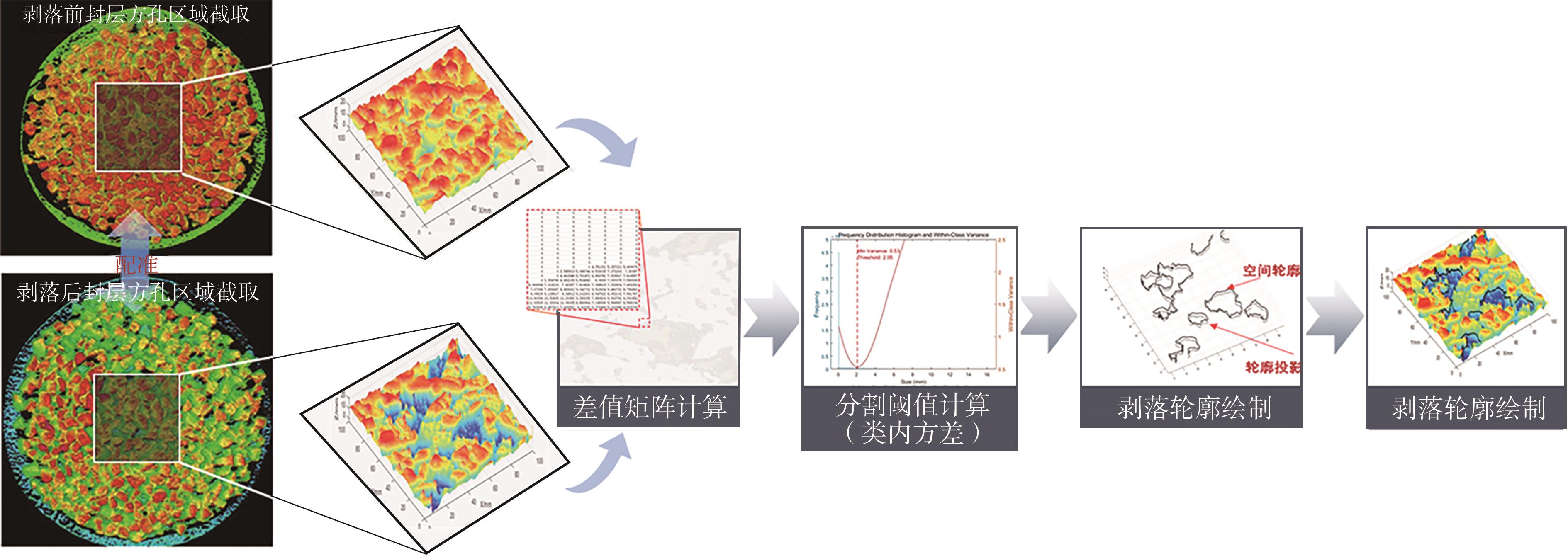
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 80-91.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240152
Previous Articles Next Articles
Quantitative Method of Aggregate Spalling Degree of Chip Seal in Three Dimension
ZHANG Yandi1, HUI Bing1,2, MA Ziye1, LI Yuanle1, WANG Hainian1,2
- 1.School of Highway,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710064,Shaanxi,China
2.Key Laboratory of Intelligent Construction and Maintenance of CAAC,Xi’an 710075,Shaanxi,China
-
Received:2024-04-03Online:2025-02-25Published:2025-02-03 -
Contact:惠冰(1982—),男,博士,教授,主要从事机场与沥青道路病害自动化检测研究。 E-mail:82628532@qq.com -
About author:张炎棣(1997—),男,博士生,主要从事沥青路面病害无损检测研究。E-mail: 506347241@qq.com -
Supported by:the National Key R & D Program of China(2021YFB2601000);the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52078048)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Yandi, HUI Bing, MA Ziye, LI Yuanle, WANG Hainian. Quantitative Method of Aggregate Spalling Degree of Chip Seal in Three Dimension[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(2): 80-91.
share this article
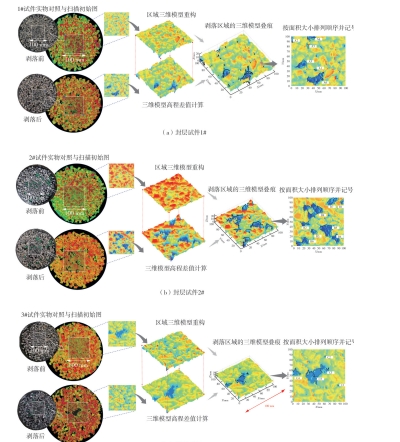
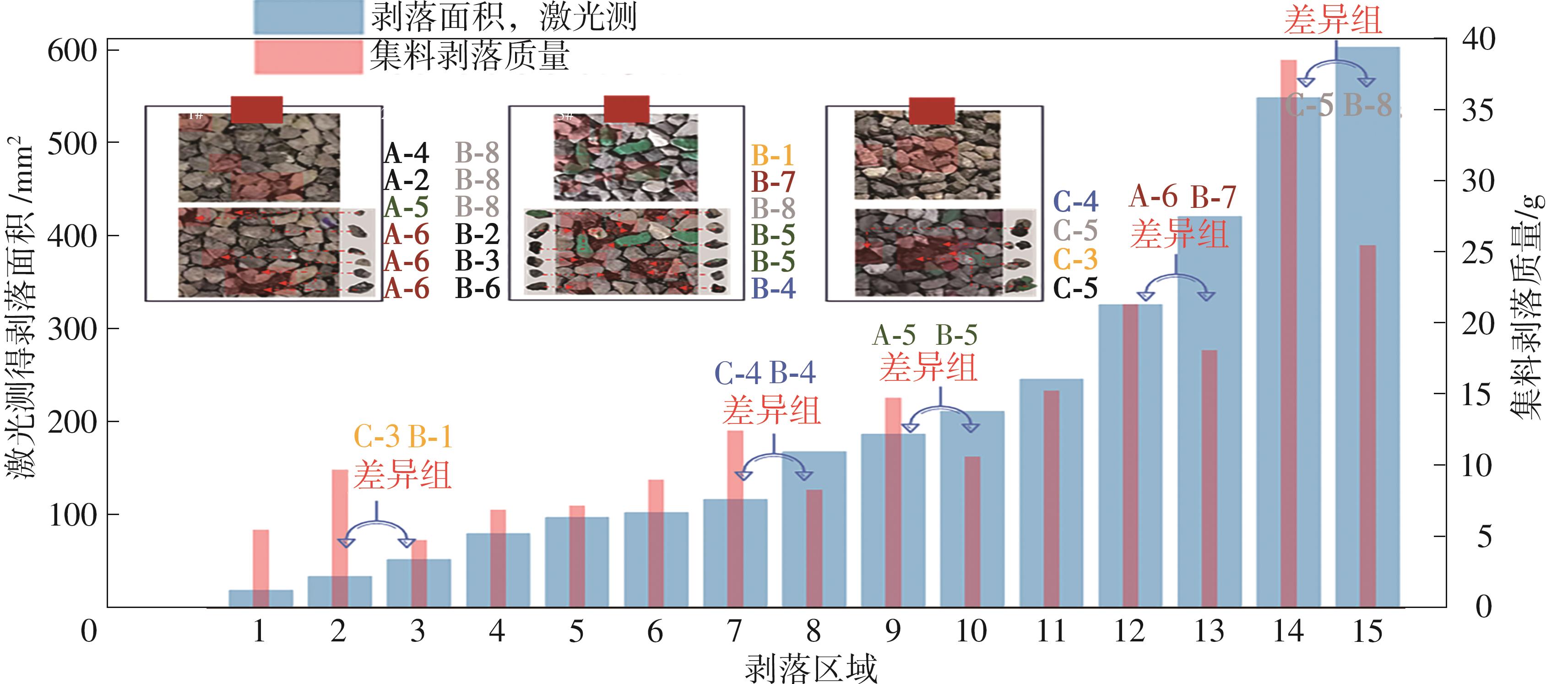
Table 3
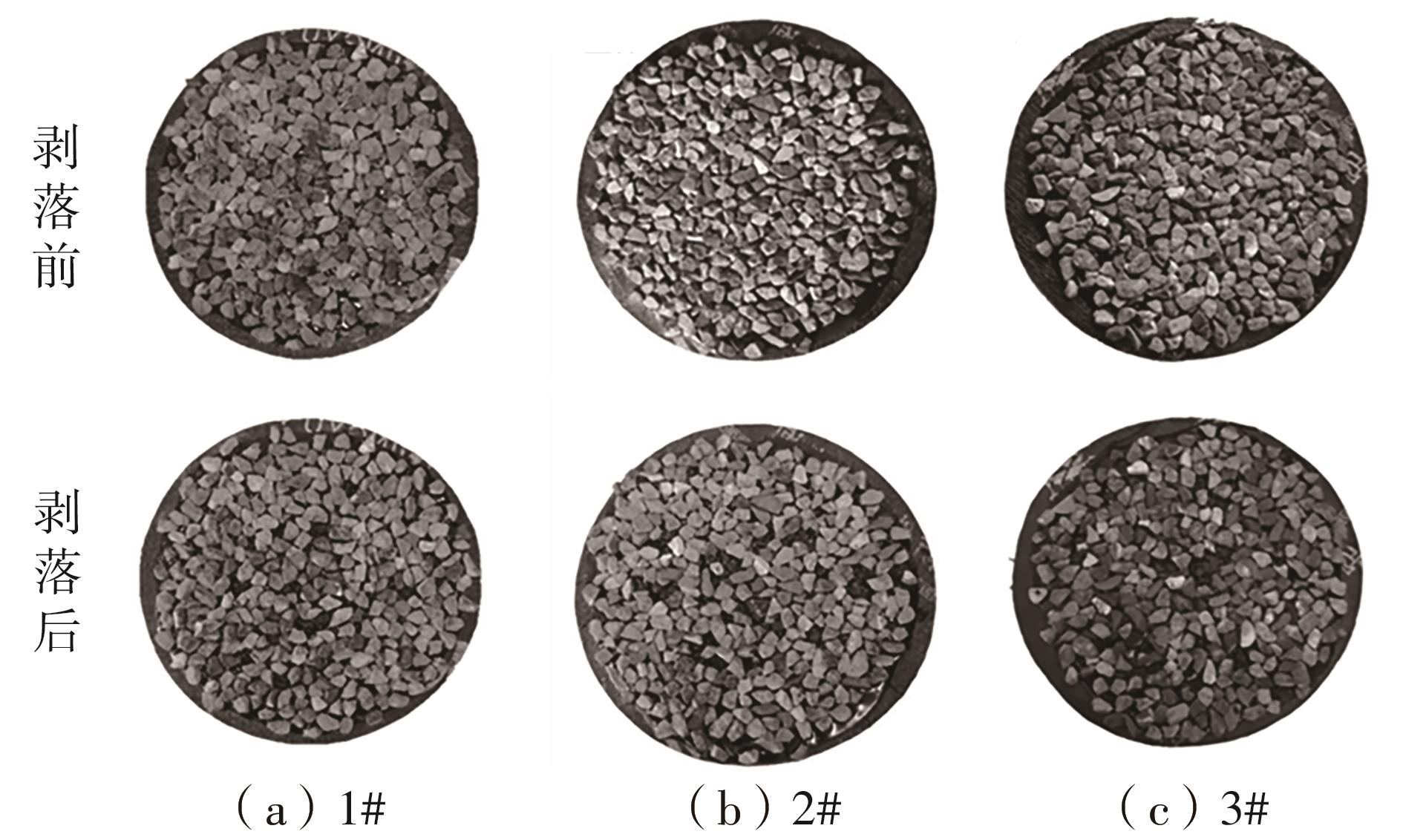
Pattern of spalling overlap of specimens and the result of spalling area"
| 区域 | 1#试件 | 区域 | 2#试件 | 区域 | 3#试件 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | |||||||
| A1 | 11.3 | 3.2 | 14.5 | 1.9 | 10.6 | B1 | 52.3 | 55.6 | 52.5 | 50.7 | 51.2 | C1 | 7.5 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 11.9 | ||||
| A2 | 20.1 | 17.5 | 19.4 | 23.5 | 17.8 | B2 | 97.1 | 100.9 | 98.7 | 93.5 | 96.4 | C2 | 16.1 | 11.6 | 1.3 | 13.3 | 9.5 | ||||
| A3 | 24.2 | 8.6 | 18.6 | 24.6 | 18.8 | B3 | 100.2 | 107.5 | 99.6 | 101.5 | 103.1 | C3 | 33.3 | 37.2 | 32.3 | 35.7 | 34.1 | ||||
| A4 | 82.1 | 75.5 | 83.3 | 79.2 | 79.5 | B4 | 167.6 | 163.6 | 170.5 | 165.4 | 168.7 | C4 | 115.7 | 120.6 | 116.4 | 115.8 | 114.3 | ||||
| A5 | 183.5 | 188.6 | 190.3 | 185.3 | 181.7 | B5 | 210.2 | 214.3 | 207.9 | 205.6 | 212.5 | C5 | 544.4 | 542.5 | 542.7 | 543.9 | 545.2 | ||||
| A6 | 323.2 | 325.6 | 320.9 | 319.7 | 329.5 | B6 | 244.2 | 241.6 | 249.5 | 244.4 | 242.8 | ||||||||||
| B7 | 418.1 | 413.4 | 415.2 | 422.3 | 417.9 | ||||||||||||||||
| B8 | 597.2 | 603.2 | 596.4 | 595.8 | 594.3 | ||||||||||||||||
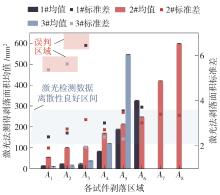
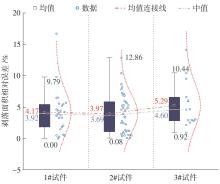
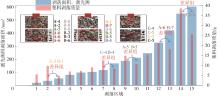
Table 5
Comparison of mass loss and spalling area about spa-lling aggregate"
| 区域 | 剥落面积/mm² | 集料剥落质量/g | 试件类型与颗粒标记 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 激光 | 人工 | |||
| 1 | 19.66 | 19.40 | 5.50 | A-2 |
| 2 | 34.52 | 32.60 | 9.70 | C-3 |
| 3 | 52.46 | 55.20 | 4.80 | B-1 |
| 4 | 79.92 | 79.00 | 6.90 | A-4 |
| 5 | 97.32 | 89.40 | 7.20 | B-2 |
| 6 | 102.38 | 100.60 | 9.00 | B-3 |
| 7 | 116.56 | 109.20 | 12.40 | C-4 |
| 8 | 167.16 | 159.20 | 8.30 | B-4 |
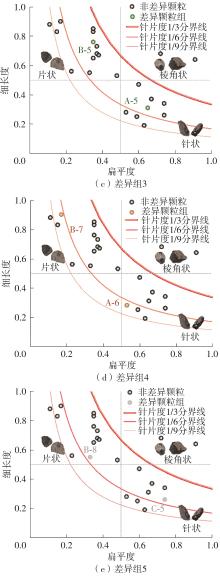
| 9 | 185.88 | 182.60 | 14.70 | A-5 |
| 10 | 210.10 | 215.40 | 10.60 | B-5 |
| 11 | 244.50 | 241.40 | 15.20 | B-6 |
| 12 | 323.78 | 309.40 | 21.20 | A-6 |
| 13 | 417.38 | 413.00 | 18.00 | B-7 |
| 14 | 543.74 | 529.00 | 38.20 | C-5 |
| 15 | 597.38 | 564.60 | 25.30 | B-8 |
| 1 | 于华洋,马涛,王大为,等 .中国路面工程学术研究综述·2020[J].中国公路学报,2020,33(10):1-66. |
| YU Huayang, MA Tao, WANG Dawei,et al .Review of academic research on Road Surface Engineering in China·2020[J].China Journal of Highway and Transportation,2020,33(10):1-66. | |
| 2 | HAIDER S W,BOZ I, KUMBARGERI Y,et al .Development of performance related specifications for chip seal treatments[J].International Journal of Pavement Engineering,2021,22(3):382-391. |
| 3 | 陈素丽,许福文,李桂芝 .同步碎石封层技术研究及在公路养护中的应用[J].公路,2005(6):174-181. |
| CHEN Suli, XU Fuwen, LI Guizhi .Research on synchronous gravel sealing technology and its application in highway maintenance[J].Highway,2005(6):174-181. | |
| 4 | KUMBARGERI Y S,BOZ I, KUTAY M E .Investiga-ting the effect of binder and aggregate application rates on performance of chip seals via digital image processing and sweep tests[J].Construction and Building Materials,2019,222:213-221. |
| 5 | 覃峰,包惠明 .同步碎石封层脱石率的试验研究[J].路基工程,2008,140(5):111-113. |
| QIN Feng, BAO Huiming. Experimental study on removal rate of synchronous gravel sealing layer[J].Roadbed Engineering,2008,140(5):111-113. | |
| 6 | 刘丽,杨森,郝培文 .基于沥青—集料粘结性能的碎石封层技术性能影响因素研究[J].武汉理工大学学报,2013,35(11):52-57. |
| LIU Li, YANG Sen, HAO Peiwen .Study on Influen-cing factors of technical performance of gravel sealing layer based on bitumen aggregate bonding property[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology,2013,35(11):52-57. | |
| 7 | 王忠勇,闫飞宇,姚江敏 .基于边缘检测的一种碎石撒布覆盖率检测方法[J].电子设计工程,2013,21(23):191-193. |
| WANG Zhongyong, YAN Feiyu, YAO Jiangmin. A detection method of gravel spread coverage based on edge detection[J].Electronic Design Engineering,2013,21(23):191-193. | |
| 8 | 赵含 .碎石封层评价方法与层间粘结性能的研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2010. |
| 9 | 惠冰,郭牧,刘晓芳 .三维激光数据密度对路面构造深度检测的影响[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(11):142-149,156. |
| HUI Bing, GUO Mu, LIU Xiaofang .Influence of 3D laser data density on depth detection of pavement structure[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2018,46(11):142-149,156. | |
| 10 | 惠冰,郭牧,王洲,等 .基于三维激光技术的路面坑槽多维度指标检测[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2018,46(1):60-66. |
| HUI Bing, GUO Mu, WANG Zhou,et al .Multi-dimensional index detection of potholes based on 3D laser technology[J].Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2018,46(1):60-66. | |
| 11 | 刘晓芳 .隧道水泥路面精铣刨宏观纹理表征与衰变规律研究[D].西安:长安大学,2019. |
| 12 | 周兴林,祝媛媛,冉茂平,等 .基于分段变维的沥青路表纹理磨光行为分析[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(4):187-195,242. |
| ZHOU Xing-lin, ZHU Yuan-yuan, RAN Mao-ping,et al .Analysis of texture polishing behavior of asphalt pavement based on segmented variable dimension[J].China Journal of Highway and Transportation,2019,32(4):187-195,242. | |
| 13 | 战友,李强,马啸天,等 .基于宏微观纹理特征融合的路面摩擦性能预测[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2021,55(4):684-694. |
| ZHAN You, LI Qiang, MA Xiaotian,et al .Pavement friction performance prediction based on macro and micro texture feature fusion[J].Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering and Technology),2021,55(4):684-694. | |
| 14 | TSAI Y, WU Y, LEWIS Z .Full-lane coverage micromilling pavement-surface quality control using emerging 3D line laser imaging technology[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering,2014,140(2):04013006. |
| 15 | HUI B, ZHANG Y, MA Z,et al .Identification and evaluation of spalling aggregate in chip seals in three dimensions[J].Construction and Building Materials,2023,364:129899. |
| 16 | JOHANNES P T, MAHMOUD E, BAHIA H .Sensitivity of ASTM D7000 Sweep test to emulsion application rate and aggregate gradation[J].Transportation research record,2011,2235(1):95-102. |
| 17 | 公路沥青路面养护技术规范: [S]. |
| 18 | 马子业,汪海年,张炎棣,等 .碎石封层的集料嵌挤状态与抗剥落性[J].建筑材料学报,2023,26(8):906-913. |
| MA Ziye, WANG Hainian, ZHANG Yandi,et al .Compaction state and spalling resistance of aggregates in crushed stone sealing layer [J].Journal of Building Materials,2023,26(8):906-913. | |
