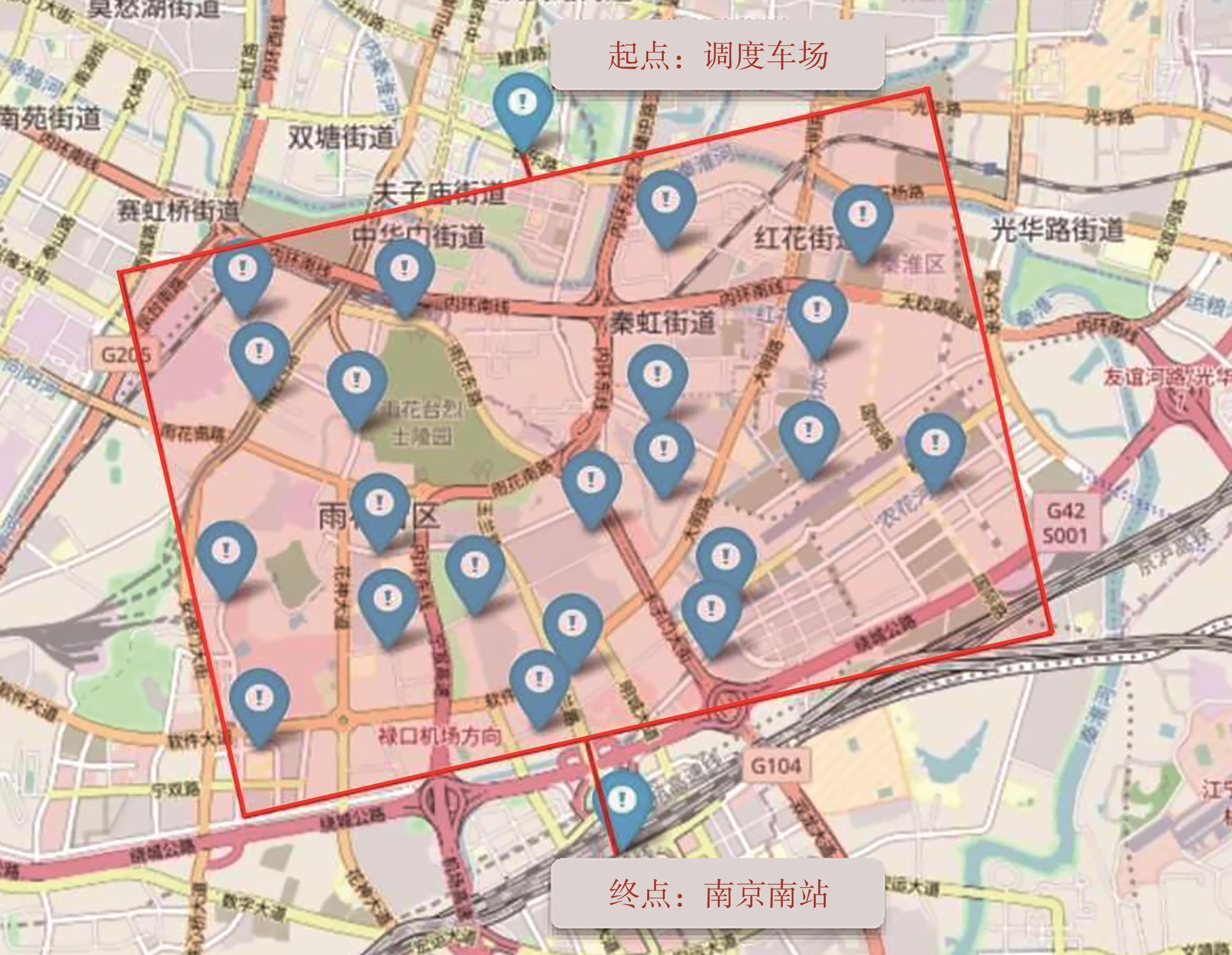
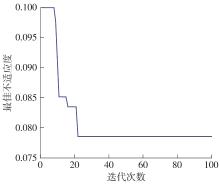
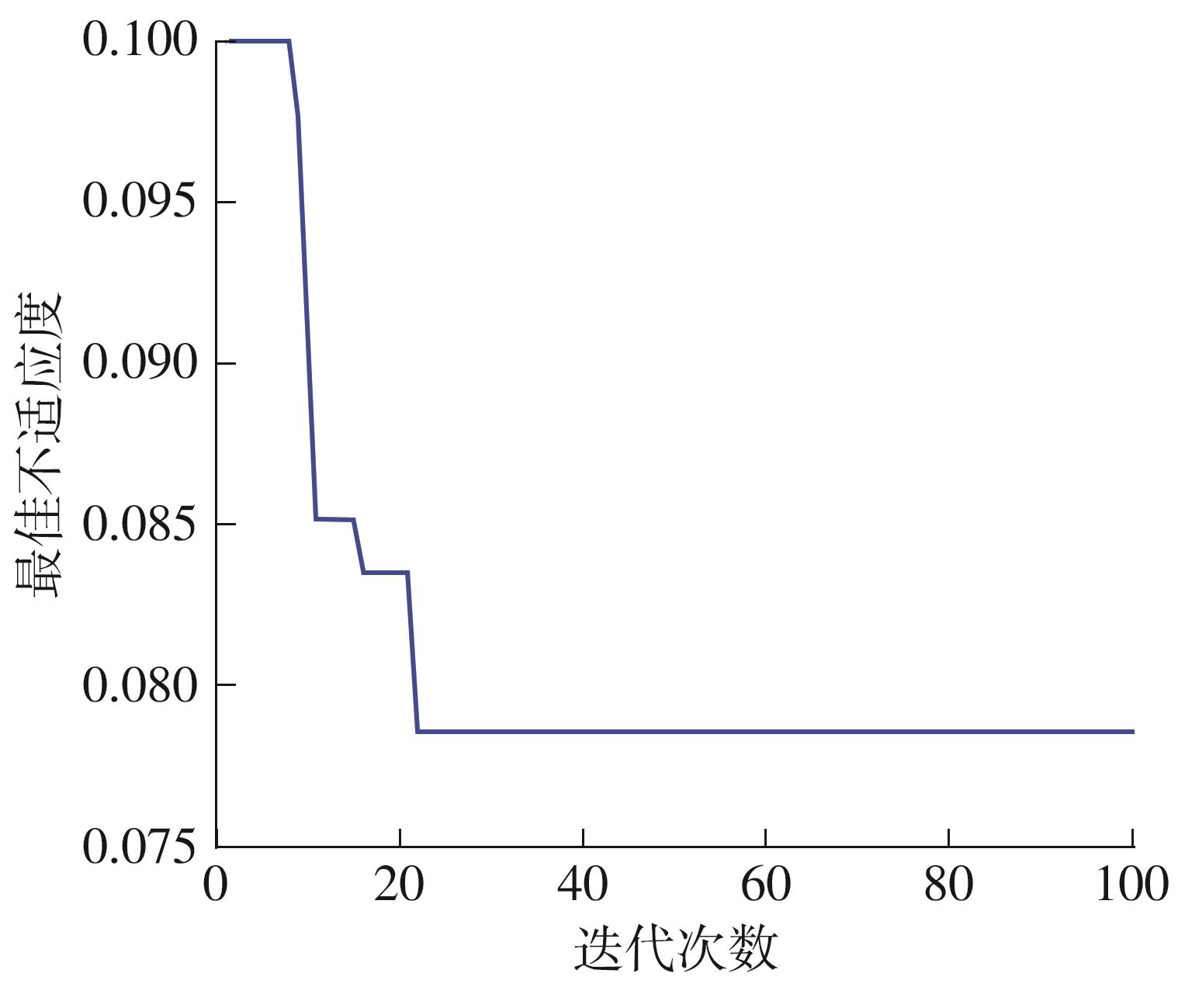
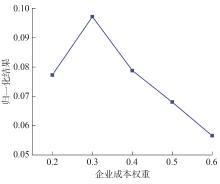
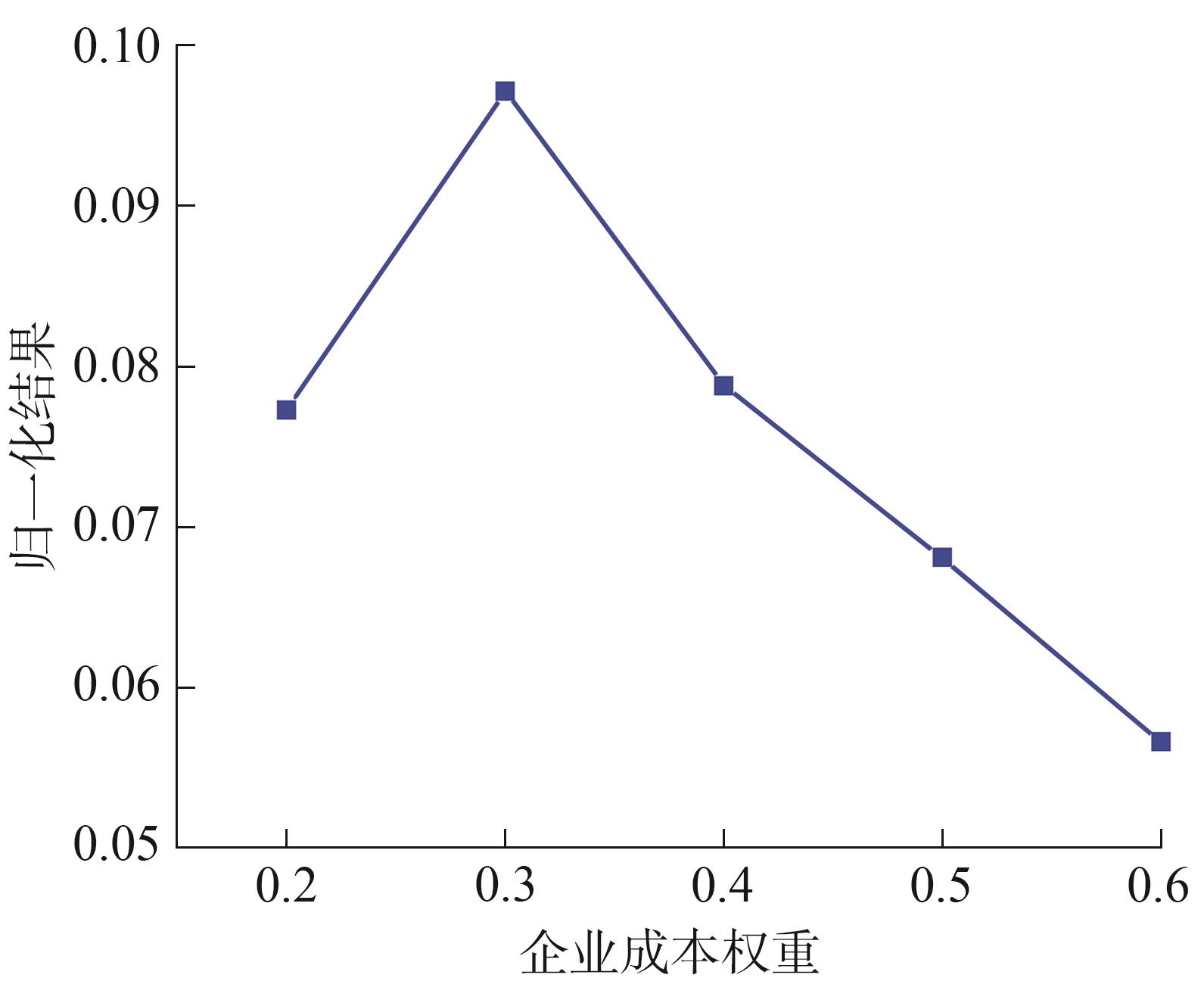
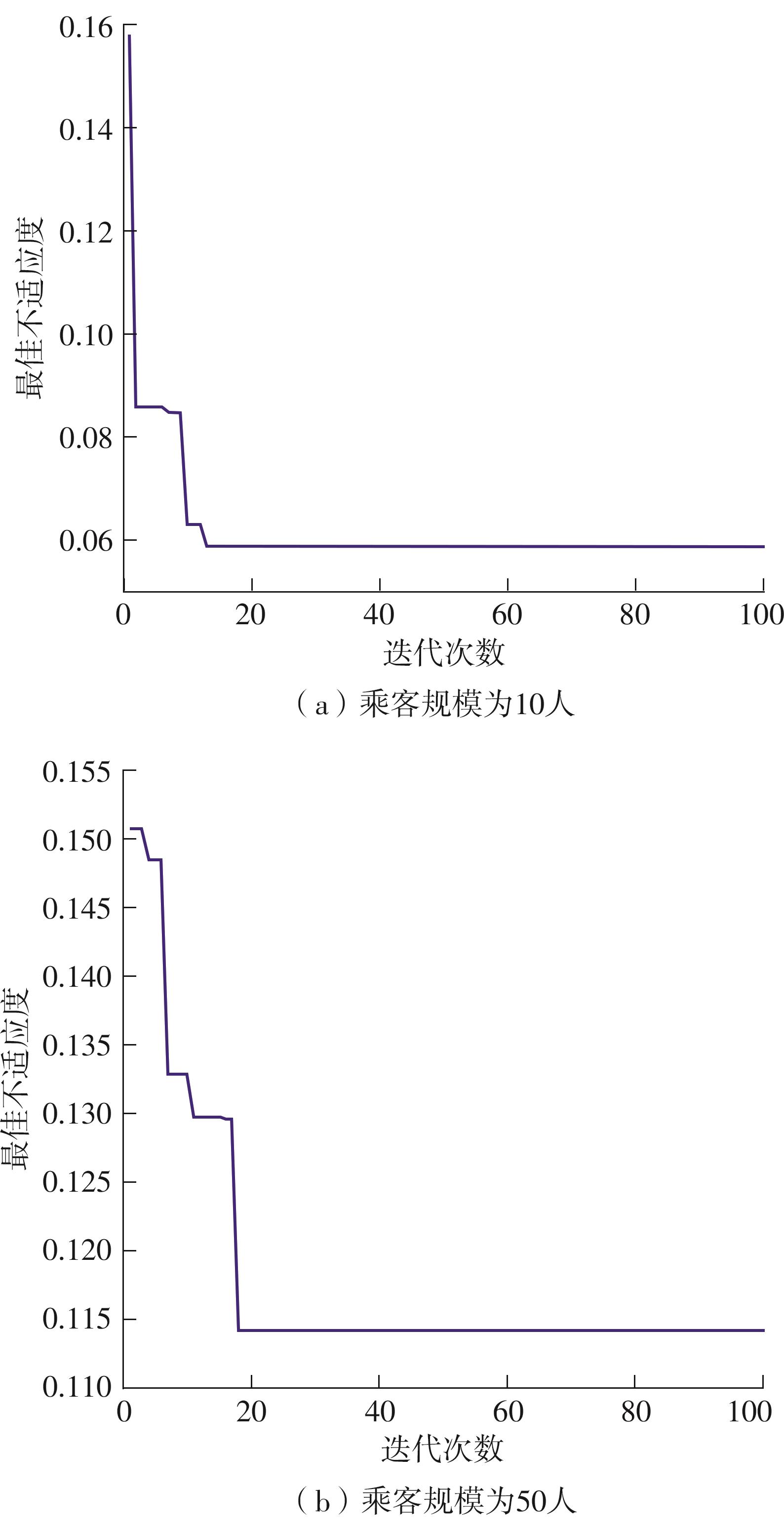
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (10): 22-30.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230224
