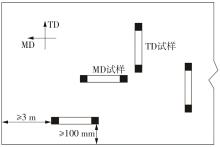
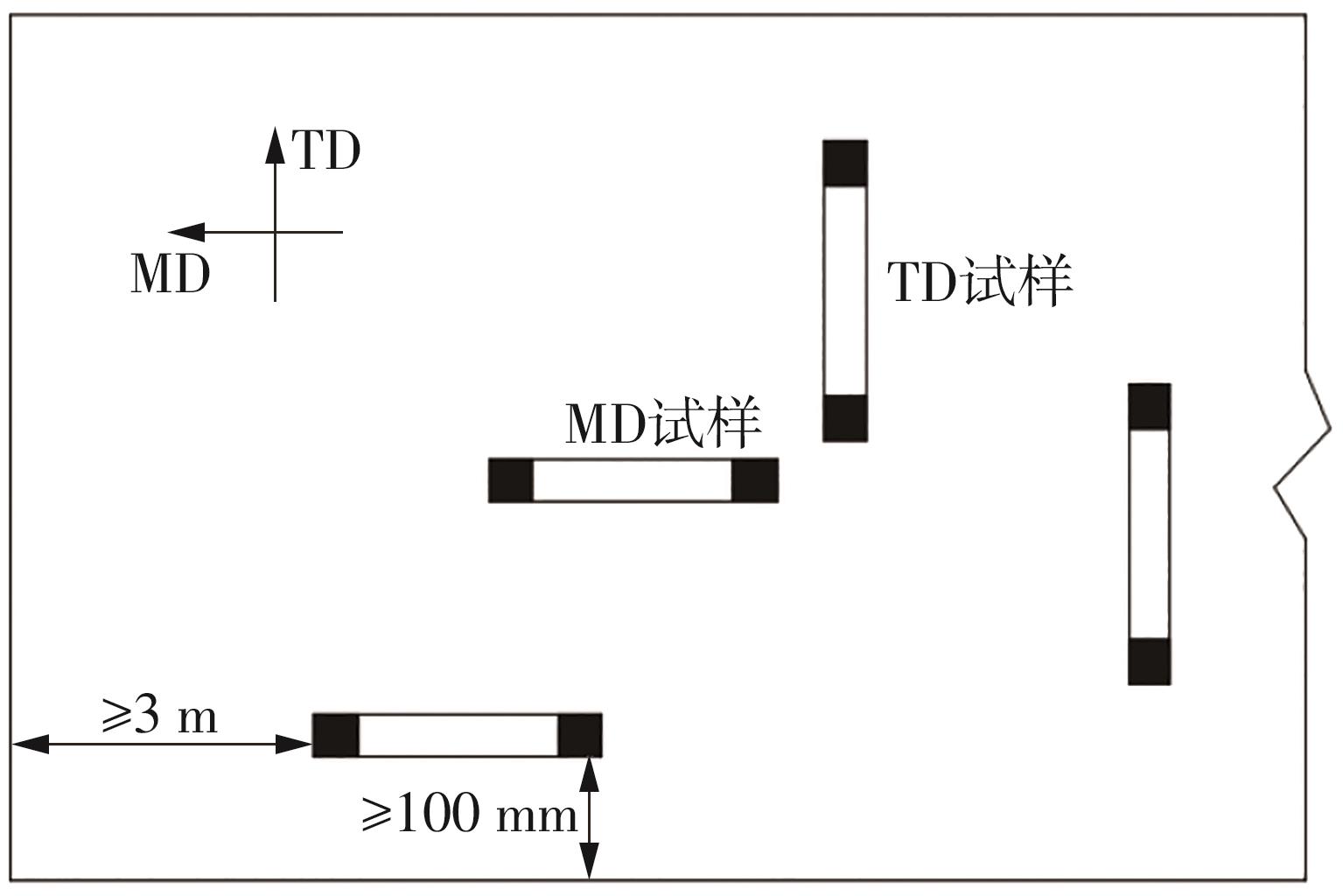
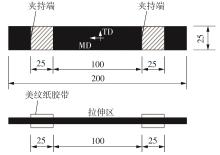
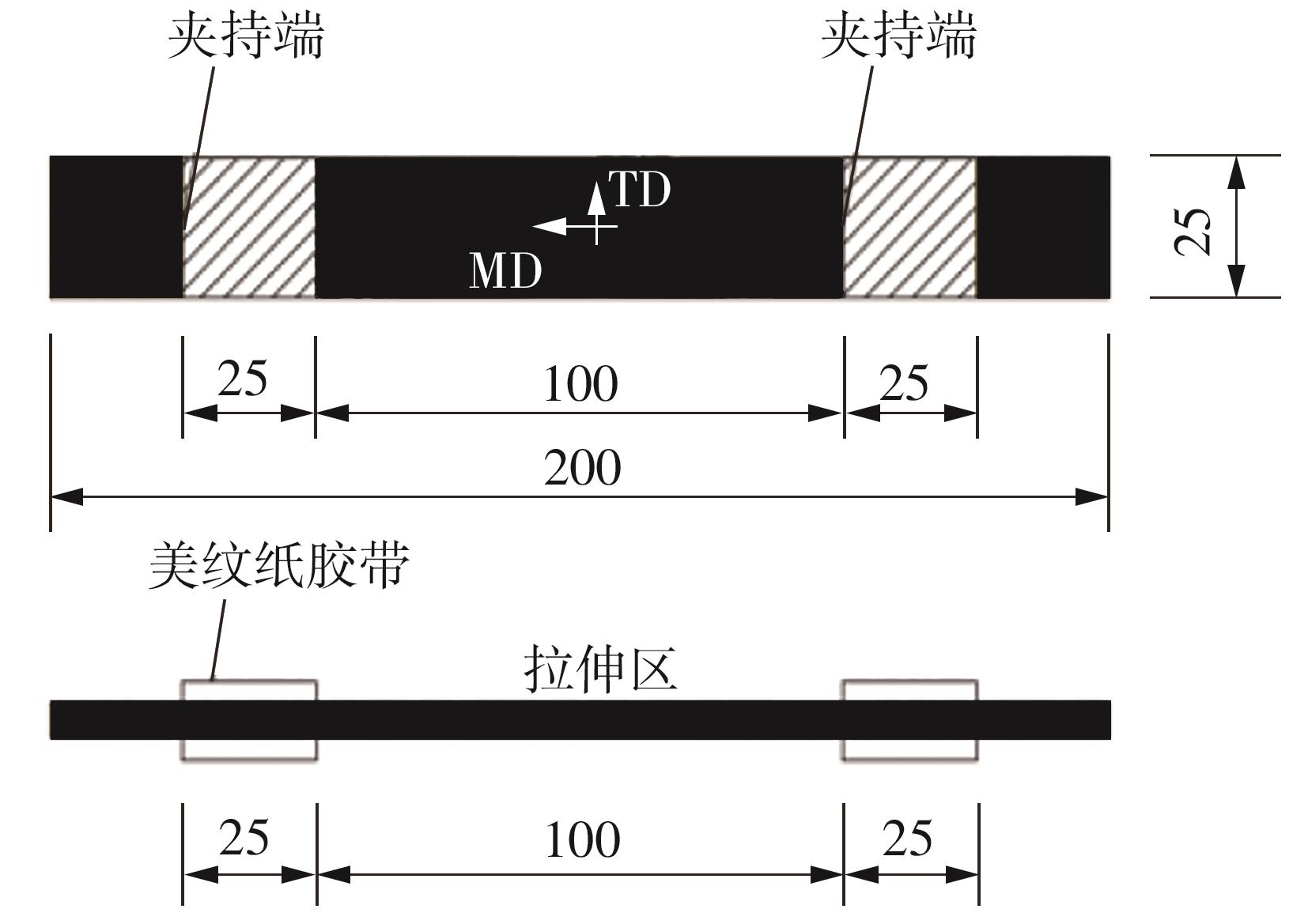
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 127-138.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230168
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Investigation into Creep Properties of Kapton Films Under Different Initial Stresses
LIU Yan( ), XUE Xinyuan, FAN Lei, CHEN Yixian
), XUE Xinyuan, FAN Lei, CHEN Yixian
- School of Civil Engineering,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710061,Shaanxi,China
-
Received:2023-04-03Online:2024-05-25Published:2023-09-08 -
About author:刘岩(1984-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事空间结构、钢结构研究。 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51908043)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LIU Yan, XUE Xinyuan, FAN Lei, et al. Investigation into Creep Properties of Kapton Films Under Different Initial Stresses[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 127-138.
share this article
Table 1
Tensile test data of uniaxial fracture"
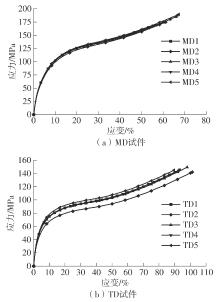
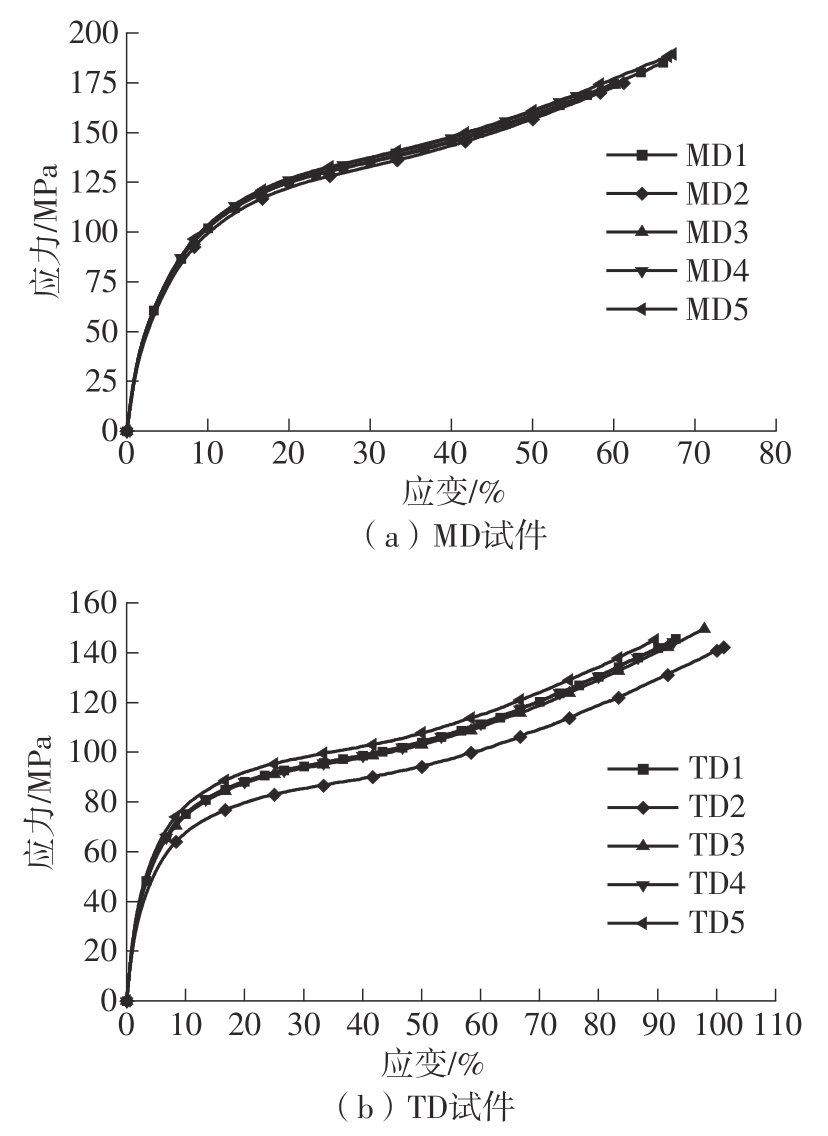
| 序号 | 弹性模量/MPa | 拉伸应变/% | 拉伸断裂应力/MPa | 序号 | 弹性模量/MPa | 拉伸应变/% | 拉伸断裂应力/MPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD1 | 799.046 | 0.659 | 184.725 | TD1 | 402.384 | 0.928 | 145.348 | ||
| MD2 | 833.900 | 0.610 | 174.478 | TD2 | 335.288 | 1.010 | 141.940 | ||
| MD3 | 862.178 | 0.599 | 173.737 | TD3 | 380.357 | 0.977 | 149.217 | ||
| MD4 | 925.843 | 0.552 | 168.353 | TD4 | 404.123 | 0.924 | 144.461 | ||
| MD5 | 806.752 | 0.670 | 189.018 | TD5 | 435.310 | 0.894 | 144.994 | ||
| 平均值 | 845.543 7 | 0.617 8 | 178.062 | 平均值 | 391.492 | 0.946 4 | 145.192 | ||
Table 2
Summary table of different initial stress data"
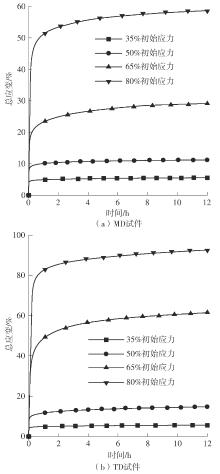
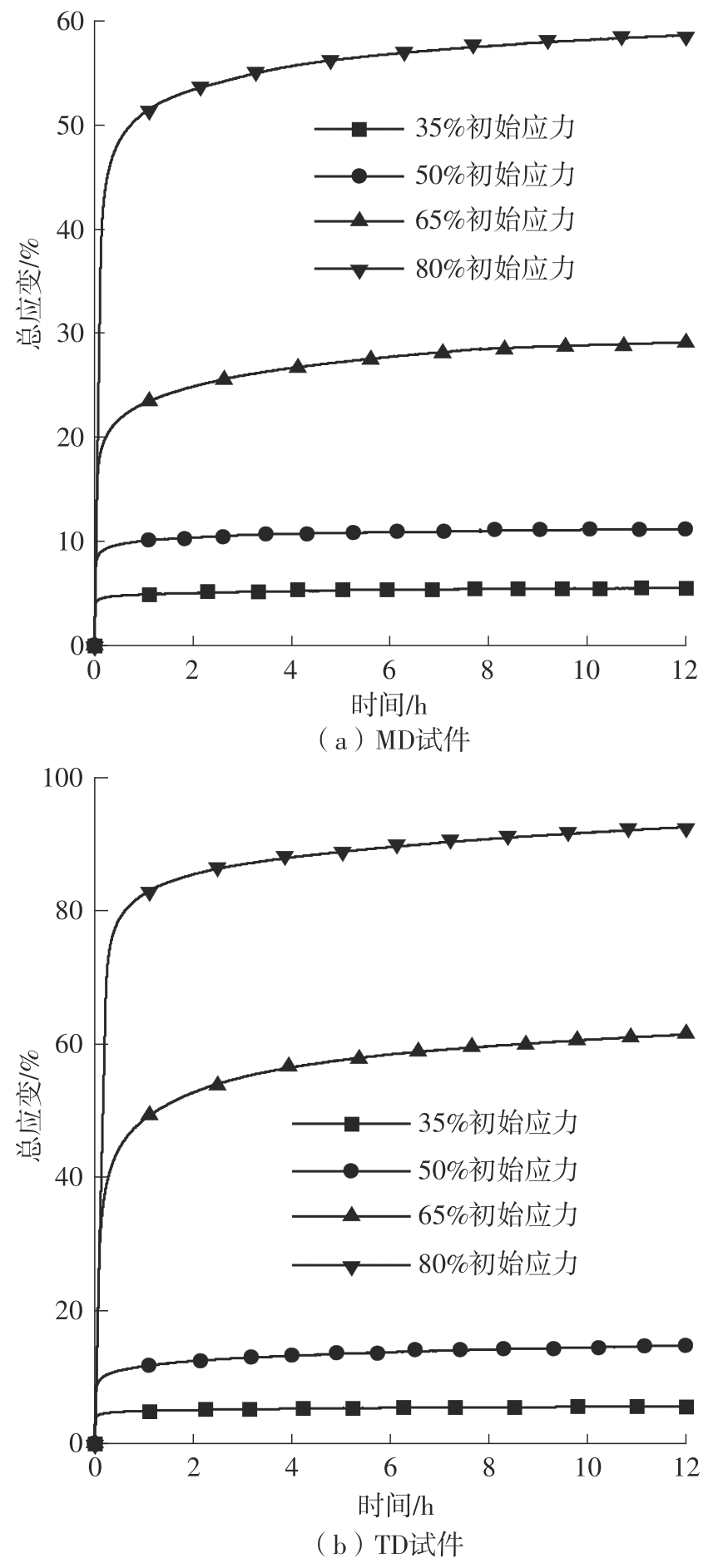
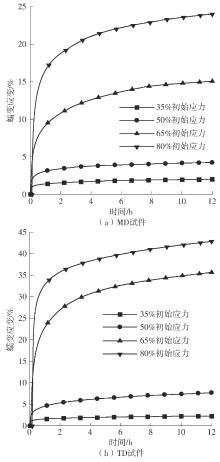
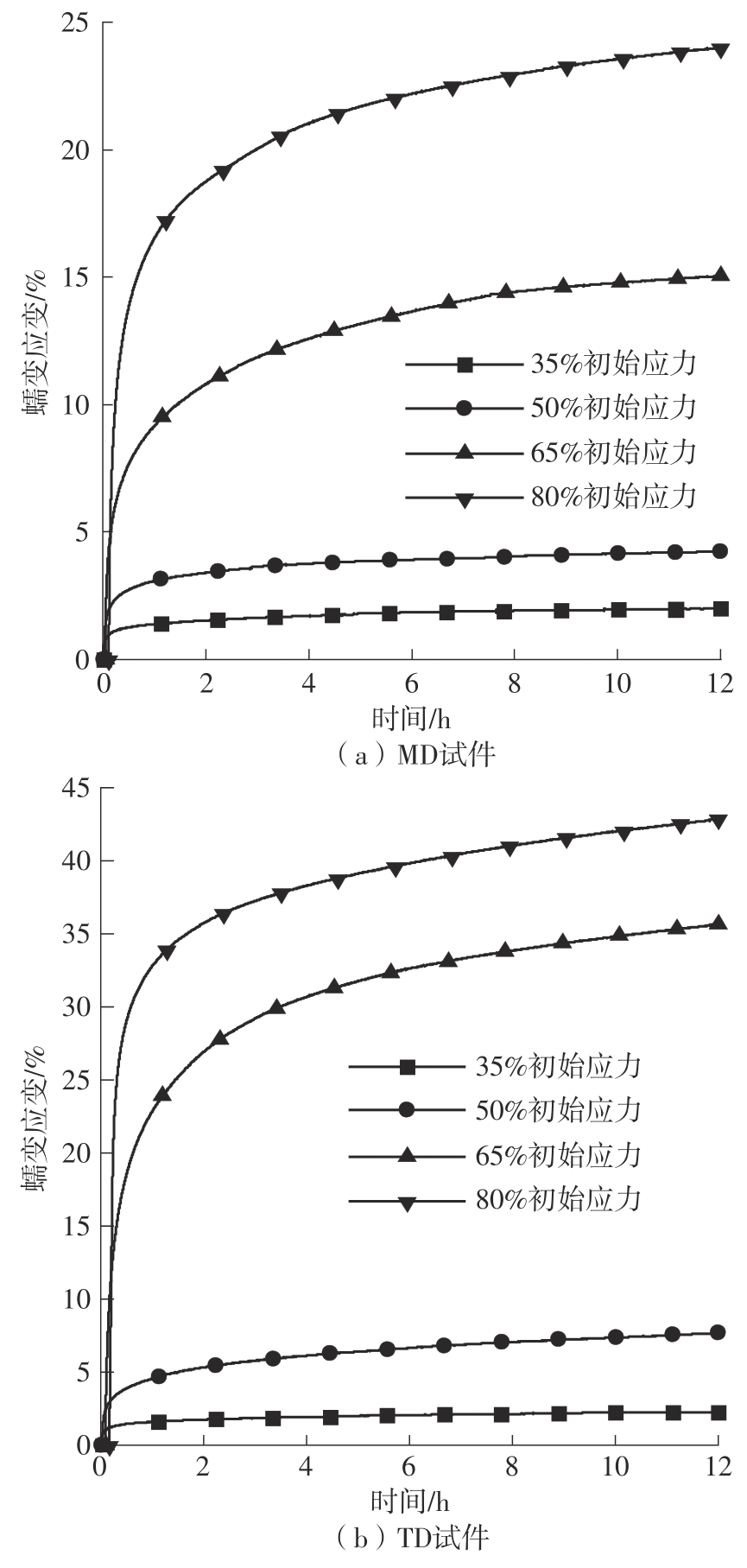
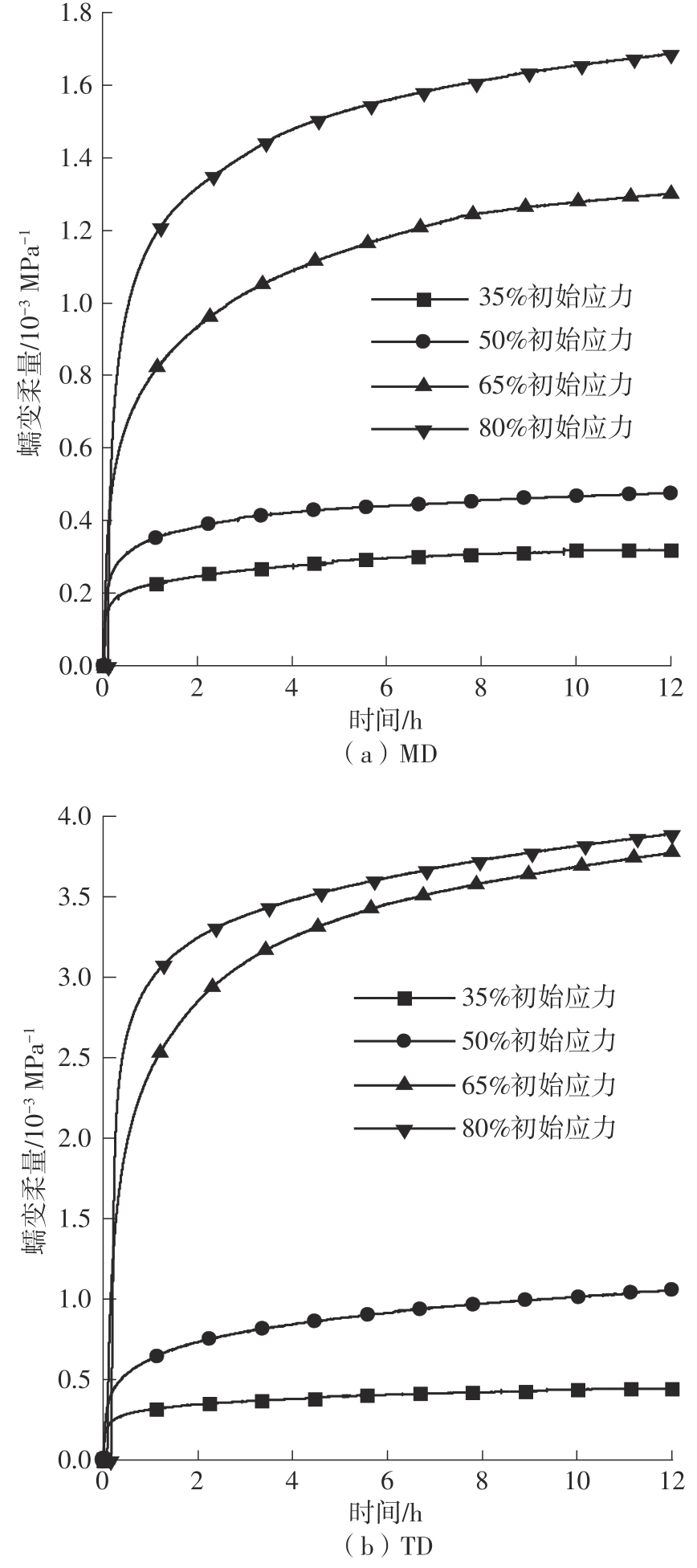
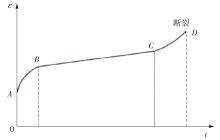
| 初始应力水平 | 方向 | 总应变量/mm | 加载应变量/mm | 绝对蠕变量/mm | 蠕变伸长率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
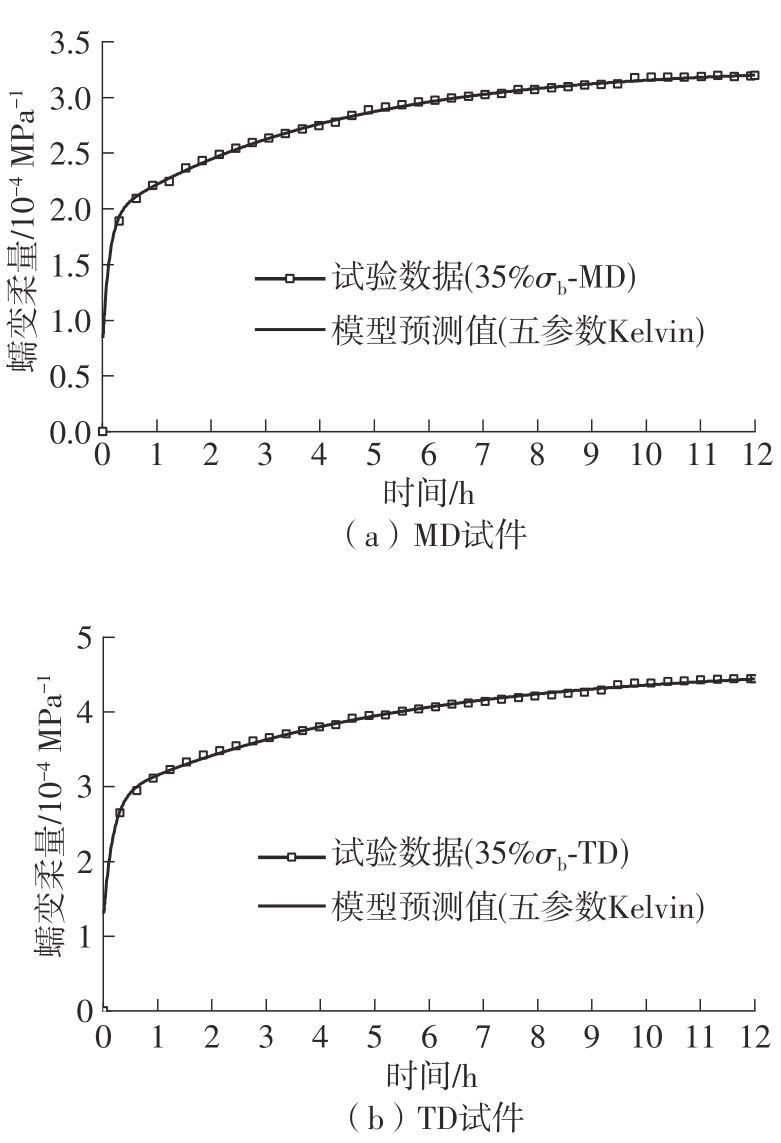
| 35% σb | MD | 5.497 | 3.506 | 1.991 | 56.79 |
| TD | 5.546 | 3.289 | 2.257 | 68.62 | |
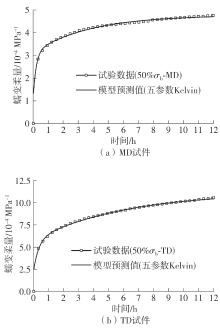
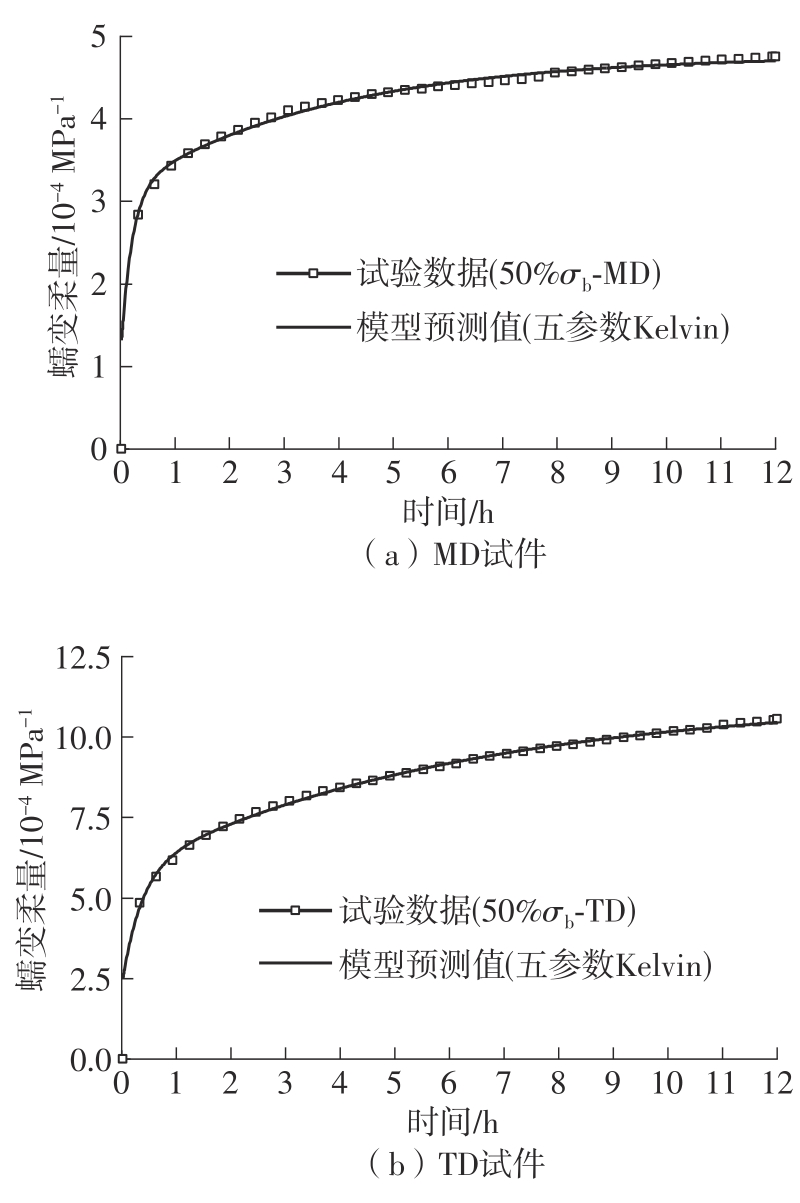
| 50% σb | MD | 11.196 | 6.961 | 4.235 | 60.84 |
| TD | 14.715 | 7.683 | 7.032 | 91.53 | |
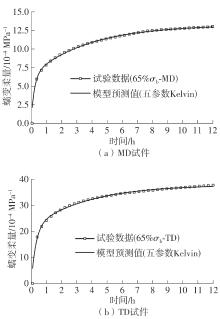
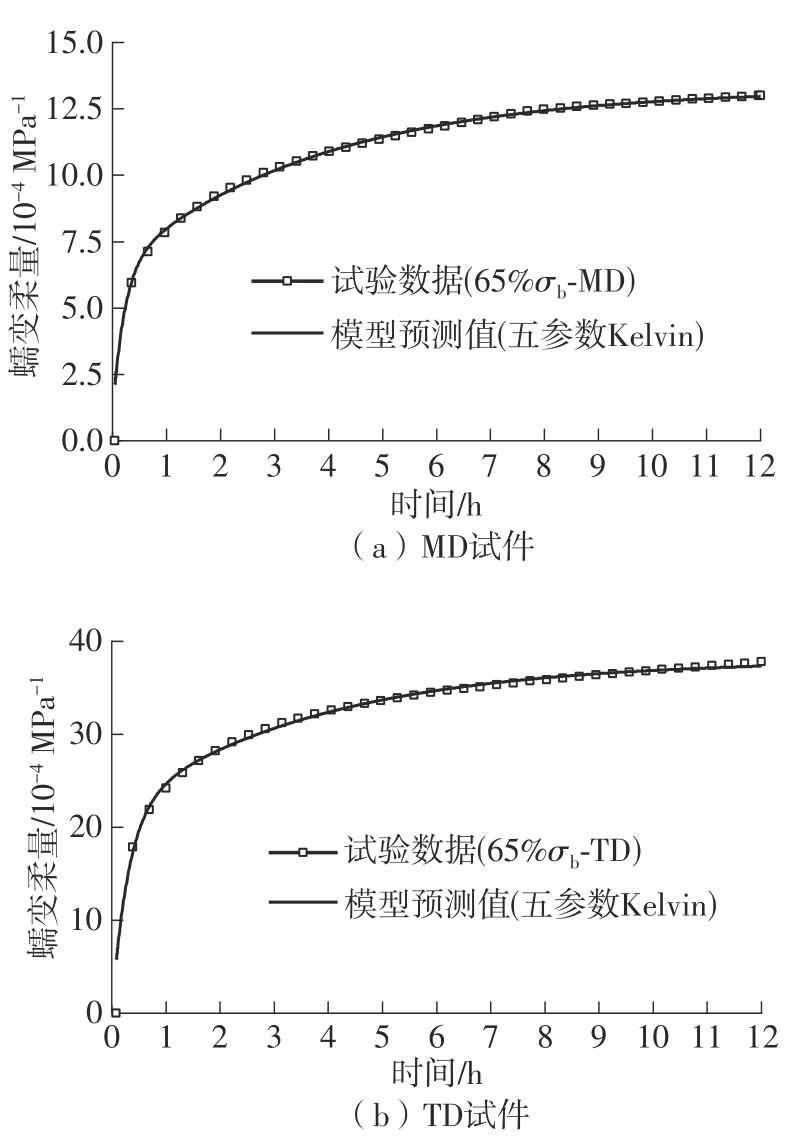
| 65% σb | MD | 29.114 | 14.066 | 15.048 | 106.98 |
| TD | 61.471 | 25.811 | 35.660 | 138.16 | |
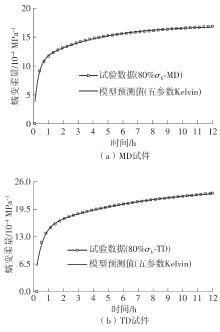
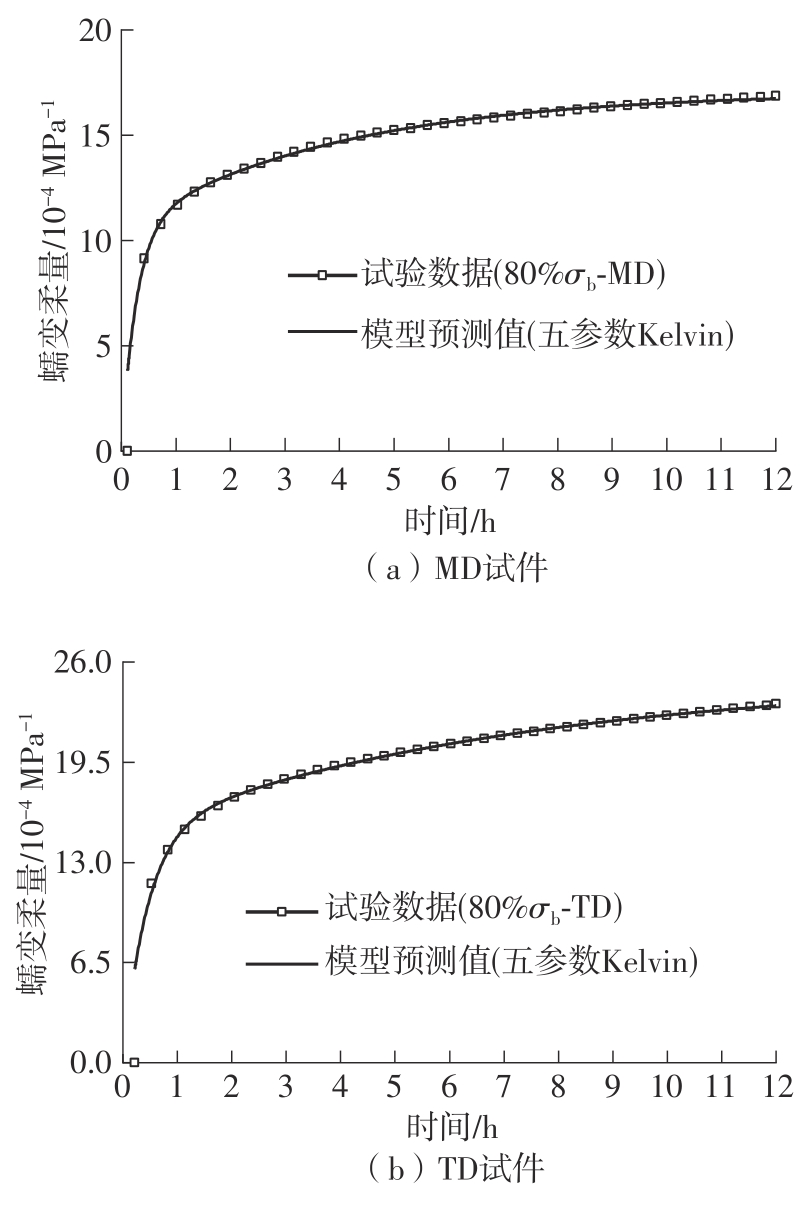
| 80% σb | MD | 58.625 | 34.613 | 24.012 | 69.37 |
| TD | 92.605 | 49.751 | 42.854 | 86.14 |
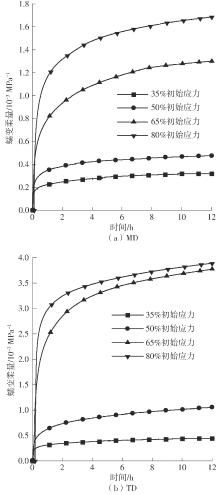
Table 5
Parameter fitting results of Burgers model"
| 初始应力水平 | 方向 | E1 | E2 | η2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35% σb | MD | 4 479.65 | 101 081.81 | -5.5 | 21 695.07 |
| TD | 3 214.78 | 75 164.31 | -5.5 | 17 189.11 | |
| 50% σb | MD | 2 880.30 | 77 548.33 | -5.5 | 10 445.77 |
| TD | 1 590.13 | 24 374.81 | -5.5 | 5 939.93 | |
| 65% σb | MD | 1 234.66 | 19 811.71 | -5.5 | 3 513.48 |
| TD | 402.94 | 7 603.19 | -5.5 | 897.70 | |
| 80% σb | MD | 851.37 | 19 222.41 | -5.5 | 2 296.37 |
| TD | 669.14 | 12 340.96 | -5.5 | 2 000.04 |
Table 7
Fitting results of five-parameter Kelvin model parameters"
| 初始应力水平 | 方向 | E0 | E1 | E2 | η1 | η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35% σb | MD | 13 683.81 | 8 337.76 | 7 439.01 | 9 827.04 | 292 746.47 |
| TD | 8 344.70 | 6 074.05 | 5 668.84 | 9 423.46 | 260 792.92 | |
| 50% σb | MD | 9 235.89 | 4 908.66 | 6 054.88 | 8 999.84 | 207 836.36 |
| TD | 4 408.88 | 2 829.81 | 1 845.91 | 8 309.39 | 94 763.48 | |
| 65% σb | MD | 10 248.10 | 1 817.93 | 1 474.09 | 3 683.70 | 51 740.00 |
| TD | 9.996×107 | 463.98 | 608.11 | 2 552.23 | 41 774.98 | |
| 80% σb | MD | 3.978×109 | 945.39 | 1 544.48 | 5 754.27 | 135 252.36 |
| TD | 9.996×108 | 987.57 | 671.79 | 144 310.41 | 6 173.63 |
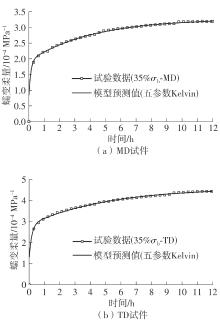
Table 8
Determination coefficients of fitting results of five creep constitutive models"
| 初始应力水平 | 可决系数 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 经典Kelvin模型 | 经典Maxwell模型 | Burgers模型 | 三参数Kelvin模型 | 五参数Kelvin模型 | ||||||
| MD | TD | MD | TD | MD | TD | MD | TD | MD | TD | |
| 35% σb | 0.728 | 0.714 | 0.813 | 0.823 | 0.967 | 0.954 | 0.813 | 0.823 | 0.997 | 0.995 |
| 50% σb | 0.734 | 0.729 | 0.831 | 0.848 | 0.943 | 0.971 | 0.831 | 0.848 | 0.993 | 0.997 |
| 65% σb | 0.807 | 0.852 | 0.788 | 0.718 | 0.975 | 0.957 | 0.788 | 0.718 | 0.999 | 0.997 |
| 80% σb | 0.800 | 0.829 | 0.713 | 0.778 | 0.943 | 0.942 | 0.713 | 0.778 | 0.996 | 0.994 |
| 1 | 王楠 .空间充气结构的充气系统设计和控制[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2008. |
| 2 | 彭路,王生,张向强 .充气管展开过程仿真研究[J].计算机仿真,2009,26(4):43-46. |
| PENG Lu, WANG Sheng, ZHANG Xiang-qiang .Simulation of the deployment of inflatable tube[J].Computer Simulation,2009,26(4):43-46. | |
| 3 | BLACK J T, COBB R G, SWENSON E D,et al .Rigidizable inflatable get-away-special experiment space flight data analysis[J].Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets,2011,48(3):477-487. |
| 4 | AL-HADDAD M A S M, JAMEL N, NORDIN A N .Flexible antenna:a review of design,materials,fabrication,and applications[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2021,1878(1):012068/1-11. |
| 5 | 敬凌霄 .多轴向经编聚酯织物增强膜材力学性能研究[D].上海:东华大学,2016. |
| 6 | 张营营,许珊珊,徐俊豪,等 .聚四氟乙烯膜材黏弹性本构关系[J].建筑结构学报,2016,37(6):245-252. |
| ZHANG Yingying, XU Shanshan, XU Junhao,et al .Viscoelastic constitutive relations of polytetrafluoroethylene coated fabrics[J].Journal of Building Structures,2016,37(6):245-252. | |
| 7 | 孟雷,吴明儿 .建筑用PTFE膜材应力松弛和徐变性能研究[J].建筑材料学报,2012,15(2):206-210. |
| MENG Lei, WU Ming-er .Study on stress relaxation and creep properties of PTFE membrane[J].Journal of Building Materials,2012,15(2):206-210. | |
| 8 | ZHANG W L, DING X, YANG X D .A plastic deformation behaviour of PVC coated plain weave membrane under relaxation condition[J].Applied Mechanics and Materials,2011,1366(71/72/73/74/75/76/77/78):3379-3384. |
| 9 | SCHIESSEL H, METZLER R, BLUMEN A,et al .Generalized viscoelastic models:their fractional equations with solutions[J].Journal of physics A:Mathematical and General,1995,28(23):6567-6584. |
| 10 | YOSHINO T, KATO S .Viscous characteristics of ETFE film sheet under equal biaxial tensions[J].Procedia Engineering,2016,155(6):442-451. |
| 11 | 赵丽萍,寇开昌,吴广磊,等 .亚胺化工艺对聚酰亚胺性能影响的研究[J].粘接,2014,35(1):59-62,66. |
| ZHAO Li-ping, KOU Kai-chang, WU Guang-lei,et al .On effect of imidization process on performances of polyimide[J].Adhesion,2014,35(1):59-62,66. | |
| 12 | HASEGAWA M, HIRANO D, FUJII M,et al .Solution‐processable colorless polyimides derived from hydrogenated pyromellitic dianhydride with controlled steric structure[J].Journal of Polymer Science Part A:Polymer Chemistry,2013,51(3):575-592. |
| 13 | 孟雷,吴明儿 .建筑用PVC膜材应力松弛性能研究[J].建筑材料学报,2013,16(5):919-922. |
| MENG Lei, WU Ming-er .Study on stress relaxation properties of PVC membrane[J].Journal of Building Material,2013,16(5):919-922. | |
| 14 | 吴明儿,刘建民,慕仝,等 .ETFE薄膜单向拉伸性能[J].建筑材料学报,2008,11(2):241-247. |
| WU Ming-er, LIU Jian-min, MU Tong,et al .Uniaxial tensile properties of ETFE foils[J].Journal of Building Material,2008,11(2):241-247. | |
| 15 | 吴明儿,慕仝,刘建明 .ETFE薄膜循环拉伸试验及徐变试验[J].建筑材料学报,2008,11(6):690-694. |
| WU Ming-er, MU Tong, LIU Jian-min .Cyclic tensile test and creep test of ETFE film[J].Cycle Loading and Creep Tests of ETFE Foil,2008,11(6):690-694. | |
| 16 | 刘俨震 .Kapton膜材拉伸力学性能试验研究及黏弹性本构模型[D].西安:长安大学,2022. |
| 17 | 叶瑾瑜 .考虑蠕变与环境影响的膜结构受力性能研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2014. |
| 18 | 张营营,张其林,周传志 .温度对PTFE膜材料力学性能的影响[J].建筑材料学报,2012,15(4):478-483. |
| ZHANG Ying-ying, ZHANG Qi-lin, ZHOU Chuan-zhi . Effects of temperature on mechanical properties of PTFE coated fabrics[J].Journal of Building Material,2012,15(4):478-483. | |
| 19 | 许珊珊 .PTFE涂层织物膜材的黏弹性性能研究[D].徐州:中国矿业大学,2017. |
| 20 | 张荣鹏,林福严 .粘弹性模型的参数换算研究[J].四川大学学报(自然科学版),2014,51(1):126-130. |
| ZHANG Rong-peng,LIN Fu-yan,Study on characteristic parameters conversion of viscoelastic constitutive models[J].Journal of Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition),2014,51(1):126-130. | |
| 21 | KREN A, NAUMOV A .Determination of the relaxation function for viscoelastic materials at low velocity impact[J].International Journal of Impact Engineering,2010,37(2):170-176. |
| 22 | ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG Q L, ZHOU C Z .The visco-elastic behaviors of PVC coated fabrics under different stress and temperatures[J].Advanced Materials Research,2011,168/169/170/171:1476-1479. |
| 23 | 张伍连,丁辛,杨旭东 .机织建筑膜材料的广义Kelvin-Voigt蠕变模型[J].天津工业大学学报,2011,30(4):19-22. |
| ZHANG Wu-lian, DING Xin, YANG Xu-dong .General Kelvin-Voigt creep model of fabric architectural membrane[J].Journal of Tianjin Polytechnic University,2011,30(4):19-22. | |
| 24 | 卓家寿,黄丹 .工程材料的本构演绎[M].北京:科学出版社,2009. |
| 25 | 王广月,李华銮,李艳琴 .复合土工膜蠕变性能的试验研究[J].岩土力学,2009,30(6):1599-1603. |
| WANG Guang-yue, LI Hua-luan, LI Yan-qin .Experimental research on creep properties of composite geomembrane[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2009,30(6):1599-1603. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||