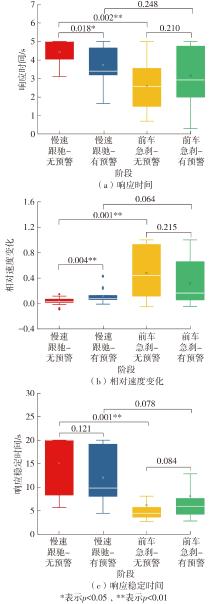
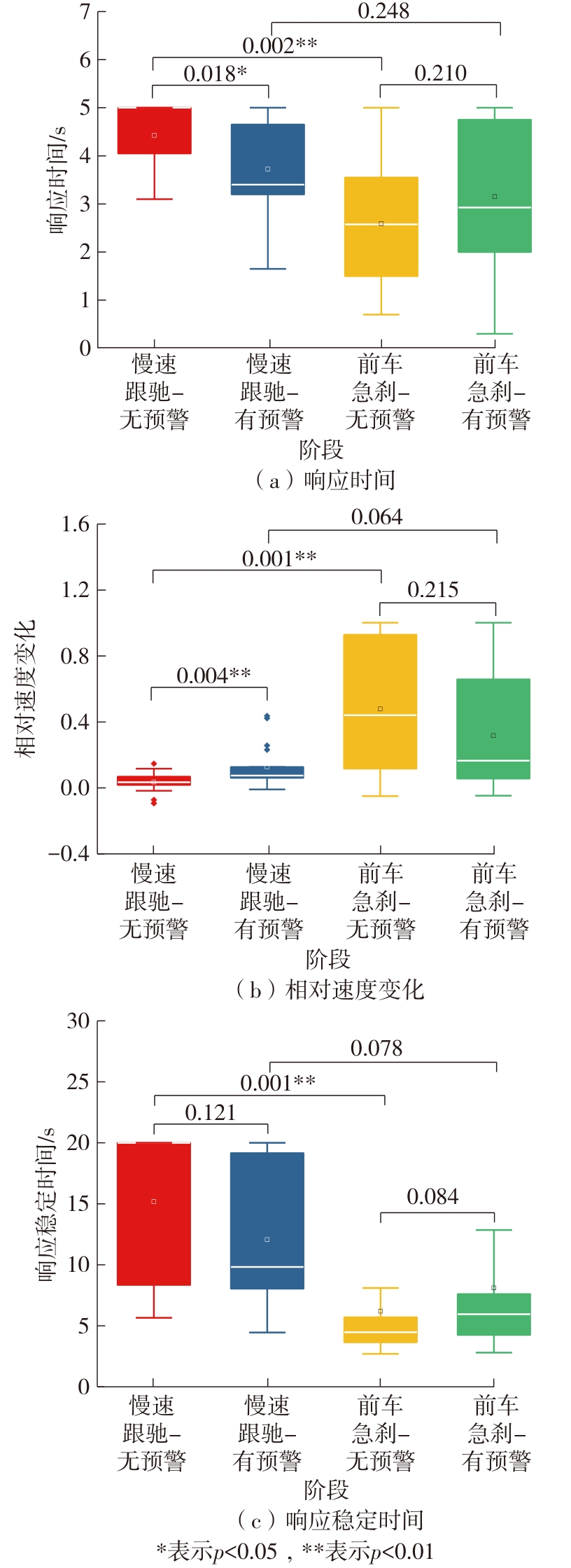
| 1 |
黄岩, 闫学东, 李晓梦, 等 . 基于多用户驾驶模拟平台的雾天高速公路跟驰模型参数标定及验证[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35( 8): 320- 330.
|
|
HUANG Yan, YAN Xuedong, LI Xiaomeng, et al . Parameter calibration and validation for car-following models on freeway under foggy conditions based on multi-user driving simulator system[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35( 8): 320- 330.
|
| 2 |
秦严严, 肖腾飞, 罗钦中, 等 . 雾天高速公路车辆跟驰安全分析及控制策略[J/OL]. 吉林大学学报(工学版)[ 2024-03-08]. .
|
|
QIN Yanyan, XIAO Tengfei, LUO Qinzhong, et al . Car-following safety analysis and control strategy for foggy freeway[J/OL]. Journal of Jilin University (Enginee-ring and Technology Edition)[ 2024-03-08]. .
|
| 3 |
尤鑫, 陈雨菲, 赵晓华, 等 . 高速公路雾天车路协同条件下可变限速系统服从度研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2019, 41( 9): 36- 44.
|
|
YOU Xin, CHEN Yufei, ZHAO Xiaohua, et al . Study on compliance of variable speed limit system under connected vehicle conditions of freeway in foggy day[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2019, 41( 9): 36- 44.
|
| 4 |
YANG G, AHMED M, GAWEESH S, et al . Connected vehicle real-time traveler information messages for freeway speed harmonization under adverse weather conditions:trajectory level analysis using driving simulator[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 146: 105707/1- 13.
|
| 5 |
李海舰, 刘中华, 陈开群, 等 . 高速公路风险防控设施应用研究综述与展望[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2024, 22( 1): 54- 78.
|
|
LI Haijian, LIU Zhonghua, CHEN Kaiqun, et al . An overview and prospect of the application of risk prevention and control facilities on highways[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2024, 22( 1): 54- 78.
|
| 6 |
江筱薇 . VMS影响下驾驶员路径选择机理及信息发布策略研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2017.
|
| 7 |
PAN Y, WU Y, XU L, et al . The impacts of connected autonomous vehicles on mixed traffic flow:a comprehensive review[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mecha-nics and its Applications, 2024, 635: 129454/1- 16.
|
| 8 |
林泓熠, 刘洋, 李深, 等 . 车路协同系统关键技术研究进展[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51( 10): 46- 67.
|
|
LIN Hongyi, LIU Yang, LI Shen, et al . Research progress on key technologies in the cooperative vehicle infrastructure system[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51( 10): 46- 67.
|
| 9 |
KAMRANI M, CONCAS S, KOURTELLIS A, et al . Drivers’reactions to connected vehicle forward collision warnings:Leveraging real-world data from the THEA CV pilot[J]. Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2023, 92: 108- 120.
|
| 10 |
SON S O, JEONG J, PARK S, et al . Effects of advanced warning information systems on secondary crash risk under connected vehicle environment[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 148: 105786/1- 7.
|
| 11 |
ZHANG Y, WU C, QIAO C, et al. The effects of warning characteristics on driver behavior in connected vehicles systems with missed warnings[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 124: 138- 145.
|
| 12 |
BELLA F, SILVESTRI M . Effects of directional auditory and visual warnings at intersections on reaction times and speed reduction times[J]. Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2017, 51: 88- 102.
|
| 13 |
HANG J, YAN X, LI X, et al . In-vehicle warnings for work zone and related rear-end collisions:a driving simulator experiment[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2022, 174: 106768/1- 11.
|
| 14 |
WU Y, ABDEL-ATY M, PARK J, et al . Effects of crash warning systems on rear-end crash avoidance behavior under fog conditions[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2018, 95: 481- 492.
|
| 15 |
ALRUWAILI A, XIE K . Modeling the influence of connected vehicles on driving behaviors and safety outcomes in highway crash scenarios across varied weather conditions:a multigroup structural equation modeling analysis using a driving simulator experiment[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2024, 199: 107514/1- 16.
|
| 16 |
赵睿, 李云, 胡宏宇, 等 . 基于V2I通信的交叉口车辆碰撞预警方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53( 4): 1019- 1029.
|
|
ZHAO Rui, LI Yun, HU Hongyu, et al . Vehicle collision warning method at intersection based on V2I communication[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53( 4): 1019- 1029.
|
| 17 |
ZHAO X, JING S, HUI F, et al . DSRC-based rea-rend collision warning system-an error-component safety distance model and field test[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2019, 107: 92- 104.
|
| 18 |
KO J, JANG J, OH C . A multi-agent driving simulation approach for evaluating the safety benefits of connected vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23( 5): 4512- 4524.
|
| 19 |
李晓梦 . 基于驾驶模拟实验的典型不利因素对驾驶行为表现的影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2016.
|
| 20 |
ALI Y, ZHENG Z, HAQUE MD M . Connectivity’s impact on mandatory lane-changing behaviour:Evidences from a driving simulator study[J]. Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies, 2018, 93: 292- 309.
|
| 21 |
BIAN Y, ZHANG X, WU Y, et al . Influence of prompt timing and messages of an audio navigation system on driver behavior on an urban expressway with five exits[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021, 157: 106155/1- 15.
|
| 22 |
ABDEL-ATY M, WANG Z, ZHENG O, et al . Advances and applications of computer vision techniques in vehicle trajectory generation and surrogate traffic safety indicators[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2023, 191: 107191/1- 13.
|
| 23 |
鲁光泉, 谭海天, 张浩 . 自动驾驶车辆对人工驾驶车辆跟驰行为影响分析[J]. 上海理工大学学报, 2023, 45( 4): 321- 331.
|
|
LU Guangquan, TAN Haitian, ZHANG Hao . Analysis of the impact of automated vehicle on the car-following behavior of manual vehicle[J]. Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, 2023, 45( 4): 321- 331.
|
| 24 |
张建华, 赵晓华, 欧居尚, 等 . 雾天桥梁可变限速值的效用评估及优化[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52( 1): 127- 138.
|
|
ZHANG Jianhua, ZHAO Xiaohua, Jushang OU, et al . Evaluation of utility and optimal of variable speed limit value for bridge in foggy condition[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52( 1): 127- 138.
|
| 25 |
ZHENG J, MA L, ZHANG W . Promotion of driver compliance with V2V information in car-following tasks via multimodal display[J]. Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2023, 94: 243- 253.
|
| 26 |
ZHAO W, GONG S, ZHAO D, et al . Effects of collision warning characteristics on driving behaviors and safety in connected vehicle environments[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2023, 186: 107053/1- 12.
|