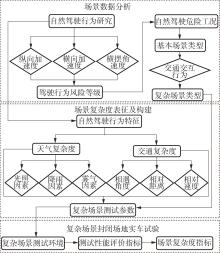
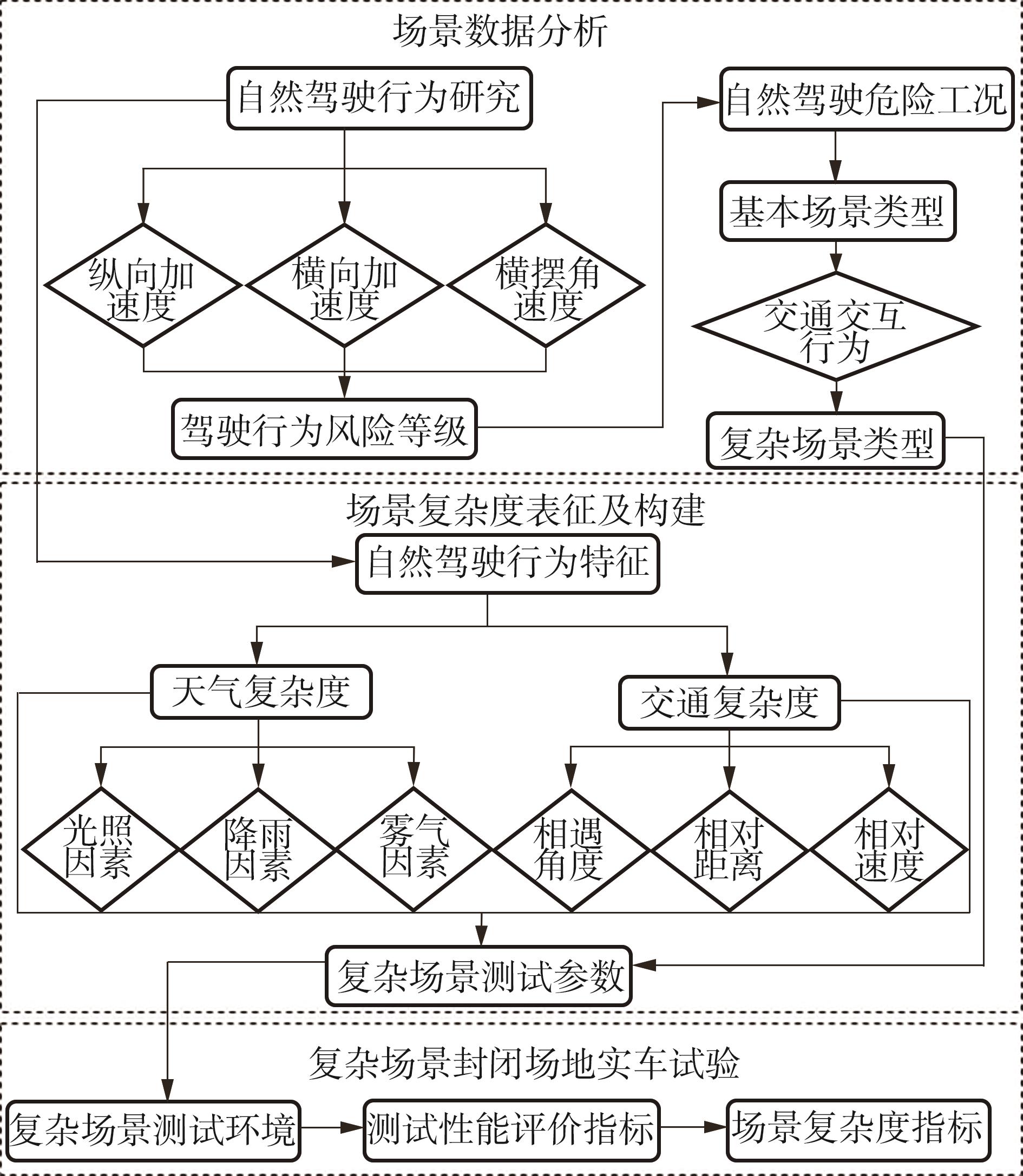
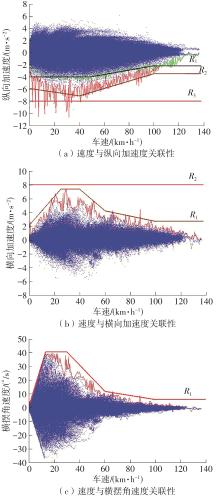
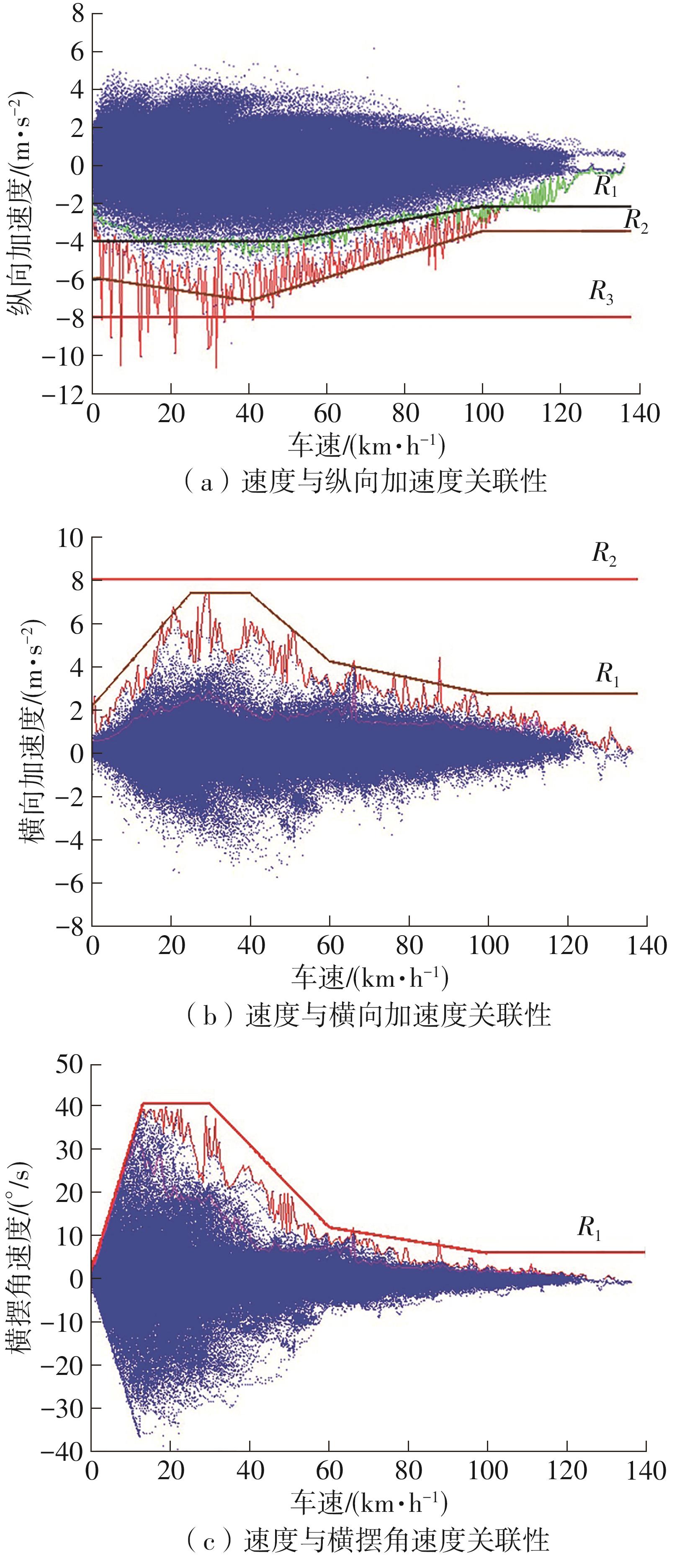
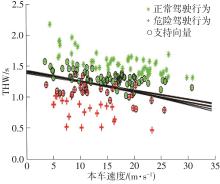
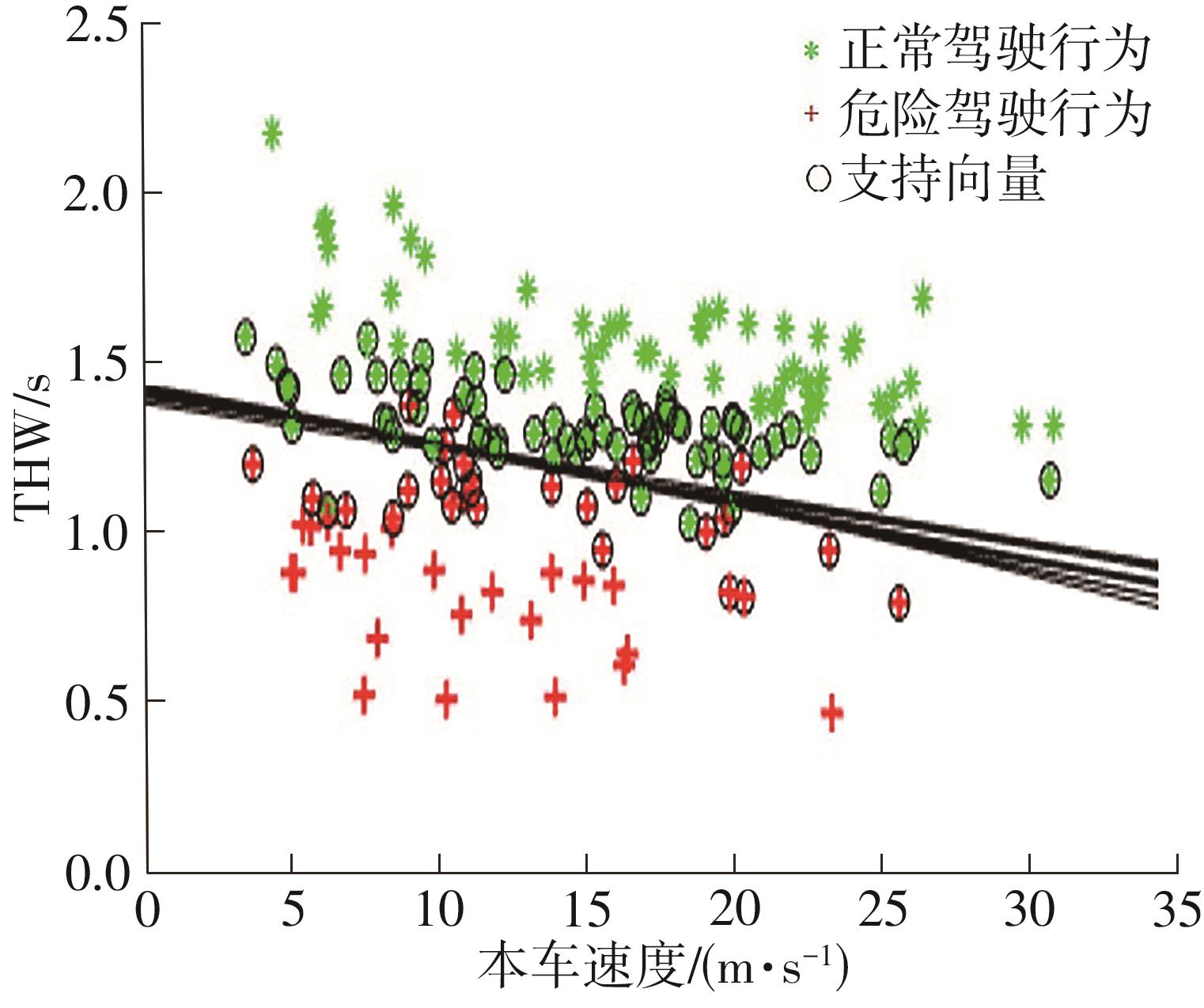
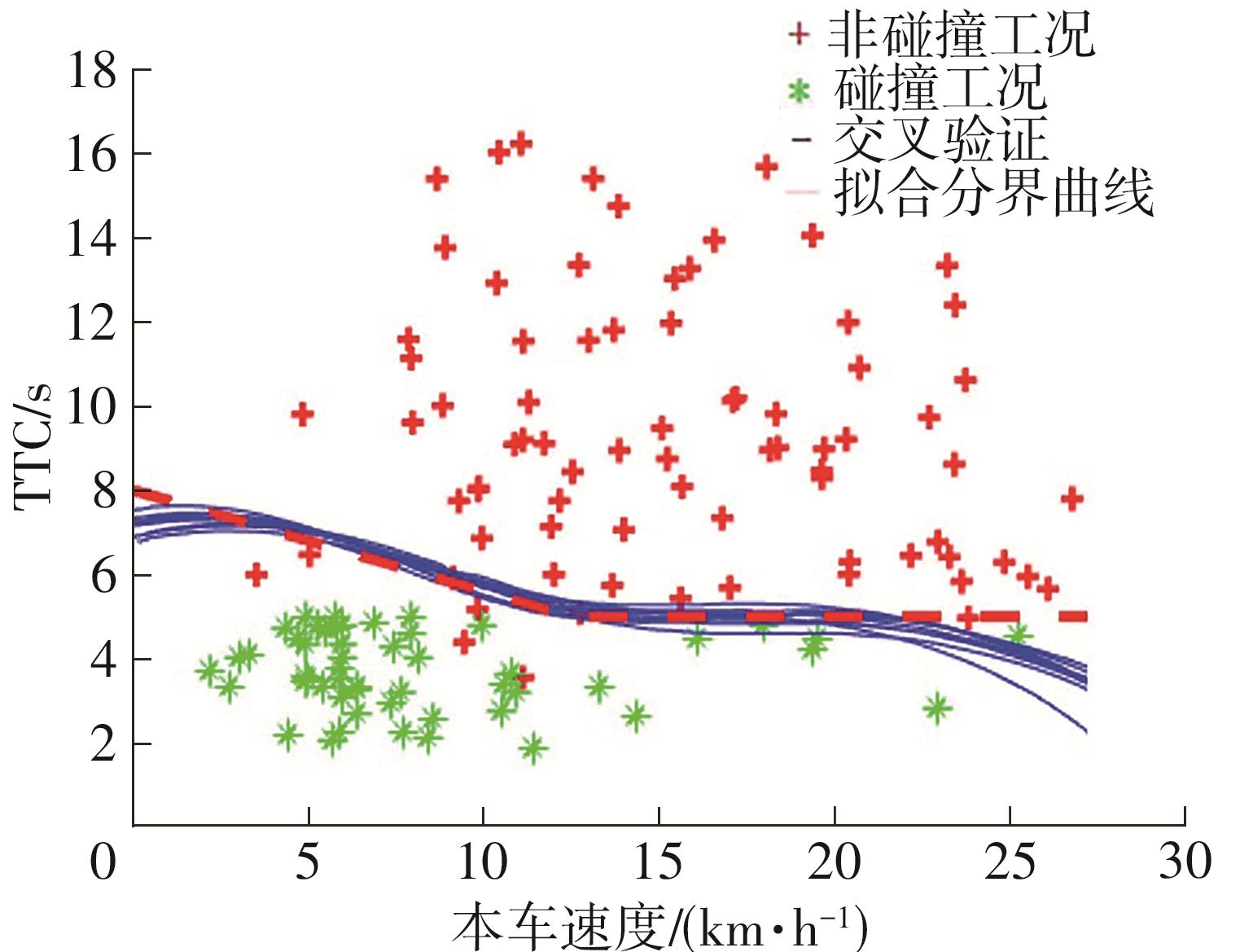
| 1 |
导航智能驾驶测评规程(2020版修订版): IVISTA SMNP TPR A0—2022 [S].
|
| 2 |
Intelligent transport systems-Forward vehicle collision systems-Performance requirements and test procedures: [S].
|
| 3 |
Intelligent transport systems-Lane departure warning systems-Performance requirements and test procedures: [S].
|
| 4 |
Intelligent transport systems-Adaptive cruise control systems-Performance requirements and test procedures: [S].
|
| 5 |
Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to automated lane keeping systems:UN ECE R157—2021 [S].
|
| 6 |
RIEDMAIE S, PONN T, LUDWIG D,et al .Survey on scenario-based safety assessment of automated vehicles[J].IEEE Access,2020,8(4):87456-87477.
|
| 7 |
HAUER F, SCHMIDT T, HOLZMÜLLER B,et al .Did we test all scenarios for automated and autonomous driving systems?[C]∥ Proceeding of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC).[S.l.]: IEEE,2019:2950-2955.
|
| 8 |
DUAN J, GAO F, HE Y,et al .Test scenario generation and optimization technology for intelligent driving systems[J].IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine,2020,14(1):115-127.
|
| 9 |
GELDER E,HOF J, CATOR E,et al .Scenario para-meter generation method and scenario representativeness metric for scenario-based assessment of automated vehicles[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2022,23(10):18794-18807.
|
| 10 |
陈吉清,舒孝雄,兰凤崇,等 .典型危险事故特征的自动驾驶测试场景构建[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(5):1-8.
|
|
CHEN Jiqing, SHU Xiaoxiong, LAN Fengchong,et al .Construction of autonomous vehicles test scenarios with typical dangerous accident characteristics[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(5):1-8.
|
| 11 |
INDAHENG F, KIM E, VISWANADHA K,et al .A scenario-based platform for testing autonomous vehicle behavior prediction models in simulation[J].arxiv preprint arxiv:2110.14870,2021.
|
| 12 |
STADLER C, MONTANARI F, BARON W,et al .A credibility assessment approach for scenario-based virtual testing of automated driving functions[J].IEEE Open Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems,2022,3(2):45-60.
|
| 13 |
李平飞,金思雨,胡文浩,等 .用于自动驾驶仿真测试的车——车事故场景复杂度评价[J].汽车安全与节能学报,2022,13(4):697-704.
|
|
LI Pingfei, JIN Siyu, HU Wenhao,et al .Complexity evaluation of vehicle-vehicle accident scenarios for autonomous driving simulation tests[J].Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy,2022,13(4):697-704.
|
| 14 |
董汉,舒伟,陈超,等 .危险驾驶工况场景的复杂度评估方法研究[J].汽车工程,2020,42(6):808-814.
|
|
DONG Han, SHU Wei, CHEN Chao,et al .Research on complexity evaluation method of dangerous driving scenes[J].Automotive Engineering,2020,42(6): 808-814.
|
| 15 |
MA B, ZHANG Z, GUO G,et al .Study on influence factors of intelligent connected vehicle (ICV) performance under complex weather conditions[C]∥ Proceeding of the 2020 E3S Web of Conferences.[S.l.]:EDP Sciences,2020,213:02024/924-927.
|
| 16 |
MA B, LI W, ZHANG Z,et al .Research on weather condition influence factors on intelligent connected vehicle[C]∥ Proceeding of Journal of Physics:Confe-rence Series.[S.l.]:IOP Publishing,2020,1550(3):032021/122-125.
|
| 17 |
LEBLANC D J, SAYER J, WINKLER C,et al .Road departure crash warning system field operational test:methodology and results.volume 1:technical report[R].Ann Arbor:Transportation Research Institute,University of Michigan,2006.
|
| 18 |
DiINGUS T A, KLAUER S, NEALE V,et al .The 100-car naturalistic driving study:phase Ⅱ-results of the 100-car field experiment[R].Washington:National Highway Traffic Safety Administration(NHTSA),United States,2006.
|
| 19 |
BARNARD Y, KOSKINEN S, NNAMAA S,et al .Data management and data sharing in field operational tests[C]∥ Proceeding of 2016 Intelligent Transportation Systems.New York:CRC Press,2016:69-82.
|
| 20 |
HANOWSKI R J, NAKATA A, OLSON R L .Metho-dological overview of the drowsy driver warning system field operational test[J].SAE Transactions,2004,4(5):610-615.
|
| 21 |
OLSON R L, HANOWSKI R J, HICKMAN J S,et al .Driver distraction in commercial vehicle operations[R].Washington:Department of Transportation,Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration,United States,2009.
|
| 22 |
ANTIN J, LEE S, HANKEY J,et al .Design of the in-vehicle driving behavior and crash risk study:in support of the SHRP 2 naturalistic driving study[R].Washington:Transportation Research Board of the National Academies,United States,2011.
|
| 23 |
ZHANG X, TAO J, TAN K,et al . Finding critical scenarios for automated driving systems:a systematic literature review[J].arXiv Preprint arXiv:2110.08664,2021.
|
| 24 |
降水量等级: [S].
|
| 25 |
雾天公路通行条件预警分级: [S].
|
| 26 |
YIM J B, PARK D J .Modeling evasive action to be implemented at the minimum distance for collision avoi-dance in a give-way situation[J].Ocean Engineering,2022,263:112-210.
|
| 27 |
ANAND K, BIANCONI G .Entropy measures for networks:toward an information theory of complex topologies[J].Physical Review E—Statistical,Nonlinear,and Soft Matter Physics,2009,80(4):45-102.
|