华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 1-13.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230293
• 交通运输工程 • 下一篇
高速公路新能源汽车碳排放量的测算及空间分布特征
- 1.华南理工大学 土木与交通学院,广东 广州 510640
2.广东联合电子服务股份有限公司,广东 广州 510620
Calculation and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Carbon Emissions from New Energy Vehicles on Expressways
WEN Huiying1( ), HE Ziqi1, HU Yuqing2, HUANG Junda1(
), HE Ziqi1, HU Yuqing2, HUANG Junda1( )
)
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangdong E-Serve United Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510620,Guangdong,China
摘要:
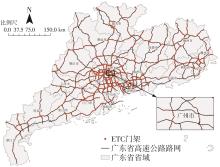
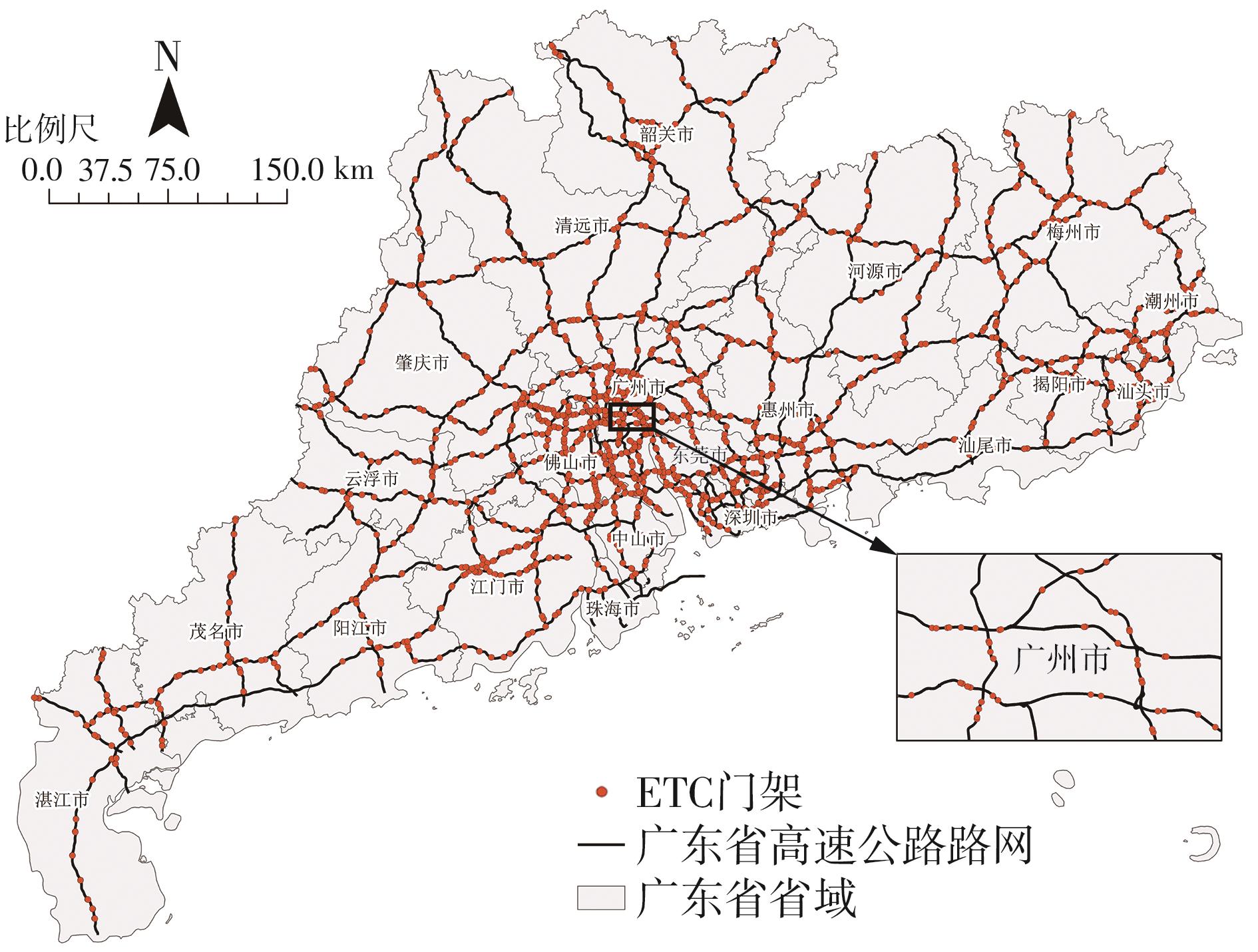
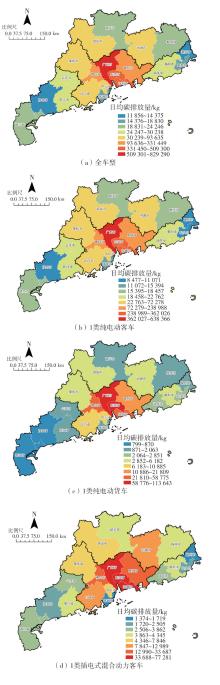
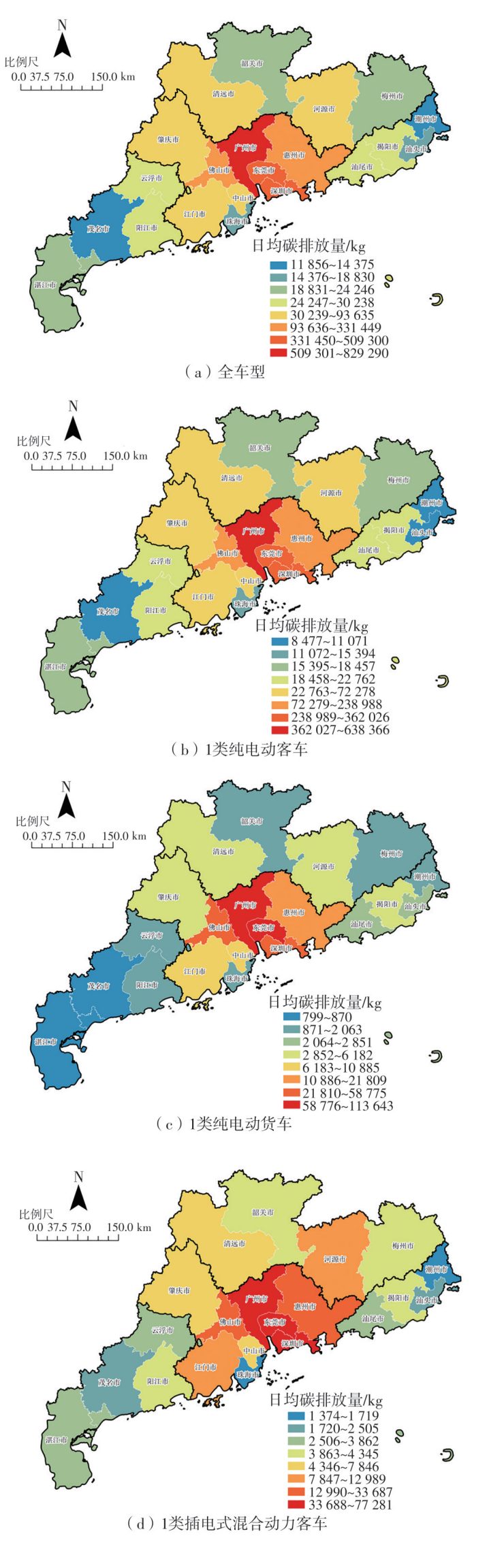
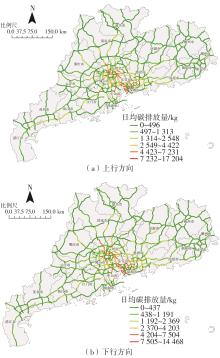
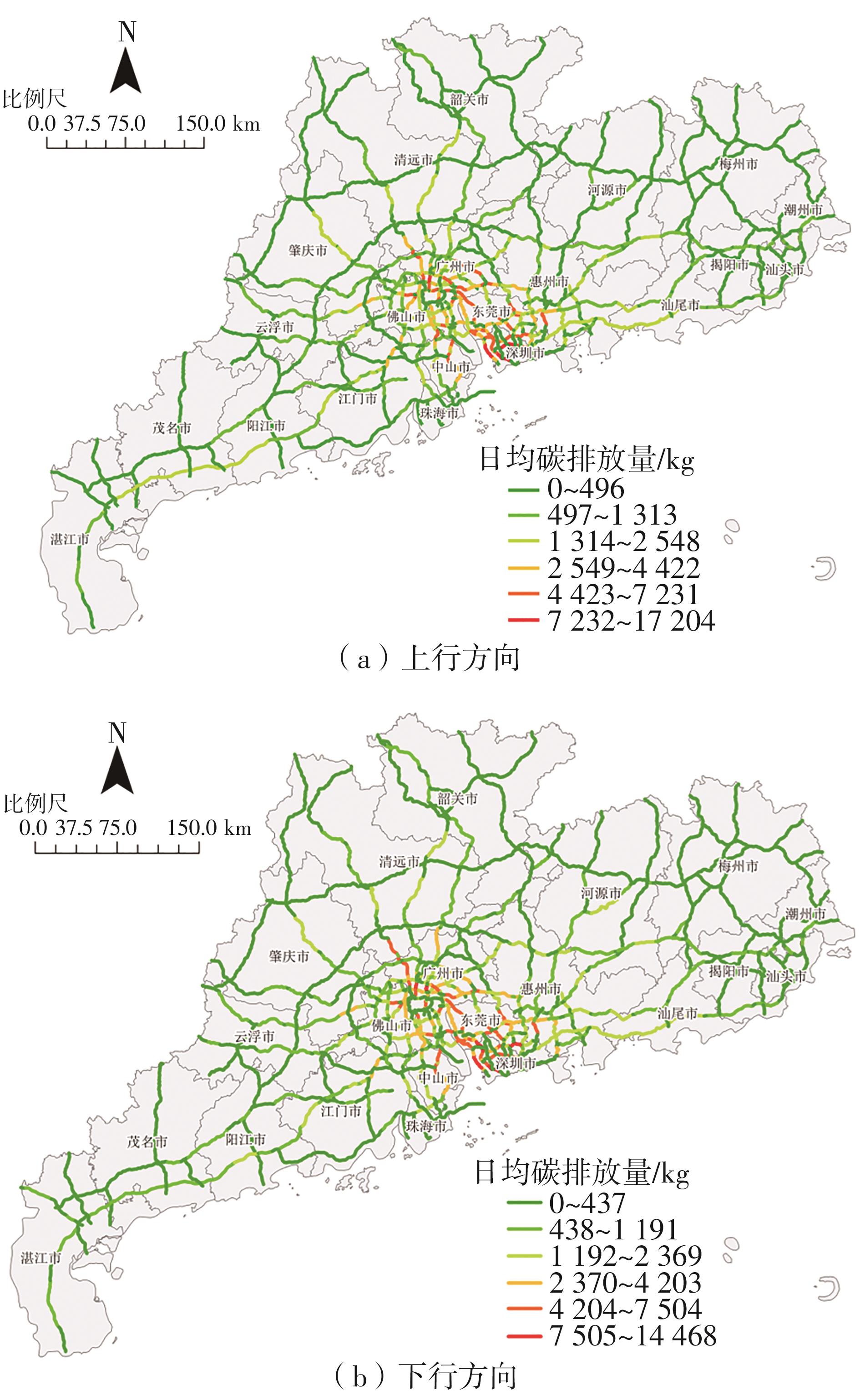
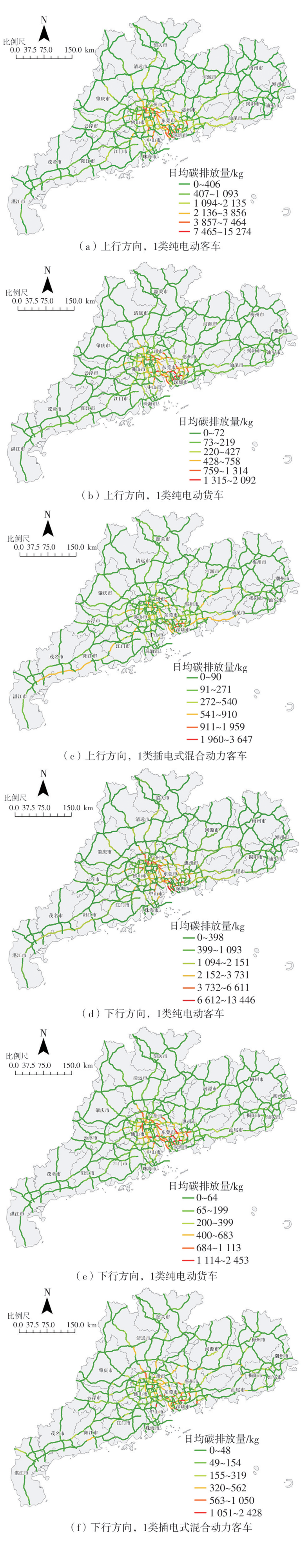
