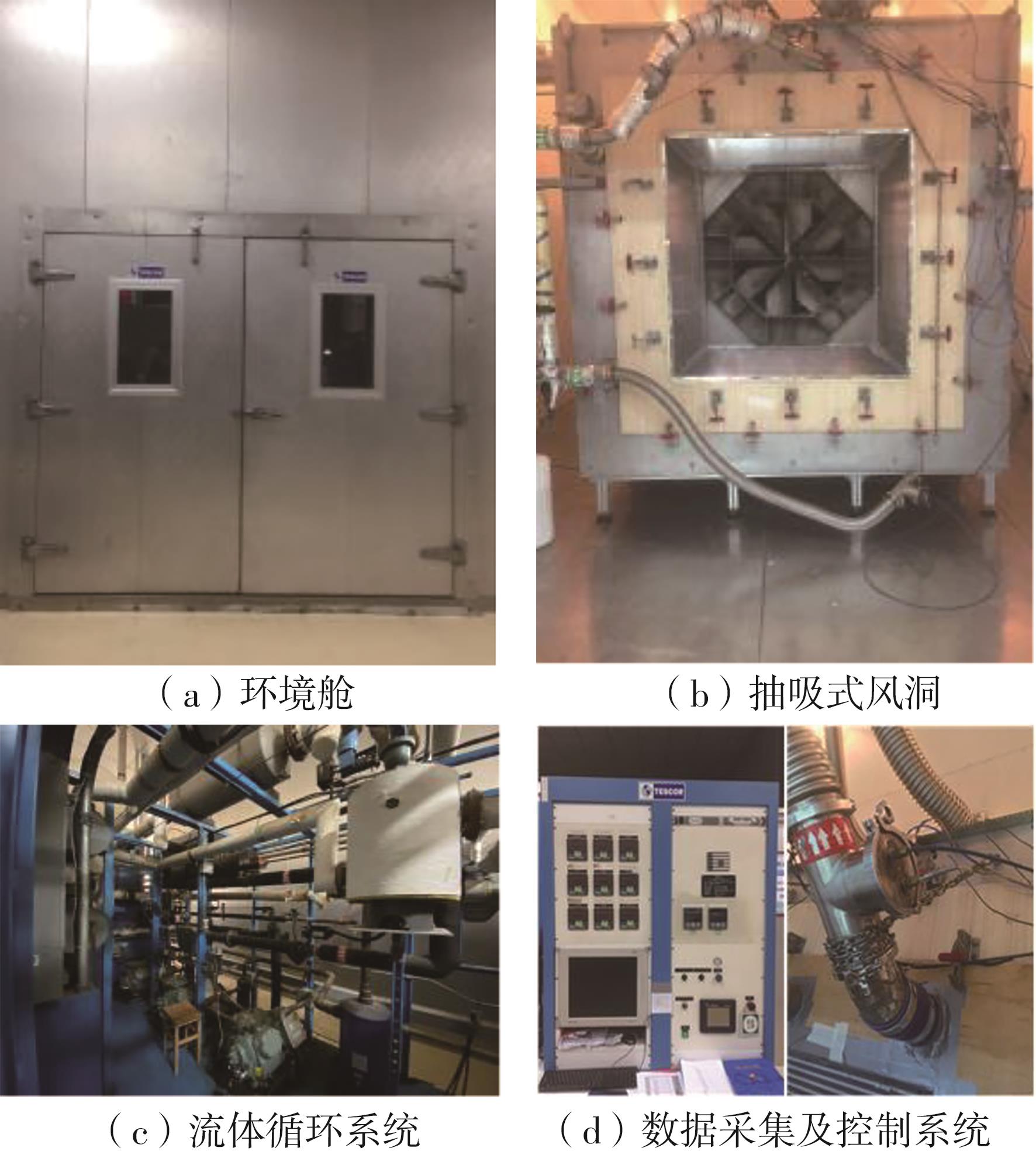
华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (7): 12-20.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220701
所属专题: 2023年机械工程
来流方向对百叶窗翅片‒后扩型涡产生器热工水力性能的影响
胡兴军 罗雨霏 张靖龙 郭鹏 王靖宇 余天明
- 吉林大学 汽车工程学院,吉林 长春 130022