| 19 | Standard test method for sweep test of bituminous emulsion surface treatment samples: [S]. |
| 20 | LI F .A methodology for characterizing pavement rutting condition using emerging 3D line laser imaging technology[D].Georgia:Georgia Institute of Technology,2012. |
| 21 | 公路工程集料试验规程: [S]. |
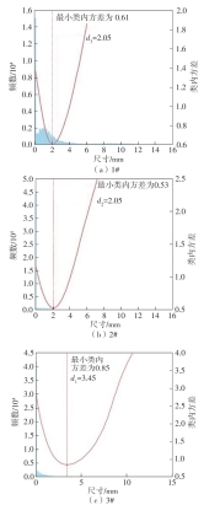
| 22 | 魏武,姜莉,王新梅 .基于最小类内方差的蛇形机器人多阈值分割[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2013,41(5):9-14. |
| WEI Wu, JIANG Li, WANG Xin-mei .Multi-threshold segmentation of snake robot based on minimum intra-class variance[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2013,41(5):9-14. |
| [1] | ZHANG Chi, GUO Tingyu, HU Ruilai, GAO Yanyang, ZHOU Yuming. Research on Average Longitudinal Slope Length of Expressway Based on Braking Behavior [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(2): 12-26. |
| [2] | WANG Duanyi, LI Yanbiao, PAN Yanzhu. Skid Resistance Deterioration and Influencing Factors of Ultra-Thin Wear Layer [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 1-9. |
| [3] | ZHENG Zhi, GUO Naisheng, YOU Zhanping. Molecular Simulation of Interaction Behavior Between Asphalt Components and Waste Wood Oil [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(12): 79-86. |
| [4] | WANG Wei, TAN Yiqiu, XU Yongjiang. Study on Internal Stress of Asphalt Mixture Under Three-Point Bending Mode [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(10): 101-111. |
| [5] | LI Baijian, HUANG Yan, FU Xinsha. Influence of Shapes of Corrugated Steel Plate on Load-Carrying Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Slab Culvert and Arch Effect with Lateral Restraint [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 110-118. |
| [6] | MAO Xuesong, WANG Yueyue, WU Qian, et al. Structure Evolution Law of Soil-Rock Mixture Fillers with Different Gradations Under Seepage [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(2): 65-75. |
| [7] | YU Bin, ZHANG Yuqin, WANG Yuchen, et al. Automated Extraction of Road Geometry Information Using Mobile LiDAR Point Cloud [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(2): 88-99. |
| [8] | ZHANG Chi, REN Shipeng, WANG Bo, et al. Speed Characteristics and Prediction of Trucks on Long and Steep Downgrade Sections [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(3): 38-49. |
| [9] | FU Guozhi, WEI Jincheng, ZHAO Yanqing, et al. Influence of Asphalt Pavements' Dynamic Effects on the Surface Acceptance Deflection [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(4): 90-96. |
| [10] | AI Changfa, HUANG Yangquan, LUO Liufen, et al. Estimation of Comprehensive Impact of External Factors on Interlayer Fatigue Life of Asphalt Pavement Based on ISS & SSDR [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(5): 58-66,74. |
| [11] | ZHANG Chi, HU Tao, LIN Xuancai, et al. Research on Exclusive Low-Speed Lane for Large Truck in Highway Continuous Long Downhill Section [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(4): 104-113. |
| [12] | LI Baijian ZHU Liangsheng FU Xinsha LI Yong . Mechanical Properties of Two Kinds of Lined Reinforced Concrete Pipe Culvert [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(6): 101-107. |
| [13] | ZHU Jianghong HAN Shuxian TONG Yanmei LI Yan YU Rongguang ZHANG Huyuan. Effect of Dry-Wet Cycles on the Deterioration of Sandstone with Various Initial Dry Densities [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(3): 126-134. |
| [14] | ZHANG Chi HOU Yudi QIN Jihan ZHANG Hong. Safety Design Method of Long Slope Downhill Slope Based on Temperature Increase of Brake Drum [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(10): 139-150. |
| [15] | LI Baijian FU Xinsha ZHU Liangsheng. Research on Mechanical Properties of Corrugated Steel Plate with Relieving Slab Based on Equivalent Stiffness#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 131-139. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||