针对高速公路大范围路网中新能源汽车由于能源消耗所产生的间接碳排放量难以统计的问题,提出了一种基于高速公路ETC收费联网数据的新能源汽车碳排放量测算方法。首先,对高速公路新能源汽车车流数据进行清洗与处理;然后,依据高速公路路网门架分布定义并划分路段单元,在此基础上对不同类型的新能源汽车进行能耗分析;最后,建立了新能源汽车运行阶段的碳排放计量模型,并以广东省为例,进行了碳排放量的测算及空间分布特征分析。结果表明:1类纯电动客车为高速公路新能源汽车碳排放的主要来源,其碳排放量占新能源汽车碳排放总量的74.20%,其次是1类纯电动货车,其碳排放量占新能源汽车碳排放总量的14.18%,1类插电式混合动力客车的碳排放量占比为11.62%;新能源汽车碳排放量较高的地市主要集中在珠三角城市群,粤东、粤西、粤北等后发地区的碳排放总量占比不足13%;新能源汽车碳排放量较高的路段主要分布在发达城市的交通枢纽和市内高速环线中,以广州都市圈和深圳都市圈为中心对周边城市高速公路路网产生辐射效应;后发地区由于高速公路路网密度较低且基础设施建设相对滞后,新能源汽车的普及率较低,相应的碳排放量普遍处于较低水平。
中图分类号: