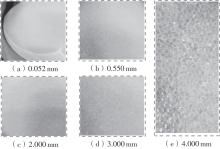
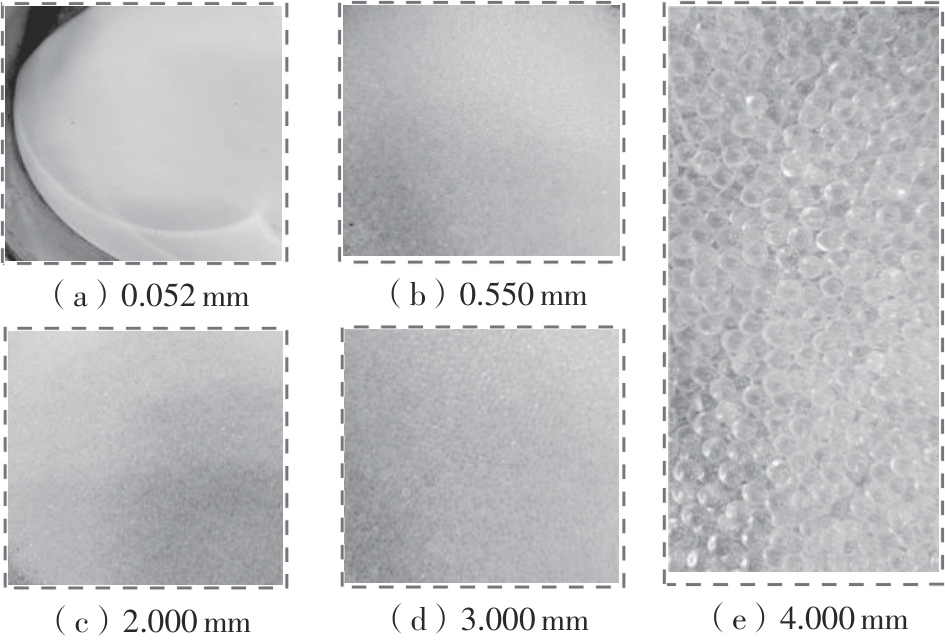
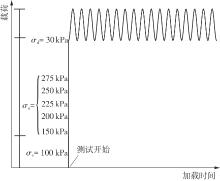
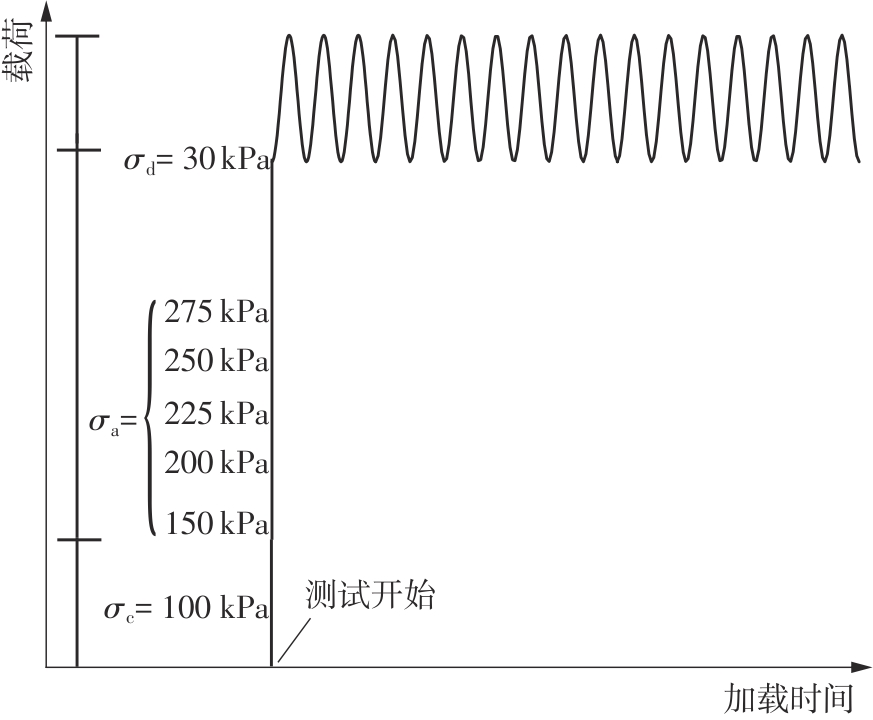
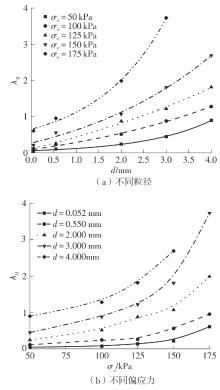
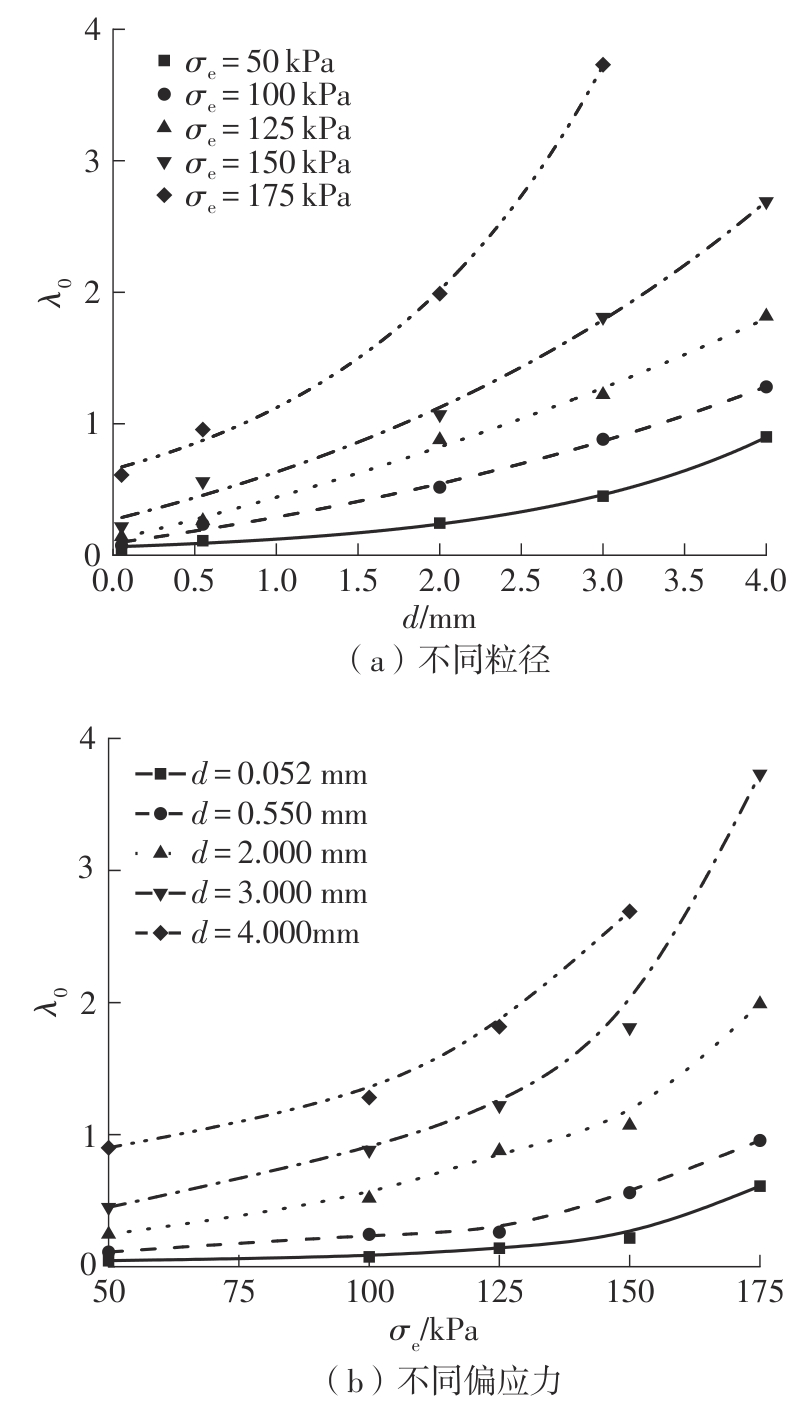
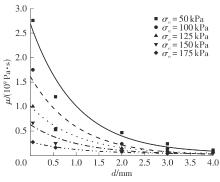
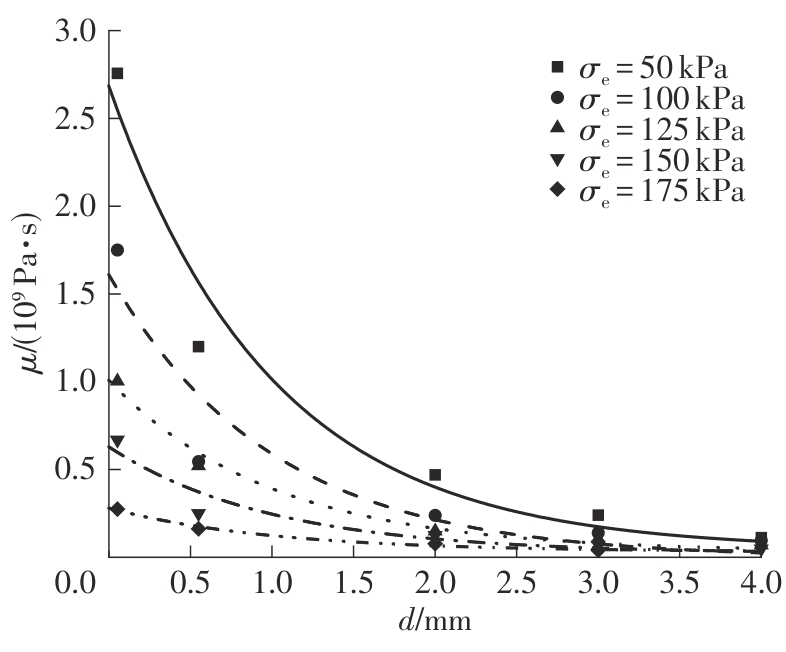
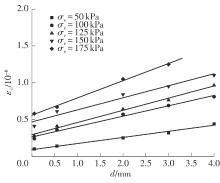
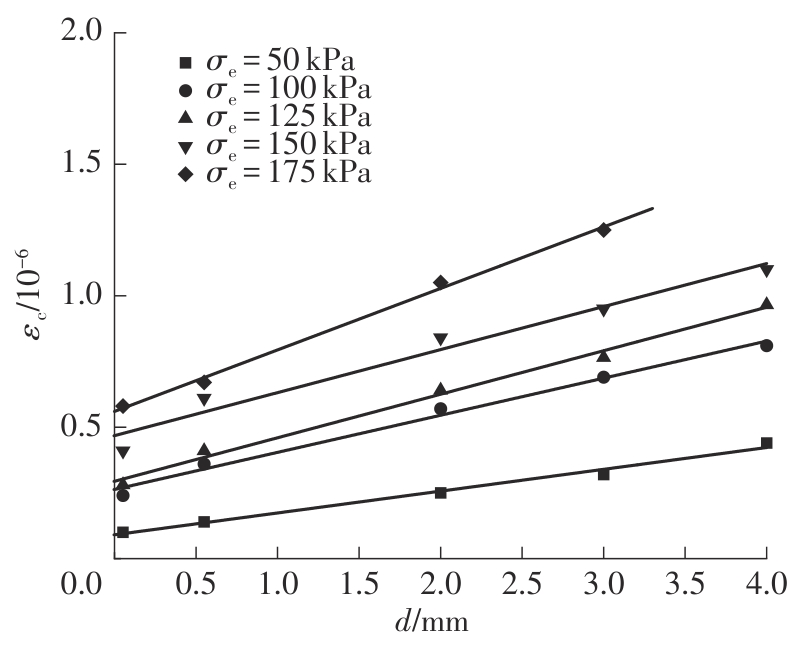
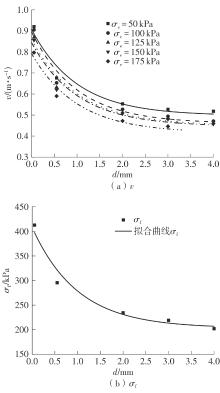
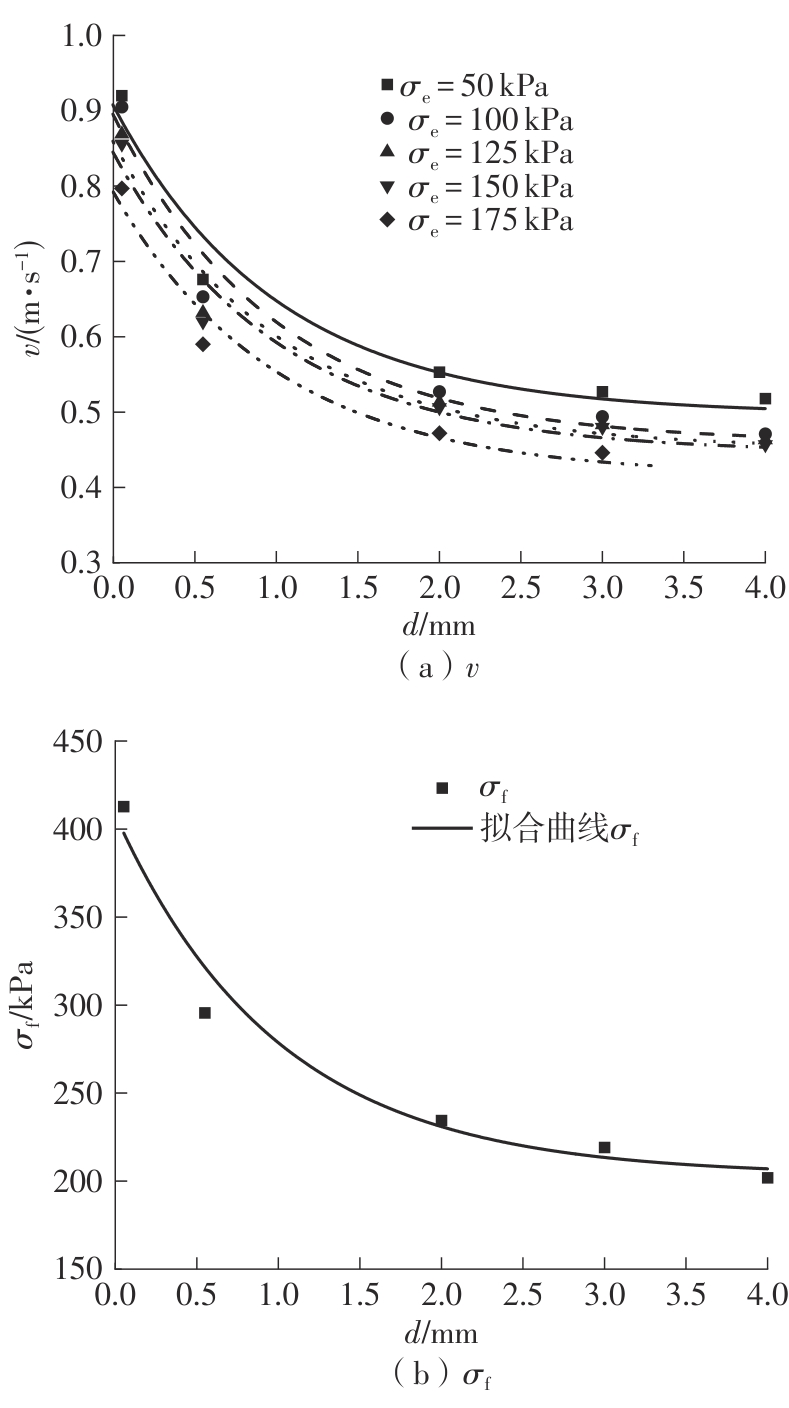
