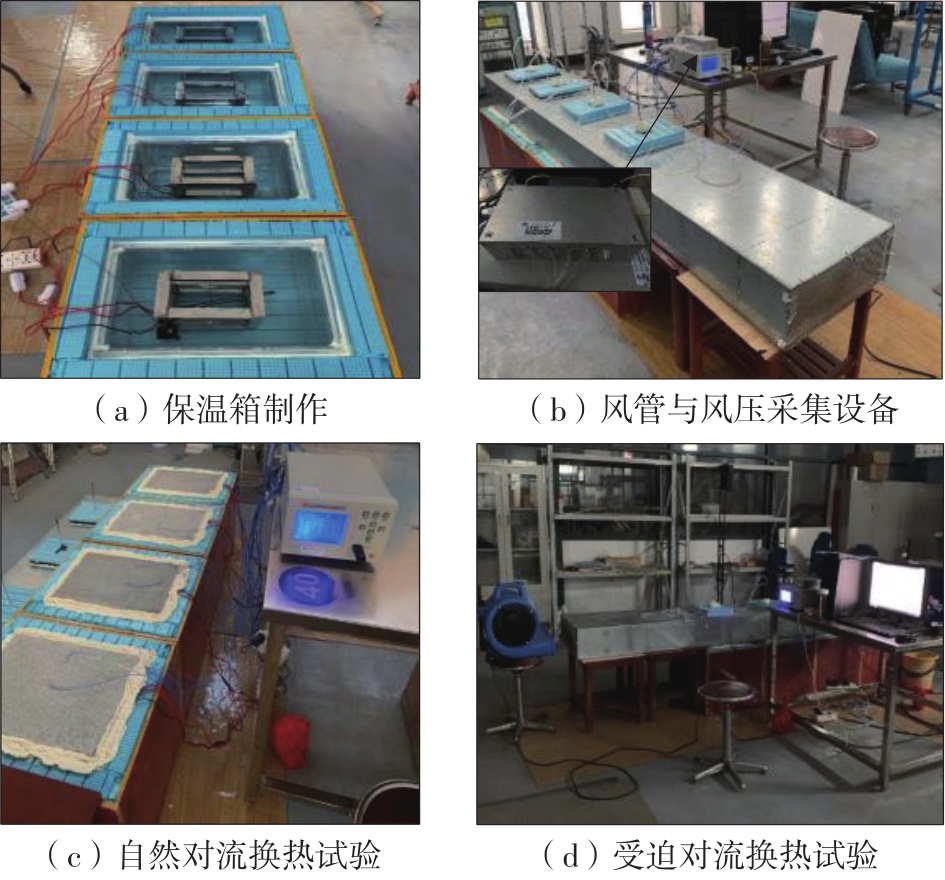
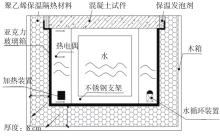
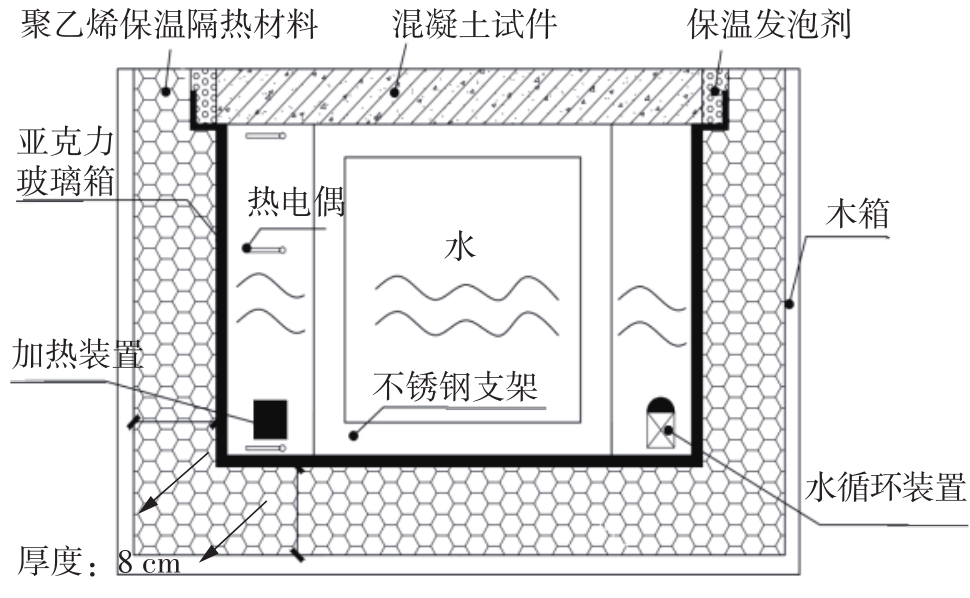
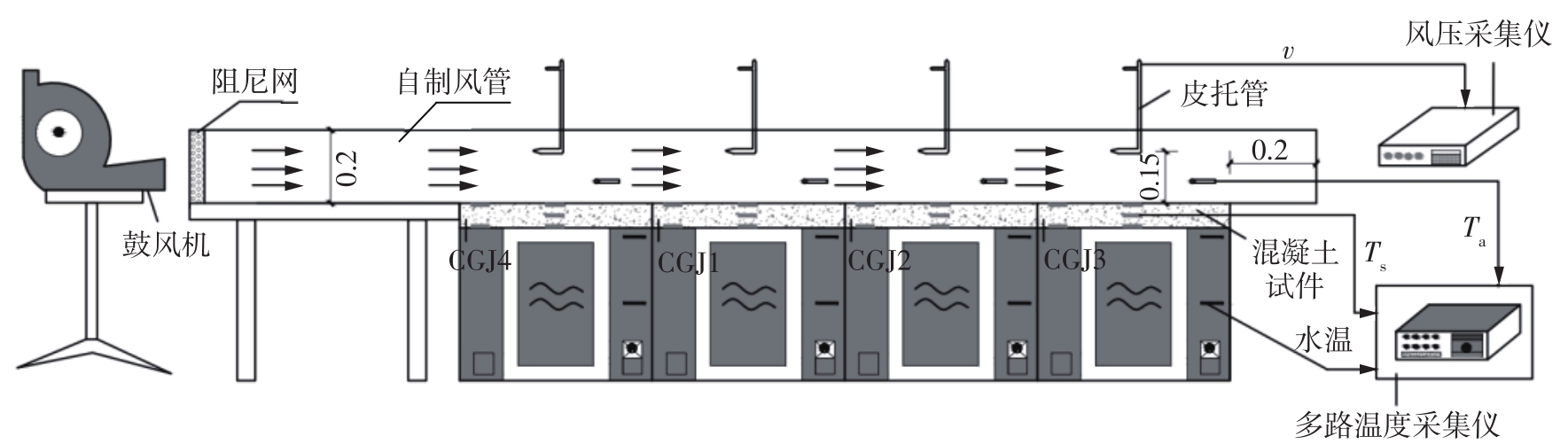
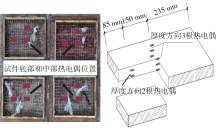
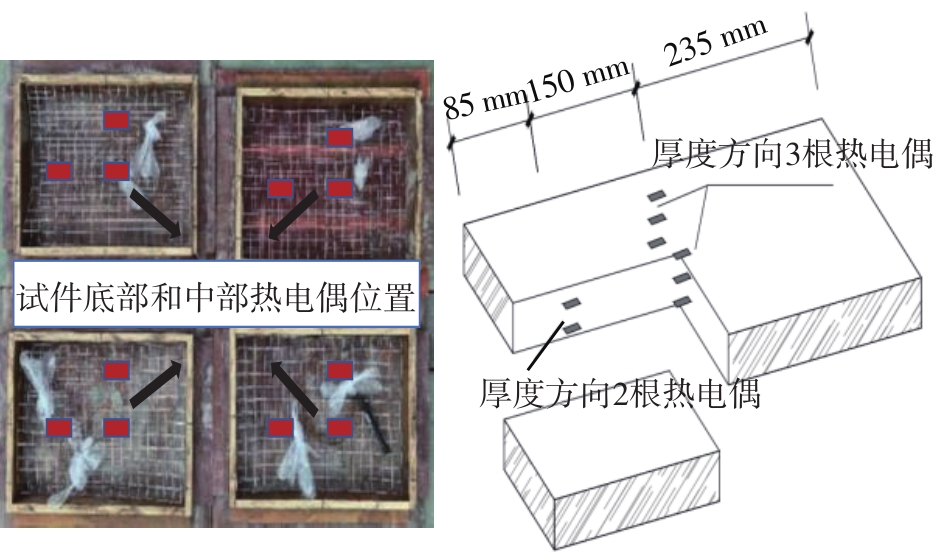
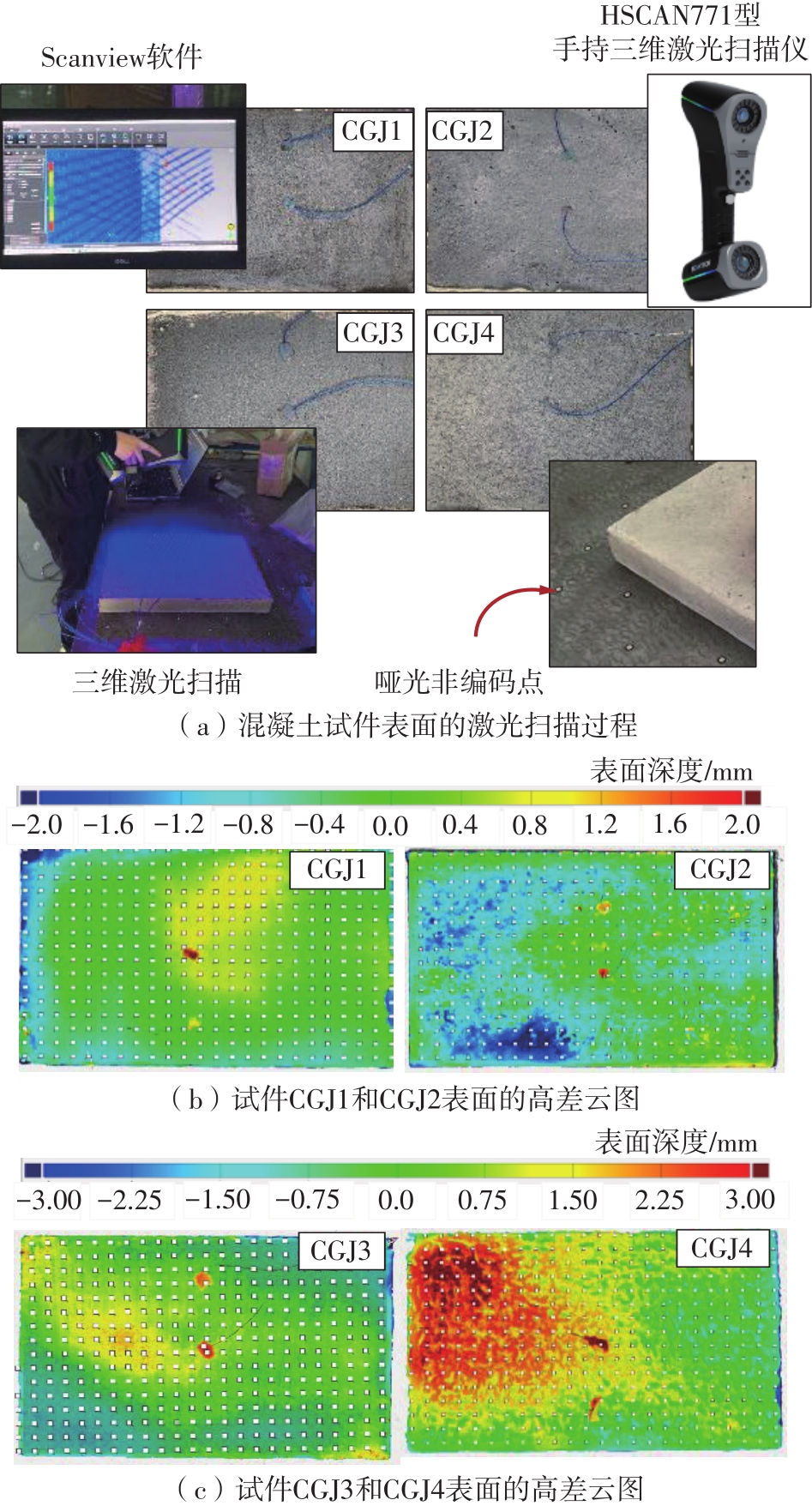
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (7): 81-89.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220638
Special Issue: 2023年土木建筑工程
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Experimental Investigation into Effect of Surface Roughness on Convective Heat Transfer of Concrete
ZHOU Linren LI Shaoji CHEN Lan
- School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2022-09-30Online:2023-07-25Published:2023-04-11 -
Contact:周林仁(1982-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事桥梁结构健康监测、检测与状态评估等的研究。 E-mail:zhoulinren@scut.edu.cn -
About author:周林仁(1982-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事桥梁结构健康监测、检测与状态评估等的研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52078220)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHOU Linren, LI Shaoji, CHEN Lan. Experimental Investigation into Effect of Surface Roughness on Convective Heat Transfer of Concrete[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 81-89.
share this article
Table 3
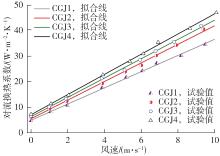
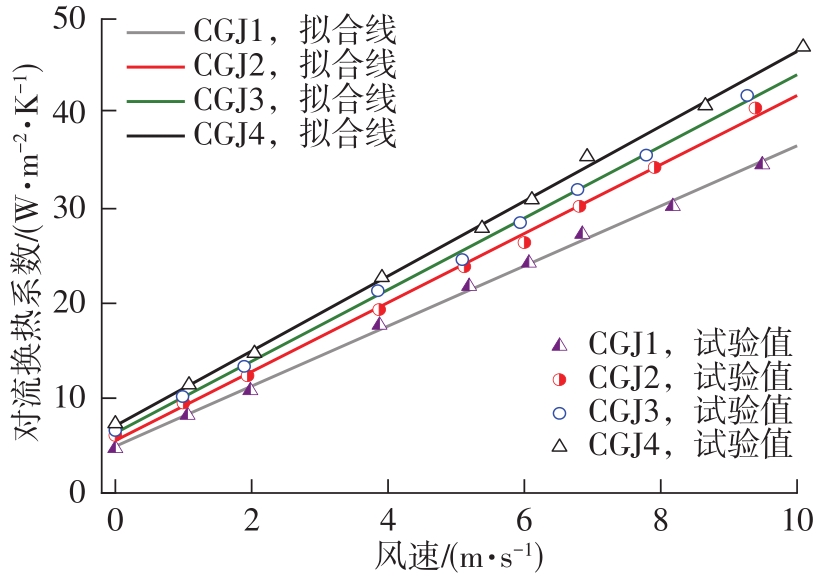
Natural convective heat transfer coefficient of CGJ1"
| Ta/℃ | 保温箱水温/℃ | 试件温度/℃ | Qt/W | Q1/W | QR/W | hc/(W·m-2·K-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上 | 中 | 下 | 上 | 中 | 下 | |||||
| 22.7 | 50.3 | 50.2 | 50.3 | 40.2 | 42.8 | 45.0 | — | — | — | — |
| 22.5 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 40.4 | 42.8 | 45.1 | 25.00 | 4.07 | 7.51 | 5.04 |
| 22.5 | 49.7 | 49.7 | 49.8 | 40.3 | 42.8 | 45.0 | 26.60 | 4.06 | 7.58 | 5.57 |
| 22.5 | 49.4 | 49.6 | 49.5 | 40.2 | 42.7 | 44.8 | 23.80 | 4.05 | 7.50 | 4.59 |
| 22.4 | 49.2 | 49.3 | 49.4 | 40.1 | 42.5 | 44.6 | 24.28 | 4.03 | 7.50 | 4.79 |
| 22.5 | 49.0 | 49.0 | 49.2 | 39.8 | 42.3 | 44.4 | 25.20 | 3.99 | 7.41 | 5.24 |
| 22.3 | 48.7 | 48.8 | 49.0 | 39.7 | 42.2 | 44.3 | 23.61 | 3.98 | 7.34 | 4.70 |
| 21.1 | 48.5 | 48.6 | 48.7 | 39.5 | 42.0 | 44.1 | 24.57 | 3.91 | 7.54 | 4.87 |
| 21.2 | 48.4 | 48.4 | 48.4 | 39.2 | 41.8 | 43.8 | 25.20 | 3.85 | 7.63 | 5.01 |
| 20.7 | 48.1 | 48.3 | 48.2 | 38.9 | 41.4 | 43.4 | 22.95 | 3.81 | 7.59 | 4.24 |
Table 4
Natural convective heat transfer coefficient of CGJ2"
| Ta/℃ | 保温箱水温/℃ | 试件温度/℃ | Qt/W | Q1/W | QR/W | hc/(W·m-2·K-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上 | 中 | 下 | 上 | 中 | 下 | |||||
| 22.7 | 50.2 | 50.2 | 50.4 | 39.7 | 43.1 | 45.8 | — | — | — | — |
| 22.5 | 49.9 | 49.9 | 50.1 | 40.0 | 43.2 | 46.0 | 26.98 | 4.08 | 7.54 | 5.92 |
| 22.5 | 49.7 | 49.6 | 49.7 | 40.0 | 43.1 | 45.8 | 28.21 | 4.07 | 7.58 | 6.29 |
| 22.5 | 49.3 | 49.5 | 49.5 | 39.8 | 42.8 | 45.5 | 28.15 | 4.06 | 7.53 | 6.32 |
| 22.4 | 49.1 | 49.2 | 49.2 | 39.6 | 42.5 | 45.5 | 27.49 | 4.03 | 7.46 | 6.16 |
| 22.5 | 48.9 | 48.9 | 48.9 | 39.6 | 42.4 | 45.4 | 26.50 | 3.99 | 7.41 | 5.85 |
| 22.3 | 48.6 | 48.7 | 48.6 | 39.4 | 42.3 | 45.2 | 27.49 | 3.98 | 7.39 | 6.27 |
| 21.1 | 48.3 | 48.3 | 48.5 | 39.2 | 42.1 | 45.0 | 28.18 | 3.92 | 7.57 | 6.31 |
| 21.2 | 48.0 | 48.0 | 47.2 | 39.1 | 41.8 | 44.8 | 27.87 | 3.86 | 7.76 | 6.02 |
| 20.7 | 47.8 | 47.8 | 47.9 | 39.0 | 41.2 | 44.2 | 27.87 | 3.84 | 7.76 | 5.58 |
Table 5
Natural convective heat transfer coefficient of CGJ3"
| Ta/℃ | 保温箱水温/℃ | 试件温度/℃ | Qt/W | Q1/W | QR/W | hc/(W·m-2·K-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上 | 中 | 下 | 上 | 中 | 下 | |||||
| 22.7 | 50.9 | 50.9 | 51.1 | 40.0 | 43.5 | 46.0 | — | — | — | — |
| 22.5 | 50.6 | 50.6 | 50.7 | 40.5 | 44.0 | 46.1 | 28.55 | 4.12 | 7.83 | 6.25 |
| 22.5 | 50.3 | 50.3 | 50.3 | 40.6 | 43.9 | 46.0 | 30.12 | 4.09 | 8.01 | 6.64 |
| 22.5 | 50.0 | 49.9 | 50.0 | 40.6 | 44.0 | 45.8 | 31.52 | 4.08 | 8.04 | 7.09 |
| 22.4 | 49.7 | 49.6 | 49.7 | 40.3 | 43.8 | 45.6 | 31.08 | 4.07 | 7.99 | 7.02 |
| 22.5 | 49.3 | 49.4 | 49.4 | 40.3 | 43.6 | 45.4 | 30.41 | 4.06 | 7.92 | 6.87 |
| 22.3 | 49.1 | 49.1 | 49.1 | 40.0 | 43.4 | 45.1 | 28.51 | 4.03 | 7.86 | 6.22 |
| 21.1 | 48.7 | 48.8 | 48.9 | 39.8 | 43.1 | 44.8 | 28.51 | 3.99 | 7.97 | 7.09 |
| 21.2 | 48.5 | 48.5 | 48.6 | 39.5 | 42.9 | 44.5 | 28.51 | 3.96 | 8.14 | 6.24 |
| 20.7 | 48.2 | 48.3 | 48.3 | 39.2 | 42.6 | 44.1 | 29.14 | 3.90 | 8.06 | 5.86 |
Table 6
Natural convective heat transfer coefficient of CGJ4"
| Ta/℃ | 保温箱水温℃ | 试件温度℃ | Qt/W | Q1/W | QR/W | hc/(W·m-2·K-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上 | 中 | 下 | 上 | 中 | 下 | |||||
| 22.7 | 50.5 | 50.5 | 50.6 | 40.5 | 43.9 | 47.2 | — | — | — | — |
| 22.5 | 50.2 | 50.1 | 50.3 | 40.6 | 44.1 | 47.2 | 31.71 | 4.08 | 8.15 | 7.22 |
| 22.5 | 49.9 | 49.8 | 49.8 | 40.6 | 44.1 | 47.1 | 32.93 | 4.07 | 8.21 | 7.61 |
| 22.5 | 49.6 | 49.4 | 49.5 | 40.6 | 44.0 | 46.9 | 30.12 | 4.06 | 8.21 | 6.55 |
| 22.4 | 49.4 | 49.1 | 49.2 | 40.3 | 43.6 | 46.5 | 32.63 | 4.03 | 8.16 | 7.57 |
| 22.5 | 49.0 | 48.8 | 48.9 | 40.1 | 43.4 | 46.2 | 34.49 | 3.99 | 8.04 | 8.41 |
| 22.3 | 48.7 | 48.5 | 48.6 | 40.0 | 43.3 | 46.0 | 31.25 | 3.96 | 8.01 | 7.26 |
| 21.1 | 48.3 | 48.4 | 48.2 | 39.6 | 43.0 | 45.6 | 30.90 | 3.90 | 8.15 | 6.92 |
| 21.2 | 48.0 | 48.1 | 47.9 | 39.5 | 42.7 | 45.4 | 30.85 | 3.85 | 8.25 | 6.77 |
| 20.7 | 47.7 | 47.8 | 47.6 | 39.1 | 42.3 | 45.0 | 32.72 | 3.81 | 8.21 | 7.50 |
| 1 | 朱伯芳 .大体积混凝土温度应力与温度控制[M].沈阳:中国水利水电出版社,2012:1-63. |
| 2 | HOSSAIN T, SEGURA S, OKEIL A M .Structural effects of temperature gradient on a continuous prestressed concrete girder bridge:analysis and field measurements[J].Structure and Infrastructure Engineering,2020,16(11):1539-1550. |
| 3 | NIU Y, WANG Y, TANG Y .Analysis of temperature-induced deformation and stress distribution of long-span concrete truss combination arch bridge based on bridge health monitoring data and finite element simulation[J].International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks,2020,16(10):1550147720945205. |
| 4 | 樊健生,刘诚,刘宇飞 .钢‒混凝土组合梁桥温度场与温度效应研究综述[J].中国公路学报,2020,33(4):1-13. |
| FAN Jian-sheng, LIU Cheng, LIU Yu-fei .Review of temperature distribution and temperature effects of steel-concrete composite girder bridges in China[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2020,33(4):1-13. | |
| 5 | LIMA J M, DE BRITO J .Management system for expansion joints of road bridges[J].Structure and Infrastructure Engineering,2010,6(6):703-714. |
| 6 | LIU Y, QIAN Z, CHEN L,et al .Investigation on temperature effect of bridge bearing system during steel bridge deck pavement paving[J].International Journal of Geomechanics,2022,22(5):05022002. |
| 7 | 杨松,李文强,黄旭,等 .基于对流换热系数修正的钢箱梁温度场研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(4):47-58,64. |
| YANG Song, LI Wenqiang, HUANG Xu,et al .Study on the temperature field of steel box beam based on the correction of convective heat transfer coefficient[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(4):47-58,64. | |
| 8 | 刘永健,刘江,张宁 .桥梁结构日照温度作用研究综述[J].土木工程学报,2019,52(5):59-78. |
| LIU Yongjian, LIU Jiang, ZHANG Ning .Review on solar thermal actions of bridge structures[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2019,52(5):59-78. | |
| 9 | 《中国公路学报》编辑部 .中国桥梁工程学术研究综述·2021[J].中国公路学报,2021,34(2):1-97. |
| Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport .Review on China’s bridge engineering research:2021[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2021,34(2):1-97. | |
| 10 | MIRSADEGHI M, COSTOLA D, BLOCKEN B,et al .Review of external convective heat transfer coefficient models in building energy simulation programs: implementation and uncertainty[J].Applied Thermal Engineering,2013,56(1/2):134-151. |
| 11 | 刘京,张文武,邵建涛 .建筑外表面对流换热系数的CFD模拟[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2009,37(8):94-98. |
| LIU Jing, ZHANG Wen-wu, SHAO Jian-tao .CFD simulation of convective heat transfer coefficient of external surfaces of buildings[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2009,37(8):94-98. | |
| 12 | 赵人达,王永宝 .日照作用下混凝土箱梁温度场边界条件研究[J].中国公路学报,2016,29(7):52-61. |
| ZHAO Ren-da, WANG Yong-bao .Study on the boundary conditions of temperature field of concrete box girder under the action of sunlight[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2016,29(7):52-61. | |
| 13 | 刘文燕,黄鼎业,华毅杰 .混凝土表面对流换流系数测试研究[J].建筑材料学报,2004,7(2):232-235. |
| LIU Wen-yan, HUANG Ding-ye, HUA Yi-jie .Concrete surface convection transfer coefficient testing study[J].Journal of Building Materials,2004,7(2):232-235. | |
| 14 | 张建荣,刘照球 .混凝土对流换热系数的风洞实验研究[J].土木工程学报,2006,39(9):39-42,61. |
| ZHANG Jianrong, LIU Zhaoqiu .Experimental wind tunnel study of convective heat transfer coefficient of concrete[J].Journal of Civil Engineering,2006,39(9):39-42,61. | |
| 15 | 宋志文,肖建庄,赵勇 .基于试验测定的混凝土热工参数反演计算[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2010,38(1):35-38. |
| SONG Zhiwen, XIAO Jianzhuang, ZHAO Yong .Inverse calculation of thermal parameters of concrete based on experimental determination[J].Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science Edition),2010,38(1):35-38. | |
| 16 | GUO Lixia, GUO Lei, ZHONG Ling,et al .Thermal conductivity and heat transfer coefficient of concrete[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Material Science Edition,2011,26(4):791-796. |
| 17 | 凯尔别克·F .太阳辐射对桥梁结构的影响[M].刘兴法,译.北京:中国铁道出版社,1981:32-36. |
| 18 | LEE J H .Investigation of extreme environmental conditions and design thermal gradients during construction for prestressed concrete bridge girders[J].Journal of Bridge Engineering,2012,17(3):547-556. |
| 19 | 郭进军,张雷顺,蔺新艳 .混凝土表面粗糙度评测新方法[J].工业建筑,2003,33(6):52-54. |
| GUO Jinjun, ZHANG Leishun, LIN Xinyan .A new method of concrete surface roughness evaluation[J].Industrial Construction,2003,33(6):52-54. | |
| 20 | 杨世铭,陶文铨 .传热学[M].4版.北京:高等教育出版社,2006:211-217. |
| 21 | 柳孝图 .建筑物理[M].2版.北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2000. |
| 22 | 李皓,刘小君,张彤,等 .表面粗糙度对接触界面间流体流动的影响[J].合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2016,39(11):1464-1467. |
| LI Hao, LIU Xiaojun, ZHANG Tong,et al .Effect of surface roughness on fluid flow between contact surface[J].Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2016,39(11):1464-1467. |
| [1] | . Combined Effect of Recycled Fine Aggregate and Clay Brick Powder on Properties of 3D Printed Concrete [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(3): 18-27. |
| [2] | WANG Xiaoxián, LIU Jiaping, MU Song, et al. Sodium β-Glycerophosphate in Concrete Affects the Inhibited Behavior of Steel Bar [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(3): 28-40. |
| [3] | LI Baijian, HUANG Yan, FU Xinsha. Influence of Shapes of Corrugated Steel Plate on Load-Carrying Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Slab Culvert and Arch Effect with Lateral Restraint [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 110-118. |
| [4] | XU Chen, XU Qindong, SUN Xuxia, WU Yongxian, ZHANG Yubin, XU Yi. Optimal Design of Steel-SFRC Composite Deck of Continuous Steel Girder [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 26-37. |
| [5] | DING Faxing, CAI Yongqiang, WANG Liping, SUN Hao, LÜ Fei, HUANG Xiuwen. Seismic Performance Analysis of Welded Multi-Cavity Double Steel Plate-Concrete Composite Shear Wall [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 15-25. |
| [6] | CHEN Zongping, QIN Weiheng, LIANG Yuhan, ZHOU Ji. Test and Bearing Capacity Calculation Method of Concrete-Filled CFRP-Stainless Steel Sandwich Tube Columns Under Axial Compression [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 1-14. |
| [7] | YANG Yonghong, TANG Zude, WANG Chun, ZHU Guanru. Influence of Alignment Indexes of Highway Turning Section on Safety Performance of Concrete Guardrail [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 90-99. |
| [8] | WU Bo, DING Jinpeng. Compressive and Chloride Resistance Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Mixed with Hole Slag [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(9): 120-128. |
| [9] | WU Bo, HUANG Tingting. Carbonation Properties and Pore Characteristics of Different Interfaces in Recycled Lump/Aggregate Concrete [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 52-60. |
| [10] | LIU Xin, YAO Yunlong, YAO Zirui, et al. Effect of Low Air Pressure on Performance and Pore Structure of Foamed Concrete in Pouring Period [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 72-80. |
| [11] | XIE Xiaoli, GOU Wenxin, PANG Mulin, et al. Dynamic Characteristics of RC Rigid Frame Arch Bridge Strengthened by Plate-Truss Combination [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 31-43. |
| [12] | WU Bo, CHEN Zhaonan, WANG Hui. Creep Behavior of Reinforced and Unreinforced Recycled Lump/Aggregate Concrete [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 35-42. |
| [13] | SUN Xiaohe, SHI Chenghua, LIU Linghui, et al. Concrete Crack Image Recognition System Based on Improved Seed Filling Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 127-136,146. |
| [14] | ZHENG Hongyu, YU Yuqi, XU Dixin, et al. Axial Compression Test of Seawater Sea-Sand Concrete Circular Column Inner-Confined by BFRP Spiral Strip [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 96-108. |
| [15] | LUO Xiaoyong, CHENG Qian, CHENG Junfeng, et al. Mechanical Properties of Hydrochloric Acid Corroded Concrete Under Cyclic Loading [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 73-85. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||