low temperature phase change materials for thermal energy storage:current status and computational per-spectives[J].Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments,2022,50:101808/1-22. |
| 20 | 张灿灿,吴玉庭,鹿院卫 .低熔点混合硝酸熔盐的制备及性能分析[J].储能科学与技术,2020,9(2):435-439. |
| ZHANG Cancan, WU Yuting, LU Yuanwei .Preparation and comparative analysis of thermophysical properties on low melting point mixed nitrate molten salts[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2020,9(2):435-439. | |
| 21 | SHI H, ZHOU H, MENG H,et al .Analysis of flowing and heat transfer of commercial molten nitrate in porous foundation material[J].Journal of Thermal Science,2023,32(4):1455-1465. |
| 22 | LU W, LIU G, XIONG Z,et al .An experimental investigation of composite phase change materials of ternary nitrate and expanded graphite for medium-temperature thermal energy storage[J].Solar Energy,2020,195:573-580. |
| 23 | ZHANG P, CHENG J, JIN Y,et al .Evaluation of thermal physical properties of molten nitrate salts with low melting temperature[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2018,176:36-41. |
| 24 | WANG Q, YANG L, SONG J .Preparation,thermal conductivity,and applications of nano-enhanced phase change materials (NEPCMs) in solar heat collection:a review[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2023,63:107047/1-33. |
| 25 | ZHU J, LENG G, YE F,et al .Form-stable LiNO3-NaNO3-KNO3-Ca(NO3)2/calcium silicate composite phase change material (PCM) for mid-low temperature thermal energy storage[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2015,106:165-172. |
| 26 | FERNÁNDEZ A G, USHAK S, GALLEGUILLOS H,et al .Thermal characterisation of an innovative quaternary molten nitrate mixture for energy storage in CSP plants[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2015,132:172-177. |
| 27 | BONK A, BRAUN M, BAUER T .Phase diagram,thermodynamic properties and long-term isothermal stability of quaternary molten nitrate salts for thermal energy storage[J].Solar Energy,2022,231:1061-1071. |
| 28 | BROSSEAU D, KELTON J W, Det al RAY .Testing of thermocline filler materials and molten-salt heat transfer fluids for thermal energy storage systems in parabolic trough power plants[J].Journal of Solar Energy Engineering,2005,127(1):109-116. |
| 29 | CHRISTENSEN A N, NORBY P, HANSON J C,et al .Phase transition of KNO3 monitored by synchrotron X-ray powder diffraction[J].Journal of Applied Crystallography,1996,29(3):265-269. |
| 30 | WANG T, MANTHA D, REDDY R G .Novel low melting point quaternary eutectic system for solar thermal energy storage[J].Applied Energy,2013,102:1422-1429. |
| 31 | LI L, YU H, WANG X,et al .Thermal analysis of melting and freezing processes of phase change materials (PCMs) based on dynamic DSC test[J].Energy and Buildings,2016,130:388-396. |
| 32 | KWASI-EFFAH C C, EGWARE H O, OBANOR A I,et al .Development and characterization of a quaternary nitrate based molten salt heat transfer fluid for concentrated solar power plant[J].Heliyon,2023,9(5):e16096/1-12. |
| 33 | 崔贤岱 .熔融盐相变材料分子动力学模拟研究[D].武汉:武汉理工大学,2022. |
| 34 | NARESH G, RAJASEKHAR A, BHARALI J,et al .Homogeneous molten salt formulations as thermal energy storage media and heat transfer fluid[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2022,50:104200/1-8. |
| 35 | REN N, WU Y, MA C,et al .Preparation and thermal properties of quaternary mixed nitrate with low mel-ting point[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2014,127:6-13. |
| 36 | JIN Y, CHENG J, AN X,et al .Accurate viscosity measurement of nitrates/nitrites salts for concentrated solar power[J].Solar Energy,2016,137:385-392. |
| 37 | RAZZAGHPANAH Z, SARUNAC N .Natural convection heat transfer from a bundle of heated circular cylinders with staggered arrangement immersed in molten solar salt[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2020,156:119900/1-15. |
| 38 | AHMAD N N B, YUNOS N B, MUHAMMAD W N A B W,et al .Effect of lithium nitrate and calcium nitrate composition on the thermal properties of quaternary molten salts mixture for heat transfer application[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2017,914:012027/1-9. |
| 39 | ALJAERANI H A, SAMYKANO M, PANDEY A K,et al .Thermophysical properties enhancement and characterization of CuO nanoparticles enhanced HITEC molten salt for concentrated solar power applications[J].International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer,2022,132:105898/1-9. |
| 40 | XIONG Y, WANG Z, XU P,et al .Experimental investigation into the thermos-physical properties by dispersing nanoparticles to the nitrates[J].Energy Procedia,2019,158:5551-5556. |
| 41 | BONK A,SAU S, URANGA N,et al .Advanced heat transfer fluids for direct molten salt line-focusing CSP plants[J].Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2018,67:69-87. |