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 74-85.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240473
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
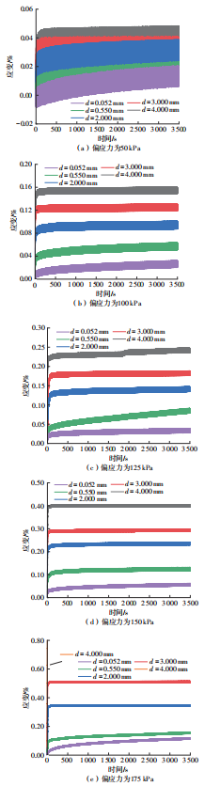
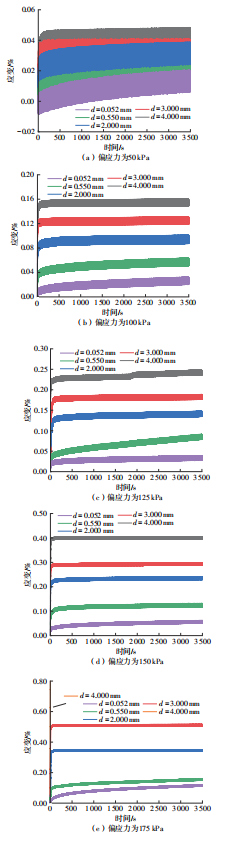
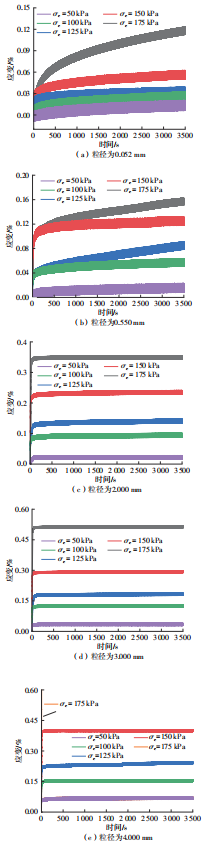
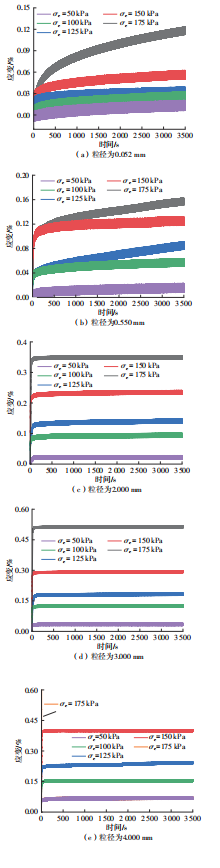
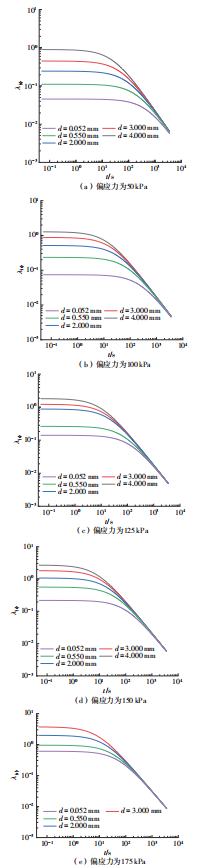
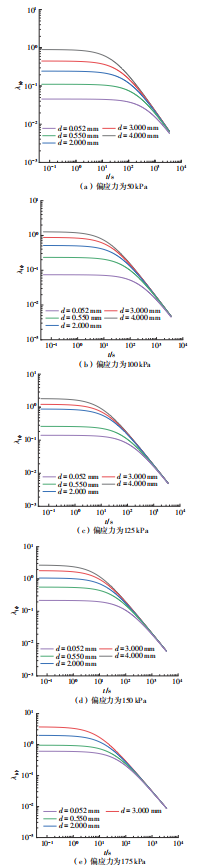
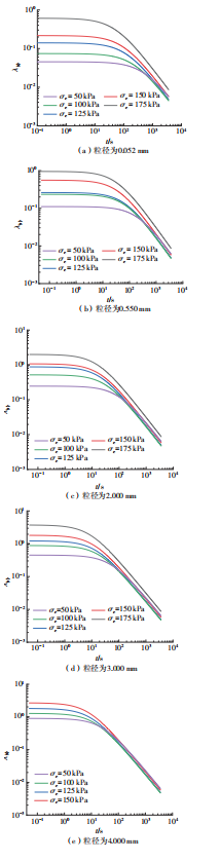
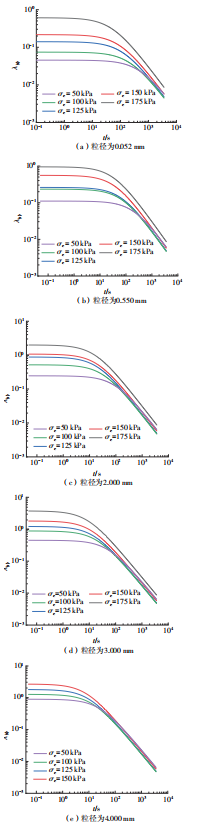