Influence of Inflow Direction on Thermal-Hydraulic Performance of Louvered Fin-Common Flow Down Vortex Generator
HU Xingjun LUO Yufei ZHANG Jinglong GUO Peng WANG Jingyu YU Tianming
- College of Automotive Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,Jilin,China
摘要:
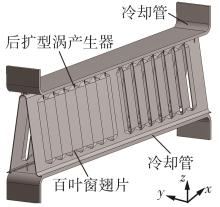
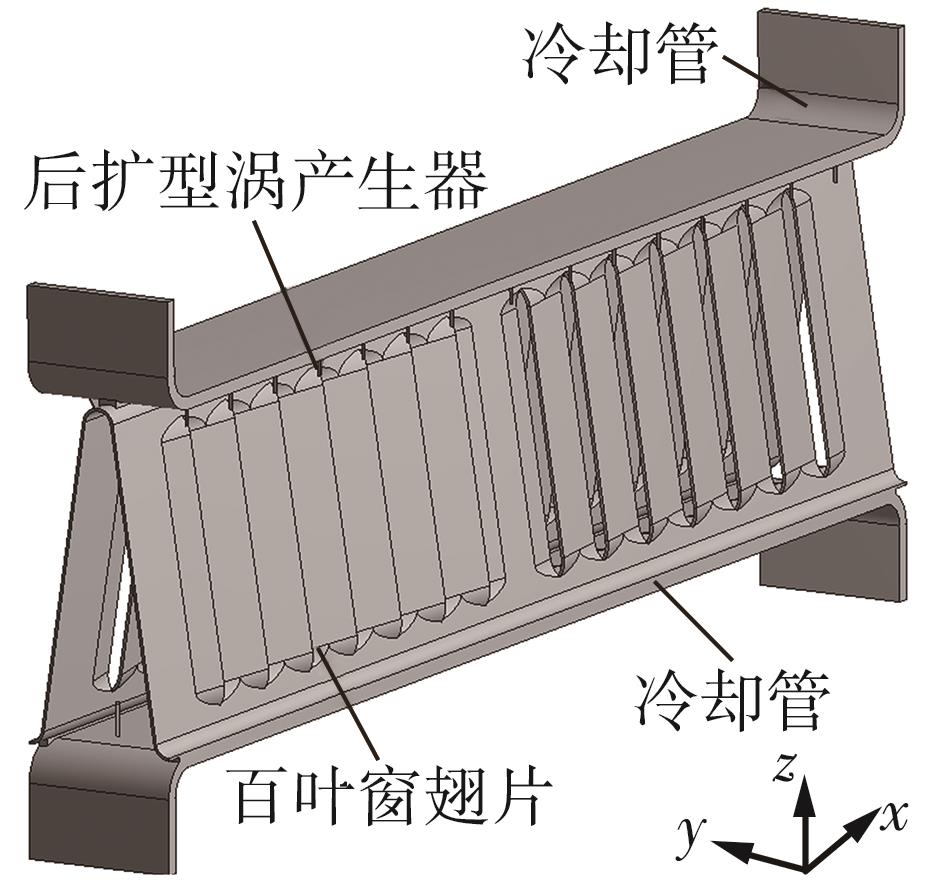
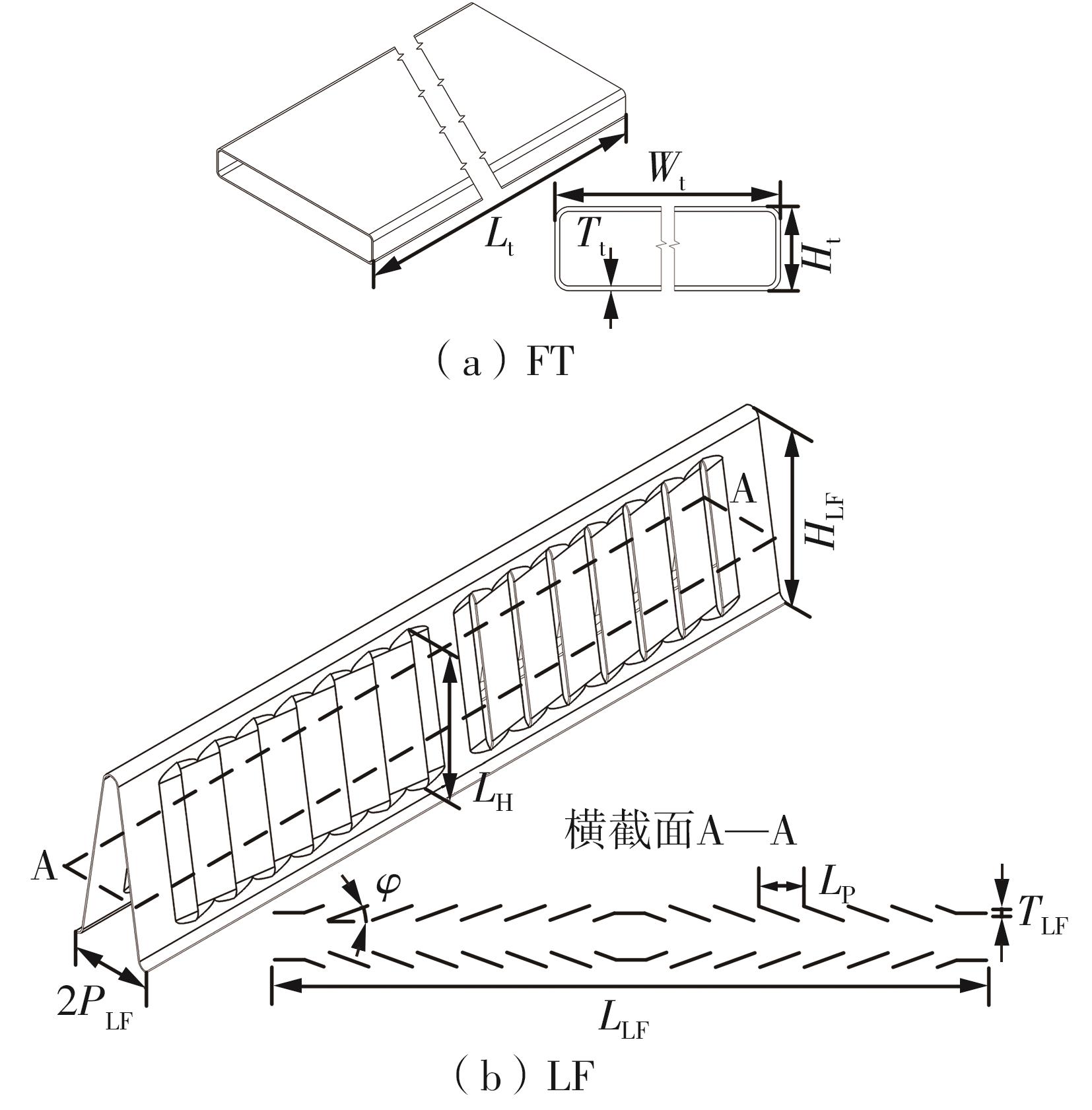
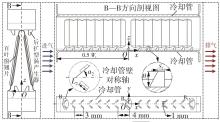
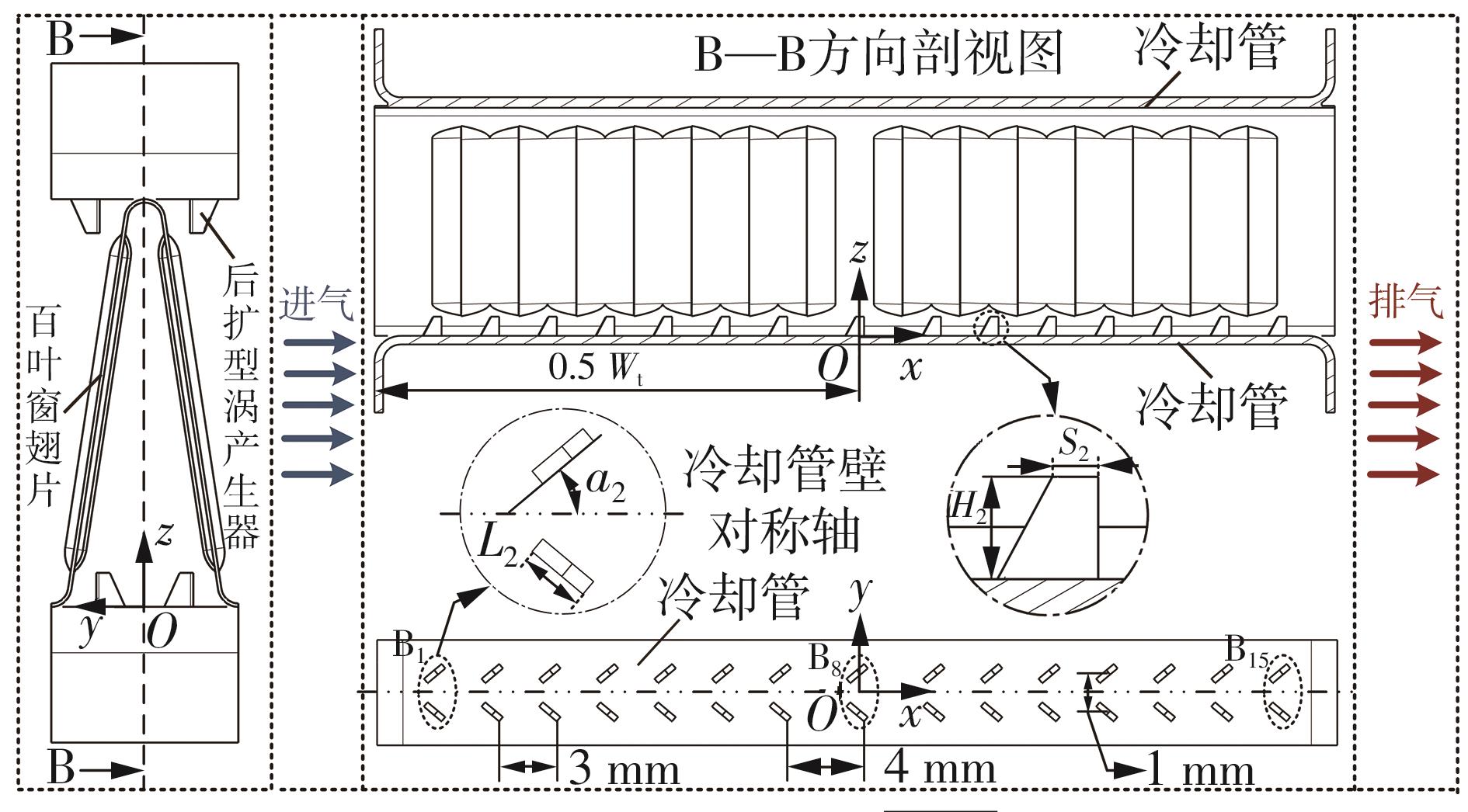
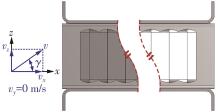
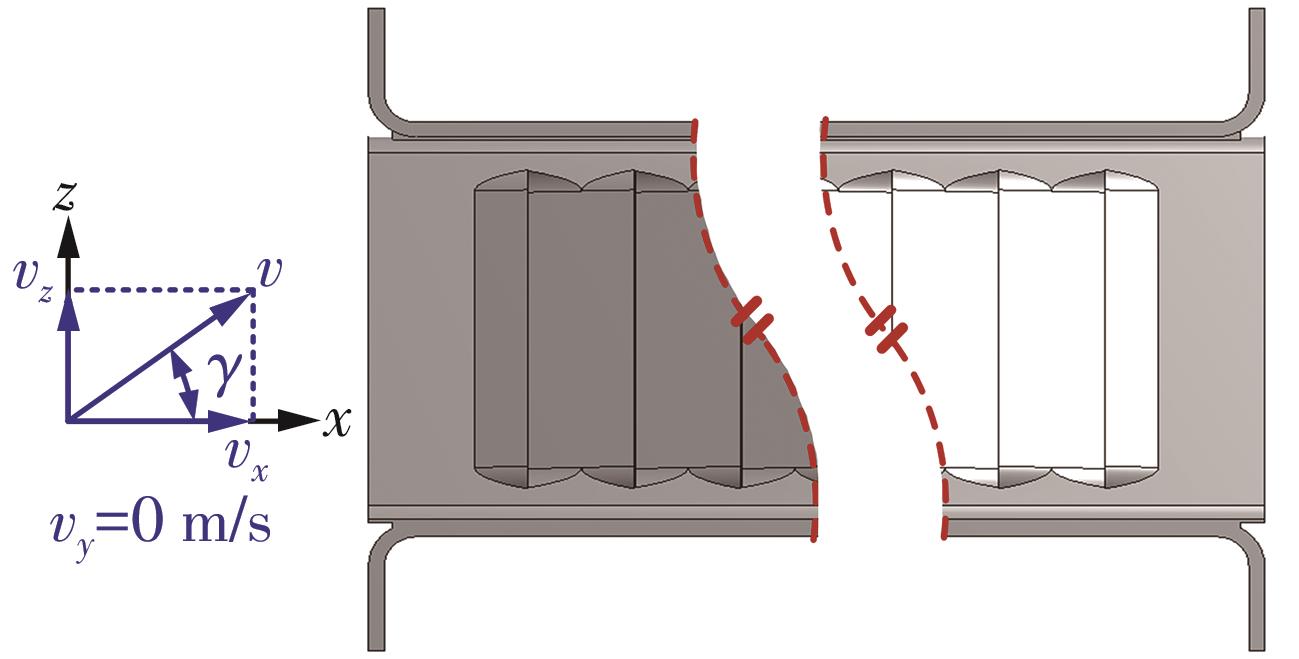
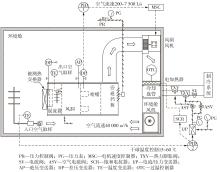
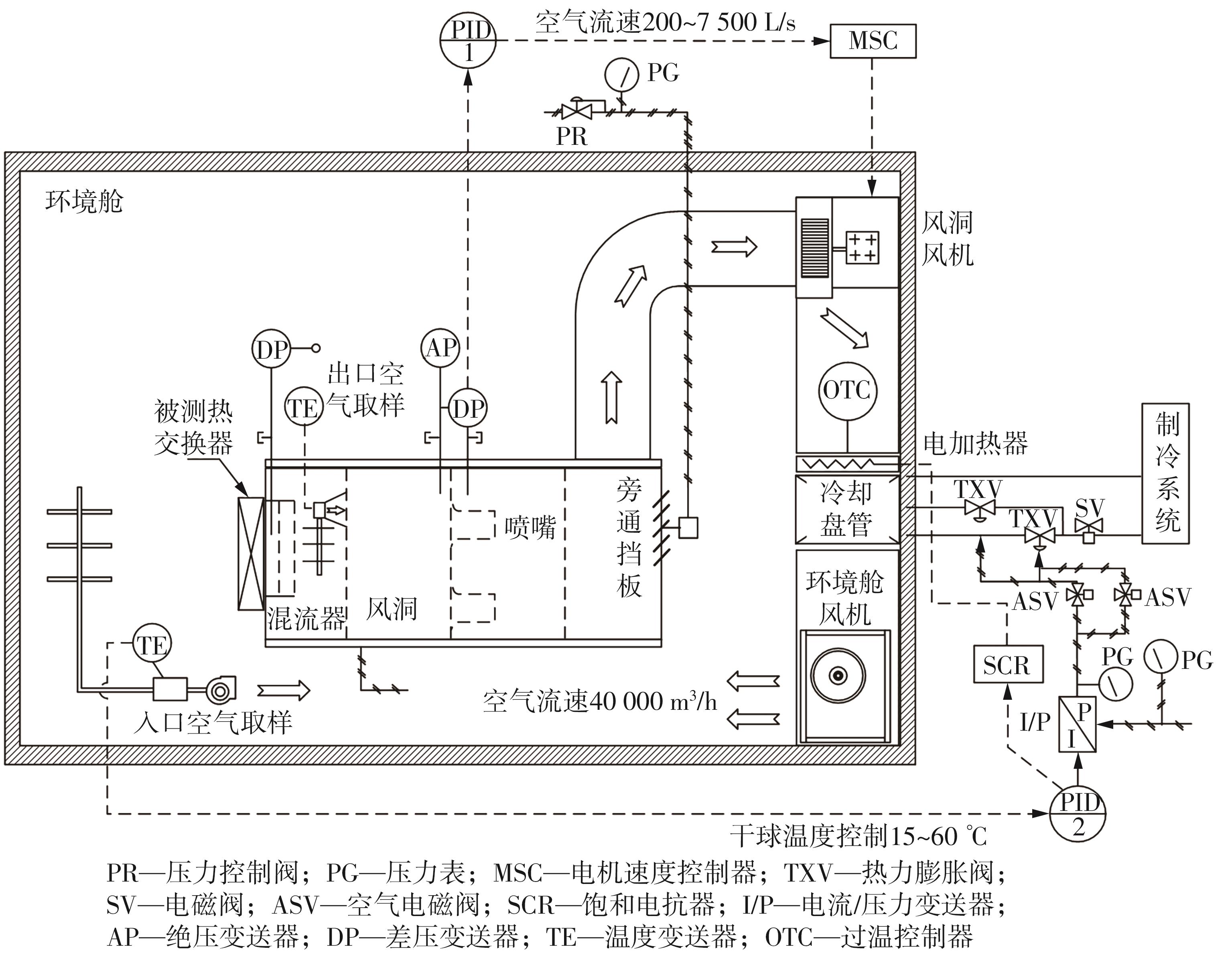