Special Issue: 2023绿色智慧交通系统专辑
• Green, Intelligent Traffic System • Previous Articles Next Articles
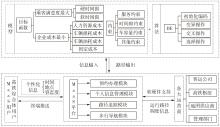
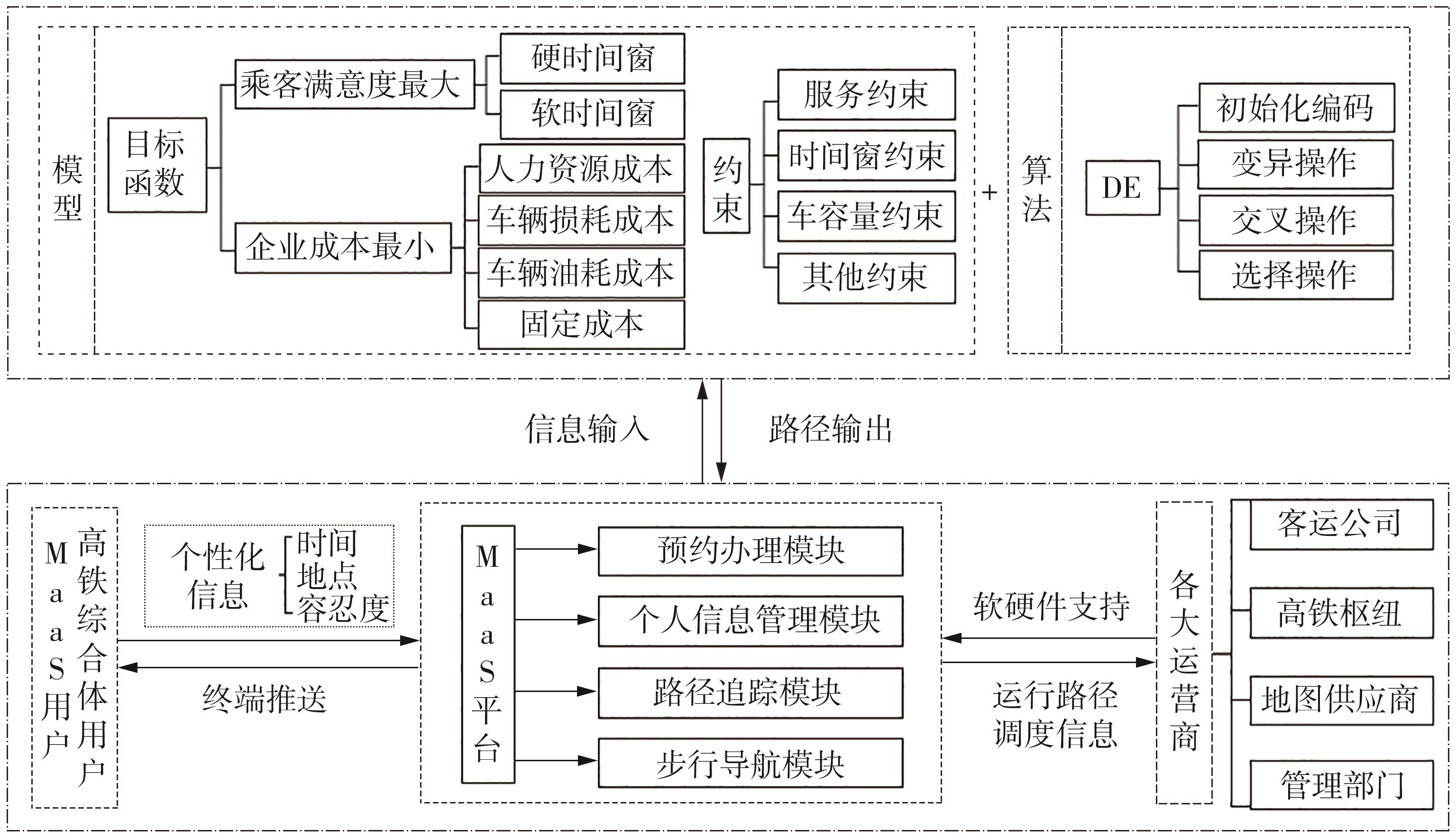
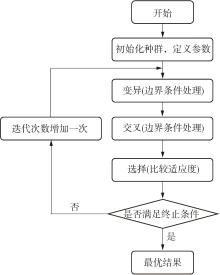
Flexible Bus Scheduling Optimization for Integrated Hub Connections in the Context of MaaS
YANG Min1 CHEN Shantao1 JIANG Ruiyu1 LI Xingze1 JIANG Zixian2 ZHANG Mingye1
- 1.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,Jiangsu,China
2.School of Computer Science and Engineering,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,Jiangsu,China