Influence of Particle Size on the Creep Behavior of Granular Materials Under Different Deviatoric Stress
LI Tao1, SHU Jiajun1,2,3, LI Yue1, WAN Limin1, WU Bingni4, DENG Zhengding3, HUANG Jingzhu3, RUBEN Galindo2
- 1.School of Mechanics and Civil Engineering,China University of Mining and Technology-Beijing,Beijing 100083,China
2.Higher Technical School of Civil Engineers,Universidad Politécnica de Madrid,Madrid 28039,Spain
3.Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Environmental Geotechnical Engineering and Hazards Control,Jiangxi University of Science and Technology,Ganzhou 341000,Jiangxi,China
4.School of Civil Engineering and Architecture,East China Jiaotong University,Nanchang 330013,Jiangxi,China
-
Received:2024-09-21Online:2025-10-25Published:2025-04-07 -
Contact:舒佳军(1998—),男,博士生,主要从事岩土力学研究。 E-mail:shujj98@qq.com -
About author:李涛(1981—),男,教授,博士生导师,主要从事城市地下工程研究。E-mail: lit@cumtb.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Major Science and Technology Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region(2024A01003);the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51508556);the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province(20232BAB203079);the Program of China Scholarship Council(202406430056)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Tao, SHU Jiajun, LI Yue, WAN Limin, WU Bingni, DENG Zhengding, HUANG Jingzhu, RUBEN Galindo. Influence of Particle Size on the Creep Behavior of Granular Materials Under Different Deviatoric Stress[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(10): 74-85.