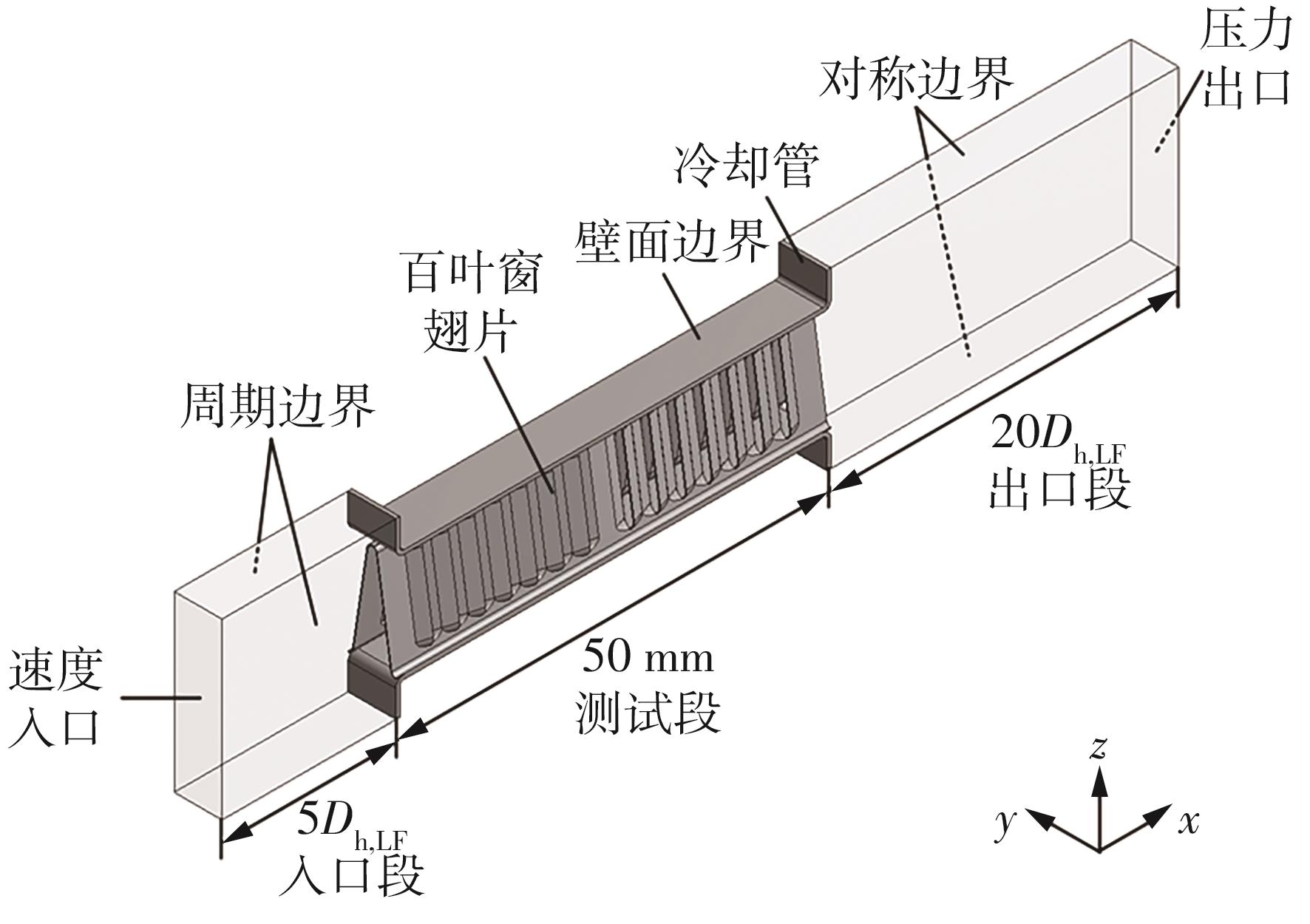
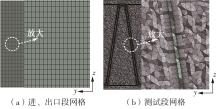
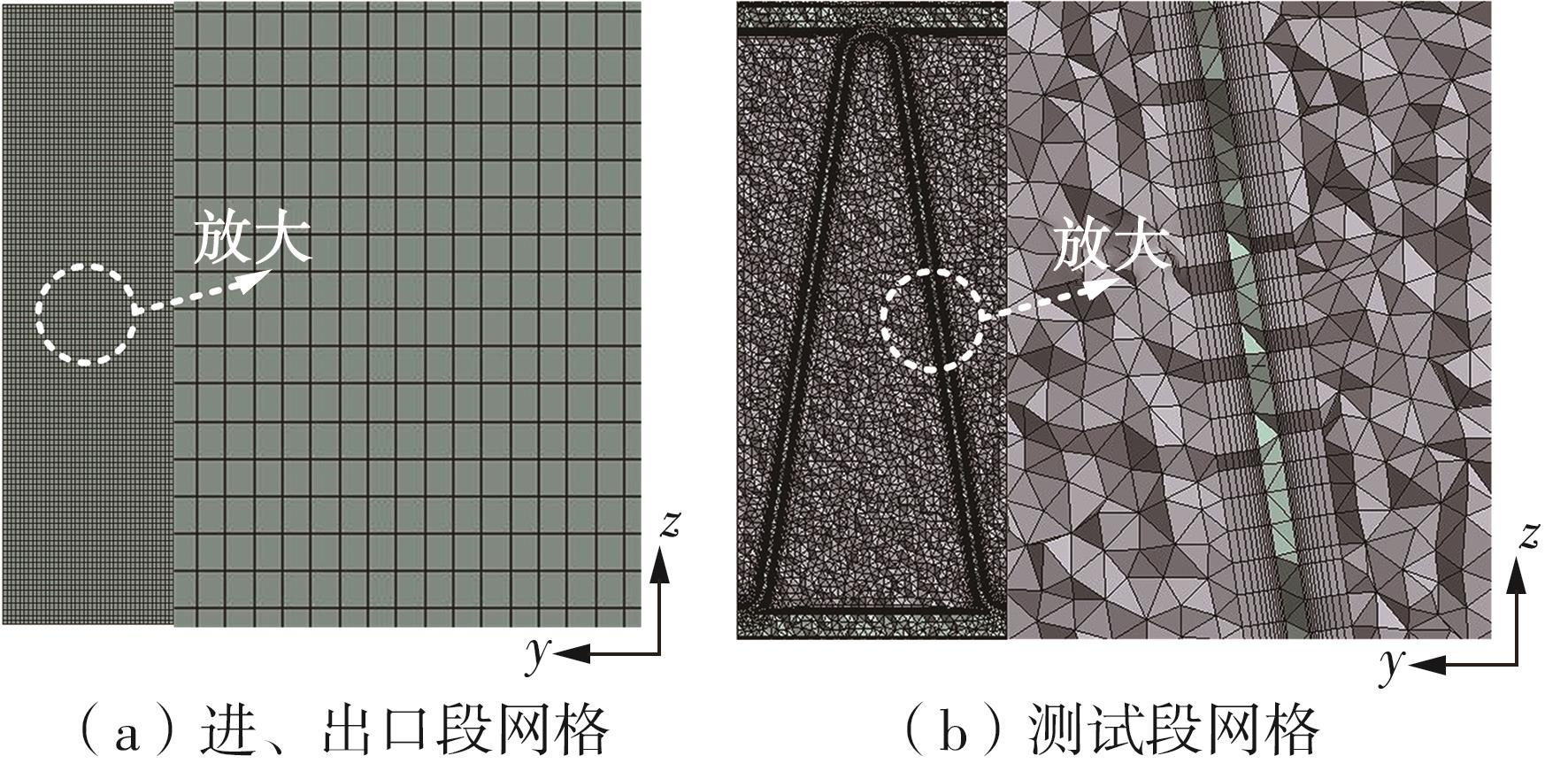
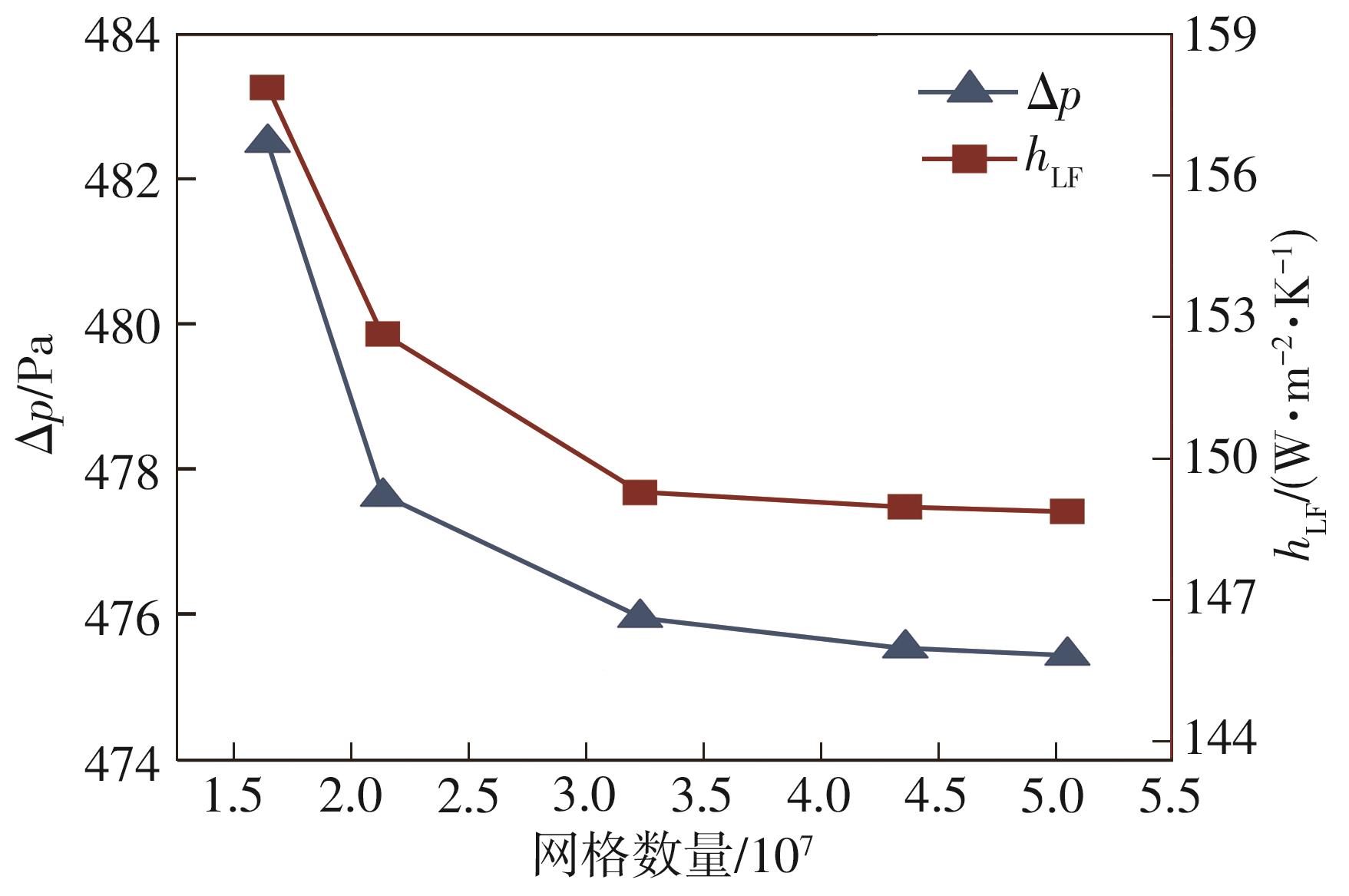
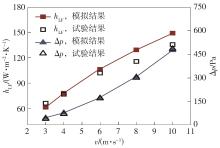
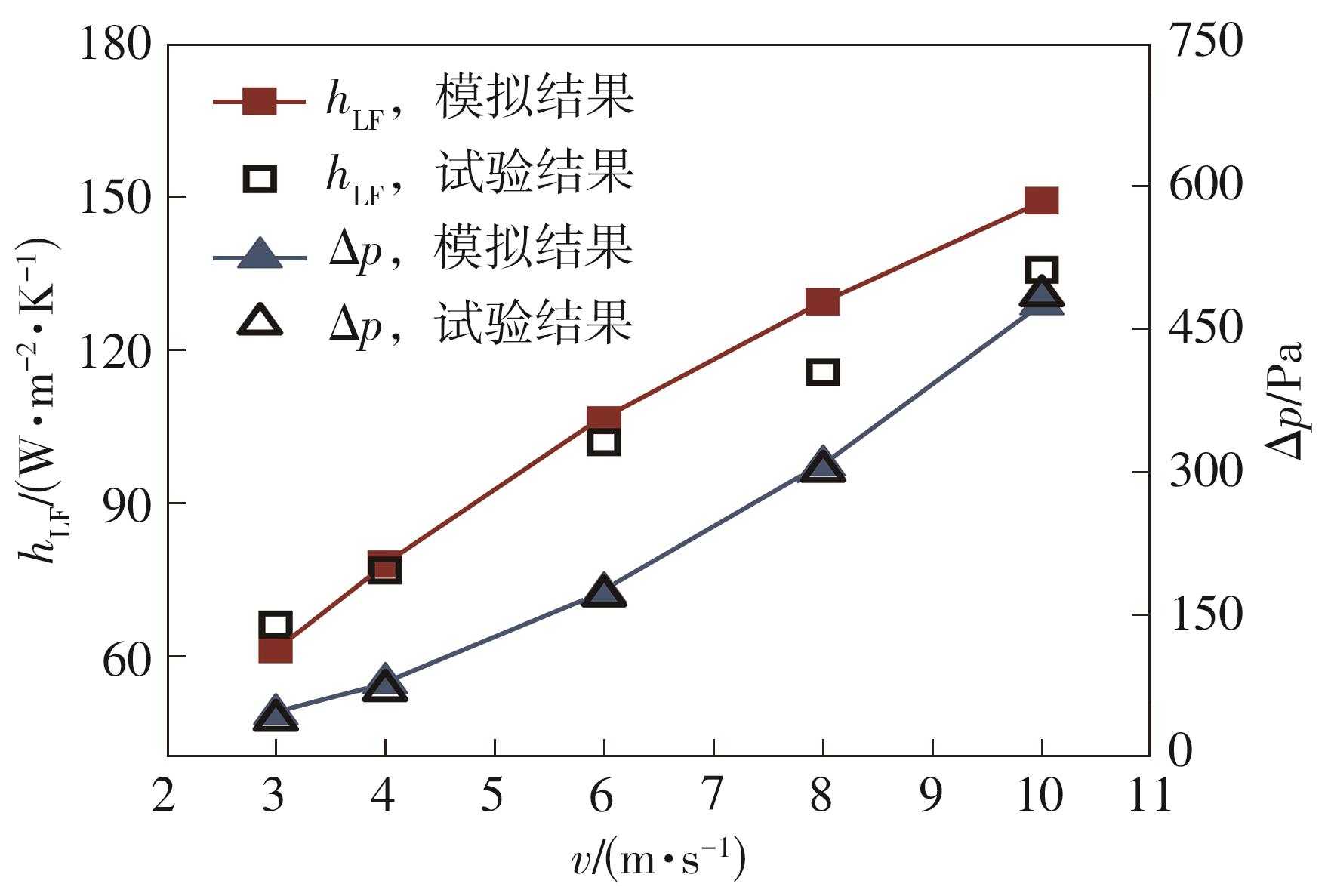
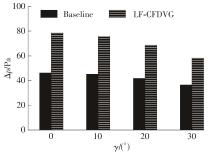
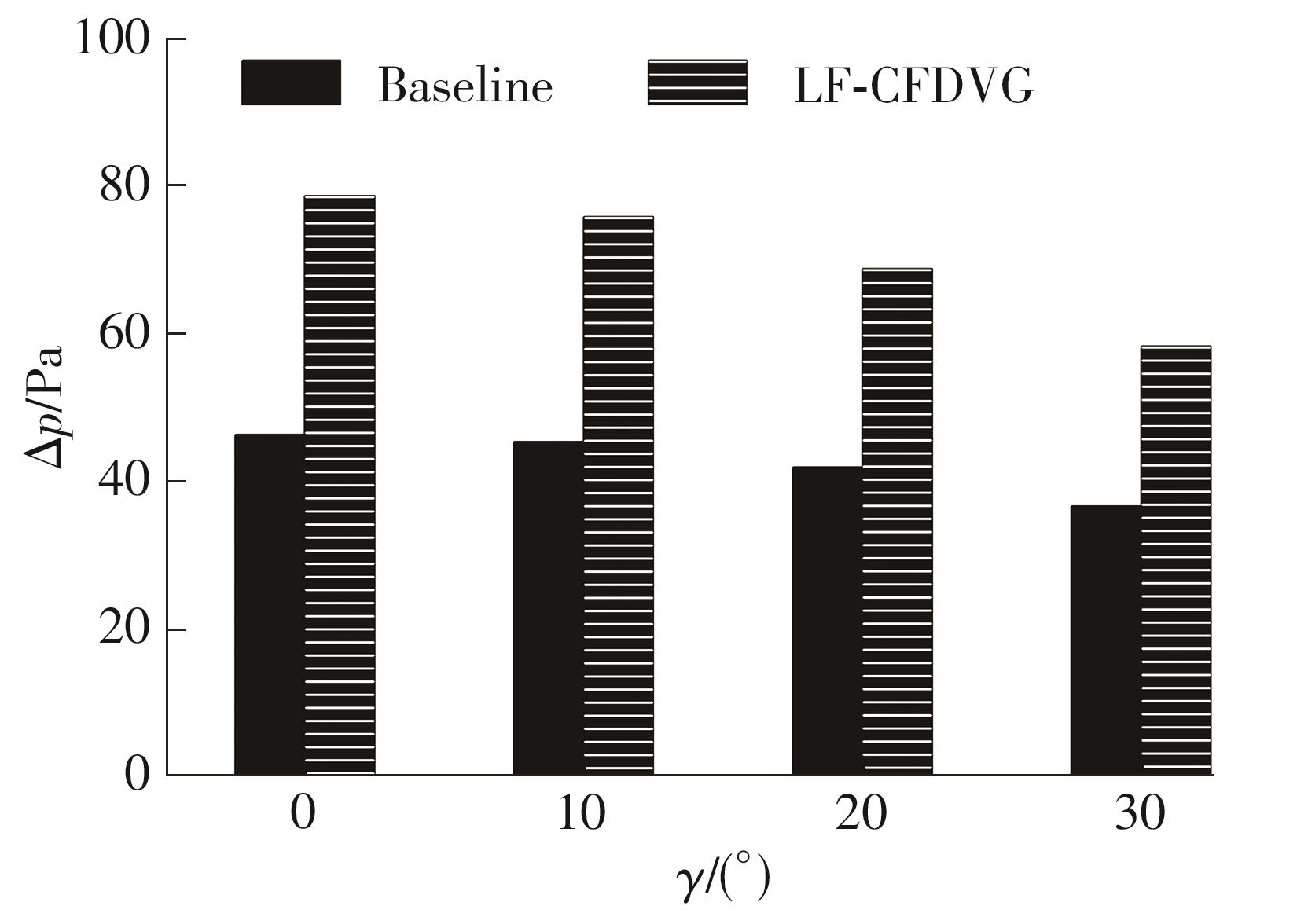
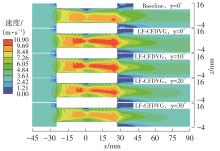
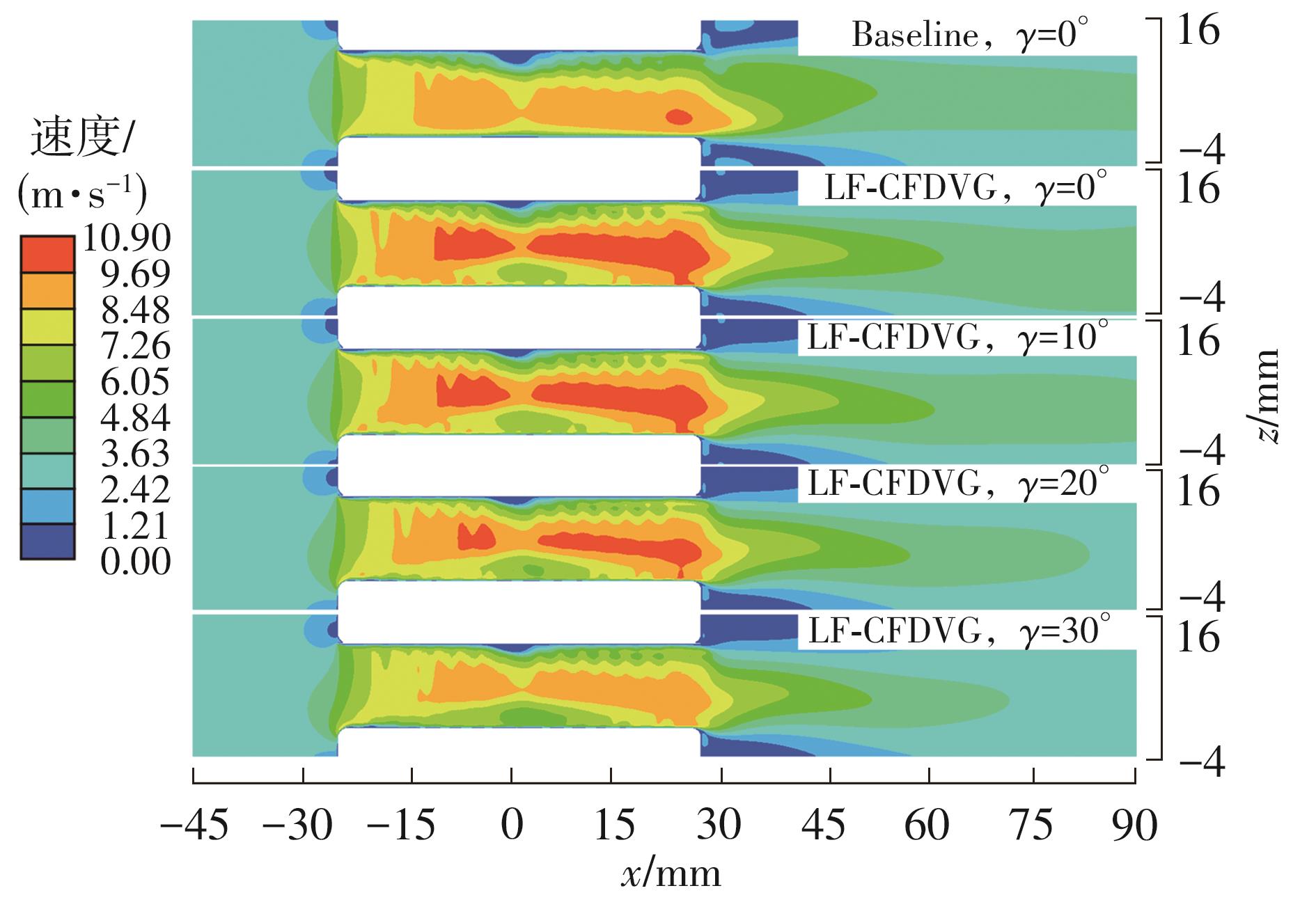
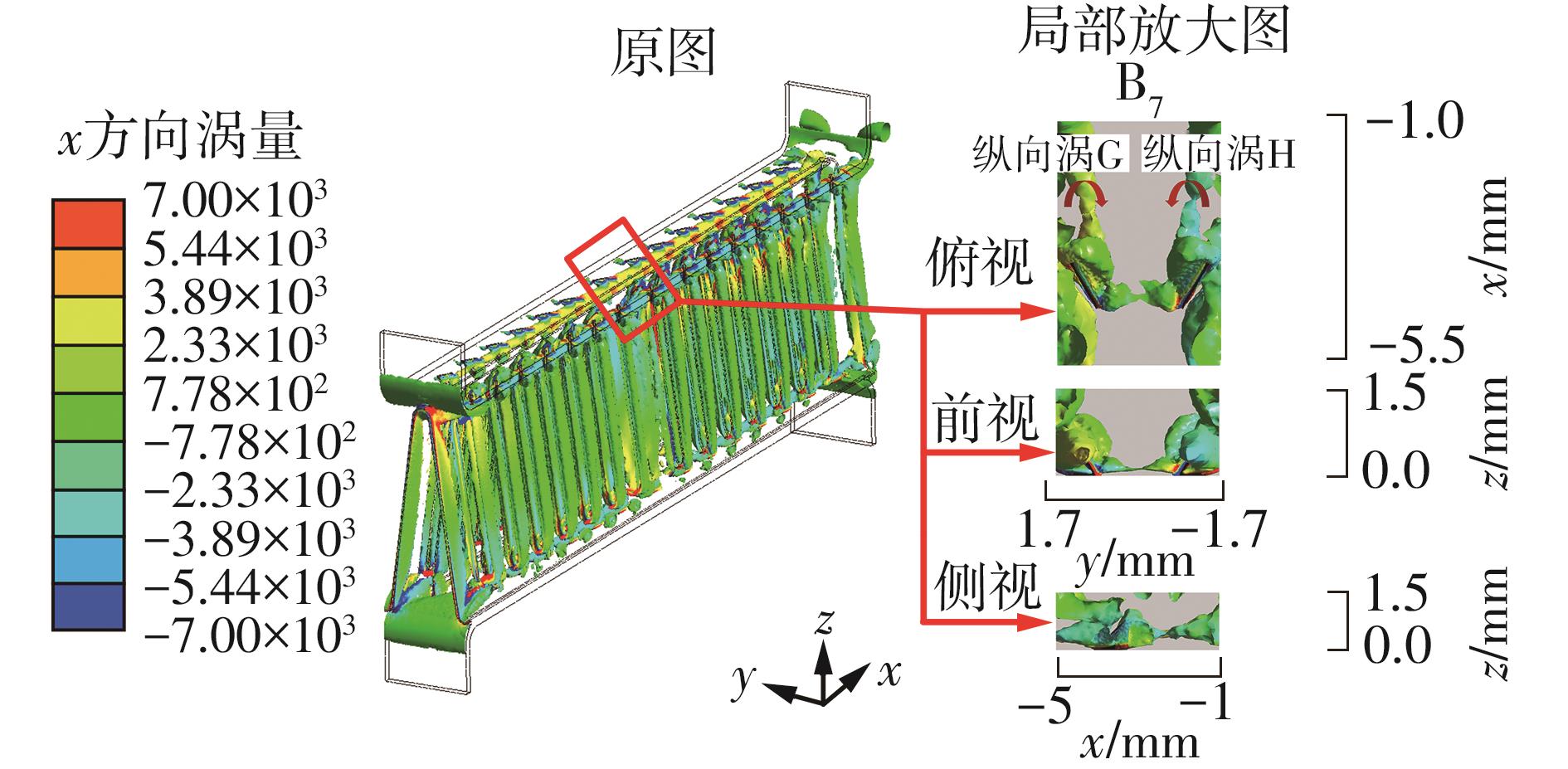
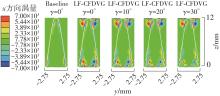
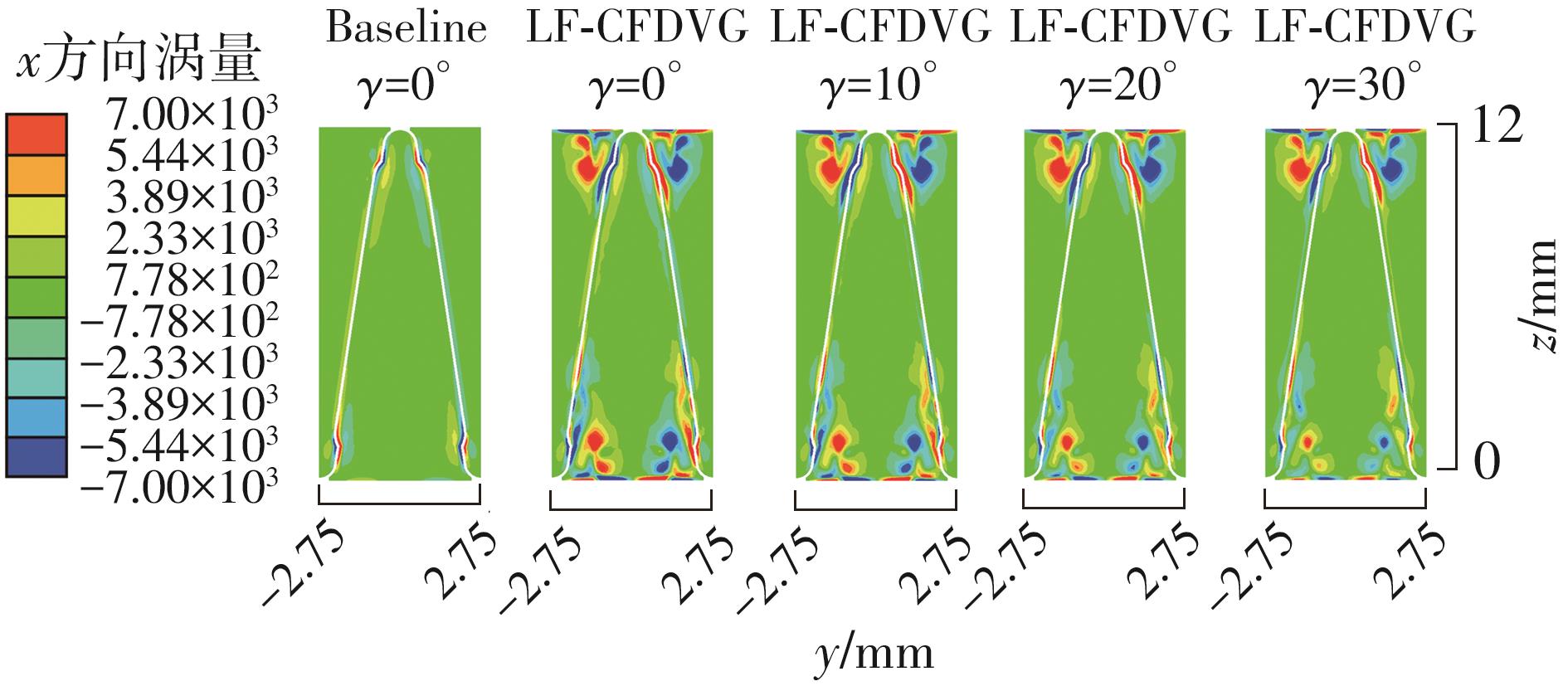
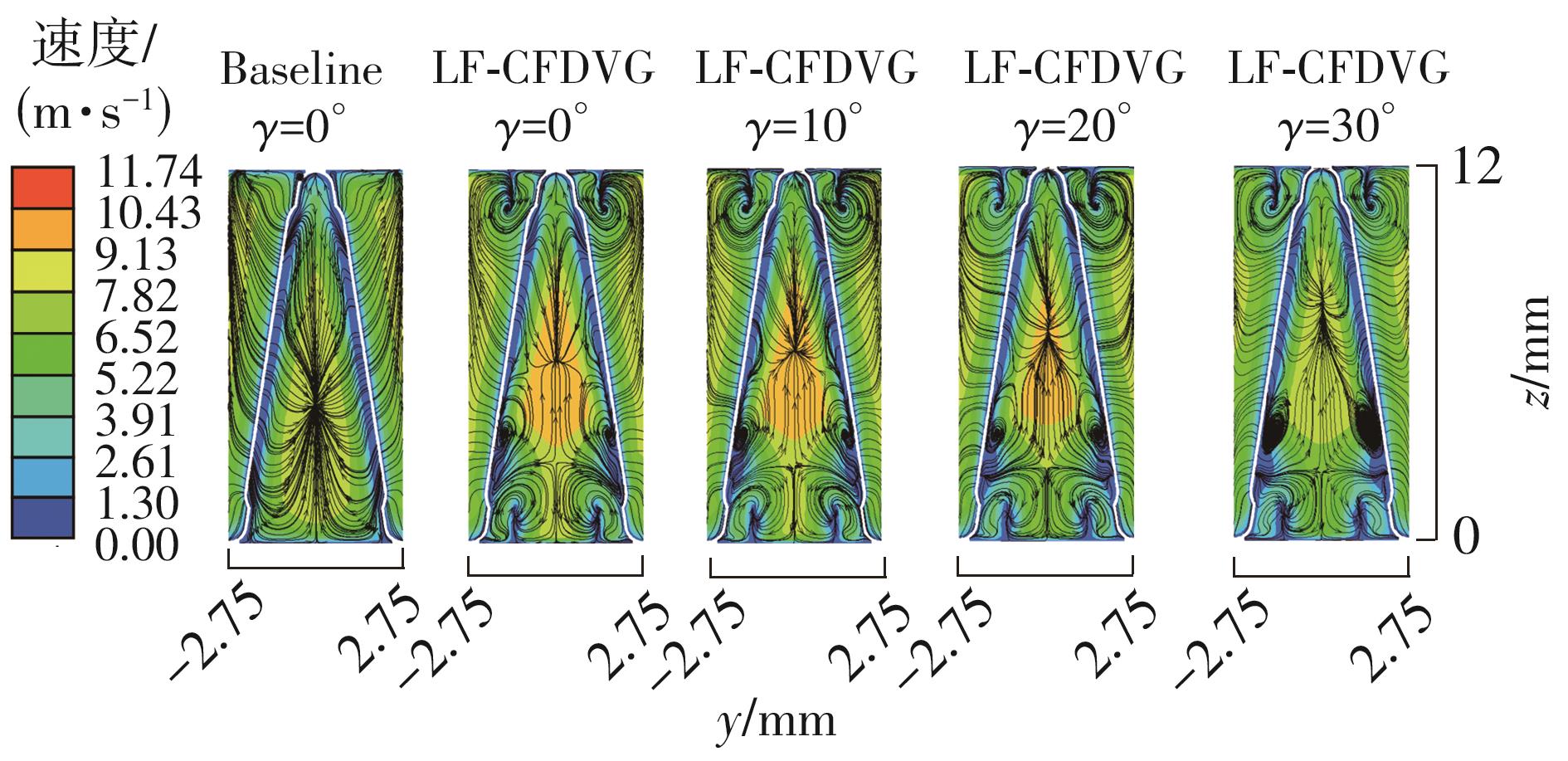
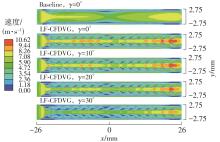
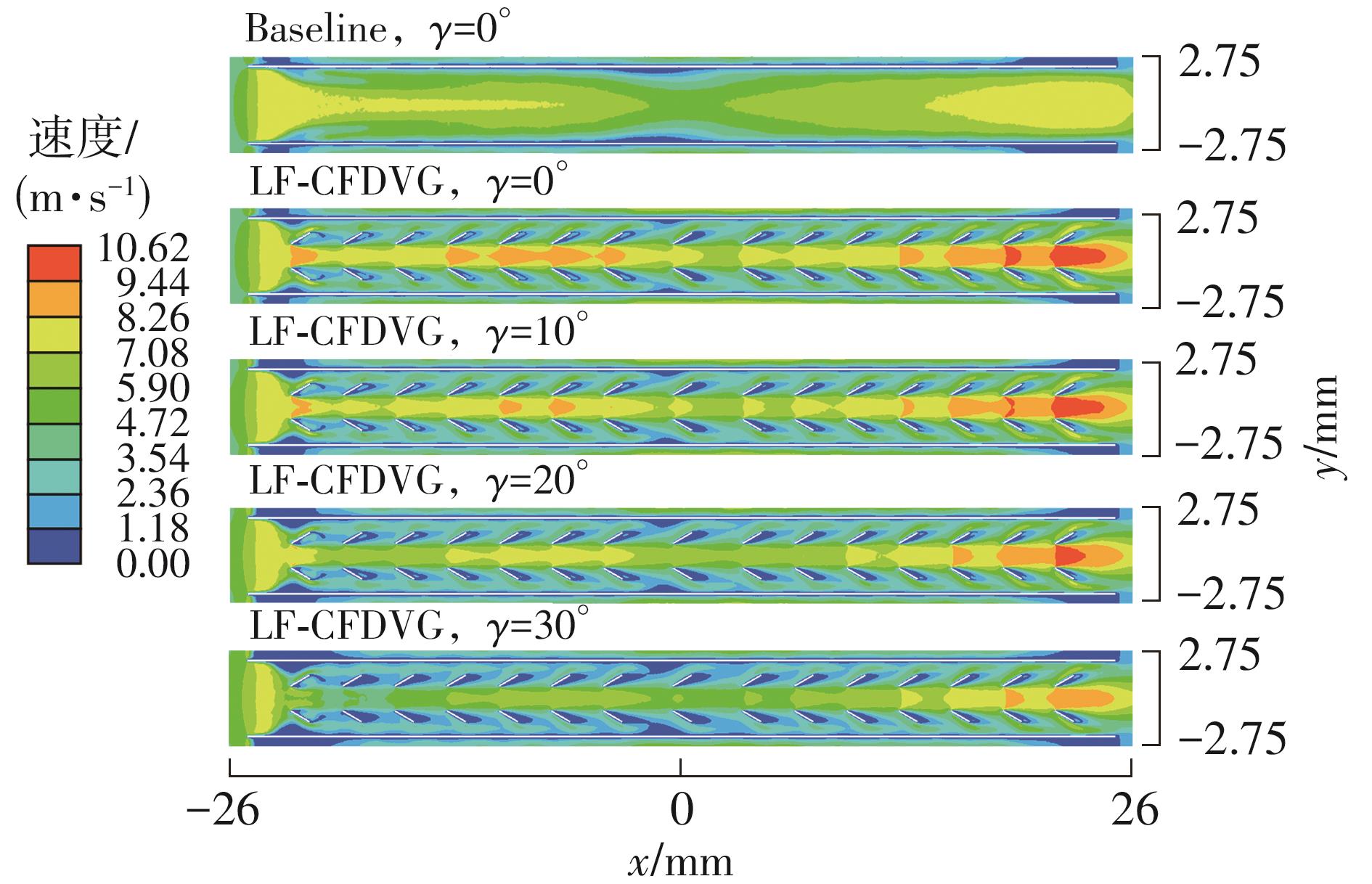
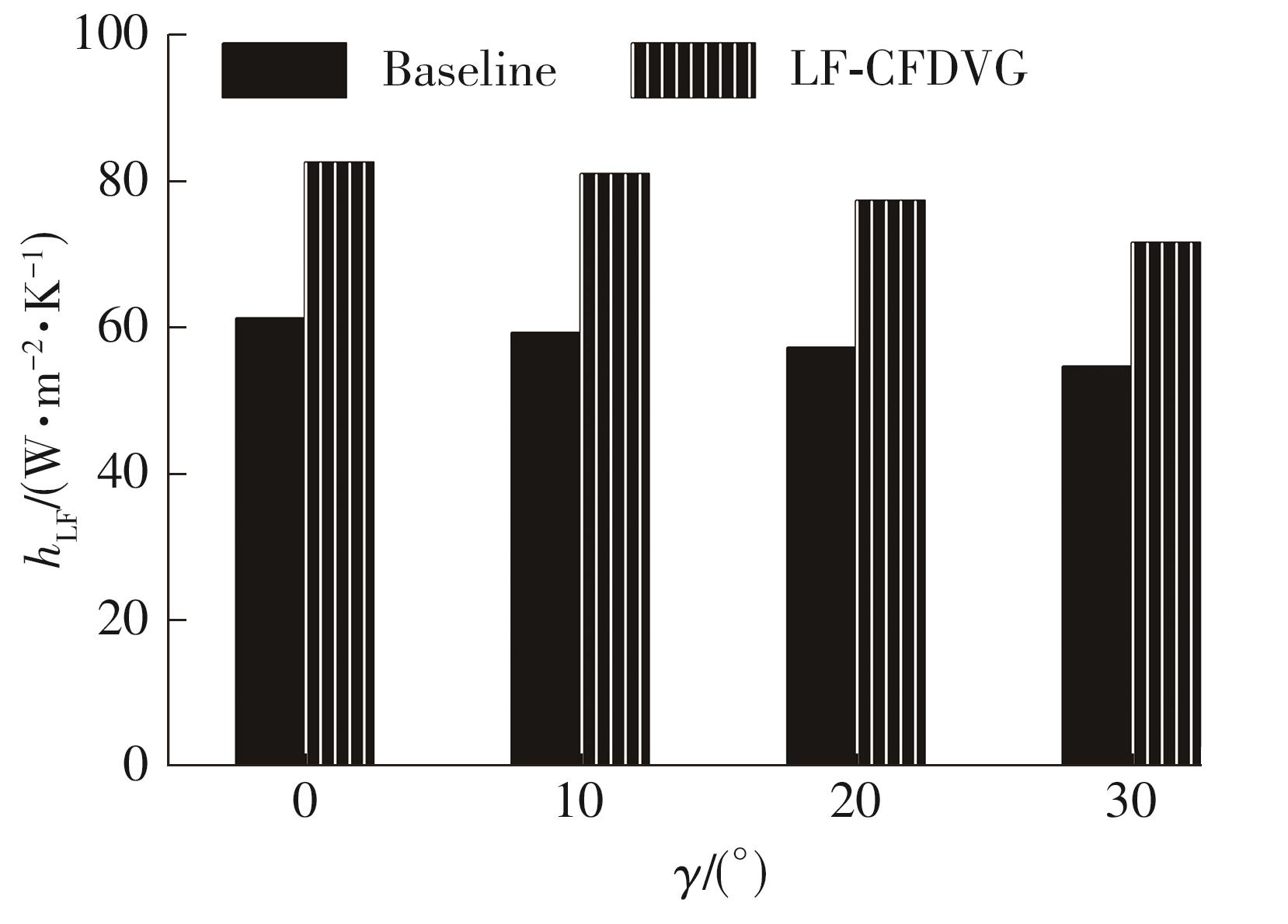
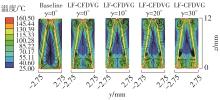
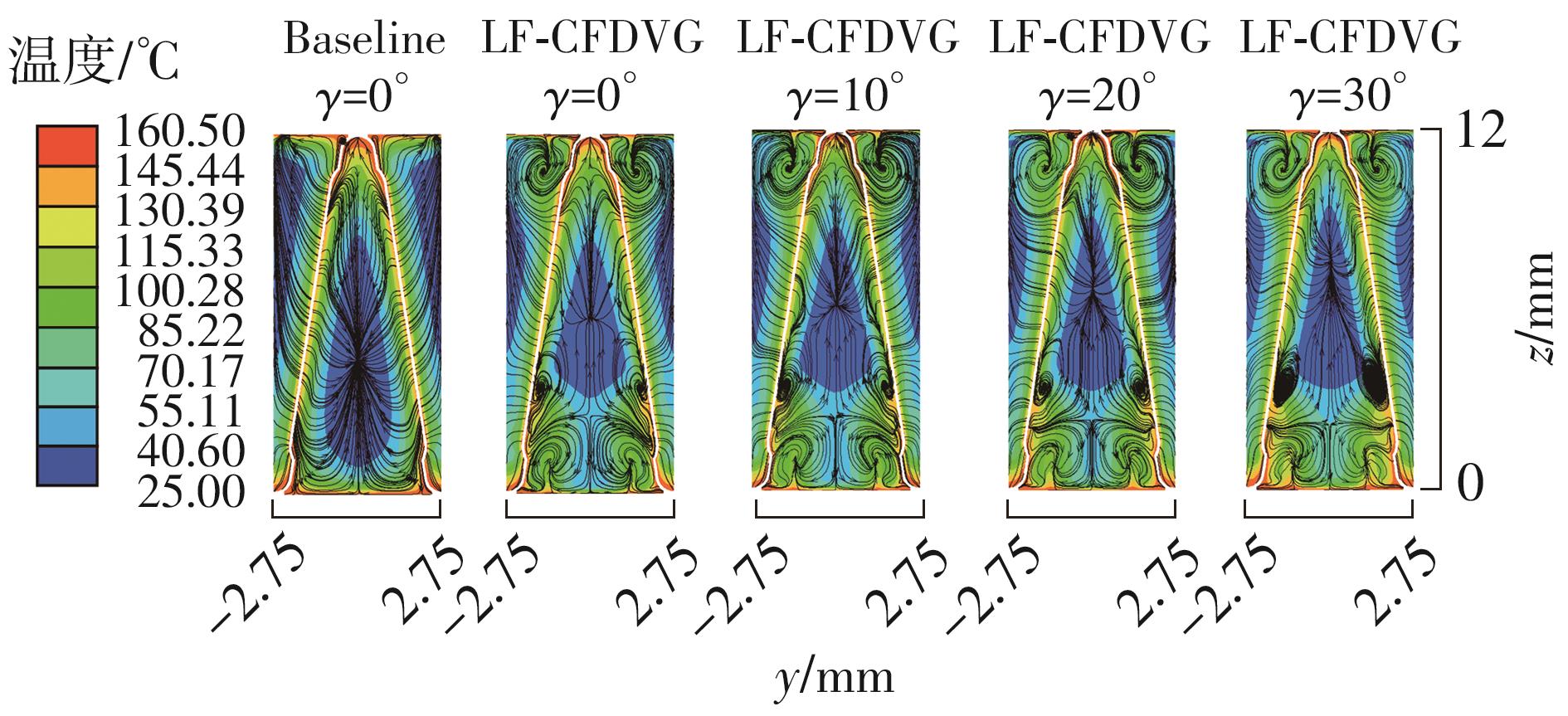
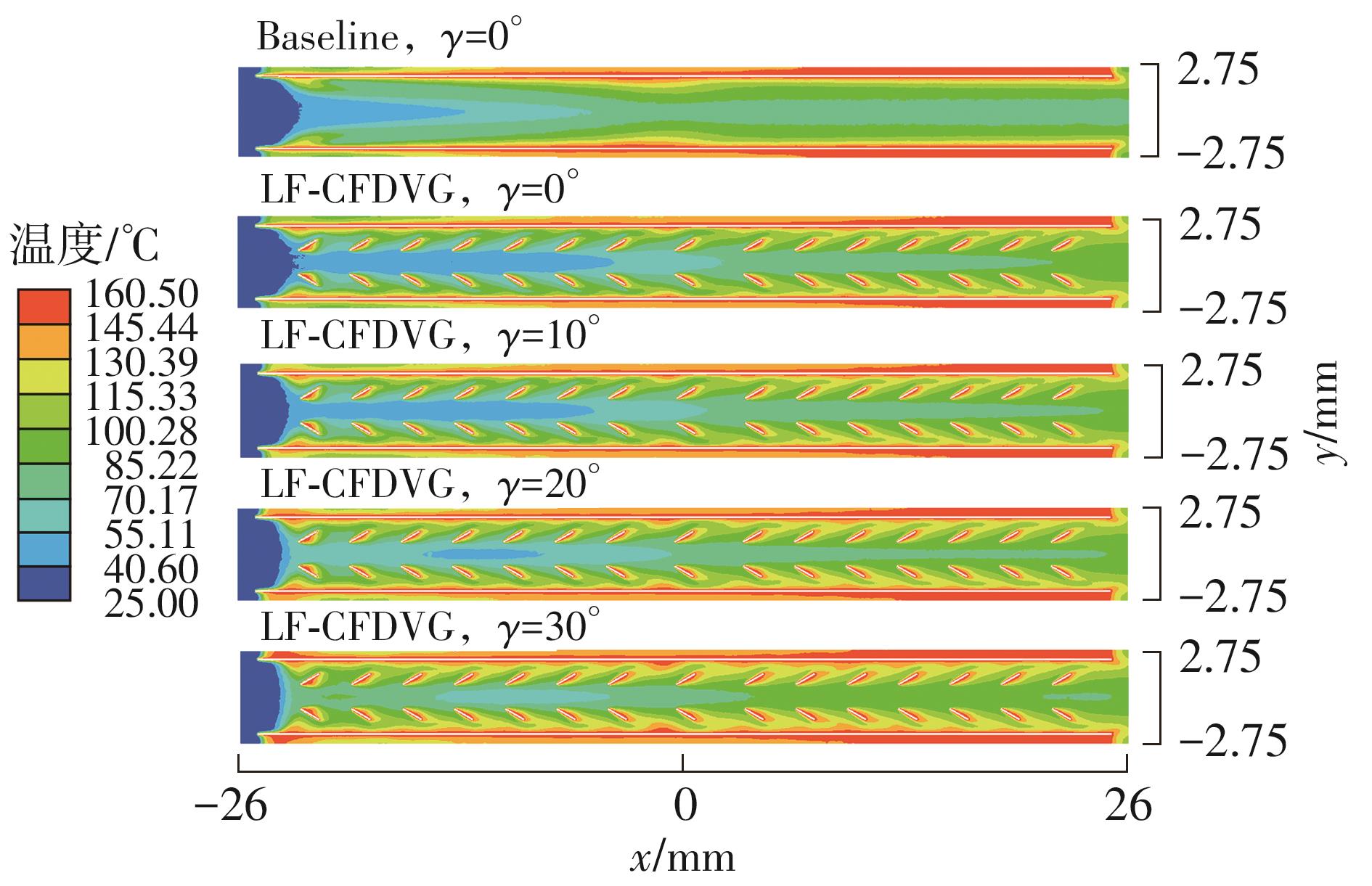
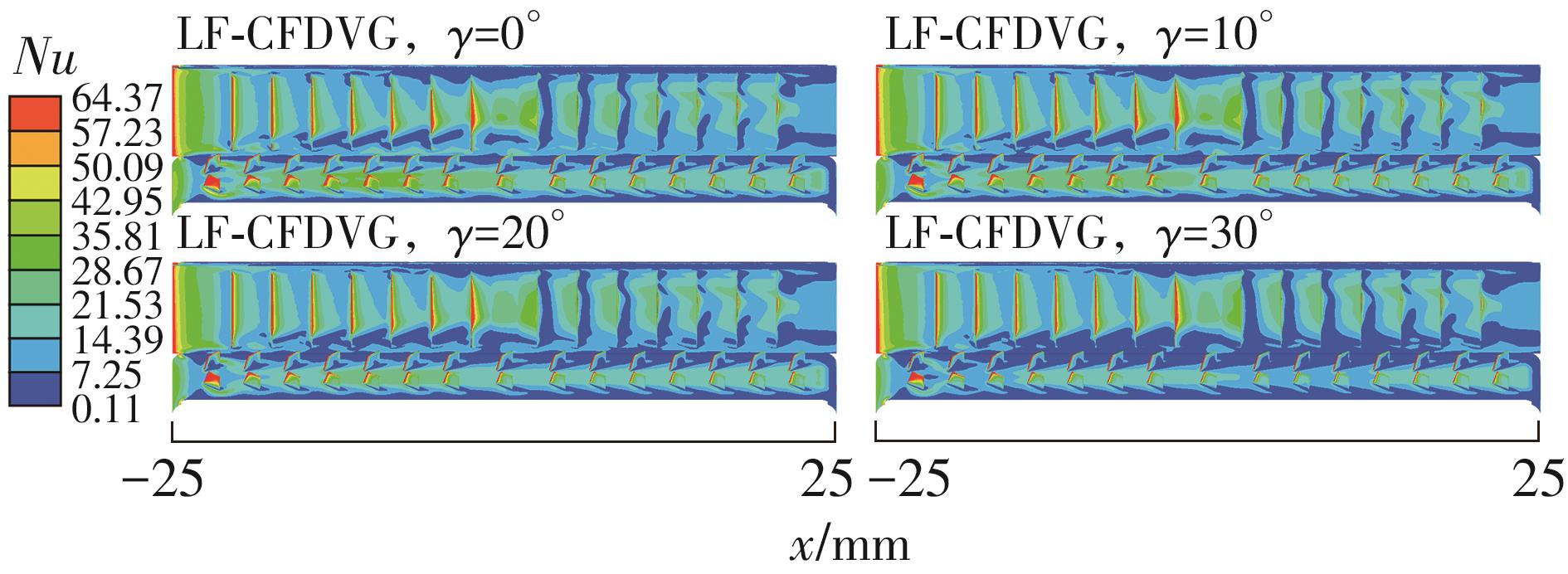
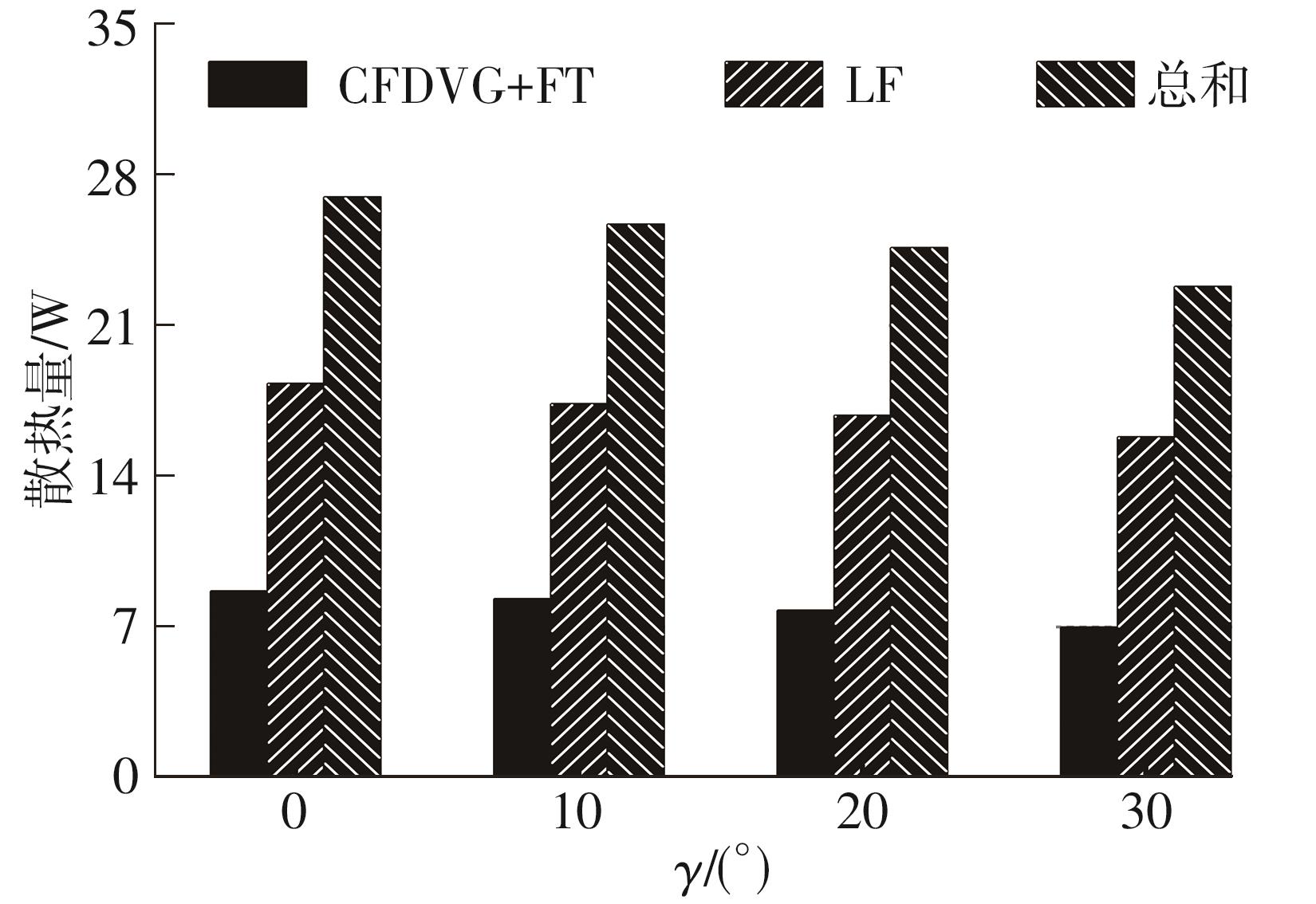
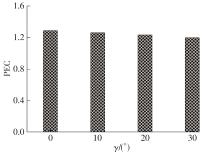
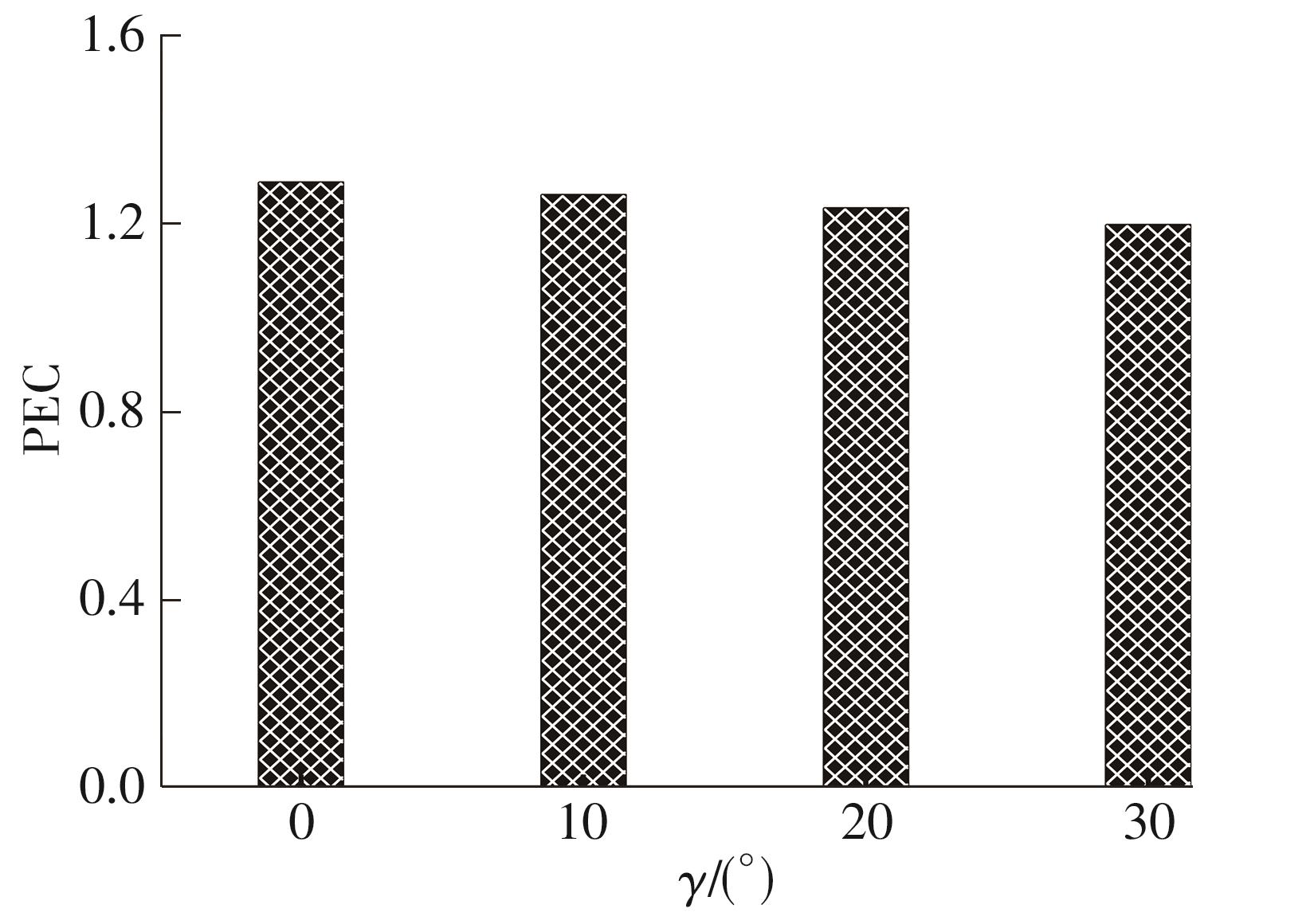
为改善百叶窗翅片-扁管式热交换器(LFHE)的热工水力性能,将后扩型涡产生器(CFDVG)布置于LFHE冷却管表面,得到百叶窗翅片-后扩型涡产生器(LF-CFDVG)。考虑到主动进气格栅(AGS)的使用将引起热交换器芯部空气来流方向的改变,进一步研究了空气速度为3 m/s时来流方向对LF-CFDVG热工水力性能的影响。结果表明:受CFDVG出现后最小自由流面积减小、空气流速增大而导致的摩擦阻力增加以及CFDVG引起的压差阻力增大的影响,LF-CFDVG的压降Δp总是大于未布置CFDVG的LFHE(Baseline)。在来流方向角γ由0°增加到30°的过程中,受空气流速减小的影响,Baseline和LF-CFDVG中的压降Δp均减小,因此增加γ可降低空气流动阻力。与此同时,在CFDVG诱导形成的纵向涡输送的高速、低温主流对CFDVG间冷却管壁的冲击下,相较于Baseline,LF-CFDVG的对流换热能力显著增强。在γ由0°增加到30°的过程中,受空气流速及纵向涡强度、尺度减小的影响,Baseline和LF-CFDVG中的对流换热系数均减小,因此增加γ有损于换热能力。另外,在γ由0°增加到30°的过程中,LF-CFDVG的综合性能不断降低,因此增加γ不利于综合性能的改善。
中图分类号: