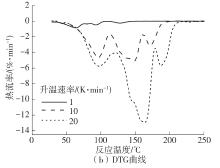
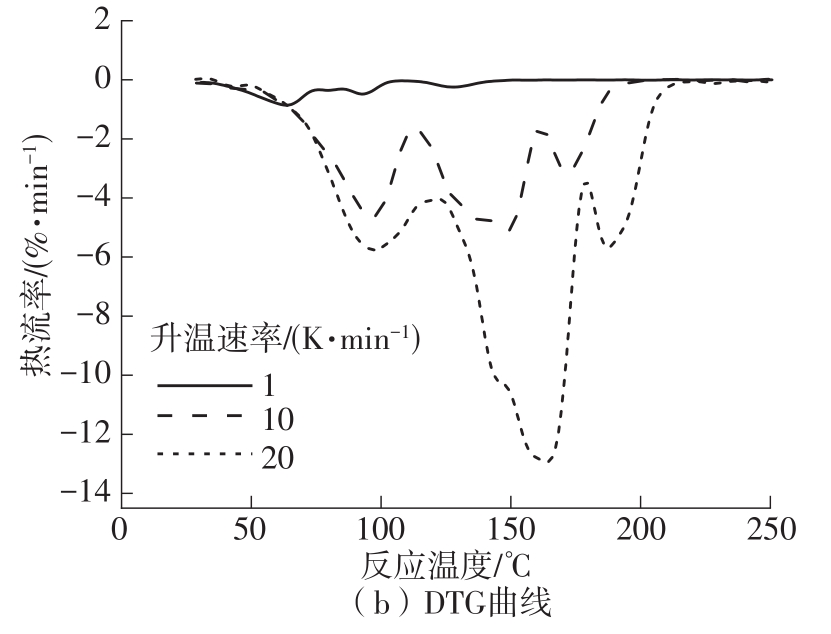
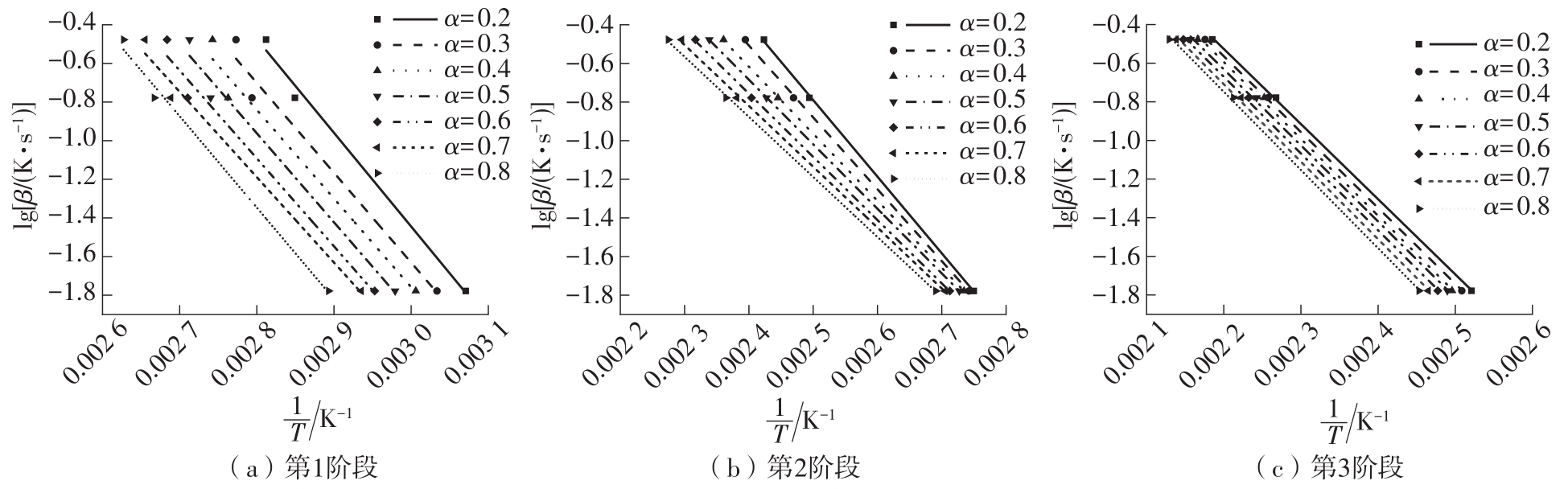
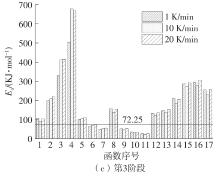
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 71-79.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220352
Special Issue: 2023年能源、动力与电气工程
Previous Articles Next Articles
Kinetics of Dehydration/Adsorption Reaction of LaCl3
LOU Bo ZHOU Daheng XIA Jun
- School of Electric Power Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-06-06Online:2023-08-25Published:2023-03-28 -
Contact:楼波(1965-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事燃烧理论与节能技术研究。 E-mail:loubo@scut.edu.cn -
About author:楼波(1965-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事燃烧理论与节能技术研究。 -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2021B1515020071)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LOU Bo, ZHOU Daheng, XIA Jun. Kinetics of Dehydration/Adsorption Reaction of LaCl3[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(8): 71-79.
share this article
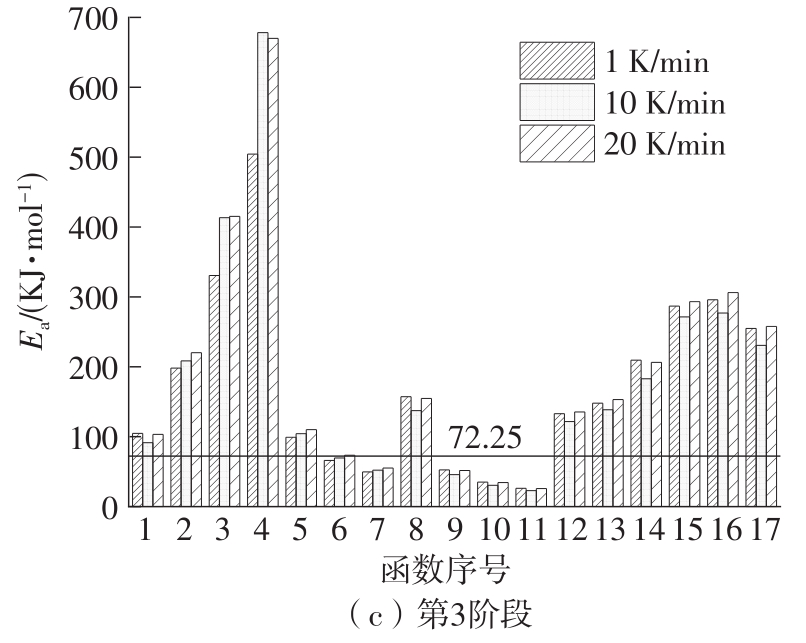
Table 2
Common solid decomposition mechanism functions"
| 序号 | 反应模型 | 模型编号 | f(α) | G(α) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 反应级数模型 | F0 | 1 | α |
| 2 | 反应级数模型 | F1 | 1-α | -ln(1-α) |
| 3 | 反应级数模型 | F2 | (1-α)2 | (1-α)-1-1 |
| 4 | 反应级数模型 | F3 | (1-α)3 | [(1-α)-2-1]/2 |
| 5 | 随机成核和随后生长 | A2 | 2(1-α)[-ln(1-α)]1/2 | [-ln(1-α)]1/2 |
| 6 | 随机成核和随后生长 | A3 | 3(1-α)[-ln(1-α)]2/3 | [-ln(1-α)]1/3 |
| 7 | 随机成核和随后生长 | A4 | 4(1-α)[-ln(1-α)]3/4 | [-ln(1-α)]1/4 |
| 8 | 幂函数法则 | P0 | (3/2)α-1/2 | α3/2 |
| 9 | 幂函数法则 | P2 | 2α1/2 | α1/2 |
| 10 | 幂函数法则 | P3 | 3α2/3 | α1/3 |
| 11 | 幂函数法则 | P4 | 4α3/4 | α1/4 |
| 12 | 几何收缩模型 | R2 | 2(1-α)1/2 | 1-(1-α)1/2 |
| 13 | 几何收缩模型 | R3 | 3(1-α)2/3 | 1-(1-α)1/3 |
| 14 | 扩散模型 | D1 | 1/(2α) | α2 |
| 15 | 扩散模型 | D2 | [-ln(1-α)]-1 | (1-α)ln(1-α)+α |
| 16 | 扩散模型 | D3 | (3/2)(1-α)2/3[1-(1-α)1/3]-1 | [1-(1-α)1/3]2 |
| 17 | 扩散模型 | D4 | (3/2)[(1-α)-1/3-1]-1 | [1-(2/3)α]-(1-α)2/3 |
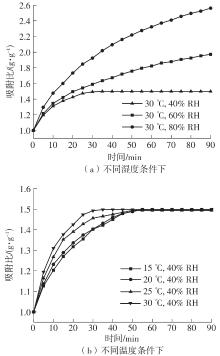
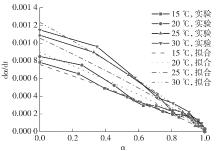
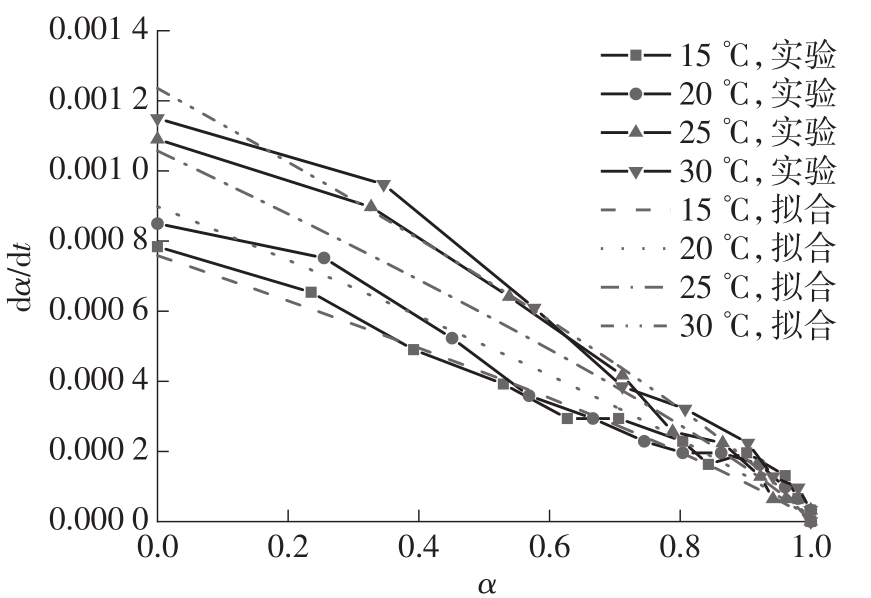
Table 3
Several common mechanism functions suitable for hydration reactions"
| 序号 | 反应模型 | 模型编号 | f(α) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 随机成核和随后生长 | A2 | 2(1-α)[-ln(1-α)]1/2 |
| 2 | 随机成核和随后生长 | A3 | 3(1-α)[-ln(1-α)]2/3 |
| 3 | 随机成核和随后生长 | A4 | 4(1-α)[-ln(1-α)]3/4 |
| 4 | 几何收缩模型 | R2 | 2(1-α)1/2 |
| 5 | 几何收缩模型 | R3 | 3(1-α)2/3 |
| 6 | 几何收缩模型 | R4 | 4(1-α)3/4 |
| 7 | 扩散模型 | D1 | 1/(2α) |
| 8 | 扩散模型 | D2 | -[1/ln(1-α)] |
| 9 | 扩散模型 | D3 | [3(1-α)2/3]/[2(1-(1-α)1/3)] |
| 10 | 扩散模型 | D4 | 3/[2((1-α)-1/3-1)] |
| 11 | 反应级数模型 | F1 | 1-α |
| 12 | 反应级数模型 | Fn | (1-α) n |
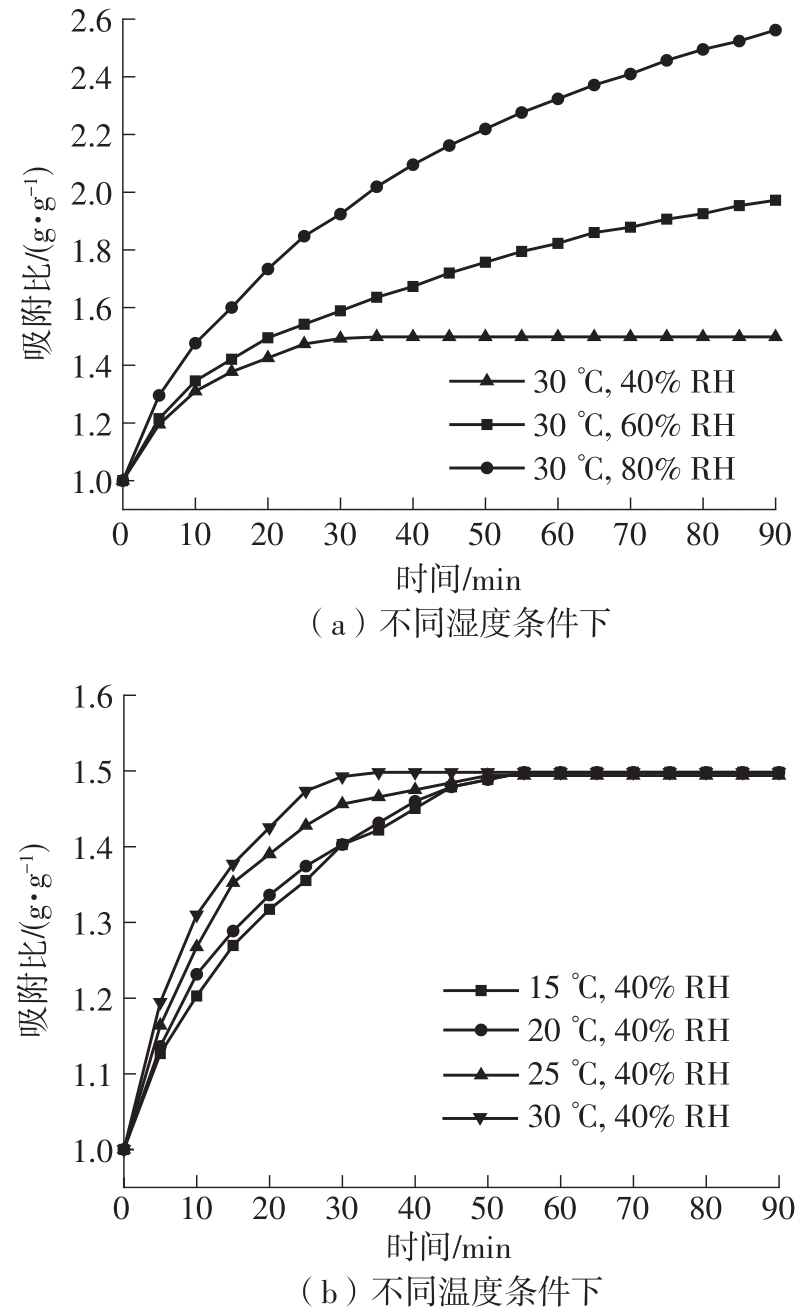
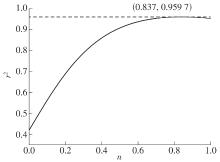
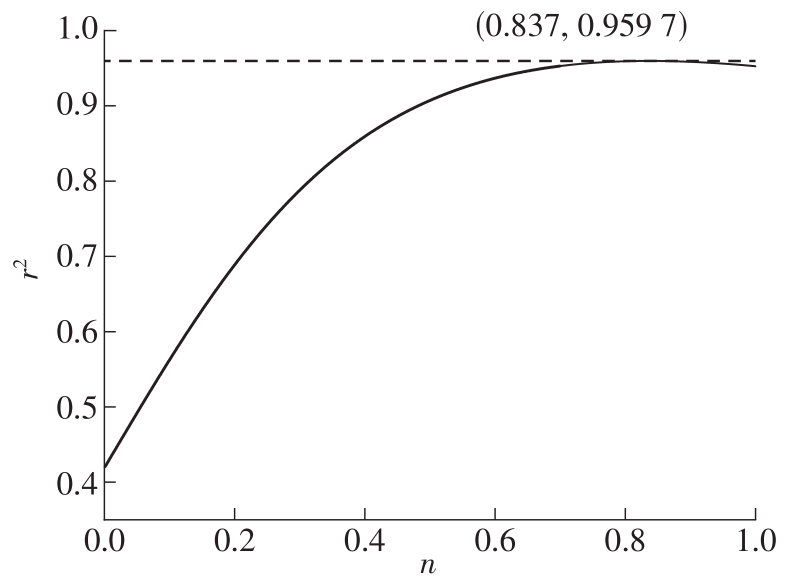
Table 4
Correlation of mechanism function f(α)"
| 序号 | r2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 ℃ | 20 ℃ | 25 ℃ | 30 ℃ | |
| 1 | 0.317 22 | 0.293 24 | 0.329 31 | 0.336 45 |
| 2 | 0.264 99 | 0.234 50 | 0.283 04 | 0.301 53 |
| 3 | 0.233 96 | 0.201 91 | 0.255 53 | 0.280 57 |
| 4 | 0.944 43 | 0.913 66 | 0.919 67 | 0.950 34 |
| 5 | 0.946 52 | 0.943 03 | 0.976 90 | 0.985 42 |
| 6 | 0.980 88 | 0.974 68 | 0.988 25 | 0.990 03 |
| 7 | 0.189 21 | 0.183 96 | 0.088 54 | 0.071 01 |
| 8 | 0.314 15 | 0.364 42 | 0.359 49 | 0.372 70 |
| 9 | 0.201 12 | 0.276 78 | 0.311 54 | 0.321 32 |
| 10 | 0.274 07 | 0.334 24 | 0.350 56 | 0.359 38 |
| 11 | 0.963 48 | 0.973 65 | 0.978 97 | 0.971 02 |
| 12 | 0.979 90 | 0.978 75 | 0.990 69 | 0.989 56 |
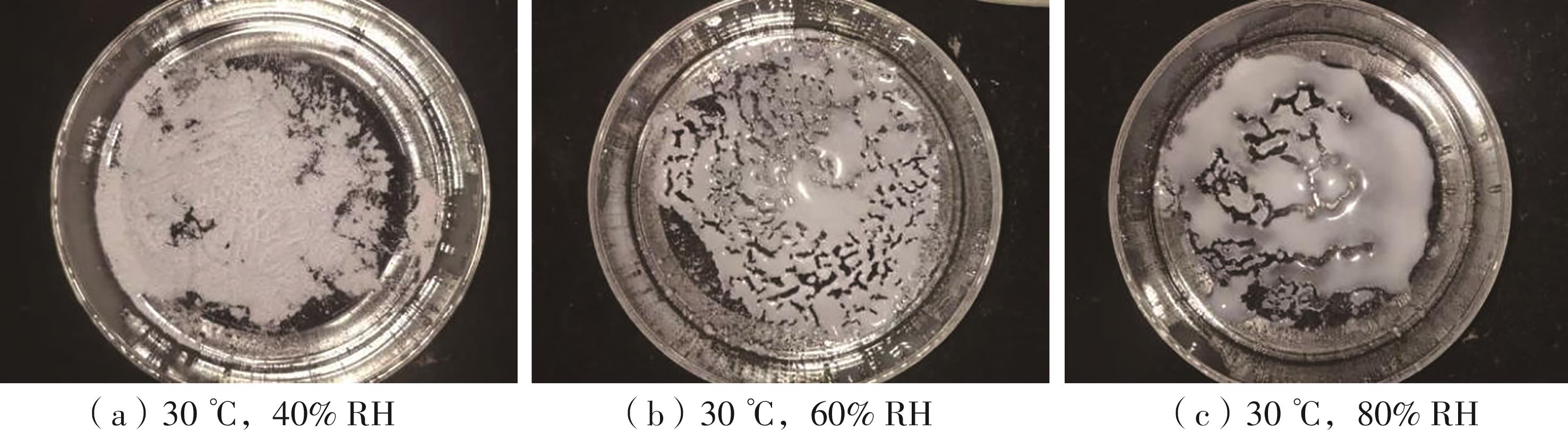
| 1 | YU N, WANG R Z, WANG L W .Sorption thermal storage for solar energy[J].Progress in Energy and Combustion Science,2013,39(5):489-514. |
| 2 | AYDIN D, CASEY S P, RIFFAT S .The latest advancements on thermochemical heat storage systems[J].Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews,2015,41:356-367. |
| 3 | KERSKES H, METTE B, BERTSCH F,et al .Development of a thermo-chemical energy storage for solar thermal applications[C]∥ Proceedings of the ISES Solar World Congress 2011.Germany-Stuttgart:International Solar Energy Society,2011:4679-4685. |
| 4 | KOUSKSOU T, BRUEL P, JAMIL A,et al .Energy storage:Applications and challenges[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2014,120:59-80. |
| 5 | ZHAO B C, WANG R Z .Perspectives for short-term thermal energy storage using salt hydrates for building heating[J].Energy,2019,189:116139/1-6. |
| 6 | 李威,陈威,王丹丹 .基于水合盐热化学储能的技术研究与进展[J].制冷与空调,2017,17(8):14-21. |
| LI Wei, CHEN Wei, WANG Dandan .Research and development of thermochemical energy storage based on hydrated salt[J].Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning,2017,17(8):14-21. | |
| 7 | 郝茂森,刘洪芝,王婉桐,等 .水合盐热化学储热材料的研究进展[J].储能科学与技术,2020,9(3):791-796. |
| HAO Maosen, LIU Hongzhi, WANG Wantong,et al .Researsh progress of thermochemical heat storage materials of hydrated salts[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2020,9(3):791-796. | |
| 8 | 翁立奎,张叶龙,姜琳,等 .基于水合盐的热化学吸附储热技术研究进展[J].储能科学与技术,2020,9(6):1729-1736. |
| WENG Likui, ZHANG Yelong, JIANG Lin,et al .Research progress on thermochemical adsorption heart storage technology based on hydrate[J].Energy Storage Science and Technology,2020,9(6):1729-1736. | |
| 9 | TRAUSEL F, JONG A, CUYPERS R .A review on the properties of salt hydrates for thermochemical storage[J].Energy Procedia,2014,48:447-452. |
| 10 | BALASUBRAMANIAN G, GHOMMEM M, HAJJ M R,et al .Modeling of thermochemical energy storage by salt hydrates[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2010,53(25/26):5700-5706. |
| 11 | CLARK R J, MEHRABADI A, FARID M .State of the art on salt hydrate thermochemical energy storage systems for use in building applications[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2020,27:101145/1-18. |
| 12 | 张雪龄,雷旭东,王菲菲,等 .水合无机盐热化学储热材料及技术研究进展[J].化工新型材料,2021,49(8):6-11. |
| ZHANG Xueling, LEI Xudong, WANG Feifei,et al .Research progress on hydrated salt thermochemical heat storage material and technology[J].New Chemical Materials,2021,49(8):6-11. | |
| 13 | N'TSOUKPOE K E, SCHMIDT T, RAMMELBERG H U,et al .A systematic multi-step screening of numerous salt hydrates for low temperature thermochemical energy storage[J].Applied Energy,2014,124:1-16. |
| 14 | 陈红兵,周昌勇,杨培志,等 .LaCl3:Ce3+晶体生长用无水氯化镧的制备[J].人工晶体学报,2006,35(4):686-691. |
| CHEN Hong-bing, ZHOU Chang-yong, YANG Pei-zhi,et al .Preparation of anhydrous lanthanum chloride for LaCl3:Ce3+ crystalg growth[J].Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2006,35(4):686-691. | |
| 15 | 龚政,陈佩珩,郭志箴,等 .七水氯化镧脱水过程的离解压和热效应[J].中国稀土学报,1985,3(2):13-16. |
| GONG Zheng, CHEN Peiheng, GUO Zhizhen,et al .Determination of dissociation pressure and thermal effect for dehydration process of lanthanum chloride heptahydrate[J].Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society,1985,3(2):13-16. | |
| 16 | 胡荣租,史启桢 .热分析动力学[M].北京:科学出版社,2001:1-18,47-112. |
| 17 | 陈梅倩,胡德豪,黄友旺 .基于热重分析法的生物质变温热解特性实验研究[J].华北电力大学学报(自然科学版),2019,46(6):99-104. |
| CHEN Meiqian, HU Dehao, HUANG Youwang .Experimental study on pyrolysis characteristics of biomass based on thermogravimetric analysis[J].Journal of North China Electric Power University(Natural Science),2019,46(6):99-104. | |
| 18 | CLARK R J, FARID M .Hydration reaction kinetics of SrCl2 and SrCl2-cement composite material for thermochemical energy storage[J].Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2021,231:111311/1-14. |
| 19 | FISHER R, DING Y, SCIACOVELLI A .Hydration kinetics of K2CO3,MgCl2 and vermiculite-based composites in view of low-temperature thermochemical energy storage[J].Journal of Energy Storage,2021,38:102561/1-18. |
| 20 | FEDUNIK-HOFMAN L, BAYON A, DONNE S W .Kinetics of solid-gas reactions and their application to carbonate looping systems[J].Energies,2019,12(2981):1-35. |
| 21 | LELE A F, KUZNIK F, RAMMELBERG H U,et al .Thermal decomposition kinetic of salt hydrates for heat storage systems[J].Applied Energy,2015,154:447-458. |
| 22 | LIAVITSKAYA T, VYAZOVKIN S .Delving into the kinetics of reversible thermal decomposition of solids measured on heating and cooling[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2017,121(28):15392-15401. |
| 23 | GAEINI M, SHAIK S A, RINDT C .Characterization of potassium carbonate salt hydrate for thermochemical energy storage in buildings[J].Energy and Buildings,2019,196:178-193. |
| 24 | 沈维道,蒋智敏,童钧耕 .工程热力学[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2001:341-346. |
| [1] |
LOU Bo XUE Yanzhen .
The Combustion Characteristic and Kinetic of Fuels Constituted with Sludge and Waste Cooking Oil
|
| [2] | ZHONG Li ZHANG Li HUANG Hong. Structure Characterization and Reaction Kinetics of TDI-TMP Prepolymer [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(6): 109-116. |
| [3] | Long Xin-feng Wu Juan. Thermal Decomposition Kinetics of Thermochemical Energy Storage System Ca(OH)2 /CaO [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(10): 75-81. |
| [4] | Chen Gang Liu Yu-sha Wen Ai He Bei-hai. Characteristic Analysis and Evaluation Model of Thermal Aging of Paper Based on Thermogravimetry [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(1): 19-23,29. |
| [5] | Zeng Xin-an Liu Xin-yu. Effect of Pulsed Electric Field on Esterification of Lactic Acid and Ethanol [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(12): 127-131. |
| [6] | Ma Yan Gao Nai-yun Yao Juan-juan Guo Hong-guang Zhang Ke-jia . Degradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Aqueous Solution by Ultrasonic Irradiation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(8): 147-152. |
| [7] | Huang Jun-kai Zheng Xue-ren Deng Wan-ling. Leakage Current and Noise Model of Polysilicon Thin-Film Transistors [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(10): 24-29,35. |
| [8] | Zhang Hui-ping Peng Guan-lan Yan Ying Guan Jian-yu Xiao Xin-yan . Intrinsic Reaction Kinetics CO on Cu-Mn of Catalytic Oxidation of Catalyst Bed [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(6): 13-16. |
| [9] | Li Xin Li Zhong Xia Qi-bi. Adsorption/Desorption Properties of Mesoporous Silca Gel Modified th CaCl2/LiCI [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 34(8): 13-17. |
| [10] | Xu Ke-feng Li Zhong Wei Shuai Xia Qi-bin. Efect of M icrowave on Reaction Activation Energy of Phenol Degradation by Fenton Reagent [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 33(12): 5-9. |
| [11] | Zhu Li-xin Cai Chang-geng Jia De-min. Polyethylene-glycol-modified Unsaturated Polyester Networks with High Crosslinking Degree(Ⅰ) : Curing Behaviors and Kinetics [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2004, 32(2): 4-9. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||