share this article
| [1] | 孙银磊,汤连生,刘洁 .非饱和土微观结构与粒间吸力的研究进展[J].岩土力学,2020,41(4):1095-1122. |
| SUN Yin-lei, TANG Lian-sheng, LIU Jie .Advances in research on microstructure and intergranular suction of unsaturated soils[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(4):1095-1122. | |
| [2] | 付宏渊,马吉倩,史振宁,等 .非饱和土抗剪强度理论的关键问题与研究进展[J].中国公路学报,2018,31(2):1-14. |
| FU Hong-yuan, MA Ji-qian, SHI Zhen-ning,et al .Key issues and research progress of shear strength theory of unsaturated soil[J].Journal of China Highway and Transport,2018,31(2):1-14. | |
| [3] | 牛庚,郭晓霞,陈凡秀,等 .水-力作用下黏土孔隙结构演化规律研究进展[J].防灾减灾工程学报,2023,43(4):905-916. |
| NIU Geng, GUO Xiaoxia, CHEN Fanxiu,et al .Research progress on evolution law of clay pore structure under hydro-mechanical effect[J].Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction Engineering,2023,43(4):905-916. | |
| [4] | GU R G, FANG Y G, JIANG Q,et al .Effect of particle size on direct shear deformation of soil[J].Geomechanics and Engineering,2022,28(22):135-143. |
| [5] | ZHANG H, WANG C, CHEN Z Y,et al .Performance comparison of different particle size distribution models in the prediction of soil particle size characteristics[J].Land,2022,11:2068/1-13. |
| [6] | TANG Y, WEI H H, CHEN Y M,et al .Modeling of permeability for granular soils considering the particle size distribution[J].Granular Matter,2023,25(2):35/1-22. |
| [7] | CHEN X, XU D S, SHEN J H,et al .Effect of particle size and particle distribution pattern on dynamic behavior of cemented calcareous sand[J].Marine Geore-sources & Geotechnology,2023,41(4):412-424. |
| [8] | WANG X, WANG X Z, SHEN J H,et al .Particle size and confining-pressure effects of shear characteristics of coral sand:an experimental study[J].Bulletin of Engineering Geology & the Environment,2022,81(3):97/1-19. |
| [9] | CHEN Q, GAO Y, YUAN Q,et al .The correlation of macro deformation and micro kinematics for dense granular material subjected to shearing[J].Computers & Geotechnics,2022,141:104523/1-11. |
| [10] | ZHAI L H, GAO Y, YUAN Q,et al .Deformation characterizations of granular material in 2D dense assembly subjected to shearing[J].Construction and Building Materials,2018,158:1065-1072. |
| [11] | MEHDI V, TOOMAJ F, MOJTABA M .Study on the shear band thickness in classical continua by a decomposed deformation field for granular materials[J].Journal of Engineering Mechanics,2019,145(11):04019087/1-11. |
| [12] | YU H S, YANG L T, LI X,et al .Experimental investigation on the deformation characteristics of granular materials under drained rotational shear[J].Geomechanics and Geoengineering:An International Journal,2015,1006267/1-17. |
| [13] | 刘恩龙,蒋炼,姜晓琼,等 .土颗粒材料中的复杂网络结构演化分析[J].岩土力学,2023,44(12):3383-3404. |
| LIU En-long, JIANG Lian, JIANG Xiao-qiong,et al .Analysis on evolution of complex network structure of soil granular materials[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2023,44(12):3383-3404. | |
| [14] | 朱雨轩,戴福初,梁莲姬 .青藏高原典型液化型高速远程滑坡形成机制分析[J].工程科学与技术,2020,52(6):10-21. |
| ZHU Yuxuan, DAI Fuchu, LIANG Lianji .Analysis on the formation mechanism of rapid and long runout landslides in liquefaction-type in Tibetan Plateau[J].Advanced Engineering Sciences,2020,52(6):10-21. | |
| [15] | 袁堂金,马硕,邱流潮 .基于两层两相光滑粒子流体动力学法的饱和土柱垮塌模拟研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报,2023,42(11):2832-2846. |
| YUAN Tangjin, MA Shuo, QIU Liuchao .Numerical study on collapse of saturated soil columns based on two-layer two phase smoothed particle hydrodynamics[J].Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2023,42(11):2832-2846. | |
| [16] | 陈国兴,孙田,王炳辉,等 .循环荷载作用下饱和砂砾土的破坏机理与动强度[J].岩土工程学报,2015,37(12):2140-2148. |
| CHEN Guo-xing, SUN Tian, WANG Bing-hui,et al .Undrained cyclic failure mechanisms and resistance of saturated sand-gravel mixtures[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,37(12):2140-2148. | |
| [17] | ZHU Q, SU L J, LIU Z Y,et al .An evaluation method for internal erosion potential of gravelly soil based on particle size distribution[J].Journal of Mountain Science,2022,19(4):1203-1214. |
| [18] | WANG C, LI S Y, LAI Y M,et al .Predicting the soil freezing characteristic from the particle size distribution based on micro-pore space geometry[J].Water Resources Research,2022,58(1):030782/1-15. |
| [19] | 尹福顺,李飒,刘鑫 .钙质粗粒料颗粒强度和压缩特性的试验研究[J].岩土力学,2023,44(4):1120-1129,1152. |
| YIN Fu-shun, LI Sa, LIU Xin .Experimental study on single particle strength and compression properties of calcareous coarse sand[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2023,44(4):1120-1129,1152. | |
| [20] | 梁传扬,吴跃东,刘坚,等 .土颗粒排列与胶结作用对人造结构性土结构性影响研究[J].岩土工程学报,2022,44(11):2135-2142. |
| LIANG Chuan-yang, WU Yue-dong, LIU Jian,et al .Influences of arrangement and cementation of soil particles on structure of artificial structural soil[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2022,44(11):2135-2142. | |
| [21] | 刘文化,杨庆,孙秀丽,等 .干湿循环条件下干燥应力历史对粉质黏土饱和力学特性的影响[J].水利学报,2017,48(2):203-209. |
| LIU Wenhua, YANG Qing, SUN Xiuli,et al .Influence of drying stress history on the mechanical beha-viors of silty clay under saturated condition[J].Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2017,48(2):203-209. | |
| [22] | 刘燕晶,王路君,朱斌,等 .考虑填充和黏结作用的含水合物沉积物弹塑性本构模型[J].岩土力学,2022,43(9):2471-2482. |
| LIU Yanjing, WANG Lujun, ZHU Bin,et al .An elastoplastic constitutive model for hydrate-bearing sediments considering the effects of filling and bonding [J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2022,43(9):2471-2482. | |
| [23] | 张嘎,王刚,尹振宇,等 .土的基本特性及本构关系[J].土木工程学报,2020,53(2):105-118. |
| ZHANG Ga, WANG Gang, YIN Zhenyu,et al .A critical review on the research of fundamental behaviors and constitutive relationships of soil [J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2020,53(2):105-118. | |
| [24] | 高乾丰,吴昕阳,曾铃,等 .红黏土裂隙湿化自愈行为及强度影响机制[J].中国公路学报,2024,37(6):157-168. |
| GAO Qian-feng, WU Xin-yang, ZENG Ling,et al .Mechanisms behind wetting self-healing behavior and its influence on the strength of lateritic soil[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2024,37(6):157-168. | |
| [25] | 张建民 .砂土动力学若干基本理论探究[J].岩土工程学报,2012,34(1):1-50. |
| ZHANG Jian-min .New advances in basic theories of sand dynamics[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2012,34(1):1-50. | |
| [26] | DEREC C, AJDARI A, LEQUEUX A .Rheology and aging:a simple approach[J].The European Physical Journal E:Soft Matter,2001,4(3):355-361. |
| [27] | NGUYEN V, DARNIGE T, BRUAND A,et al .Creep and fluidity of a real granular packing near jamming[J].Physical Review Letters,2011,107(13):138303/1-4. |
| [28] | PONS A, AMON A, DARNIGE T,et al .Mechanical fluctuations suppress the threshold of soft-glassy solids:the secular drift scenario[J].Physical Review E,2015,92(2):020201/1-6. |
| [29] | PONS A, DARNIGE T, CRASSOUS J,et al .Spatial repartition of local plastic processes in different creep regimes in a granular material[J].A Letters of Journal Exploring the Frontiers of Physics,2016,113(2):28001/1-7. |
| [30] | ESPÍNDOLA D, GALAZ B, MELO F .Ultrasound induces aging in granular materials[J].Physical Review Letters,2012,109(15):158301/1-4. |
| [31] | TONG L H, QI B W, XU C J .Fluidity characteristic of granular materials within low frequency dynamics[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2021,202/203:106508/1-6. |
| [1] | LIU Yan, XUE Xinyuan, FAN Lei, et al. Investigation into Creep Properties of Kapton Films Under Different Initial Stresses [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 127-138. |
| [2] | YU Qijun, MA Ting, ZHANG Tongsheng, et al.. Effect of Particle Size on Hydration Kinetics and Microstructure Development of Recycled Brick Powder-Cement Pastes [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(11): 63-73. |
| [3] | WU Bo, CHEN Zhaonan, WANG Hui. Creep Behavior of Reinforced and Unreinforced Recycled Lump/Aggregate Concrete [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 35-42. |
| [4] | TANG Mian, CHE Tianxin, SONG Xuming, et al. Study on Pre-tightening Force of Cable Clamp of Self-anchored Suspension Bridge Based on Creep Theory [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(1): 59-68. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xia, ZAN Shengjie, LI Bing, et al. Property Characterization and Emulsion Stability of Solid Lipid Particles Prepared by Ultrasonic Treatment [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(11): 27-37. |
| [6] | YANG Shiyu, ZHAO Renda, ZENG Xianshuai, et al. Research Progress of Long-Term Time-Dependent Deformation of Geopolymer Concrete [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(12): 91-104. |
| [7] | GAO Jun-feng WANG Hai-nian YOU Zhan-ping CHEN Xi JIANG Xin. High-Temperature Performance Evaluation of Bio-Asphalt on the Basis of MSCR Test [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(11): 24-30. |
| [8] | HOU Xian-jun XU Jing LIU Jin-ping DU Song-ze LI Meng-meng. Particulate Emission Characteristics of Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel /Ethanol Blends [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(9): 144-150. |
| [9] | SONG Dan-qing XIANG Guo-sheng. Triaxial Tests of Deformation Characteristics of Bottom Ash from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(7): 116-122. |
| [10] | Ye Jun Li Wen- hao Xiong Jian. Relationship Between Size as Well as Size Distribution and Fluorescence Properties of CMC/Eu Complex Nanoparticles Synthesized at Different pH Values [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(6): 73-78,120. |
| [11] | Zhang Jun Duan Ya- hui. Research on Concrete Creep and Relaxation Based on the Generalized Kelvin Model with Variable Coefficients [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(2): 74-80. |
| [12] | Wang Yi-min Zou Chao Gao Shui-qin. Deformation of Reinforced Soil Retaining Wall on Soft Soil Ground Considering Creep Effects [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(4): 113-118,126. |
| [13] | Su Cheng Chen Zhao-shuan Xu Yu-feng Pang Jian. Probability Analysis of Shrinkage and Creep Effect of Prestressed Concrete Cable-Stayed Bridges [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(7): 8-14. |
| [14] | Zhang De-yu Huang Xiao-ming Gao Ying. Three-Dimension Virtual Uniaxial Creep Test of Asphalt Mixture by Using Discrete Element Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(7): 15-20. |
| [15] | Liu Shu-mei Sun Zhi-song Zhang Yu Zhang Li-ping Zhao Jian-qing. Preparation and Formation Mechanism of Narrow-Dispersed Poly( Aminopropyl /Phenylsilsesquioxane) Microspheres [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(4): 95-100,106. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||