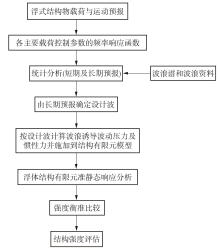
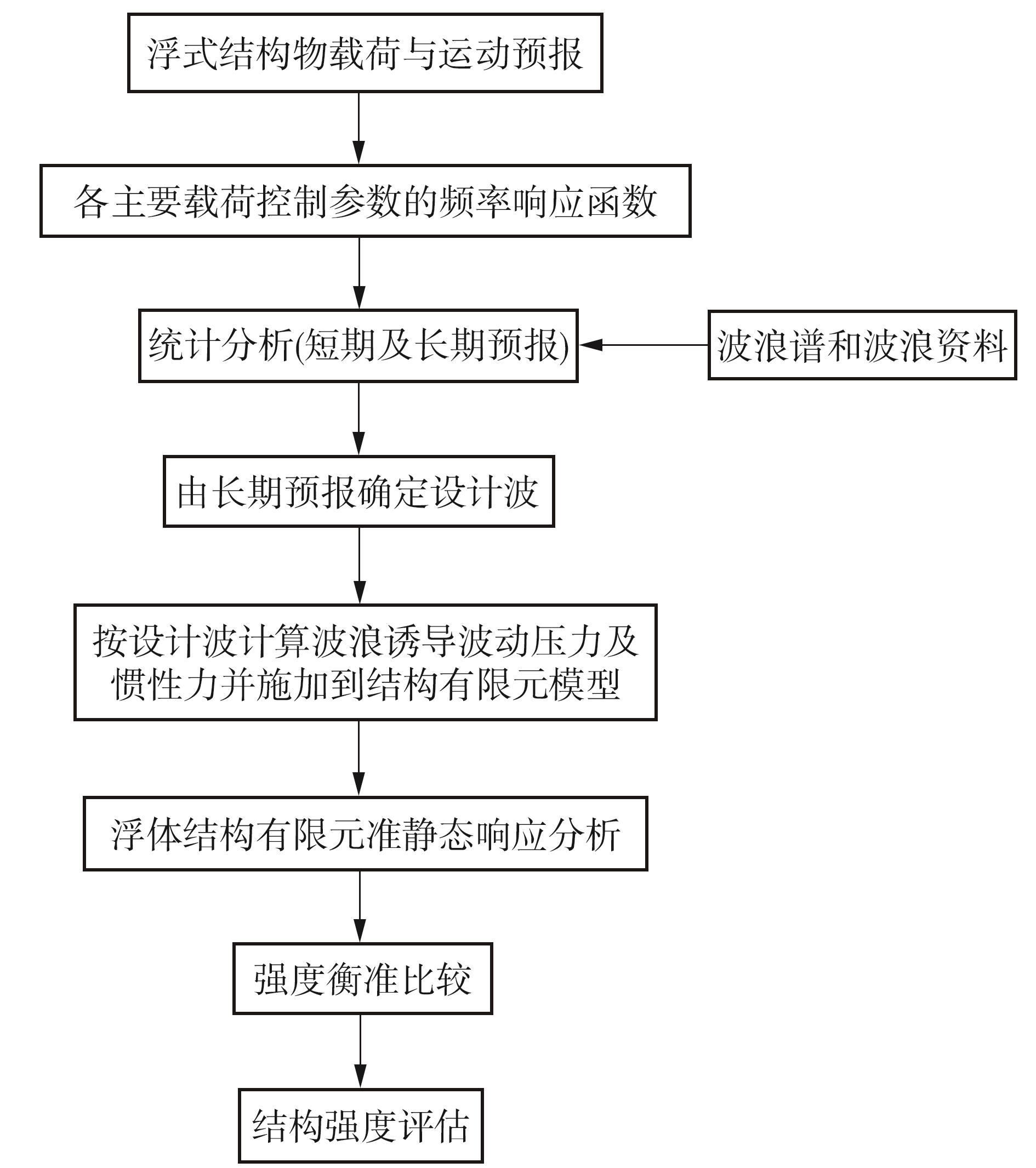
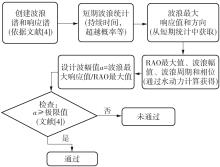
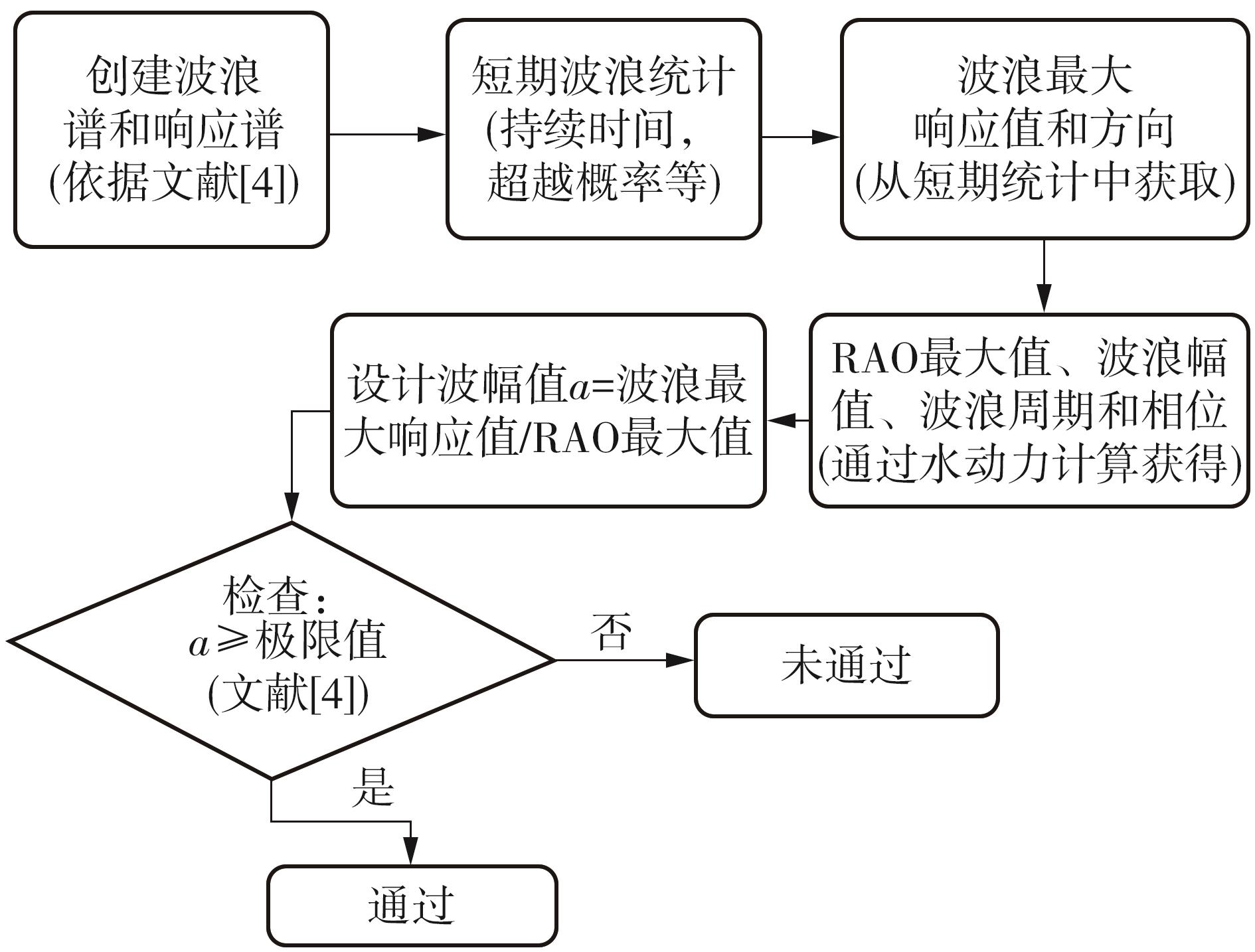
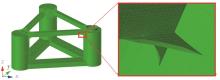
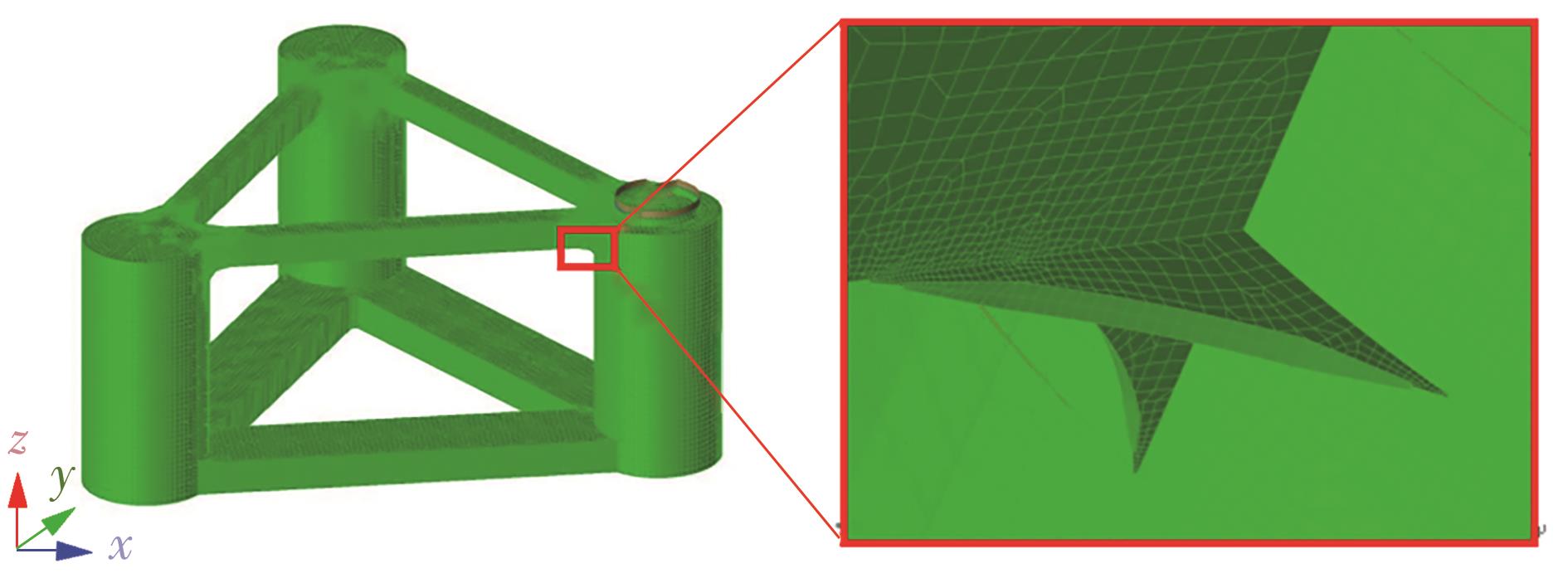
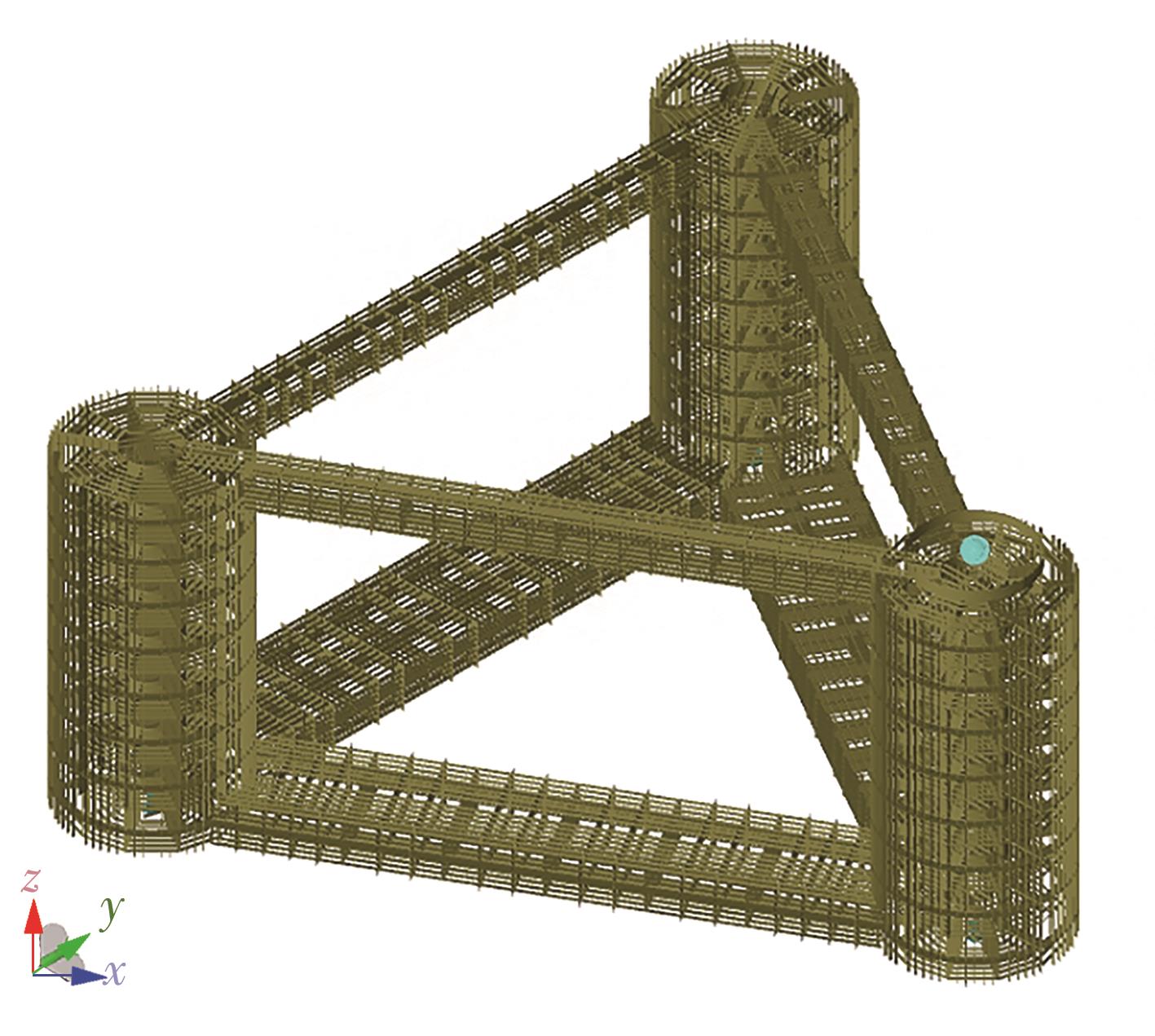
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 92-106.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240165
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on the Structural Strength of Floating Offshore Wind Turbine Platform Based on Long and Short Term Design Waves
LI Ping, WANG Hongbo, CHEN Chaohe
- School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2024-04-09Online:2025-02-25Published:2025-02-03 -
Contact:陈超核(1962—),男,教授,博士生导师,主要从事船舶与海洋结构设计研究。 E-mail:chenchaohe@scut.edu.cn -
About author:李平(1989—),男,博士生,主要从事海洋结构物结构设计研究。E-mail: liping_1013@163.com -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51979111);the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province(2020B1111010001)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Ping, WANG Hongbo, CHEN Chaohe. Research on the Structural Strength of Floating Offshore Wind Turbine Platform Based on Long and Short Term Design Waves[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(2): 92-106.
share this article
Table 1
Wave probability for the South China Sea S4 region"
| 有义波高/m | 概率 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.51) | 41) | 51) | 61) | 71) | 81) | 91) | 101) | 111) | |
| 0~0.50 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.029 | 0.029 | 0.015 | 0.005 | 0.001 | — | — |
| 0.50~0.85 | — | 0.008 | 0.031 | 0.037 | 0.021 | 0.008 | 0.002 | — | — |
| 0.85~1.25 | — | 0.007 | 0.034 | 0.050 | 0.033 | 0.013 | 0.004 | 0.001 | — |
| 1.25~1.85 | — | 0.005 | 0.037 | 0.072 | 0.057 | 0.025 | 0.008 | 0.002 | — |
| 1.85~2.50 | — | 0.001 | 0.019 | 0.055 | 0.057 | 0.03 | 0.010 | 0.002 | — |
| 2.50~3.25 | — | — | 0.007 | 0.032 | 0.046 | 0.031 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| 3.25~4.00 | — | — | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.024 | 0.022 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| 4.00~5.00 | — | — | — | 0.002 | 0.012 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| 5.00~6.00 | — | — | — | — | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| 6.00~7.50 | — | — | — | — | — | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| 7.50~9.00 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.001 | 0.001 | — |
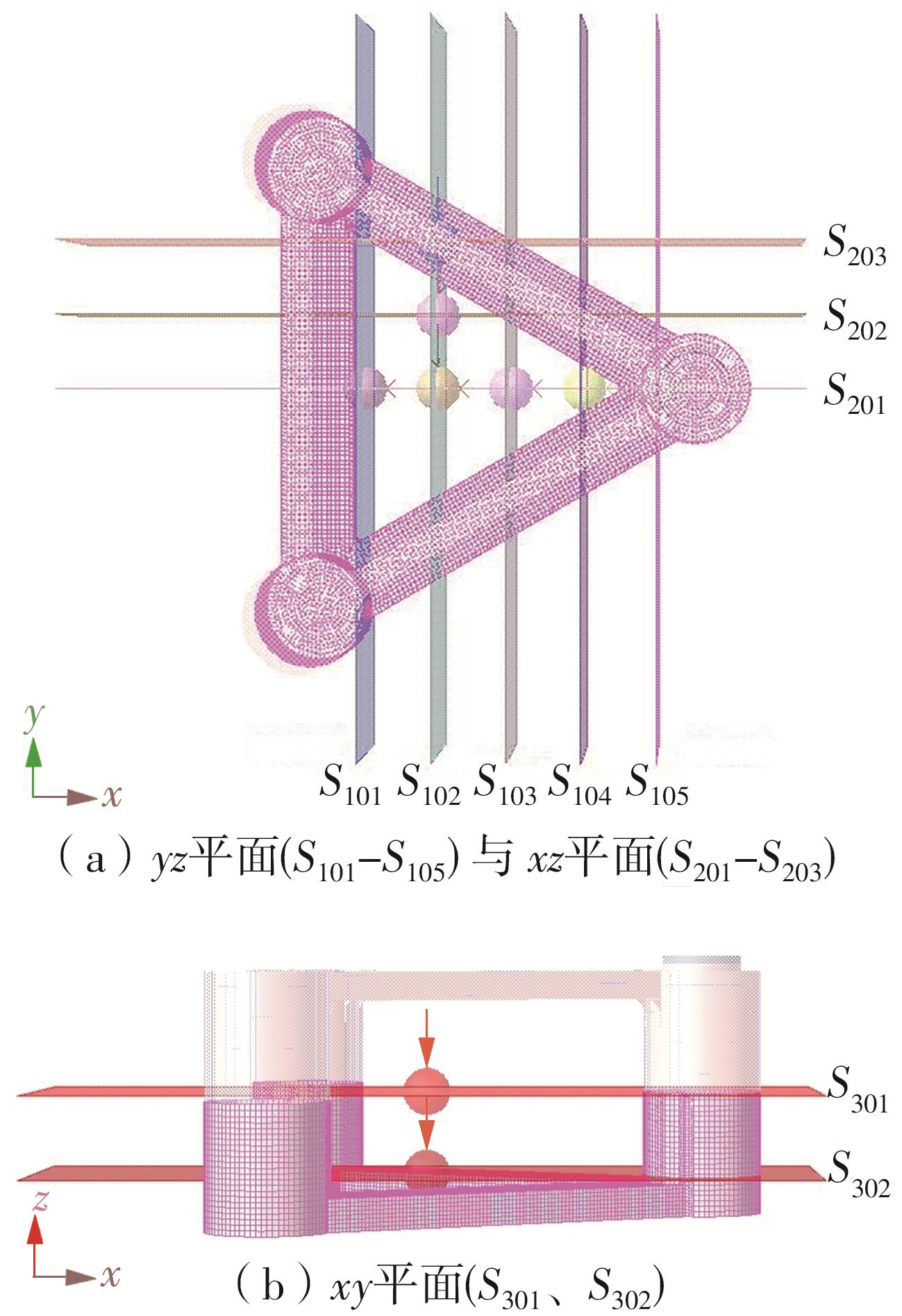
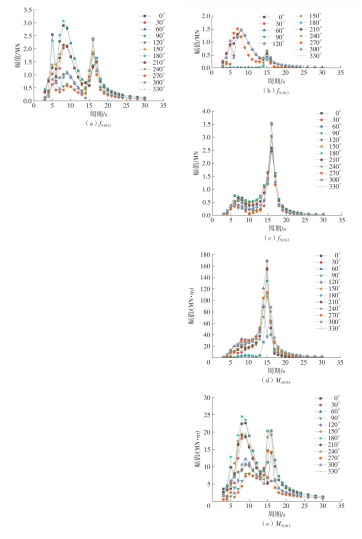
Table 6
Cross-section loads selected for design waves"
| 剖面载荷名称 | 物理意义 |
|---|---|
| f | x方向分离力 |
| fS1012/MN | y方向剪切力 |
| fS1013/MN | z方向剪切力 |
| M | 绕x轴扭矩 |
| MS1015/(MN·m) | 绕y轴弯矩 |
| fS2011/MN | x方向剪切力 |
| fS2012/MN | y方向分离力 |
| fS2013/MN | z方向剪切力 |
| MS2014/(MN·m) | 绕x轴弯矩 |
| MS2015/(MN·m) | 绕y轴扭矩 |
| fS3011/MN | x方向剪切力 |
| fS3012/MN | y方向剪切力 |
| fS3013/MN | z方向分离力 |
| MS3014/(MN·m) | 绕x轴弯矩 |
| MS3015/(MN·m) | 绕y轴弯矩 |
Table 7
Design wave parameters based on long-term design wave methods"
| 载荷控制参数 | 长期统计值 | RAO最大值 | 浪向/(°) | 波浪周期/s | 相位/(°) | 波高/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fS1011 | 13.90 | 3.07 | 180 | 8 | 8.177 | 9.07 |
| fS1012 | 7.76 | 1.51 | 270 | 7 | -112.214 | 10.29 |
| fS1013 | 9.83 | 3.54 | 120 | 16 | -158.407 | 5.55 |
| MS1014 | 538.00 | 168.0 | 240 | 15 | 56.750 | 6.40 |
| MS1015 | 129.00 | 24.5 | 180 | 8 | -176.812 | 10.49 |
| fS1021 | 13.40 | 3.03 | 180 | 8 | 9.634 | 8.84 |
| fS1022 | 8.03 | 1.58 | 300 | 8 | -153.560 | 10.17 |
| fS1023 | 5.80 | 2.03 | 120 | 16 | -147.994 | 5.71 |
| MS1024 | 399.00 | 129.00 | 60 | 15 | -58.019 | 6.22 |
| MS1025 | 150.00 | 28.50 | 0 | 8 | 131.866 | 10.54 |
| fS1031 | 13.00 | 2.95 | 180 | 8 | 10.986 | 8.81 |
| fS1032 | 8.03 | 1.62 | 300 | 8 | -156.089 | 9.90 |
| fS1033 | 5.15 | 1.75 | 0 | 16 | 60.104 | 5.88 |
| MS1034 | 314.00 | 103.0 | 60 | 15 | -57.936 | 6.08 |
| MS1035 | 173.00 | 32.4 | 120 | 16 | -150.027 | 10.65 |
| fS1041 | 12.80 | 2.84 | 180 | 8 | 12.058 | 9.04 |
| fS1042 | 7.80 | 1.62 | 270 | 6 | -106.351 | 9.64 |
| fS1043 | 9.00 | 3.59 | 0 | 16 | 41.224 | 5.01 |
| MS1044 | 260.00 | 86.8 | 60 | 15 | -57.979 | 5.99 |
| MS1045 | 199.00 | 47.0 | 150 | 16 | -101.221 | 8.45 |
| fS1051 | 21.80 | 7.77 | 0 | 16 | -146.089 | 5.62 |
| fS1052 | 6.93 | 1.44 | 270 | 6 | -107.195 | 9.61 |
| fS1053 | 13.40 | 5.20 | 0 | 16 | 37.708 | 5.17 |
| MS1054 | 222.00 | 74.4 | 60 | 15 | -58.162 | 5.97 |
| MS1055 | 326.00 | 111.0 | 0 | 16 | 54.424 | 5.89 |
| fS2011 | 7.71 | 1.60 | 90 | 6 | 76.318 | 9.65 |
| fS2012 | 34.60 | 13.20 | 0 | 16 | -142.254 | 5.23 |
| fS2013 | 3.76 | 0.92 | 150 | 7 | 66.961 | 8.13 |
| MS2014 | 370.00 | 116.0 | 300 | 15 | 118.912 | 6.39 |
| MS2015 | 227.00 | 69.4 | 60 | 15 | 122.961 | 6.53 |
| fS2021 | 9.31 | 1.88 | 330 | 8 | 168.148 | 9.89 |
| fS2022 | 13.90 | 2.88 | 0 | 16 | -167.726 | 9.67 |
| fS2023 | 6.49 | 2.08 | 150 | 16 | 88.435 | 6.26 |
| MS2024 | 187.00 | 51.4 | 180 | 16 | 113.099 | 7.28 |
| MS2025 | 221.00 | 59.8 | 120 | 16 | 20.883 | 7.37 |
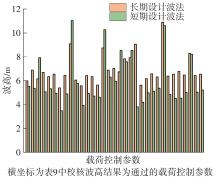
Table 9
Design wave parameters based on short-term design wave method"
| 载荷控制参数 | 短期预报响应最大值 | RAO最大值 | 浪向/(°) | 波浪周期/s | 波高/m | 波高极限/m | 校核波高 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fS1011 | 19.50 | 2.84 | 180 | 9 | 13.73 | 13.36 | 否决 |
| fS1012 | 9.39 | 1.26 | 330 | 9 | 14.91 | 13.36 | 否决 |
| fS1013 | 6.55 | 2.56 | 180 | 16 | 5.12 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| MS1014 | 419.00 | 168.00 | 240 | 15 | 4.98 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| MS1015 | 161.00 | 24.50 | 180 | 8 | 13.16 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1021 | 19.10 | 3.03 | 180 | 8 | 12.63 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1022 | 9.55 | 1.49 | 330 | 8 | 12.78 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1023 | 4.95 | 1.34 | 0 | 16 | 7.37 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| MS1024 | 302.00 | 129.00 | 60 | 15 | 4.71 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| MS1025 | 194.00 | 28.20 | 180 | 8 | 13.79 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1031 | 18.70 | 2.95 | 180 | 8 | 12.69 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1032 | 9.78 | 1.62 | 60 | 8 | 12.04 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1033 | 4.33 | 1.75 | 0 | 16 | 4.94 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| MS1034 | 236.00 | 103.00 | 60 | 15 | 4.58 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| MS1035 | 216.00 | 32.40 | 0 | 8 | 13.32 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1041 | 18.30 | 2.84 | 180 | 8 | 12.89 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1042 | 9.64 | 1.58 | 60 | 8 | 12.20 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1043 | 4.92 | 3.06 | 330 | 16 | 3.21 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| MS1044 | 196.00 | 86.60 | 240 | 15 | 4.53 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| MS1045 | 226.00 | 43.90 | 0 | 16 | 10.27 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| fS1051 | 20.40 | 7.64 | 180 | 16 | 5.34 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| fS1052 | 8.43 | 1.34 | 60 | 8 | 12.62 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS1053 | 8.02 | 4.41 | 330 | 16 | 3.64 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| MS1054 | 170.00 | 74.30 | 240 | 15 | 4.57 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| MS1055 | 240.00 | 110.00 | 180 | 16 | 4.37 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| fS2011 | 9.40 | 1.52 | 60 | 8 | 12.38 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS2012 | 23.20 | 10.90 | 150 | 16 | 4.27 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| fS2013 | 4.41 | 0.92 | 120 | 7 | 9.55 | 9.90 | 通过 |
| MS2014 | 272.00 | 93.10 | 150 | 16 | 5.85 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| MS2015 | 192.00 | 69.40 | 60 | 15 | 5.52 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| fS2021 | 12.50 | 1.88 | 330 | 8 | 13.26 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS2022 | 17.20 | 2.62 | 300 | 8 | 13.07 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS2023 | 5.02 | 1.26 | 210 | 16 | 7.94 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| MS2024 | 163.00 | 46.20 | 120 | 16 | 7.05 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| MS2025 | 173.00 | 43.50 | 60 | 15 | 7.94 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| fS2031 | 11.90 | 1.78 | 150 | 8 | 13.39 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| fS2032 | 17.40 | 3.31 | 300 | 16 | 3.52 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| fS2033 | 5.83 | 3.01 | 180 | 15 | 3.88 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| MS2034 | 135.00 | 20.50 | 120 | 8 | 13.15 | 11.70 | 否决 |
| MS2035 | 155.00 | 67.20 | 150 | 16 | 4.62 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| fS3011 | 8.74 | 3.69 | 180 | 16 | 4.75 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| fS3012 | 10.10 | 4.06 | 60 | 15 | 4.98 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| fS3013 | 10.70 | 2.16 | 180 | 16 | 9.87 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| MS3014 | 535.00 | 238.00 | 240 | 15 | 4.49 | 20.35 | 通过 |
| MS3015 | 529.00 | 252.00 | 0 | 16 | 4.20 | 21.10 | 通过 |
| fS3021 | 11.10 | 5.29 | 0 | 16 | 4.20 | 21.10 | 通过 |
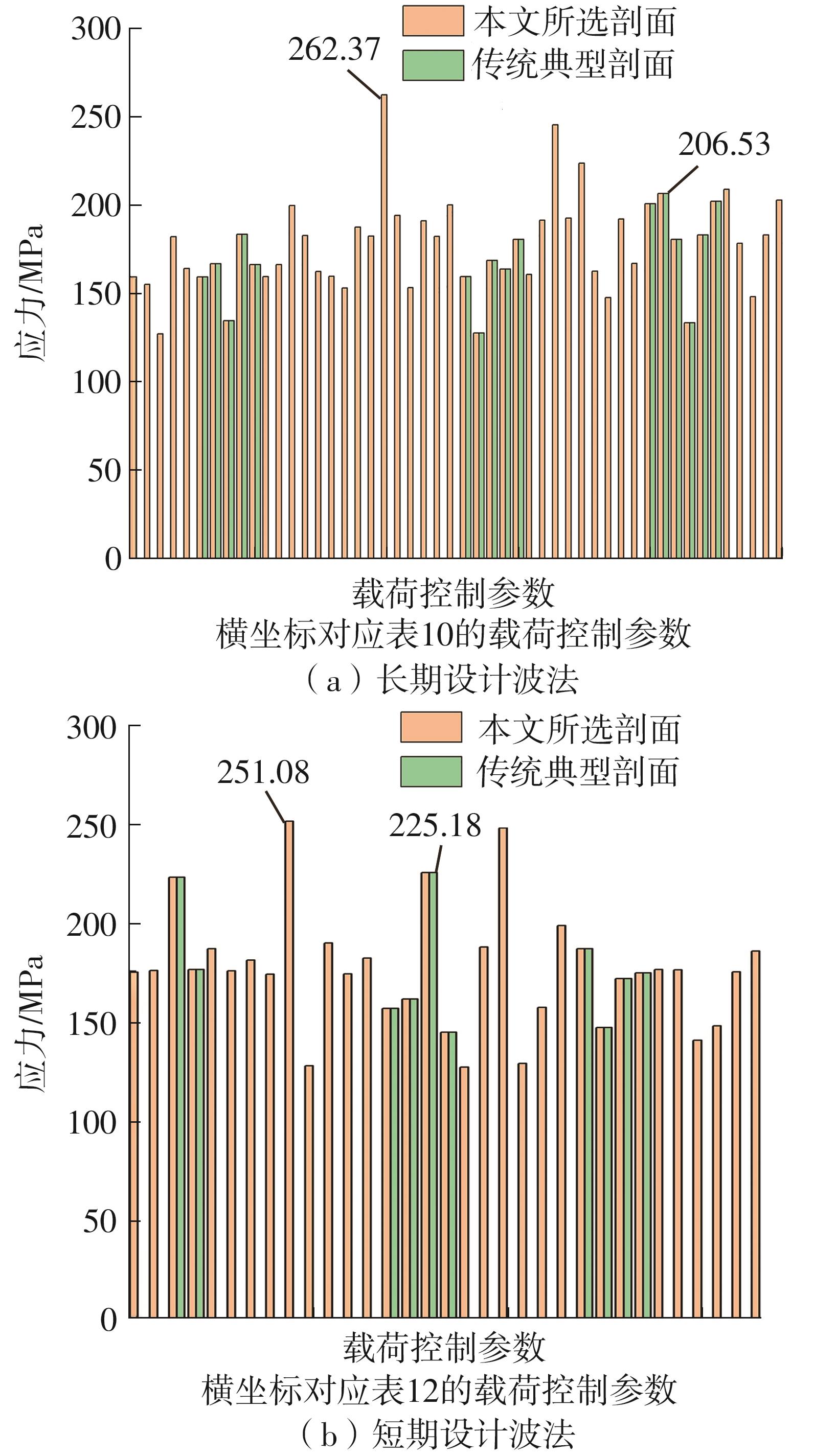
Table 10
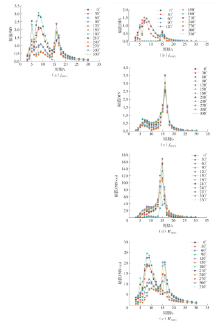
Stress results of FOWT platform based on long-term design wave"
| 载荷控制参数 | 浪向/(°) | 波浪周期/s | 相位/(°) | 波高/m | 计算最大应力/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fS1011 | 180 | 8 | 8.177 | 9.07 | 159.28 |
| fS1012 | 270 | 7 | -112.214 | 10.29 | 155.04 |
| fS1013 | 120 | 16 | -158.407 | 5.55 | 126.97 |
| MS1014 | 240 | 15 | 56.750 | 6.40 | 181.96 |
| MS1015 | 180 | 8 | -176.812 | 10.49 | 163.97 |
| fS1021 | 180 | 8 | 9.634 | 8.84 | 159.31 |
| fS1022 | 300 | 8 | -153.560 | 10.17 | 166.82 |
| fS1023 | 120 | 16 | -147.994 | 5.71 | 134.51 |
| MS1024 | 60 | 15 | -58.019 | 6.22 | 183.40 |
| MS1025 | 0 | 8 | 131.866 | 10.54 | 166.23 |
| fS1031 | 180 | 8 | 10.986 | 8.81 | 159.44 |
| fS1032 | 300 | 8 | -156.089 | 9.90 | 166.32 |
| fS1033 | 0 | 16 | 60.104 | 5.88 | 199.74 |
| MS1034 | 60 | 15 | -57.936 | 6.08 | 182.66 |
| MS1035 | 120 | 16 | -150.027 | 10.65 | 162.38 |
| fS1041 | 180 | 8 | 12.058 | 9.04 | 159.68 |
| fS1042 | 270 | 6 | -106.351 | 9.64 | 152.96 |
| fS1043 | 0 | 16 | 41.224 | 5.01 | 187.52 |
| MS1044 | 60 | 15 | -57.979 | 5.99 | 182.30 |
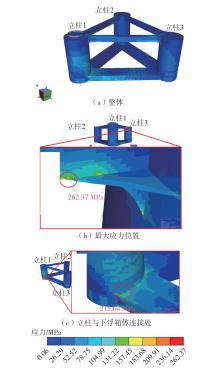
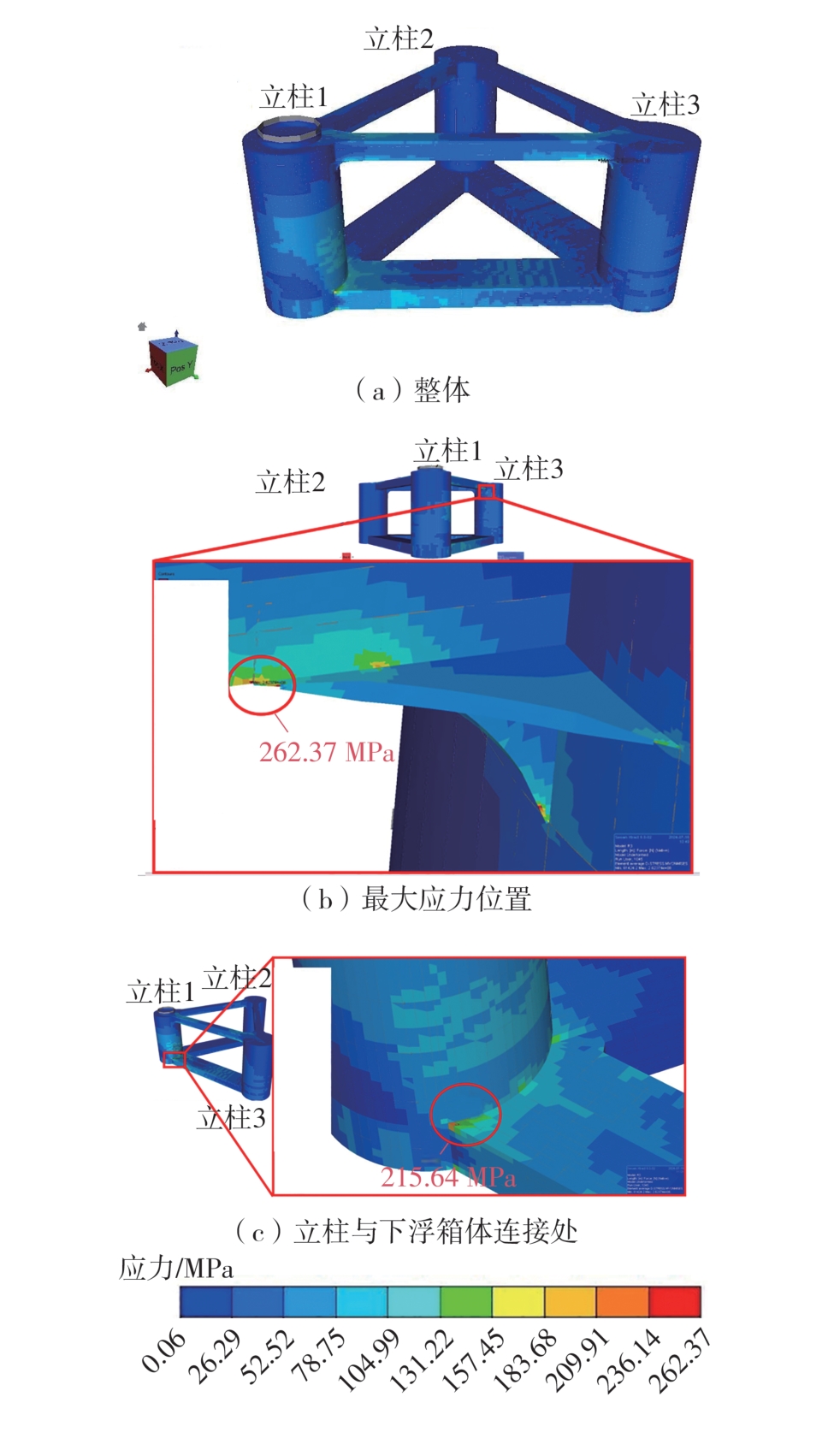
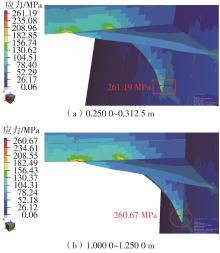
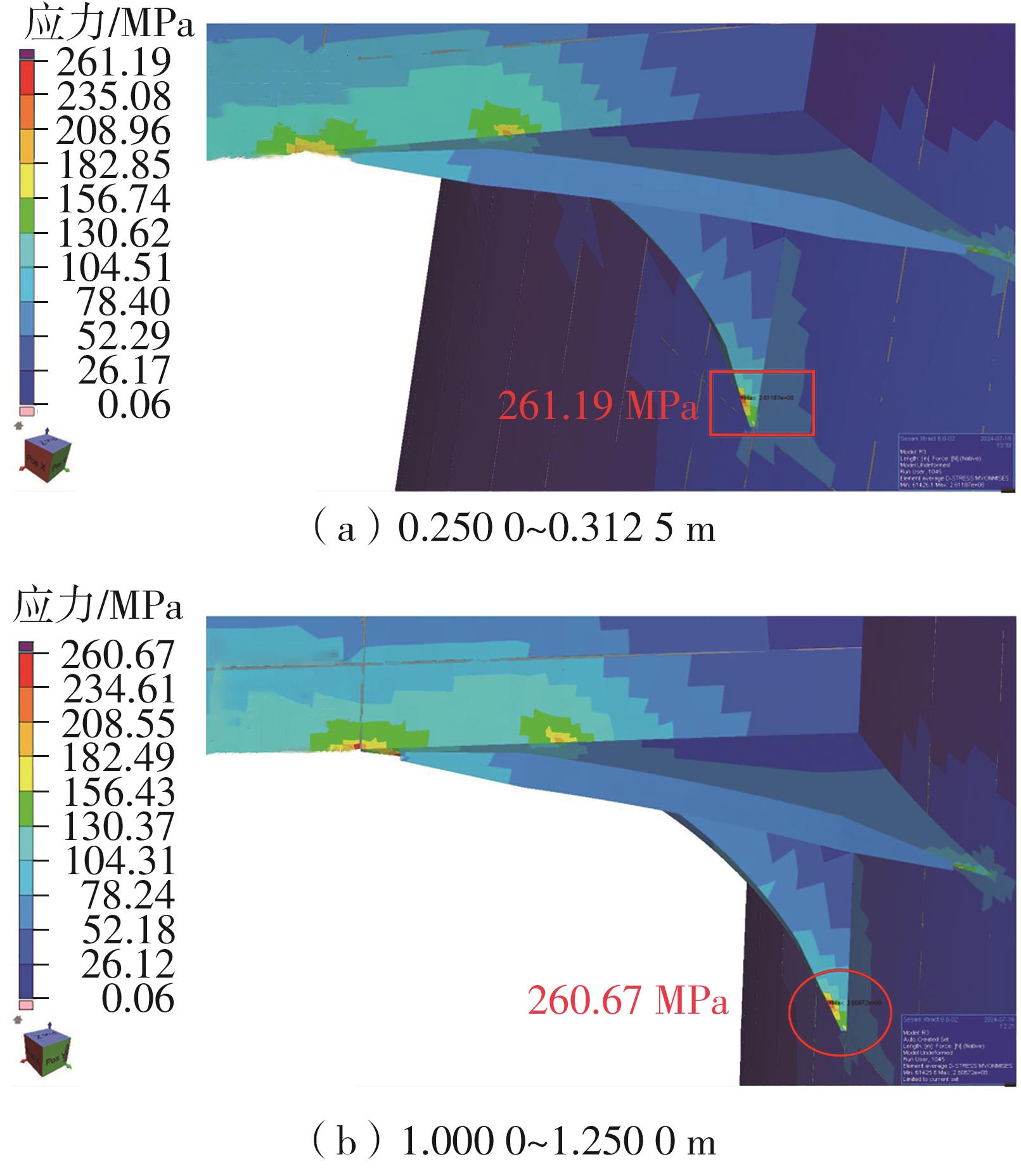
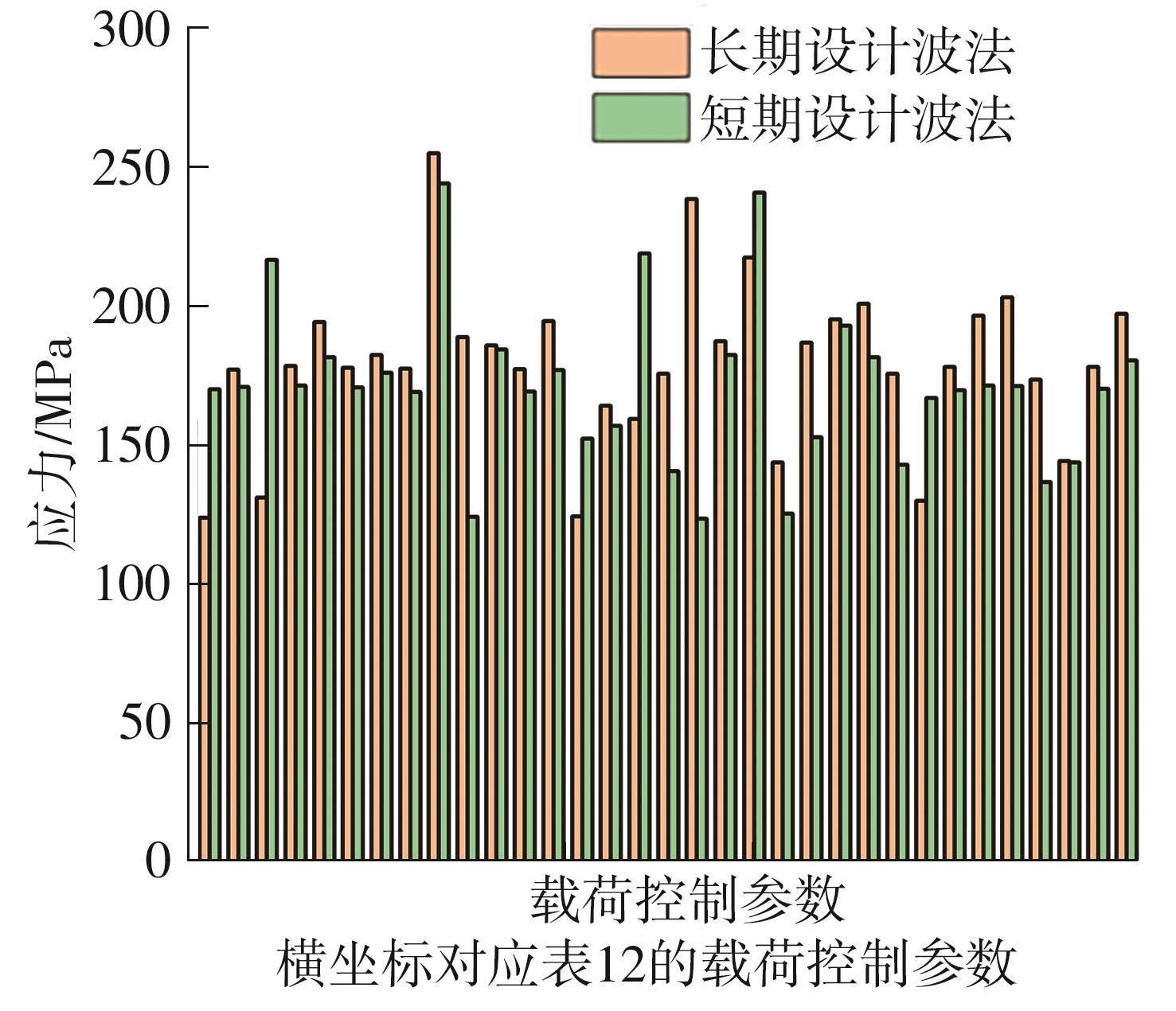
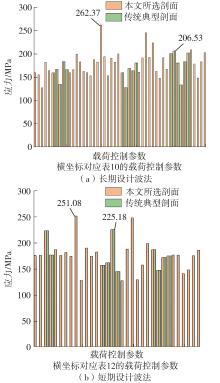
| MS1045 | 150 | 16 | -101.221 | 8.45 | 262.37 |
| fS1051 | 0 | 16 | -146.089 | 5.62 | 194.03 |
| fS1052 | 270 | 6 | -107.195 | 9.61 | 153.10 |
| fS1053 | 0 | 16 | 37.708 | 5.17 | 191.03 |
| MS1054 | 60 | 15 | -58.162 | 5.97 | 182.22 |
| MS1055 | 0 | 16 | 54.424 | 5.89 | 200.02 |
| fS2011 | 90 | 6 | 76.318 | 9.65 | 159.50 |
Table 12
Stress results of FOWT platform based on short-term design wave method"
| 载荷控制参数 | 浪向/(°) | 波浪周期/s | 相位/(°) | 波高/m | 计算最大应力/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fS1013 | 180 | 16 | -148.390 | 5.12 | 174.74 |
| MS1014 | 240 | 15 | 56.750 | 4.98 | 175.64 |
| fS1023 | 0 | 16 | 121.690 | 7.37 | 222.80 |
| MS1024 | 60 | 15 | -58.020 | 4.71 | 176.08 |
| fS1033 | 0 | 16 | 60.100 | 4.94 | 186.67 |
| MS1034 | 60 | 15 | -57.940 | 4.58 | 175.46 |
| fS1043 | 330 | 16 | 52.340 | 3.21 | 180.92 |
| MS1044 | 240 | 15 | 56.600 | 4.53 | 173.63 |
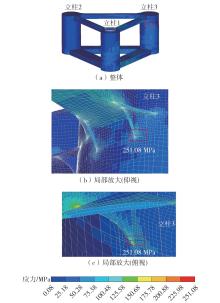
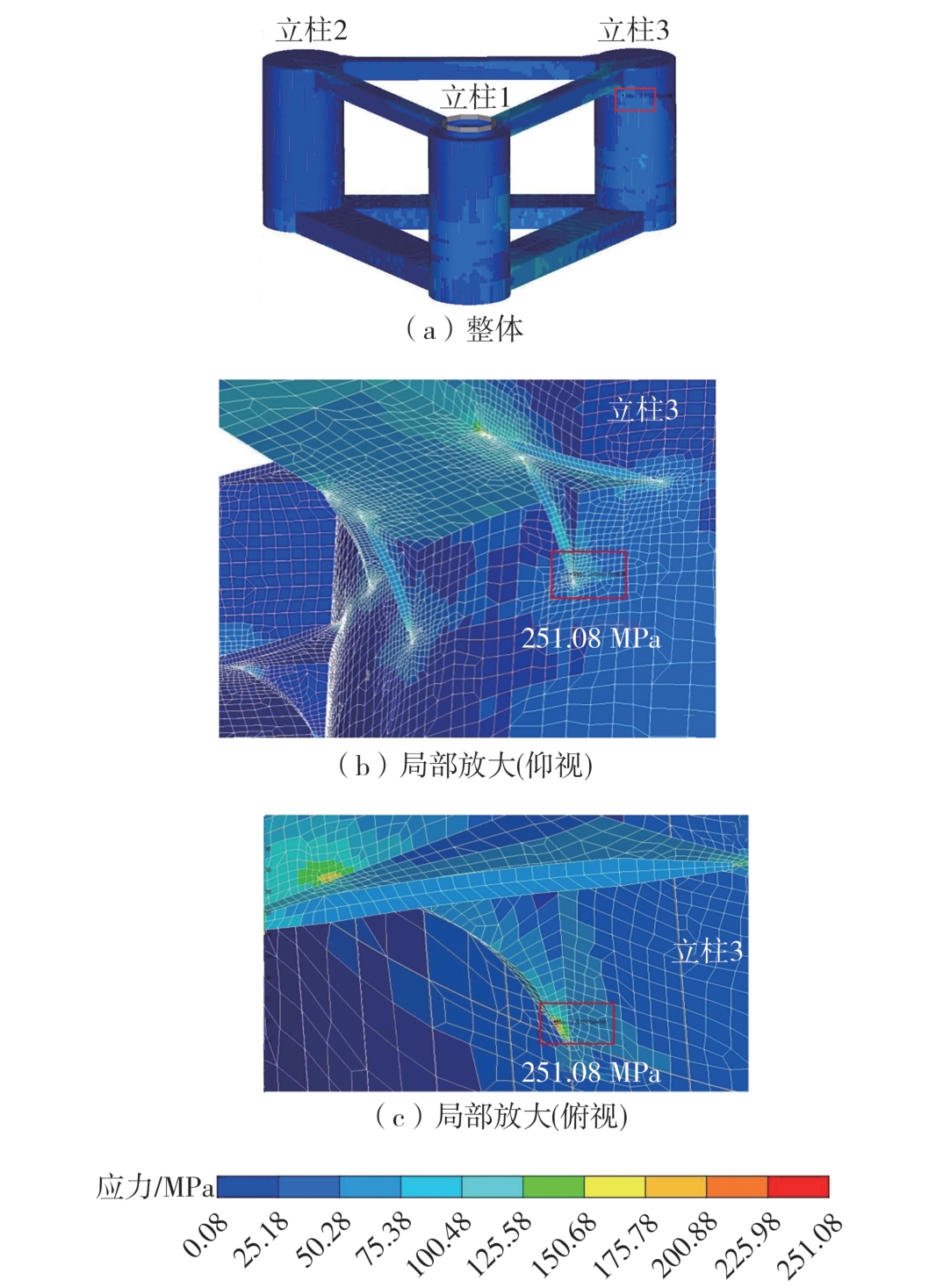
| MS1045 | 0 | 16 | 81.570 | 10.27 | 251.08 |
| fS1051 | 180 | 16 | 146.640 | 5.34 | 127.31 |
| fS1053 | 330 | 16 | 47.060 | 3.64 | 189.55 |
| MS1054 | 240 | 15 | 56.780 | 4.57 | 173.89 |
| MS1055 | 180 | 16 | -55.140 | 4.37 | 181.82 |
| fS2012 | 150 | 16 | 132.440 | 4.27 | 156.44 |
| fS2013 | 120 | 7 | 68.230 | 9.55 | 161.18 |
| MS2014 | 150 | 16 | 112.340 | 5.85 | 225.18 |
| MS2015 | 60 | 15 | 122.960 | 5.52 | 144.42 |
| fS2023 | 210 | 16 | 125.920 | 7.94 | 126.71 |
| MS2024 | 120 | 16 | 60.040 | 7.05 | 187.39 |
| MS2025 | 60 | 15 | 108.150 | 7.94 | 247.68 |
| fS2032 | 300 | 16 | 152.270 | 3.52 | 128.64 |
| 1 | RAVINTHRAKUMAR S, LEIRA B J, HAVER S, et al. Evaluation of extreme design wave loads for hull girder strength assessment[J].Trends in the Analysis and Design of Marine Structures,2019,2(1):23-30. |
| 2 | SOHN J M, CHEON H, HONG K,et al .Equivalent design wave approach for structural analysis of floating pendulum wave energy converter[J].Ships and Offshore Structures,2016,11(6):645-654. |
| 3 | LI H, REN H, WEI T, et al .Study on the Wave Loads and Strength Assessment Method on Semi-Submersible Platform[C]∥Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering.Honolulu:OMAE,2009:463-471. |
| 4 | Column-Stabilized unit:DNVGL-RP-C103—2015 [S]. |
| 5 | DONG Y, ZHANG J, ZHONG S,et al .Simplified strength assessment for preliminary structural design of floating offshore wind turbine semi-submersible platform[J].Journal of Marine Science and Engineering,2024,12(2):259-276. |
| 6 | 孙寅博,窦培林 .Truss Spar 结构浮式风机基础总体强度分析[J].舰船科学技术,2021,43(4):107-110. |
| SUN Yinbo, DOU Peilin .Overall strength analysis of truss spar floating wind turbine foundation[J].Ship Science and Technology,2021,43(4):107-110. | |
| 7 | YANG Y, CHEN C, ZHAO W,et al .An innovative method of assessing yield strength of floater hull for semi-submersible floating wind turbine in whole life period[J].Ocean Engineering,2023,270:113679/1-16. |
| 8 | LIN J, WU W, PENG Z .Overall strength analysis of floating offshore wind turbine foundation[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2023,2419(1):012017/1-10. |
| 9 | 唐友刚,王涵,陶海成,等 .海上风机半潜型浮式基础结构设计及整体强度分析[J].中国造船,2013,54(3):85-93. |
| TANG Yougang, WANG Han, TAO Haicheng,et al .Structure design and global strength analysis for semi-submersible floating foundation of offshore wind turbine[J].Shipbuilding of China,2013,54(3):85-93 | |
| 10 | 桑松,于梅,石晓,等 .基于设计波法的半潜型浮式风力机结构强度校核[J].太阳能学报,2019,40(1):185-191. |
| SANG Song, YU Mei, SHI Xiao,et al .Strength check on deep sea semi-submersible floating wind turbine based on design wave method[J].Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica,2019,40(1):185-191. | |
| 11 | 聂焱 .浮式风机基础结构强度设计[J].水电与新能源,2019,33(4):74-78. |
| NIE Yan .Structural strength design of the floating wind turbine Foundation[J].Hydropower and New Engegy,2019,33(4):74-78. | |
| 12 | 宋兆波 .大型浮式海上风机平台结构设计和动力特性研究[D].大连:大连理工大学,2022. |
| 13 | 范文华,滕斌,丛培文,等 .准陷波现象对多柱平台特征内力影响的研究[J].中国海洋平台,2016,31(2):68-74. |
| FAN Wenhua, TENG Bin, CONG Peiwen,et al .Near-trapping effect on characteristic internal forces of the multi-cylinder platform[J].China Offshore Platform,2016,31(2):68-74. | |
| 14 | 方钟圣 .西北太平洋波浪统计集[M].北京:国防工业出版社,1996. |
| 15 | 张朝阳 .深水半潜平台总体强度分析中波浪载荷计算与简化建模方法研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2012. |
| 16 | 中国船级社 .海上浮动设施入级规范[R].北京:人民交通出版社,2023. |
| 17 | 廖海翔 .基于SVR的非结构网格变形技术研究[D].长沙:国防科技大学,2020. |
| 18 | SILVA De SO E, BERTHELSEN P A, ELIASSEN L,et al .Definition of the INO Windmoor 12 MW base case floating wind turbine[J].Sintef Ocean,2021,11(1):1-82. |
| 19 | BOGE S N, EKERHOVD D W .A hydro-aerodynamic analysis of a floating offshore wind turbine to assist in floater selection[D].Trondheim:NTNU,2022. |
| 20 | 李红涛,邓贤锋 .半潜式平台整体结构设计的波浪载荷研究[J].中国海上油气,2015,27(2):98-103. |
| LI Hongtao, DENG Xianfeng .Study on wave loads for global structural design of semi-submersibles[J].China Offshore Oil and Gas,2015,27(2): 98-103. | |
| 21 | 梁双令,齐江辉,章红雨,等 .基于设计波法的海洋核动力平台波浪载荷计算[J].舰船科学技术,2019,41(7):90-94. |
| LIANG Shuangling, QI Jianghui, ZHANG Hongyu,et al .Wave loads calculation of marine nuclear power platform based on design wave methods[J].Ship Science and Technology,2019,41(7):90-94. | |
| 22 | 吉华宇 .深水半潜平台总体强度设计波分析方法研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2019. |
| 23 | Structural design of offshore units- method:DNVGL-OS-C201—2017[S]. |
| 24 | Wind turbines-Part 3-1,design requirements for fixed offshore wind turbines: [S]. |
| 25 | Part 3-2:design requirements for floating offshore wind turbines: [S]. |
| 26 | 中国船级社 .海上浮式风机平台指南[R].北京:人民交通出版社,2021. |
| 27 | 中国船级社 .海上浮式装置入级规范[R].北京:人民交通出版社,2020. |
| [1] | Ren Zhi- gui Chen Jin Wang Shu- chun Pang Xiao- ping Huang Ding- hong Ma Jin- cheng. Dynamic Stress Test and Transient Analysis of Hydraulic Excavator [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(1): 22-28. |
| [2] | Yang Chun Wu Yi He Ming-ji Zheng Jun-guang Zhang Chun-mei. Seismic Behaviors of SRC Beam Transfer Structure with Energy Dissipation Haunch Braces [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(12): 138-143,164. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||