华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 42-50.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230327
基于合成数据集的多目标识别与6-DoF位姿估计
胡广华 欧美彤 李振东
- 华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,广东 广州 510640
Multi-Object Recognition and 6-DoF Pose Estimation Based on Synthetic Datasets
HU Guanghua OU Meitong LI Zhendong
- School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
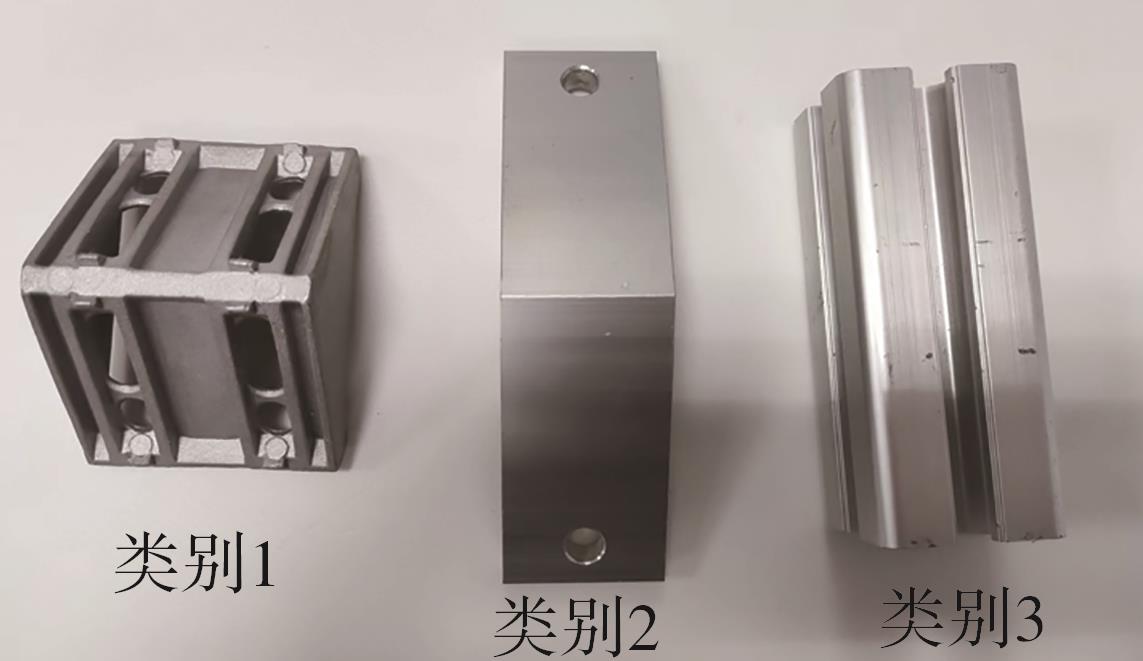
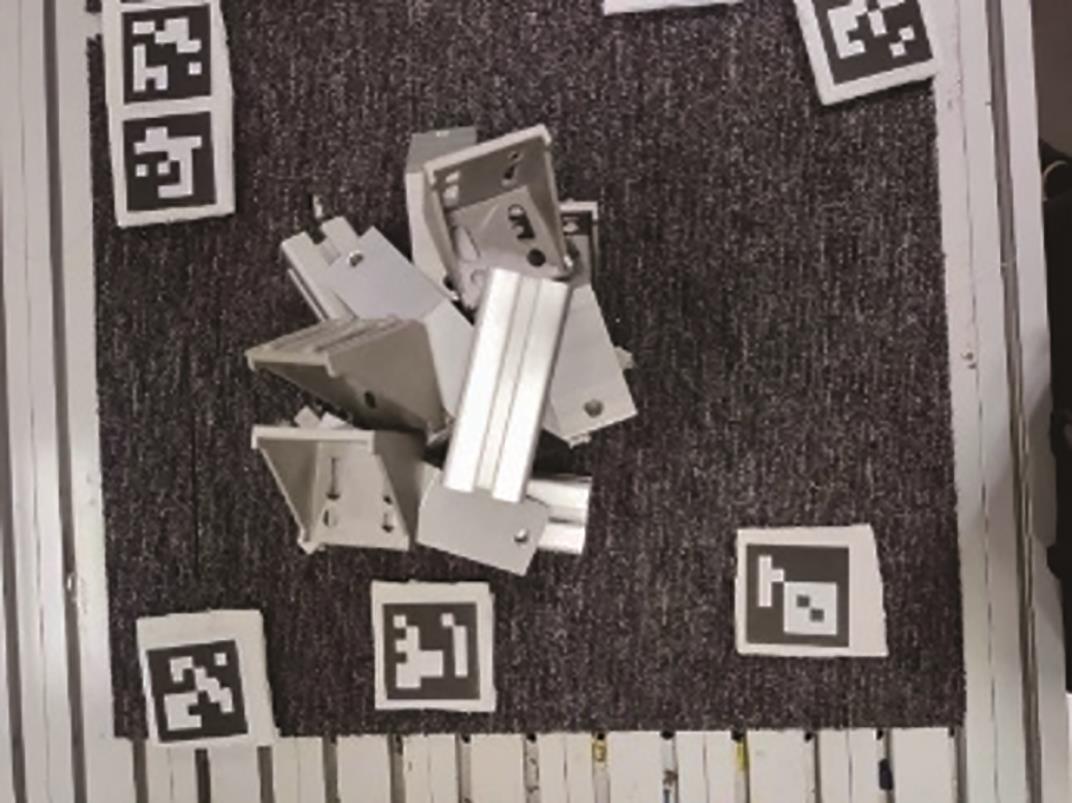
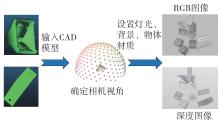
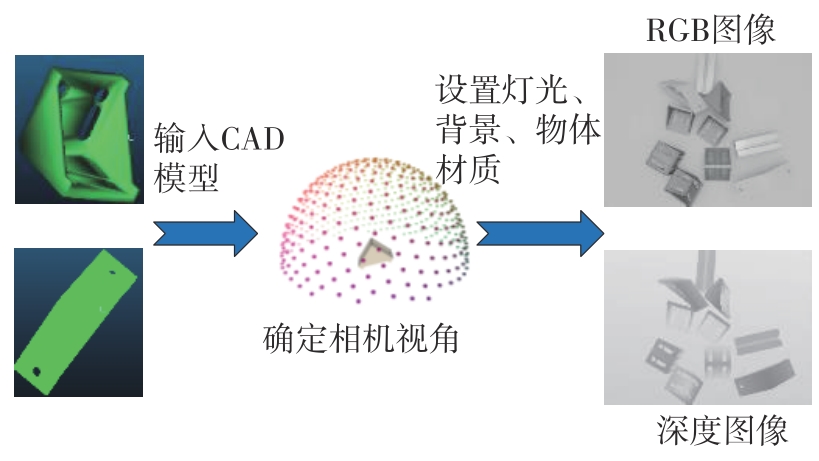
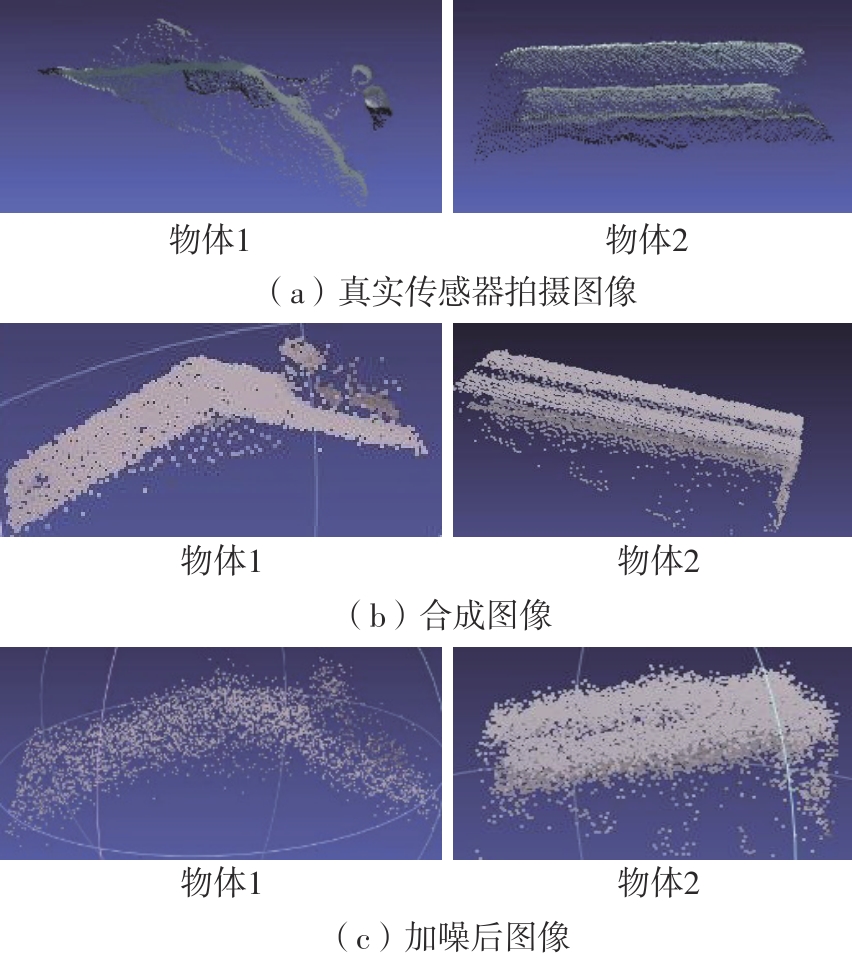
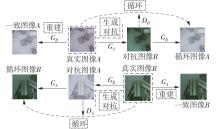
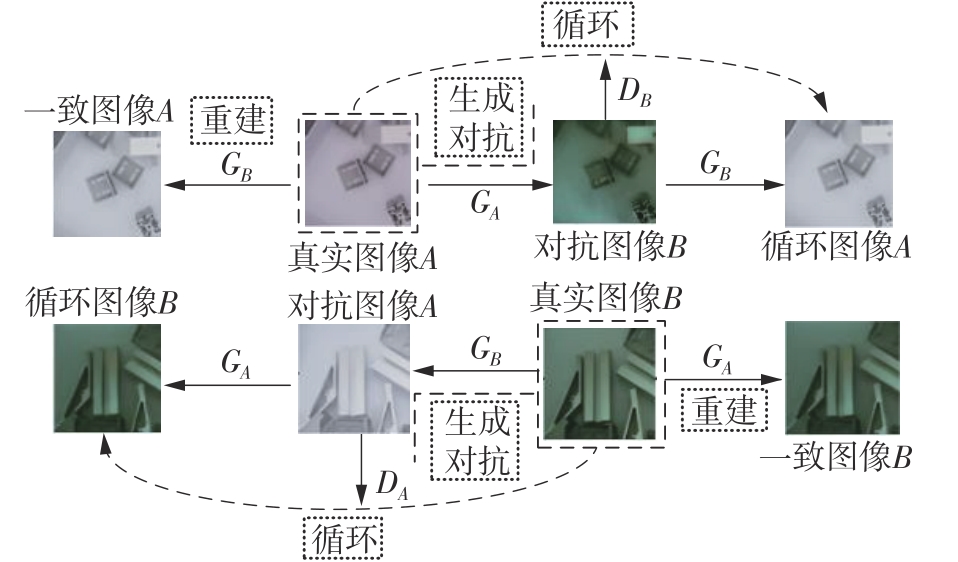
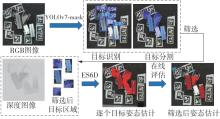
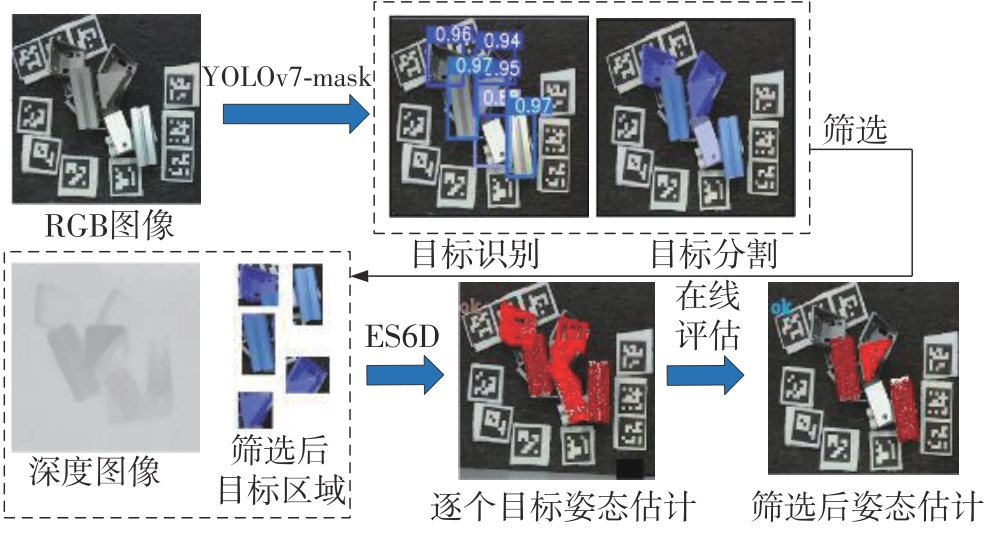
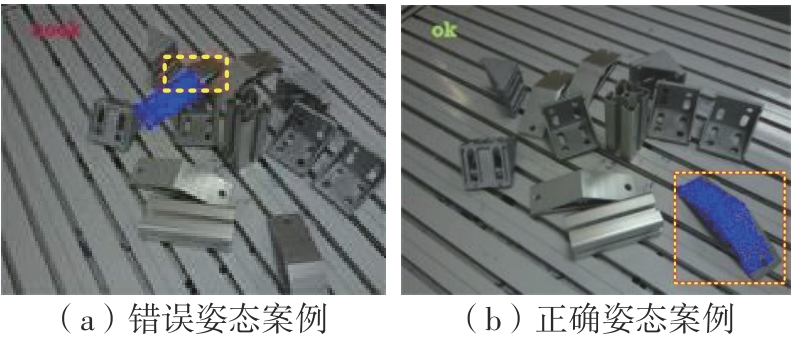
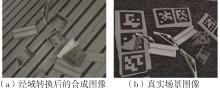
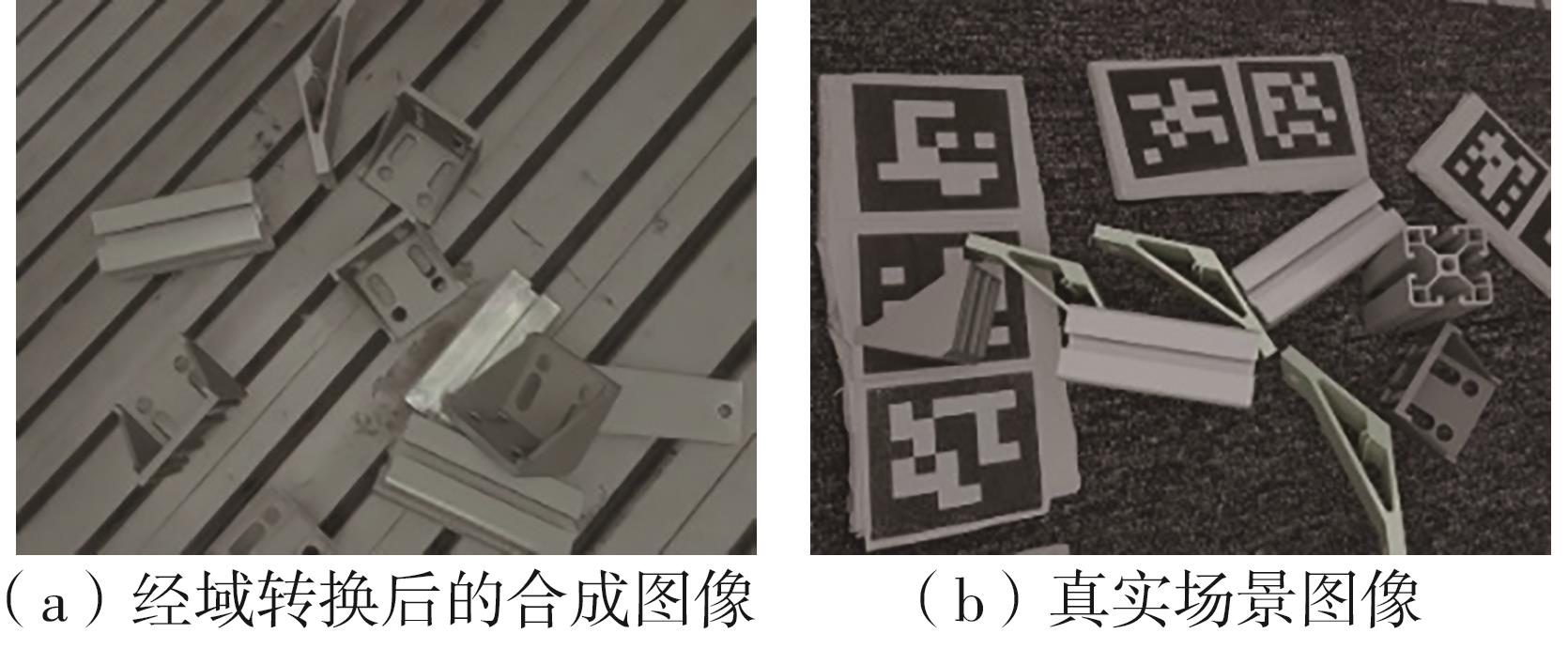
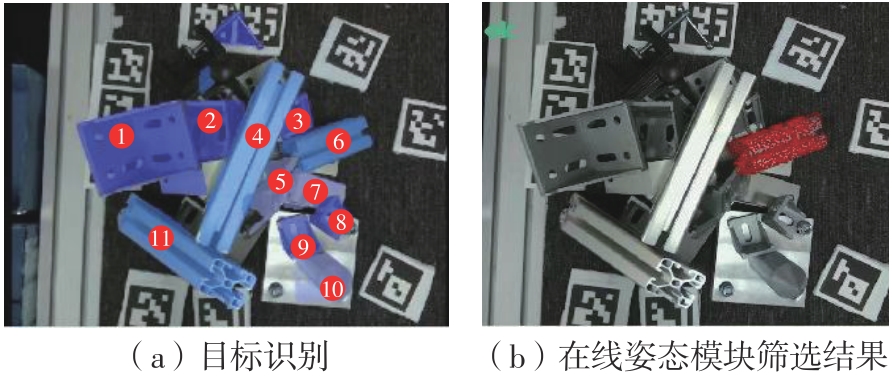
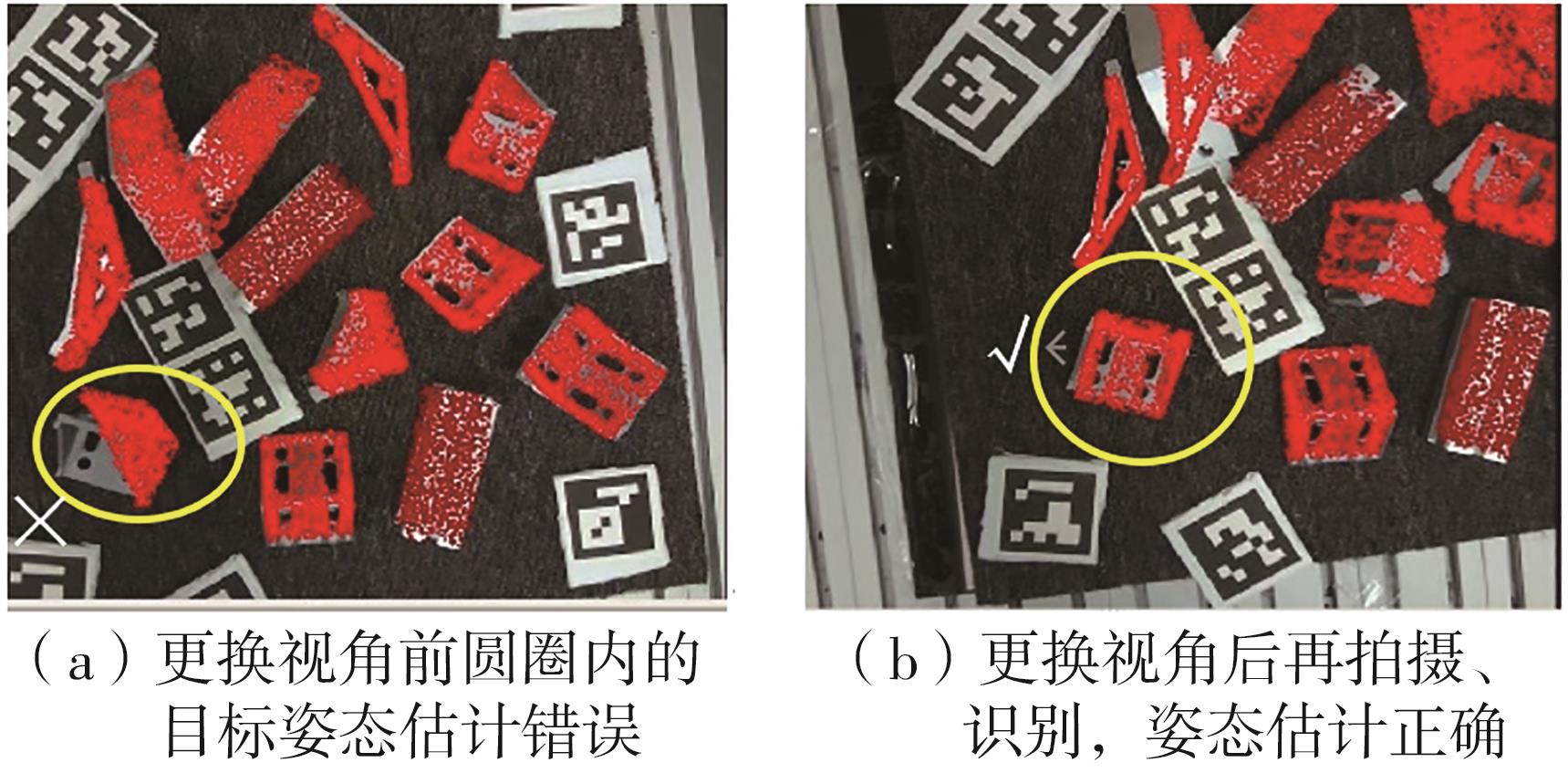
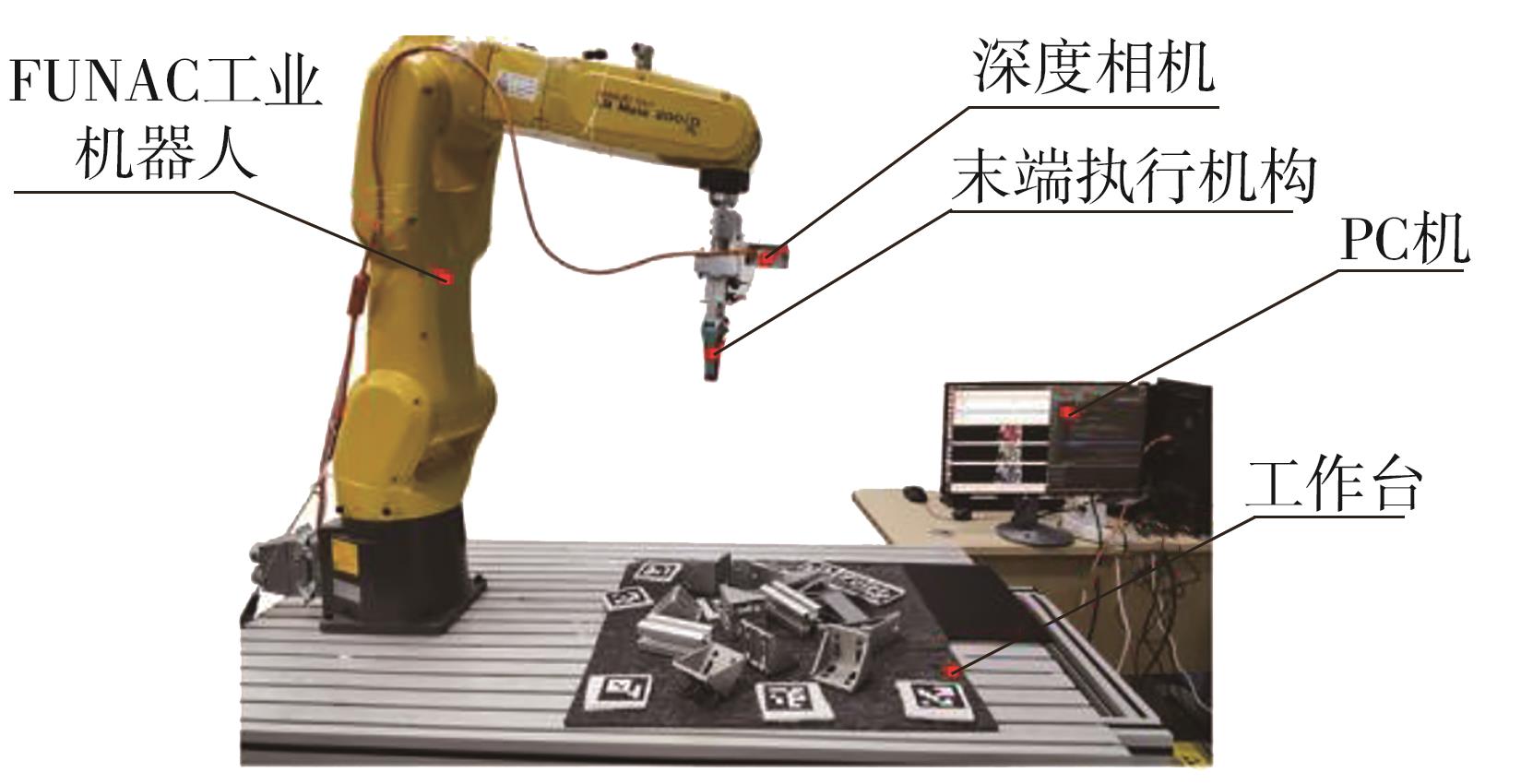
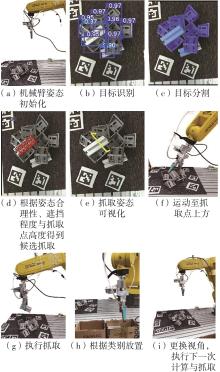
