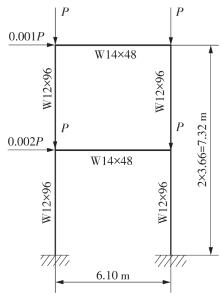
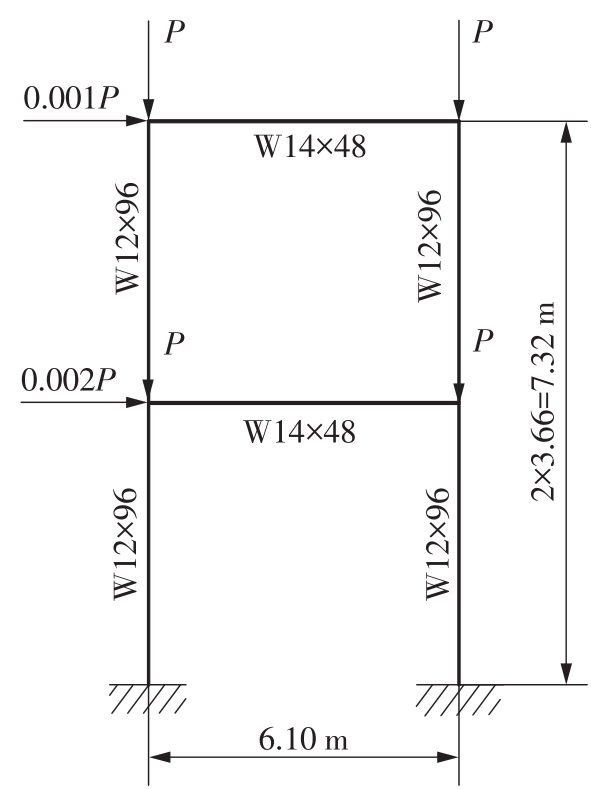
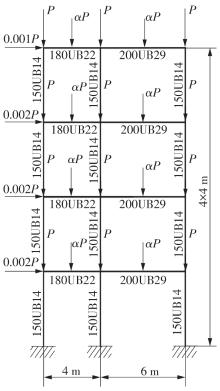
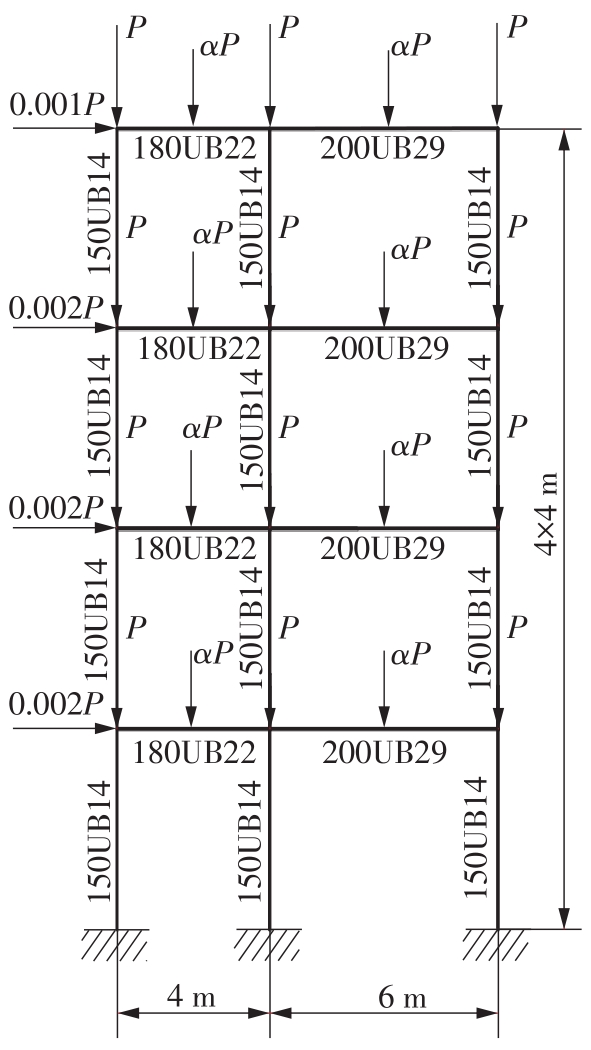
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (7): 90-99.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220423
Special Issue: 2023年土木建筑工程
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Generalized Plastic Hinge Method for Ultimate Strength Analysis of Steel Frames Considering Residual Stress
BAI Dalian YANG Lufeng YIN Yuqi
- School of Civil Engineering & Architecture/Key Laboratory of Disaster Prevention and Structural Safety of the Ministry of Education,Guangxi University,Nanning 530004,Guangxi,China
-
Received:2022-07-04Online:2023-07-25Published:2023-01-27 -
Contact:殷玉琪(1996-),女,博士生,主要从事结构承载安全性研究。 E-mail:yinyuqi1127@163.com -
About author:柏大炼(1990-),男,博士,主要从事结构承载安全性研究。E-mail:baidl90@163.com -
Supported by:the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China(51738004)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
BAI Dalian, YANG Lufeng, YIN Yuqi. Generalized Plastic Hinge Method for Ultimate Strength Analysis of Steel Frames Considering Residual Stress[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 90-99.
share this article
| 1 | Eurocode 3:Design of steel structures-part 1-1:general rules and rules for buildings:DS/EN 1993-1-1 [S]. |
| 2 | WALPORT F, GARDNER L, NETHERCOT D A .A method for the treatment of second order effects in plastically-designed steel frames[J].Engineering Structures,2019,200:109516. |
| 3 | DE-ALVARENGA A R .Plastic-zone advanced analysis-formulation including semi-rigid connection[J].Engineering Structures,2020,212:110435. |
| 4 | 陈朝晖,陶宇宸,杨永斌 .基于刚体准则的空间框架弹塑性非线性分析方法[J].建筑结构学报,2020,41(10):139-149. |
| CHEN Zhaohui, TAO Yuchen, YANG Yongbin .Elasto-plastic nonlinear analysis method for spatial frame based on rigid body rule[J].Journal of Building Structures,2020,41(10):139-149. | |
| 5 | CHEN W F, LUI E M .Stability design of steel frames[M].Boca Raton:CRC Press,2018. |
| 6 | LIEW J Y R, WHITE D W, CHEN W F .Second-order refined plastic-hinge analysis for frame design. Part Ⅰ[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,1993,119(11):3196-3216. |
| 7 | LIEW J Y R, WHITE D W, CHEN W F .Second-order refined plastic-hinge analysis for frame design. Part Ⅱ[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,1993,119(11):3217-3237. |
| 8 | CHEN W F, TOMA S .Advanced analysis of steel frames:theory,software,and applications[M].Boca Raton:CRC Press,2018. |
| 9 | THAI H T, NGUYEN T K, LEE S,et al .Review of nonlinear analysis and modeling of steel and composite structures[J].International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics,2020,20(4):2030003. |
| 10 | ZIEMIAN R D, MCGUIRE W .Modified tangent modulus approach,a contribution to plastic hinge analysis[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2002,128(10):1301-1307. |
| 11 | THAI H T,UY B, KANG W H,et al .System reliability evaluation of steel frames with semi-rigid connections[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2016,121:29-39. |
| 12 | PIRES D, BARROS R C, SILVEIRA R A M,et al .An efficient inelastic approach using SCM/RPHM coupling to study reinforced concrete beams, columns and frames under fire conditions[J].Engineering Structures,2020,219:110852. |
| 13 | ZHOU Y, HUANG D, LI T,et al .Second-order arbitrarily-located-refined plastic hinge model for high-strength steel frame design[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2022,190:107112. |
| 14 | RAHMAN M K .Ultimate strength estimation of ships’ transverse frames by incremental elastic-plastic finite element analysis[J].Marine Structures,1998,11(7):291-317. |
| 15 | YANG L F, LIU J M, YU B,et al .Failure path-independent methodology for structural damage evolution and failure mode analysis of framed structures[J].International Journal of Damage Mechanics,2017,26(2):274-292. |
| 16 | 杨绿峰,柏大炼,杨大尉 .刚架结构极限承载力分析的广义塑性铰研究[J].土木工程学报,2020,53(4):31-37. |
| YANG Lufeng, BAI Dalian, YANG Dawei .Generalized plastic hinge for ultimate bearing capacity of rigid-framed structures[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2020,53(4):31-37. | |
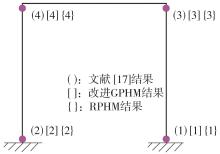
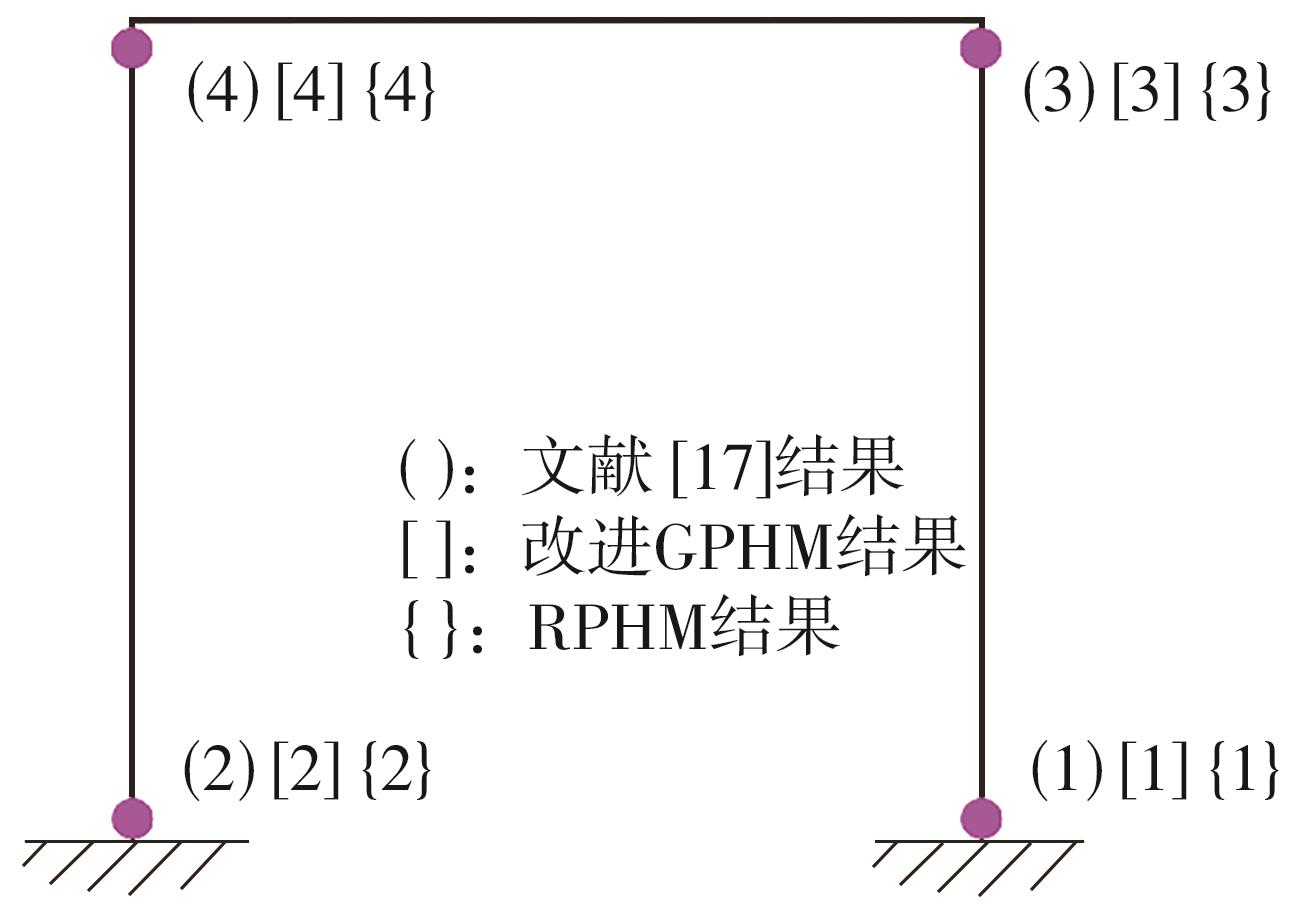
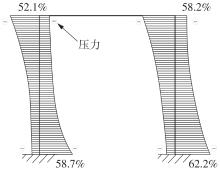
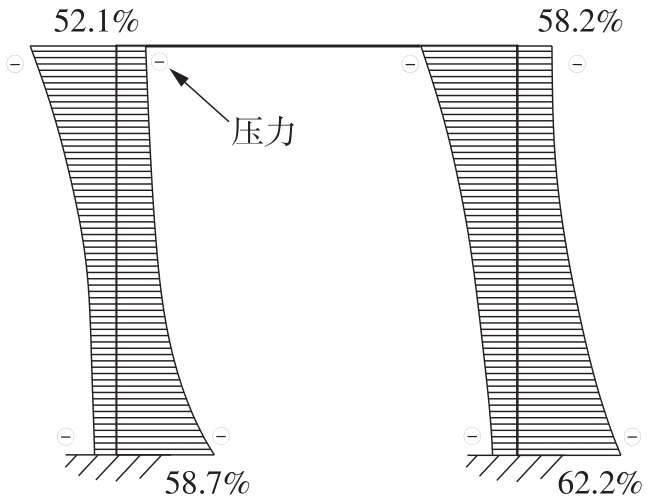
| 17 | 杨绿峰,殷玉琪,柏大炼 .基于平衡向量的刚架结构极限承载力分析的广义塑性铰法[J].工程力学,2021,38(12):49-56. |
| YANG Lufeng, YIN Yuqi, BAI Dalian .Balanced vector based generalized plastic hinge method for ultimate bearing capacity of frame structures[J].Engineering Mechanics,2021,38(12):49-56. | |
| 18 | ZUBYDAN A H .A simplified model for inelastic second order analysis of planar frames[J].Engineering Structures,2010,32(10):3258-3268. |
| 19 | FORABOSCHI P .Predictive formulation for the ultimate combinations of axial force and bending moment attainable by steel members[J].International Journal of Steel Structures,2020,20(2):705-724. |
| 20 | DUAN L, CHEN W F .A yield surface equation for doubly symmetrical sections[J].Engineering Structures,1990,12(2):114-119. |
| 21 | 杨绿峰,赵玉峰,解威威 .方形钢管混凝土框架二阶效应下极限承载力的高效线弹性迭代分析[J].土木工程学报,2022,55(2):1-10. |
| YANG Lufeng, ZHAO Yufeng, XIE Weiwei .Linear elastic iteration with high efficiency for ultimate bearing capacity of square-profile CFST frame with second order effect[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2022,55(2):1-10. | |
| 22 | ECCS .Manual on the stability of steel structures[M].2nd ed.Brussels:European Convention for Constructional Steelwork,1976. |
| 23 | LIEW J Y R, CHEN W F .Implications of using refined plastic hinge analysis for load and resistance factor design[J].Thin-Walled Structures,1994,20:17-47. |
| 24 | Specification for structural steel buildings:AI [S]. |
| 25 | 钢结构设计标准: [S]. |
| 26 | VOGEL U .Calibrating frames[J].Stahlbau,1985,54(10):295-301. |
| 27 | CHAN S L, CHUI P P T .Non-linear static and cyclic analysis of steel frames with semi-rigid connections[M].Amsterdam:Elsevier,2000. |
| 28 | ZIEMIAN R D, MCGUIRE W .Structural analysis software-mastan 2 v5.1[CP/OL].(2022-08-30) [2022-10-13].. |
| [1] | LI Junye, TIAN Gongqiang, WANG Xinpeng, et al.. Analysis of Forming Characteristics of Conductive Slip Ring Brush Wire by Finite Element Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(11): 140-150. |
| [2] | ZHANG Junhao, CHENG Xiuquan, XIA Qinxiang, et al. Study on Residual Stress Control of Damaged Aircraft Component Based on Non-uniform Overlap Ratio Laser Shock Peening [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(3): 73-79. |
| [3] | LING Yuhong, WU Shan, GU Jingxin, et al. A Comparative Study on Vibration Isolation Methods of Metro Superstructure#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(4): 1-8. |
| [4] | WANG Suguo. Influence of Monolithic Slab on the Actual Axial Force of Frame Beam in RC Frame Structure [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(7): 10-18. |
| [5] | MA Xiaoming OU Qingyang. Numerical Simulation for Hole-drilling Strain Gage Method Applied on Curved Surface [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(12): 25-31. |
| [6] | LI Wanrun ZHANG Guangli LIU Yufei FANG Zhao LI Aiqun DU Yongfeng. Welding Residual Stress Simulation and Experimental Verification in Beamto-Column Joints of Q345B Steel [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(10): 114-123. |
| [7] | WU Shang-sheng YU Zhong-ming. Cold Rolling Process and Numerical Simulation of Residual Stress for Flexspline of Harmonic Reducer [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(2): 52-58. |
| [8] | XU Xiao SHUAI Gao-peng CHENG Xiu-quan XIA Qin-xiang. Influence of Decolorization Procedures on Color Value and Molecular Structure of Sugar Beet Pectin#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(12): 71-77. |
| [9] | WEI De-min LIU De-yuan LI Di. Nonlinear Response of Reinforced Concrete Frame Structures Under Symmetrical Impact [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(2): 8-13. |
| [10] | GUO Meng LIU Zhi-yuan HUANG Wei WANG Shuang-jiao YUAN Quan . Experiment on Seismic Performance of Earthquake Damage Frame Strengthened with Aerated Concrete Block Composite Wall [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(10): 117-124. |
| [11] | Kong Jin-xing Deng Fei Zhao Wei He Ning. Effects of Cooling/Lubrication Conditions on Surface Integrity of Pure Iron Materials During Turning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(6): 89-95. |
| [12] | Zhang Jia-hua Yang Xiao-li Zhang Biao Xu Jing-shu Yang Zi-han. Stability Analysis of Shallow Bias Tunnels Based on Nonlinear Failure Criterion [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(8): 97-103,121. |
| [13] | Wu Bo Qin Meng-yang Ye Bang-yan He Ai-dong. Experimental Investigation into Scatter of Surface Residual Stress Caused by Turning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(7): 73-77. |
| [14] | Qin Meng-yang Ye Bang-yan He Ai-dong. Investigation into Residual Stress of Pre-Stress Cutting Based on Thermo-Mechanical Coupling Analysis [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(1): 47-52. |
| [15] | Huang Zhi-tao Tian Wen-huai. Microstructure and Stress Distribution of GCr15 Steel Balls After Surface Deformation-Hardening Treatment [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(6): 84-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||