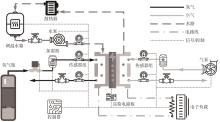
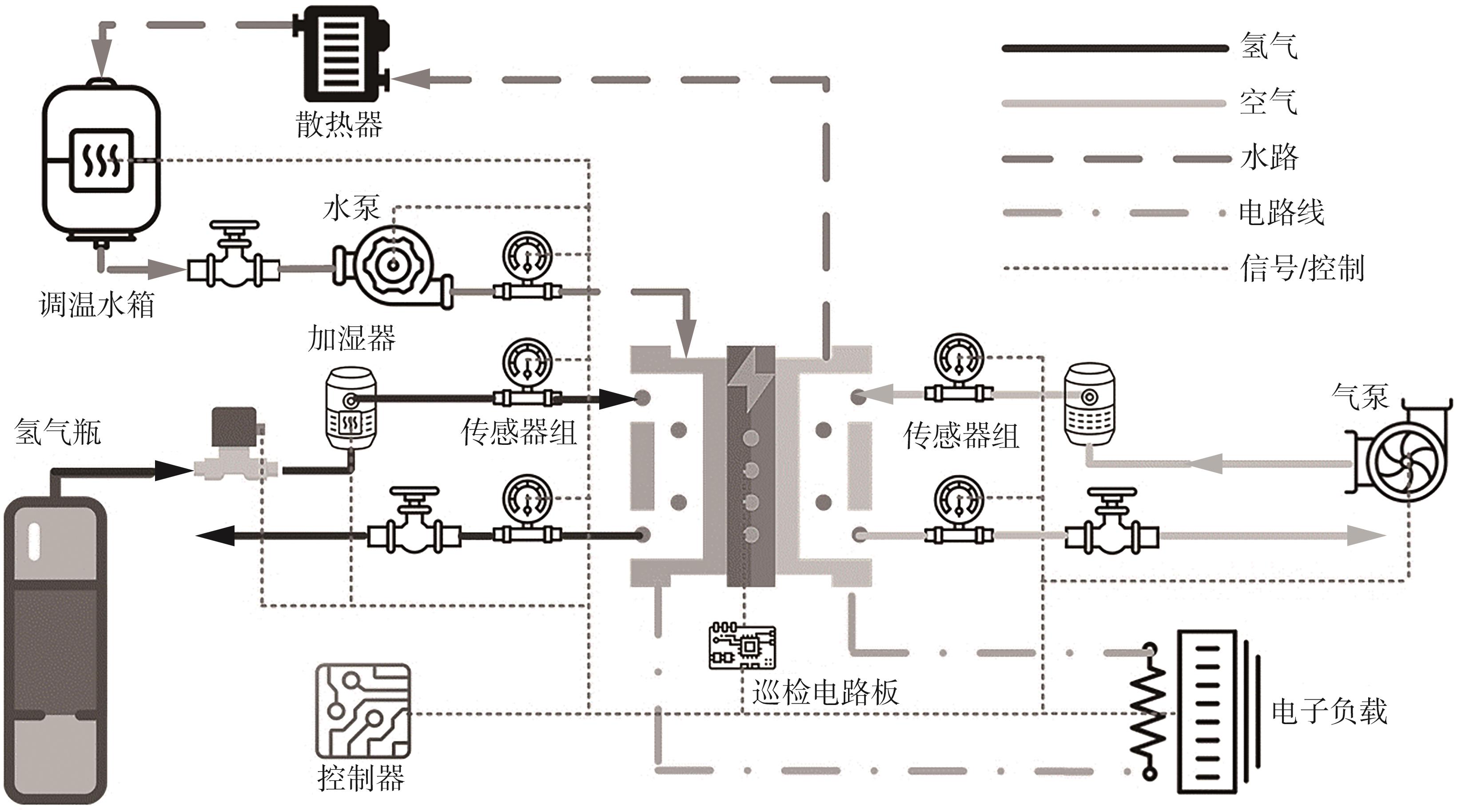
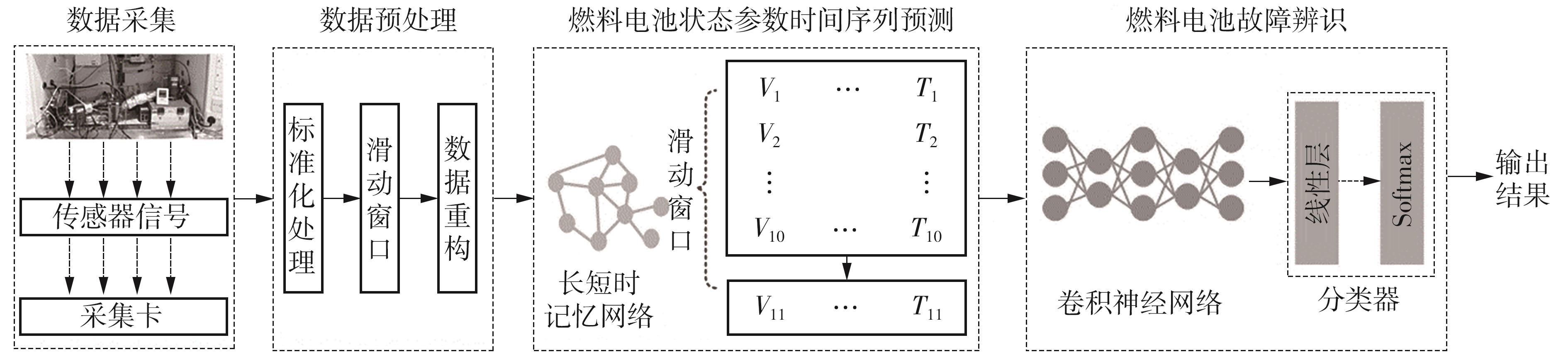
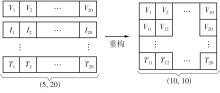
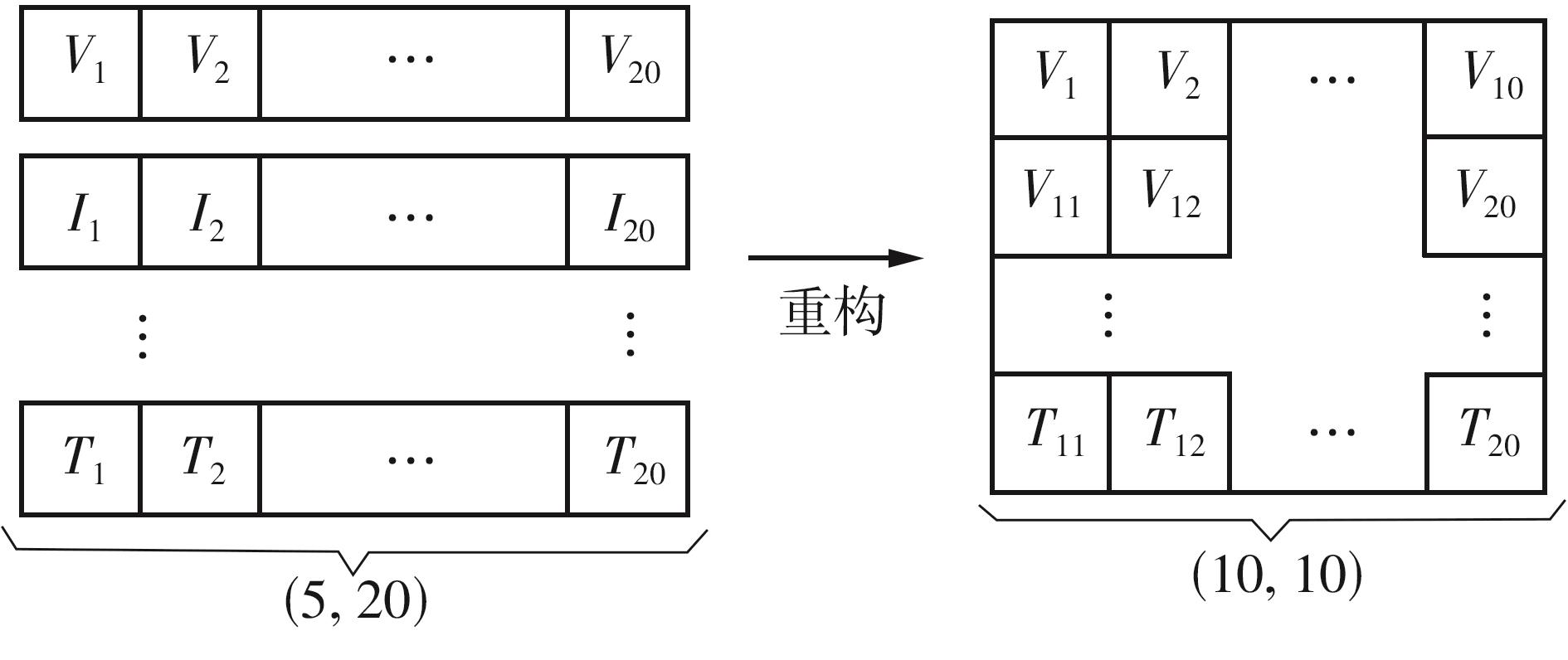
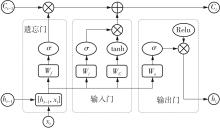
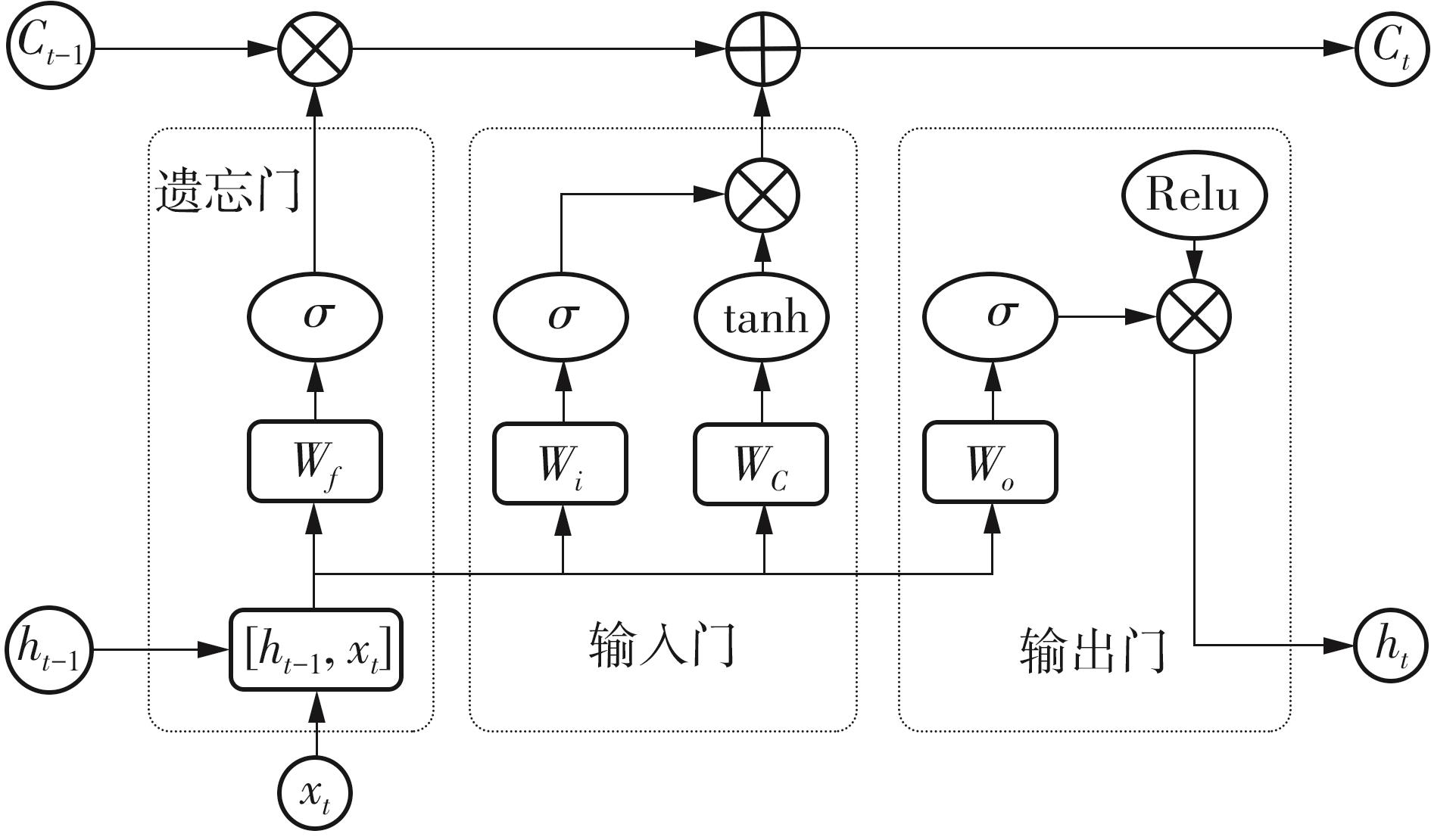
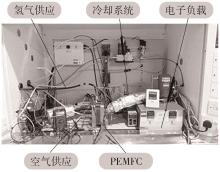
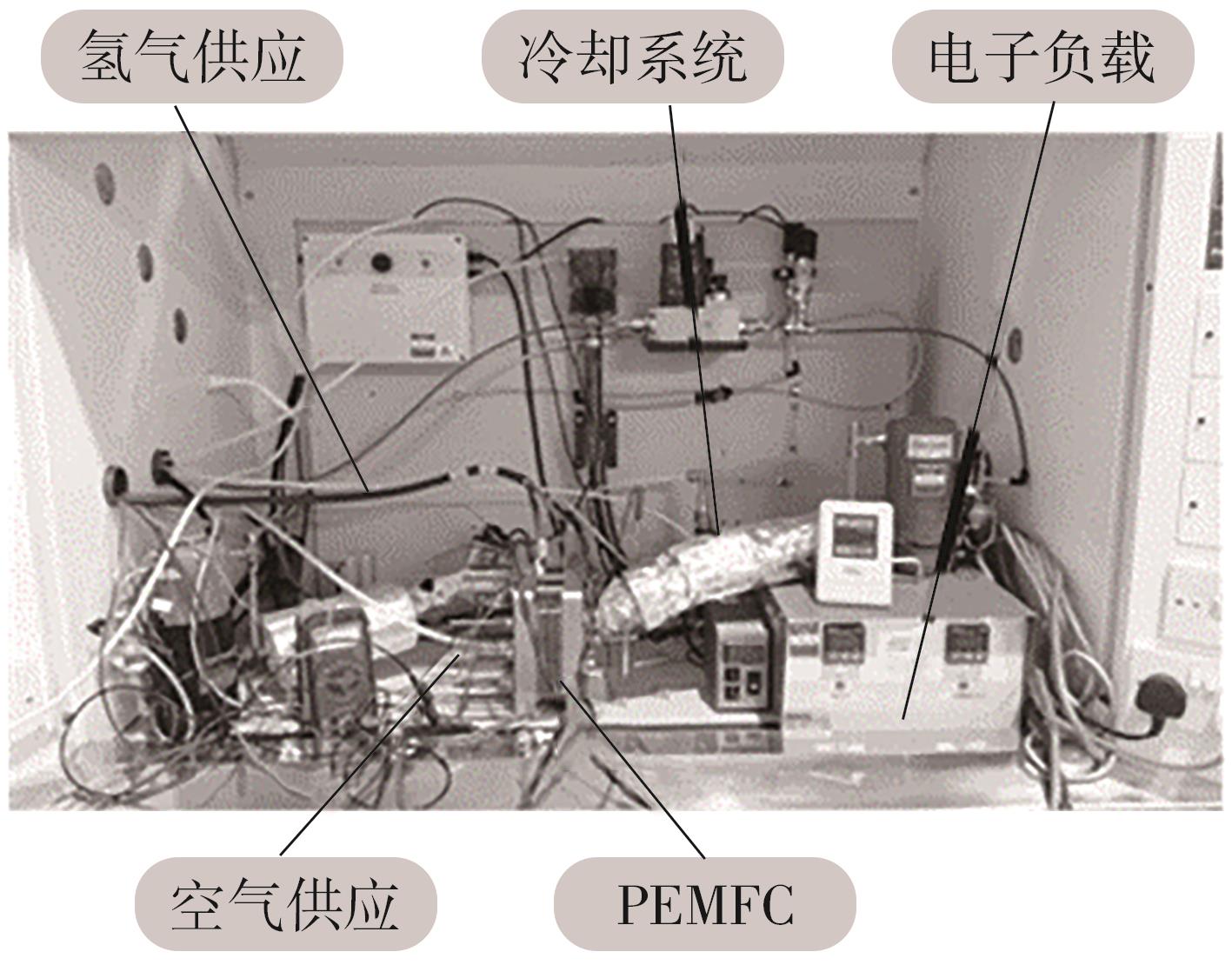
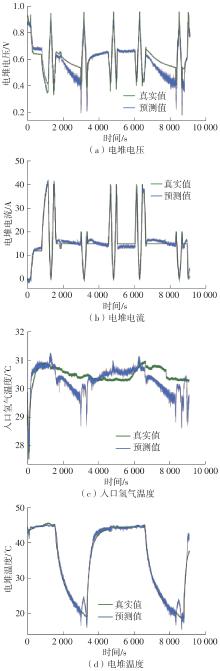
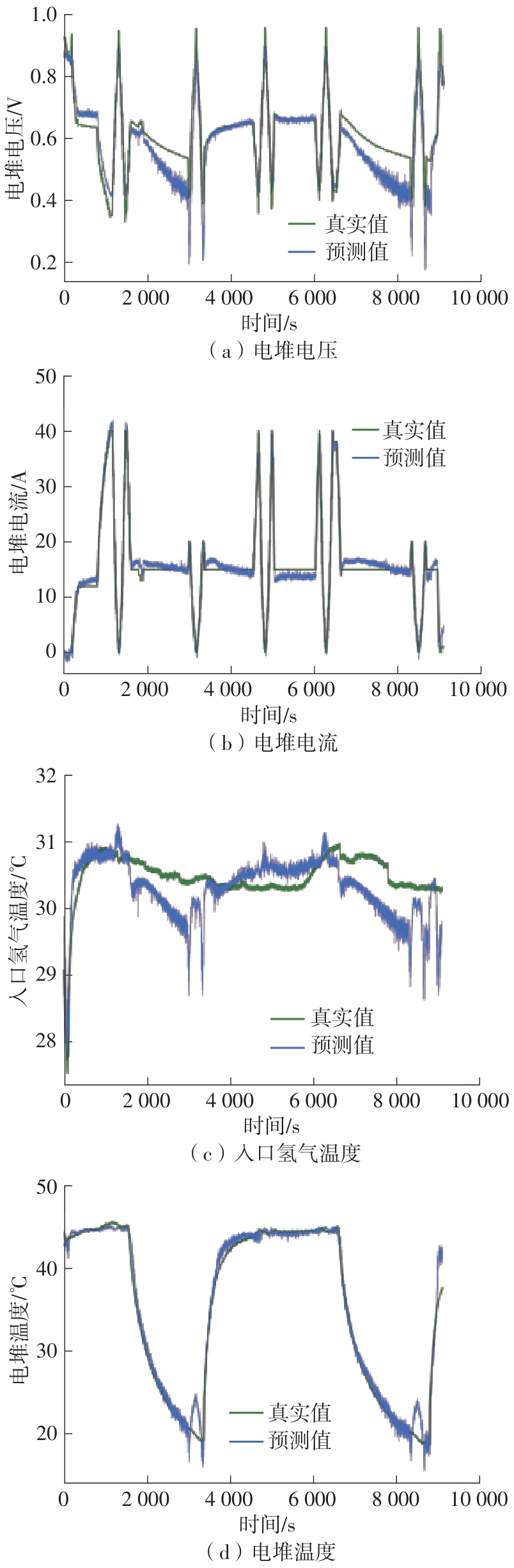
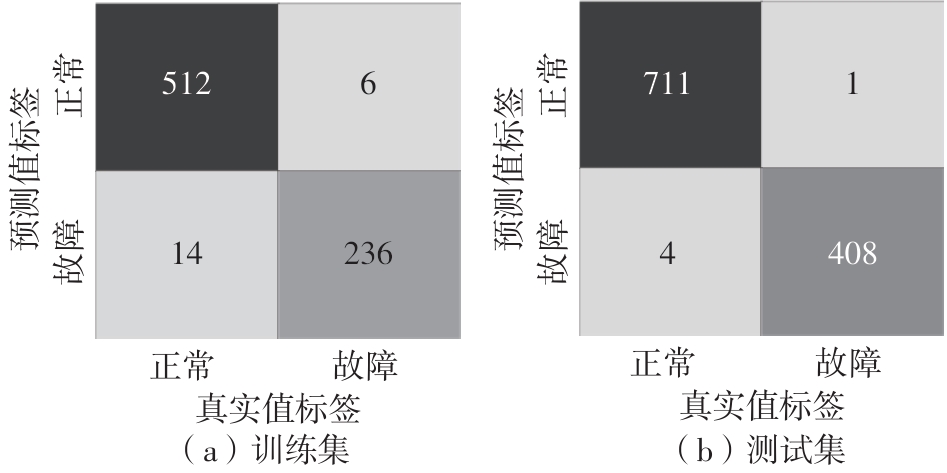
| [1] |
赵天宇,陈东,霍为炜,等 .氢燃料电池汽车能量管理系统模糊控制仿真研究[J].重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2022,36(3):36-40.
|
|
ZHAO Tianyu, CHEN Dong, HUO Weiwei,et al .Simulation of energy management system of hydrogen fuel cell vehicle based on fuzzy control[J].Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science),2022,36(3):36-40.
|
| [2] |
井绪宝,刘丛浩,郭宇,等 .应用LADRC的车用质子交换膜燃料电池温湿度控制优化研究[J].重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2023,37(5):54-59.
|
|
JING Xubao, LIU Conghao, GUO Yu,et al .Research on optimization of temperature and humidity control of proton exchange membrane fuel cells for vehicles using LADRC[J].Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science),2023,37(5):54-59.
|
| [3] |
安治国,张东阳,张振,等 .阶梯型流道对质子交换膜燃料电池性能的影响[J].重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2022,41(12):134-140,150.
|
|
AN Zhiguo, ZHANG Dongyang, ZHANG Zhen,et al .Influence of stepped flow channel on the performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J].Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science),2022,41(12):134-140,150.
|
| [4] |
LI H W, QIAO B X, LIU J N,et al .A data-driven framework for performance prediction and parameter optimization of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2022,271:116338/1-15.
|
| [5] |
ZHANG Y F, MA R, XIE R Y,et al .A degradation prediction method for PEM fuel cell based on deep temporal feature extraction and transfer learning[J].IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification,2024,10(1):203-212.
|
| [6] |
MIN W, LIANGFEI X, XIAOFAN Y .A coupled CFD model for an accurate and fast prediction of the unsteady operation process of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2022,272:116317/1-16.
|
| [7] |
ZIHAN T, CHU Z, JINLIN X,et al .Evolutionary gate recurrent unit coupling convolutional neural network and improved manta ray foraging optimization algorithm for performance degradation prediction of PEMFC[J].Applied Energy,2023,336:120821/1-14.
|
| [8] |
张宁,霍为炜,孙超,等 .应用模糊规则的燃料电池水管理容错控制[J].重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2022,36(5):78-83.
|
|
ZHANG Ning, HUO Weiwei, SUN Chao,et al .Fault tolerant control of fuel cell water management based on fuzzy rules[J].Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science),2022,36(5):78-83.
|
| [9] |
孙铁生,陈山,孙红,等 .质子交换膜燃料电池发动机热管理特性仿真分析[J].重庆大学学报,2023,46(4):27-36.
|
|
SUN Tiesheng, CHEN Shan, SUN Hong,et al .Simulation analysis on thermal management characteristics of proton-exchange-membrane fuel-cell engine[J].Journal of Chongqing University,2023,46(4):27-36.
|
| [10] |
张雪霞,蒋宇,孙腾飞,等 .质子交换膜燃料电池水淹和膜干故障诊断研究综述[J].西南交通大学学报,2020,55(4):828-838,864.
|
|
ZHANG Xuexia, JIANG Yu, SUN Tengfei,et al .Review on fault diagnosis for flooding and drying in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J].Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2020,55(4):828-838,864.
|
| [11] |
DU R, WEI X, WANG X,et al .A fault diagnosis model for proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on impedance identification with differential evolution algorithm[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2021,46(78):38795-38808.
|
| [12] |
LIU Z, SUN Y, MAO L,et al .Efficient fault diagnosis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell using external magnetic field measurement[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2022,266:115809/1-13.
|
| [13] |
雍加望,赵倩倩,冯能莲 .基于非线性动态模型的质子交换膜燃料电池故障诊断[J].化工学报,2022,73(9):3983-3993.
|
|
YONG Jiawang, ZHAO Qianqian, FENG Nenglian .Fault diagnosis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on nonlinear dynamic model[J].CIESC Journal,2022,73(9):3983-3993.
|
| [14] |
XIAO F, CHEN T, ZHANG J,et al .Water management fault diagnosis for proton-exchange membrane fuel cells based on deep learning methods[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2023,48(72):28163-28173.
|
| [15] |
刘昕宇,韩莹,陈维荣,等 .基于改进SSA-DBN的质子交换膜燃料电池水故障智能分类方法[J].电力自动化设备,2024,44(4):18-24.
|
|
LIU Xinyu, HAN Ying, CHEN Weirong,et al .Intelligent classification method of water faults for proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on improved SSA-DBN[J].Electric Power Automation Equipment,2024,44(4):18-24.
|
| [16] |
RUBIO M A, SANCHEZ D G, GAZDZICKI P,et al .Failure mode diagnosis in proton exchange membrane fuel cells using local electrochemical noise[J].Journal of Power Sources,2022,541:231582/1-10.
|
| [17] |
ZUO B, ZHONG Z H, CHENG J S,et al .Data-driven flooding fault diagnosis method for proton-exchange membrane fuel cells using deep learning technologies[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2022,251:115004/1-9.
|
| [18] |
谢雨岑 .基于深度学习的燃料电池性能衰退预测研究[D].成都:电子科技大学,2021.
|
| [19] |
符灏 .质子交换膜燃料电池系统的动态建模与优化控制[D].南京:东南大学,2022.
|
| [20] |
HUANG W, JIAN Q, FENG S,et al .A hybrid optimization strategy of electrical efficiency about cooling PEMFC combined with ultra-thin vapor chambers[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2022,254:115301/1-15.
|
| [21] |
HUO W, LI W, ZHANG Z,et al .Performance prediction of proton-exchange membrane fuel cell based on convolutional neural network and random forest feature selection[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2021,243:114367/1-10.
|
| [22] |
DAI W, WANG H J, YUAN X Z,et al .A review on water balance in the membrane electrode assembly of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2009,34(23):9461-9478.
|
| [23] |
KANDLIKAR S G, GAROFALO M L, LU Z .Water management in a PEMFC:water transport mechanism and material degradation in gas diffusion layers[J].Fuel Cells,2011,11(6):814-823.
|
| [24] |
LIM B H, MAJLAN E H, DAUD W,et al .Effects of flow field design on water management and reactant distribution in PEMFC:a review[J].Ionics,2016,22:301-316.
|
| [25] |
KONG I M, JUNG A, KIM Y S,et al .Numerical investigation on double gas diffusion backing layer functionalized on water removal in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J].Energy,2017,120:478-487.
|
| [26] |
GU X, HOU Z, CAI J .Data-based flooding fault diagnosis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell systems using LSTM networks[J].Energy and AI,2021,4:100056/1-12.
|
| [27] |
LUO Z, CHANG Z, ZHANG Y,et al .Electro-osmotic drag coefficient and proton conductivity in Nafion® membrane for PEMFC[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2010,35(7):3120-3124.
|
| [28] |
MAO L, JACKSON L, HUANG W,et al .Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell fault diagnosis and sensor abnormality identification using sensor selection method[J].Journal of Power Sources,2020,447:227394/1-10.
|
| [29] |
LIU M H, ZENG A L, CHEN M X,et al .SCINET:time series modeling and forecasting with sample convolution and interaction[C]∥ Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.[S.l.]:NIPS,2022:5816-5828.
|