| 42 | TULIMON M F, MUHAMMAD W N A W, MOHAMAD M N A,et al .Characterization and thermal properties of nitrate based molten salt for heat reco-very system[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2017,914:012016/1-6. |
| 43 | 何聪,鹿院卫,宋文兵,等 .新型相同钠离子混合熔盐相图预测及物性测量[J].储能科学与技术,2021,10(5):1729-1734. |
| HE Cong, LU Yuanwei, SONG Wenbing,et al.The phase diagram prediction and experimental study of ternary same cation systems[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2021,10(5):1729-1734. | |
| 44 | RAADE J W, PADOWITZ D .Development of molten salt heat transfer fluid with low melting point and high thermal stability[J].Journal of Solar Energy Engineering,2011,133(3):031013/1-6. |
| 45 | QIAN T, LI J, MIN X,et al .Diatomite:a promi-sing natural candidate as carrier material for low,middle and high temperature phase change material[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2015,98:34-45. |
| 46 | LIN Q, XU Y, YANG X,et al .Thermal stability and microstructure of sodium nitrite in multicomponent molten salts:an experimental analysis[J].Solar Energy,2024,283:113008/1-10. |
| 47 | 倪海欧,孙泽,路贵民,等 .NaNO3-KNO3-NaNO2三元混合相变熔盐结构与物性的分子动力学模拟[J].储能科学与技术,2017,6(4):669-674. |
| NI Haiou, SUN Ze, LU Guimin,et al .Molecular dynamics simulation of structure and physical properties of NaNO3-KNO3-NaNO2 ternary phase-change molten salts [J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2017,6(4):669-674. | |
| 48 | OROZCO M A, ACURIO K, VÁSQUEZ-AZA F .Thermal storage of nitrate salts as phase change mate-rials (PCMs)[J].Materials,2021,14:7223/1-18. |
| [1] | LOU Bo, ZHOU Daheng, XIA Jun. Kinetics of Dehydration/Adsorption Reaction of LaCl3 [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(8): 71-79. |
| [2] | LI Yajun ZHANG Jinwen. Highly Accurate Prediction Models for Thermophysical Properties of PCMs [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(9): 131-138. |
| [3] | LIAO Junxu LU Hao DAI Kangxu CAO Hua ZHAO Hongbin HAN Lifen XU Yongjun FANG Yutang. Tribological Properties of Nitrogen-Containing Lubricant Additives [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(7): 70-78. |
| [4] | LI Jing CHEN Xuyang LEI Rubai ZHANG Ding FAN Chunlei. Research on Thermal Performance Of Bi-In-Sn-Sb Quaternary Alloy Interface Materials [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(11): 39-46. |
| [5] | CAI Ze-xiang YANG Huan-huan YU Chao-yun LI Xiao-hua. A Method to Assess Commutation Failure of HVDC Systems Taking Space-Time Discreteness into Consideration [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(7): 33-40. |
| [6] | XIAO Xin-yan ZHANG Deng-ke. Properties of Asphalt Modified with Montmorillonite After a Modification by Isophorone Diisocyanate [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(2): 116-121. |
| [7] | YIN Su-hong GAO Fan GUO Hui YANG Xu. Phase Change of Steel Slag During Reconstruction by Lime [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(6): 47-52. |
| [8] | Xiao Xin-yan Zhang Deng-ke Yan Ying Zhu Wen-qiang. Properties of Asphalt Modified with Organic Montmorillonite/Epoxy Resin [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(2): 139-143,150. |
| [9] | Zhao Li- ying Liu Ping- an Zeng Fan- cong Liao Ying- feng. Preparation and Properties of High Thermal Shock-Resistant Infrared Radiant Energy- Saving Coatings [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(6): 46-50. |
| [10] | Liu Shu-mei Feng Meng Sun Zhi-song Zhao Jian-qing Yuan Yan-chao. Synthesis and Properties of Spiro and Caged Bicyclic Phosphate [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(10): 25-30. |
| [11] | Ye Jun Li Wen- hao Xiong Jian. Synthesis,Structure and Thermal Property of Dialdehyde Carboxymethyl Cellulose Prepared at Low pH Value [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(6): 127-132. |
| [12] | Xiao Xin- yan Cai Xi- song Wan Cai- xia. Preparation and Film Properties of Cross- Linking Siliconated Polyurethane- Fluorinated Acrylate Hybrid Emulsion [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(10): 13-19. |
| [13] | Gao Xue-nong Li De-lun Sun Tao Cao Xin He Wen-xiang. Performance of Temperature-Controlled Electronic Heat Sink with Composite Paraffin /Expanded Graphite Phase Change Material [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(1): 7-12. |
| [14] | Li Hui Fu Shi-yu Peng Lin-cai Zhan Huai-yu. Immobilization of Laccase via Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly and Its Enzymatic Properties [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(9): 158-164. |
| [15] | Zuo Yuan-zhi Yang Xiao-xi Ding Jing. Heat Transfer Analysis on High-temperature Heat Exchanger of Shell & Tubes with Molten-salt Phase Change Materials [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(1): 42-47. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||