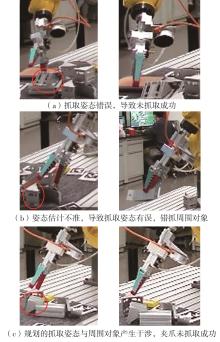
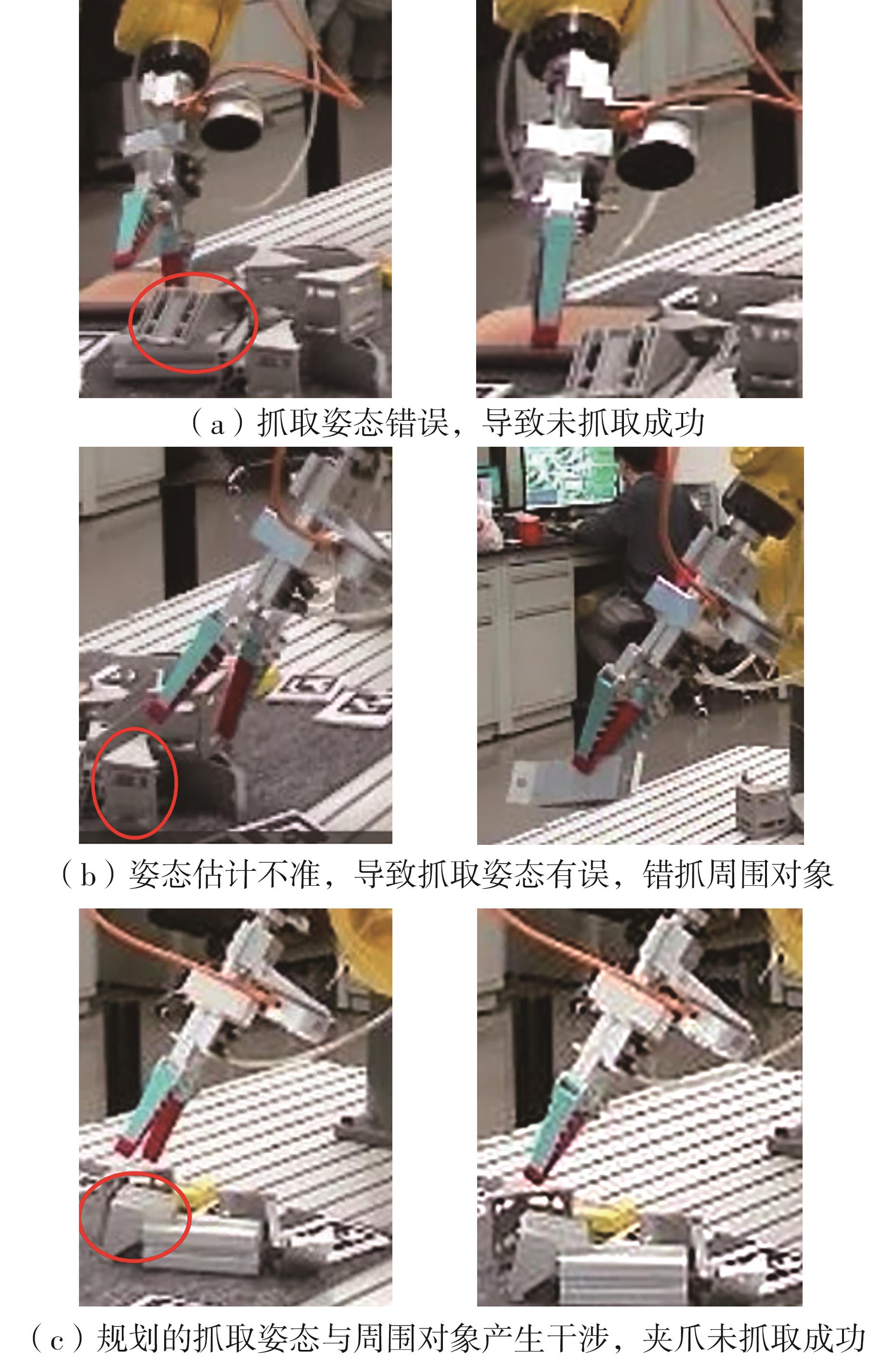
多目标识别及六自由度(6-DoF)位姿估计是实现物料无序堆放状态下机器人自动分拣的关键。近年来,基于深度神经网络的方法在目标识别及位姿估计领域受到广泛关注,但此类方法依赖大量训练样本,而样本的采集及标注费时费力,限制了其实用性。其次,当成像条件差、目标相互遮挡时,现有位姿估计方法无法保证结果的可靠性,进而导致抓取失败。为此,文中提出了一种基于合成数据样本的目标识别、分割及位姿估计方法。首先,以目标对象的3维(3D)几何模型为基础,利用3D图形编程工具生成虚拟场景的多视角RGB-D合成图像,并对生成的RGB图像及深度图像分别进行风格迁移和噪声增强,从而提高合成数据的真实感,以适应真实场景的检测需要;接着,利用合成数据集训练YOLOv7-mask实例分割模型,运用真实数据进行测试,结果验证了该方法的有效性;然后,以分割结果为基础,基于ES6D目标位姿估计模型,提出了一种在线姿态评估方法,以自动滤除严重失真的估计结果;最后,采用基于主动视觉的位姿估计校正策略,引导机械臂运动到新的视角重新检测,以解决因遮挡而导致位姿估计偏差的问题。在自行搭建的6自由度工业机器人视觉分拣系统上进行了实验,结果表明,文中提出的方法能较好地适应复杂环境下工件的识别与6-DoF姿态估计要求。
中图分类号: