华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (12): 53-63.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220832
所属专题: 2023年机械工程
大幅面SLM成型仓结构优化及其流场特性
刘国勇1,2 张文鹏1 张铜鑫1 朱冬梅1 曾新喜1
- 1.北京科技大学 机械工程学院,北京 100083
2.北京科技大学 顺德创新学院,广东 佛山 528399
Structural Optimization and Flow Field Characteristics of Large Format SLM Forming Bin
LIU Guoyong1,2 ZHANG Wenpeng1 ZHANG Tongxin1 ZHU Dongmei1 ZENG Xinxi1
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083,China
2.Shunde Innovation School,University of Science and Technology Beijing,Foshan 528399,Guangdong,China
摘要:
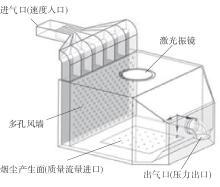
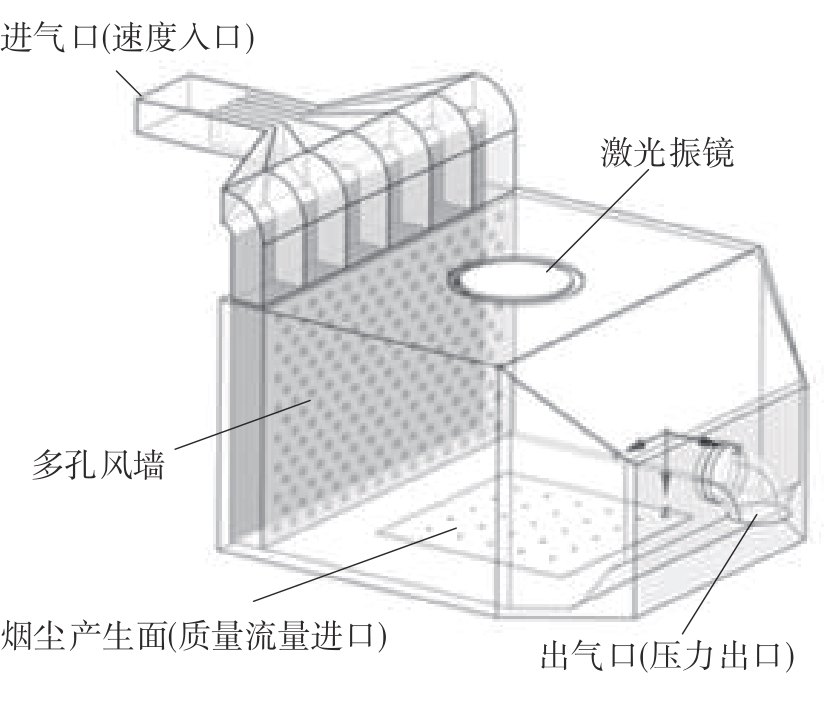
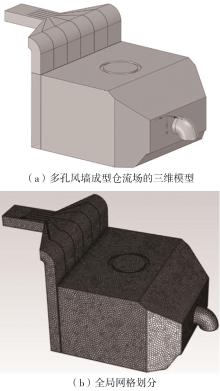
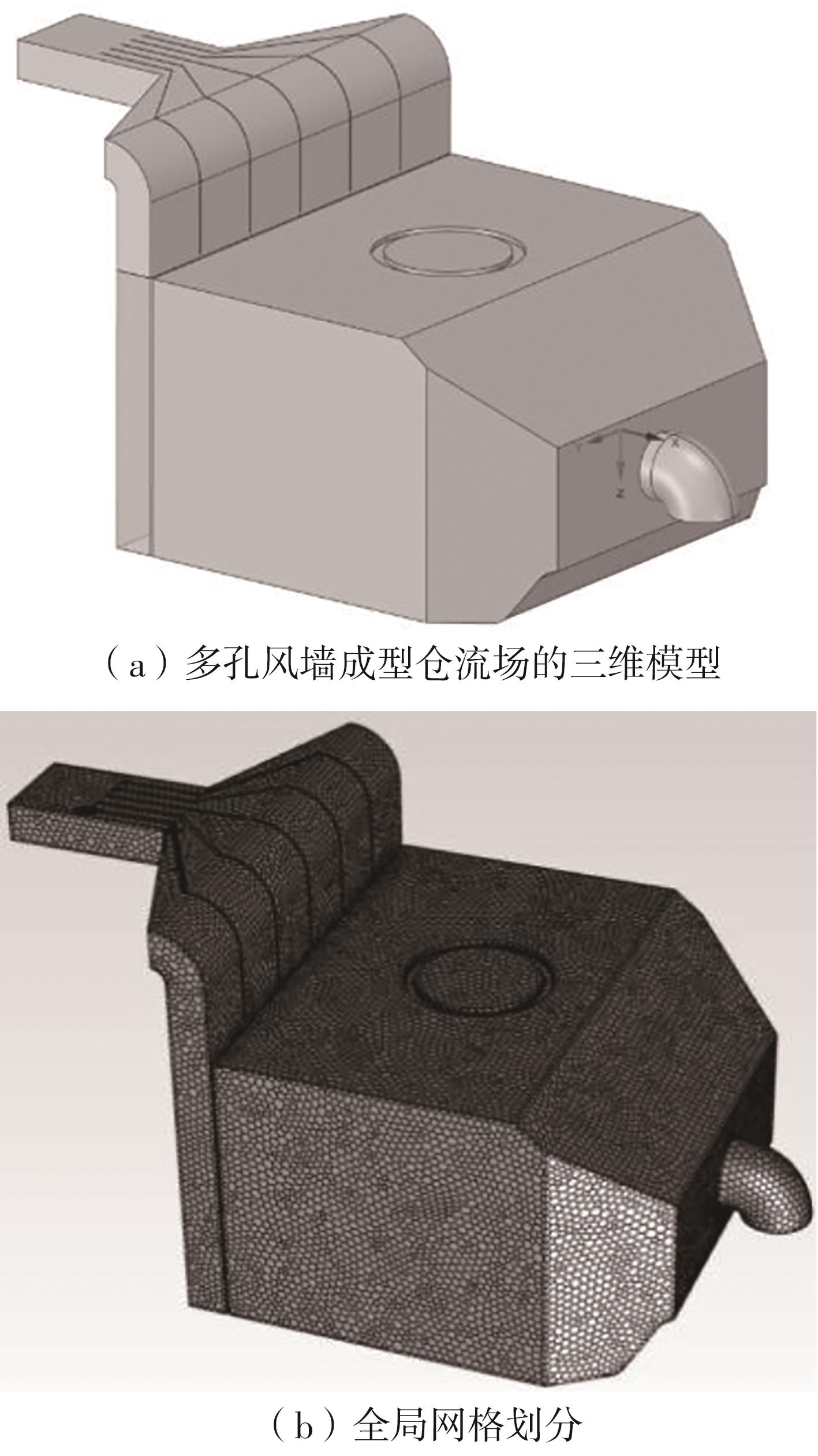
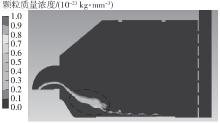
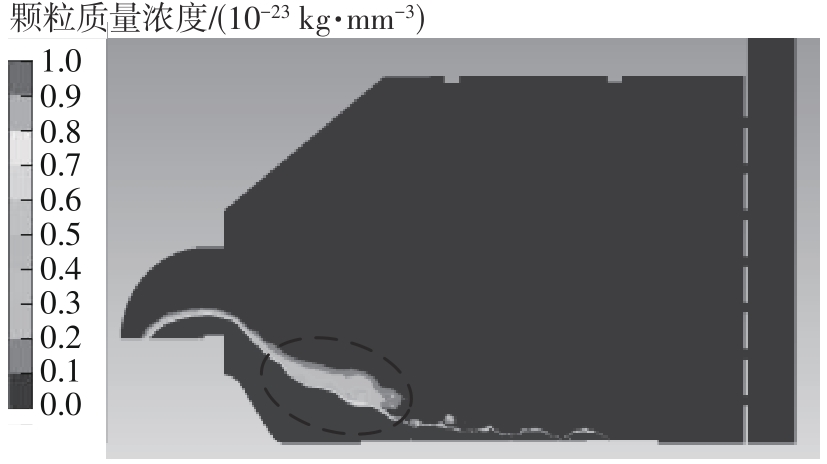
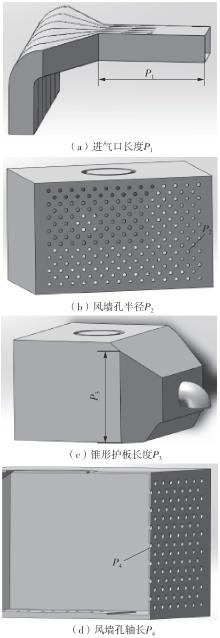
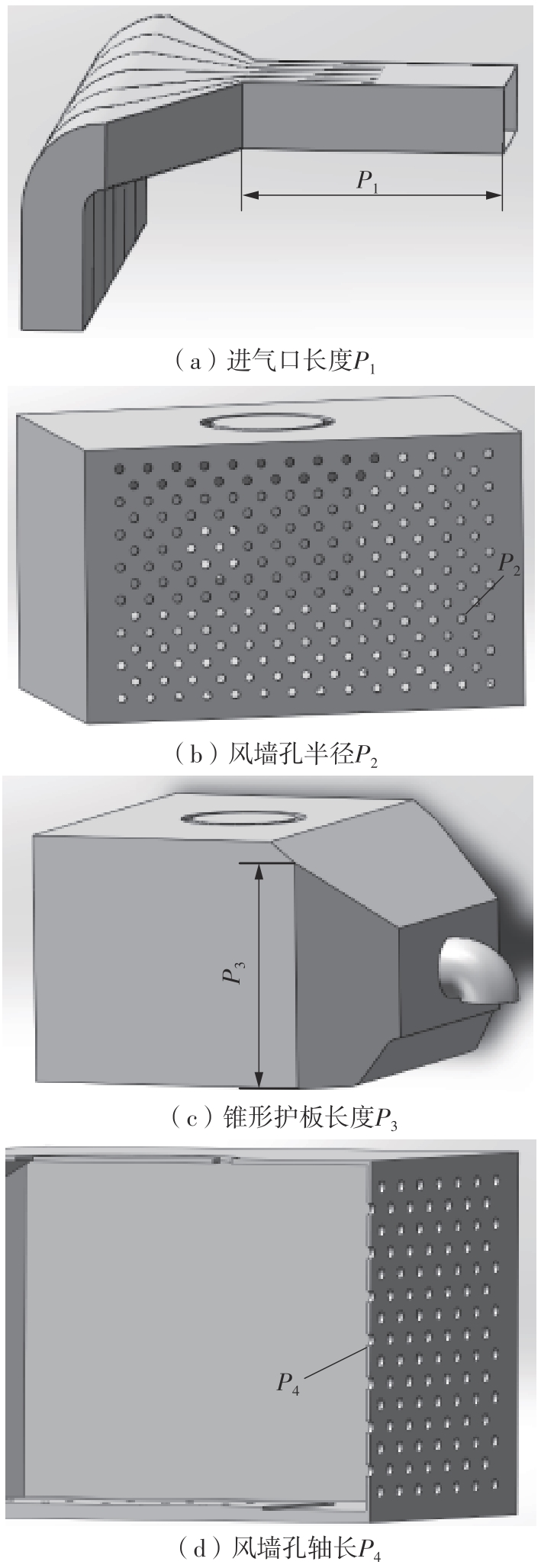
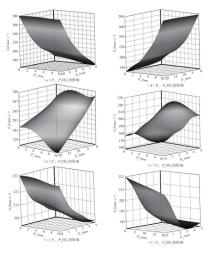
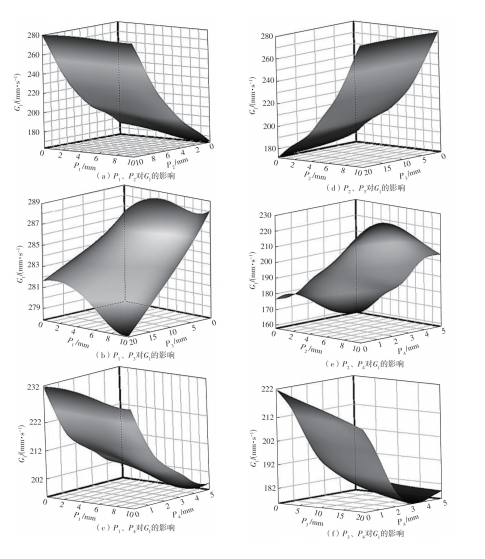
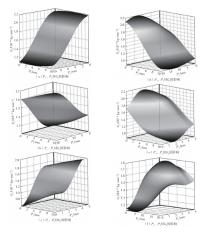
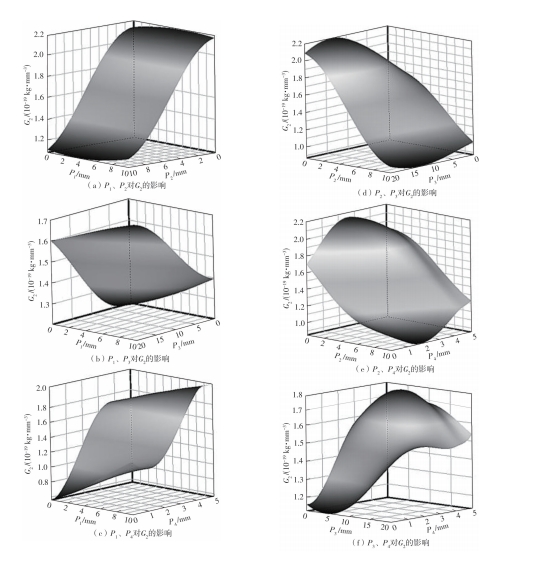
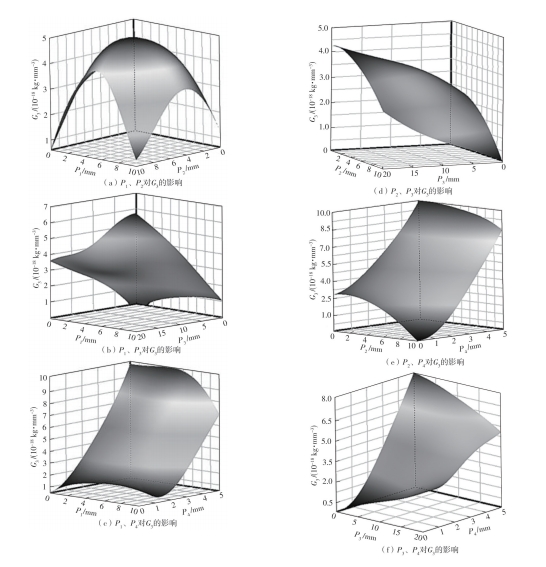
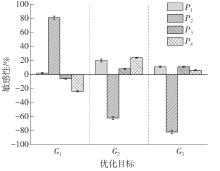
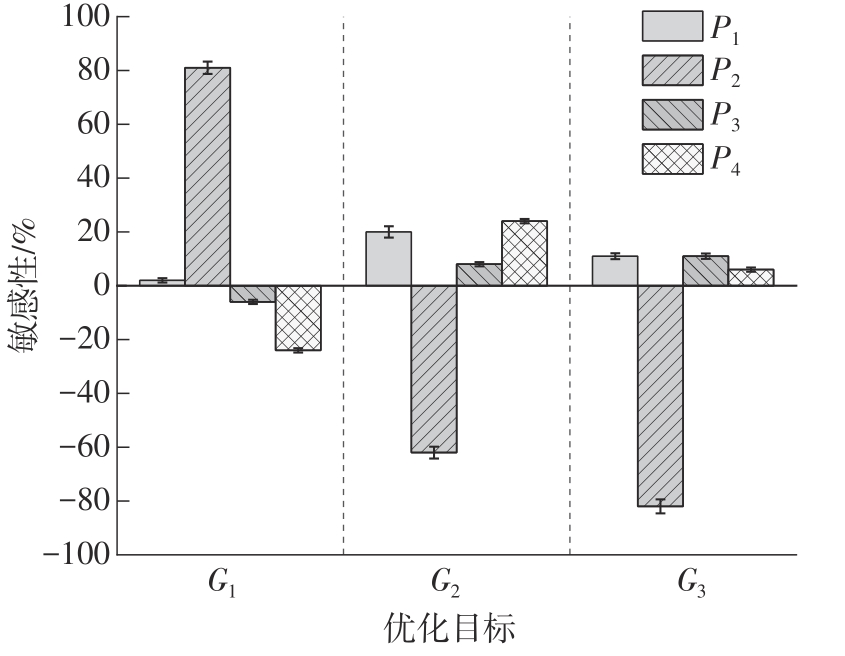
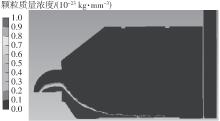
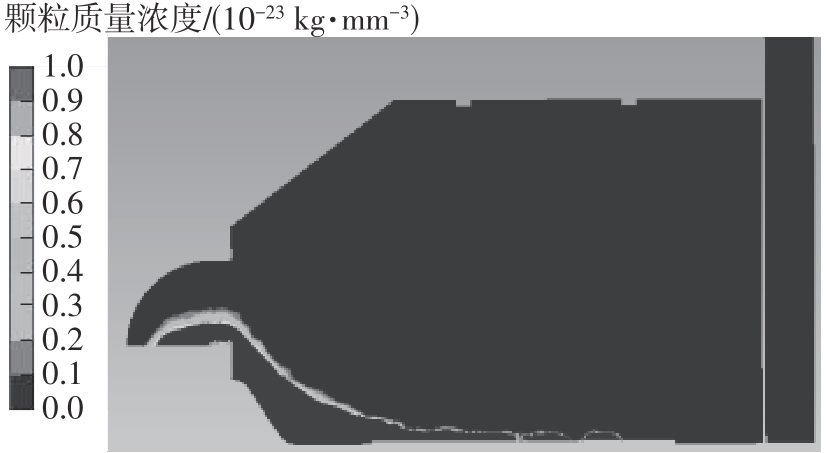
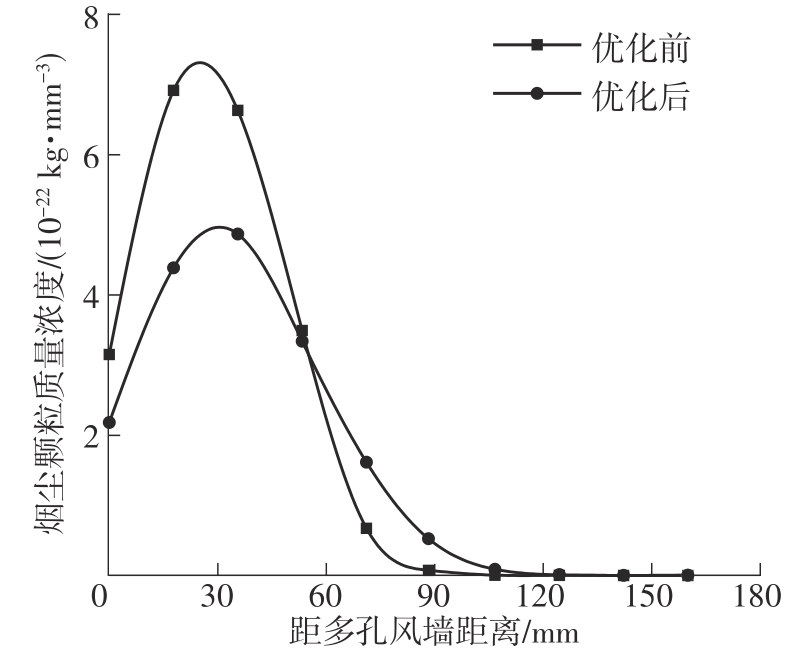
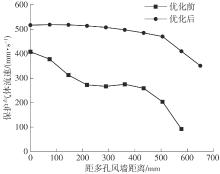
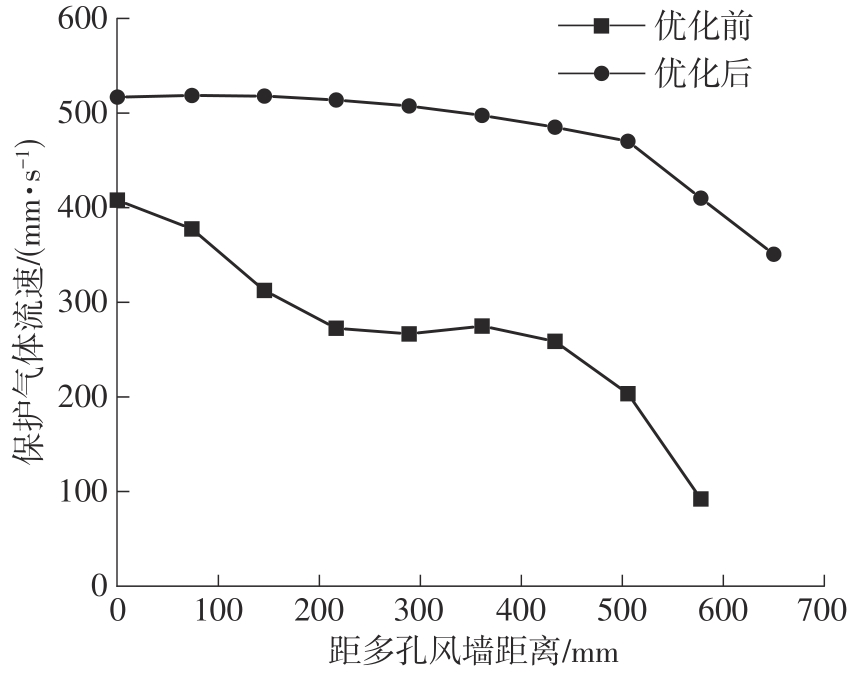
为探析激光选区熔化(SLM)成型仓内部的烟尘颗粒分布规律及排烟效率,本研究基于所建立的大幅面多孔风墙成型仓模型,采用Fluent离散相模型分析保护气体和烟尘颗粒在成型仓内部的流动规律,进而通过ANSYS中的多目标优化模块,基于多目标遗传算法(MOGA)对多孔风墙成型仓结构进行了优化。分别以成型仓进气口长度P1、风墙孔半径P2、锥形护板长度P3和风墙孔轴长P4作为优化变量,以成型仓内部中间截面保护气体的平均流动速度、成型仓进出口烟尘颗粒的质量浓度差以及整个成型仓内烟尘颗粒质量浓度的最大值作为优化目标,从而获得各个优化变量与优化目标的响应面及敏感性分析结果,并对优化前后的优化目标进行对比。结果表明:针对所优化的4个变量,对成型仓内中间截面保护气体流速影响的大小顺序是P2>P4>P3>P1,对进出口颗粒质量浓度差影响的大小顺序是P2>P4>P1>P3,对多孔风墙成型仓内最大颗粒质量浓度影响的大小顺序是P2>P1>P3>P4,多孔风墙的孔径大小对烟尘颗粒在成型仓内的流动起到最关键的作用。通过多目标遗传算法,得到优化后成型仓进气口长度为358 mm,风墙孔半径为20 mm,锥形护板长度为589 mm,风墙孔轴长为6 mm。与成型仓结构优化前进行对比,优化后成型仓内部中间截面保护气体流速提升了11.3%,进出口颗粒质量浓度差降低了16.8%,空间最大颗粒质量浓度降低23.9%,烟尘颗粒向外扩散的趋势有所减小,成型台面上方30 mm处通过的保护气体流速增加了21%,保护气体可以更加高效地将烟尘颗粒携带出成型仓。
中图分类号: