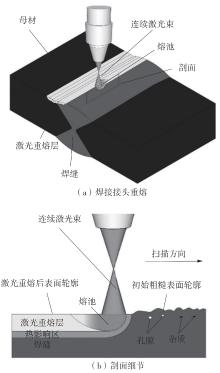
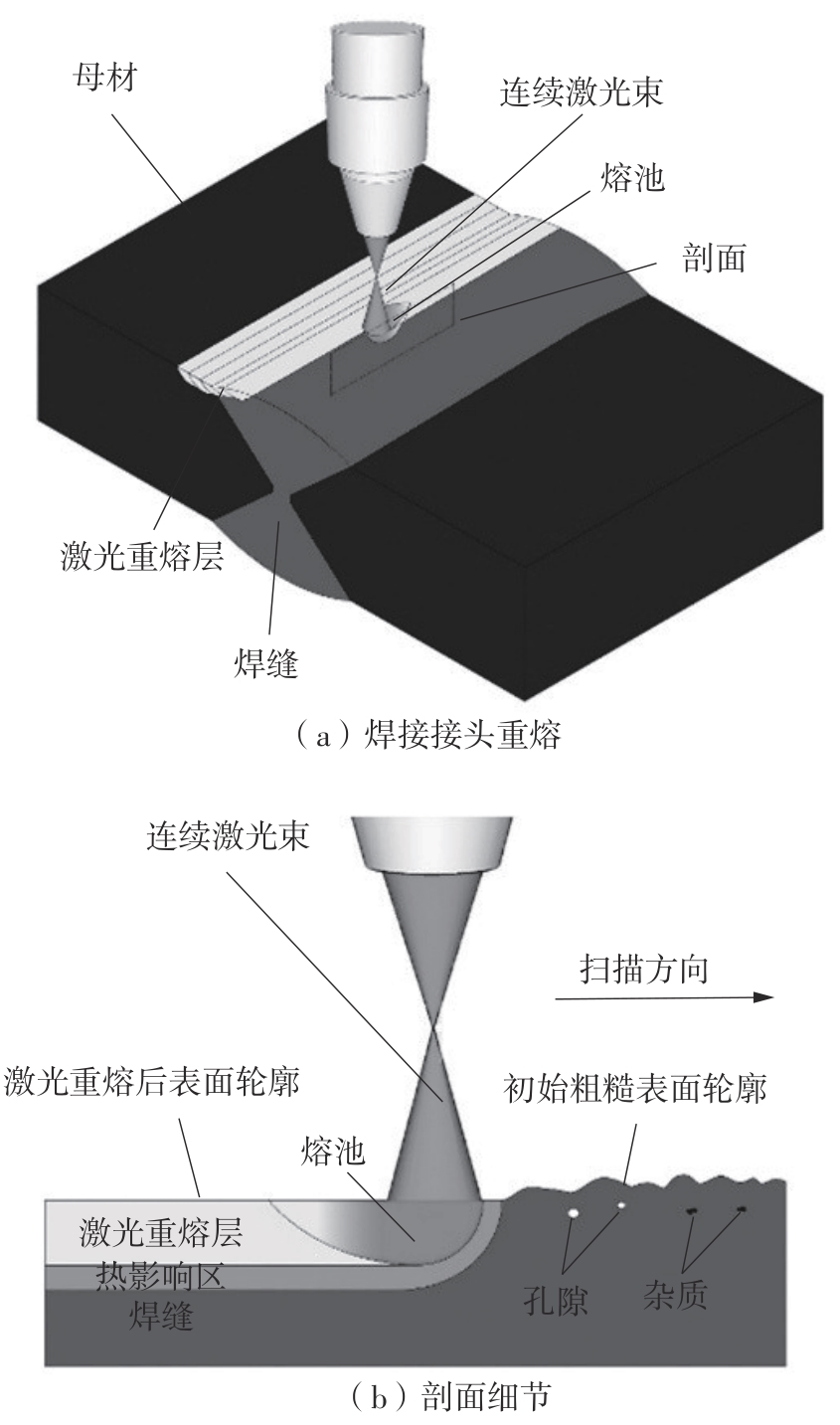
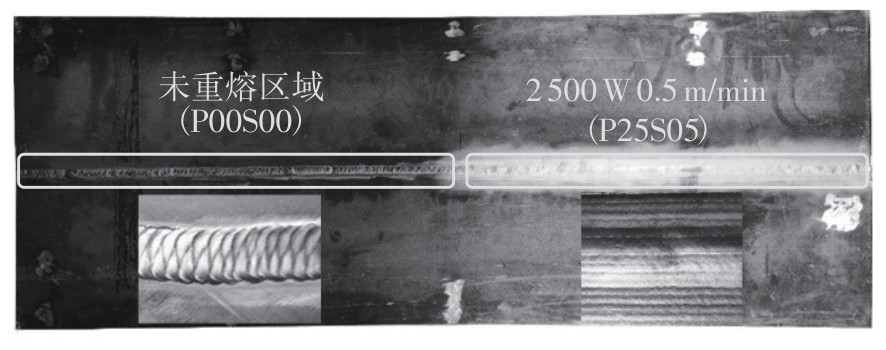
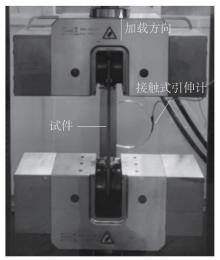
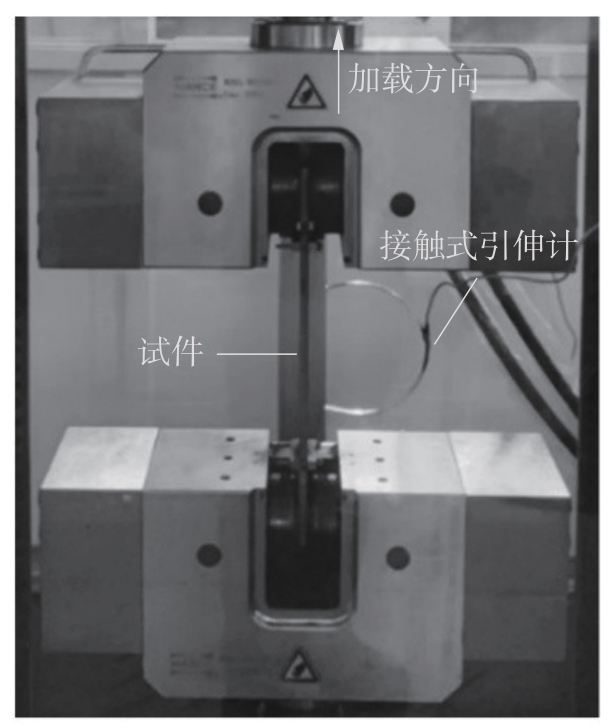
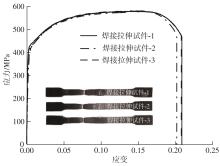
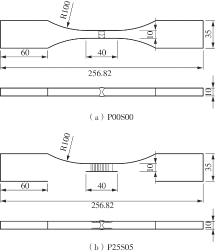
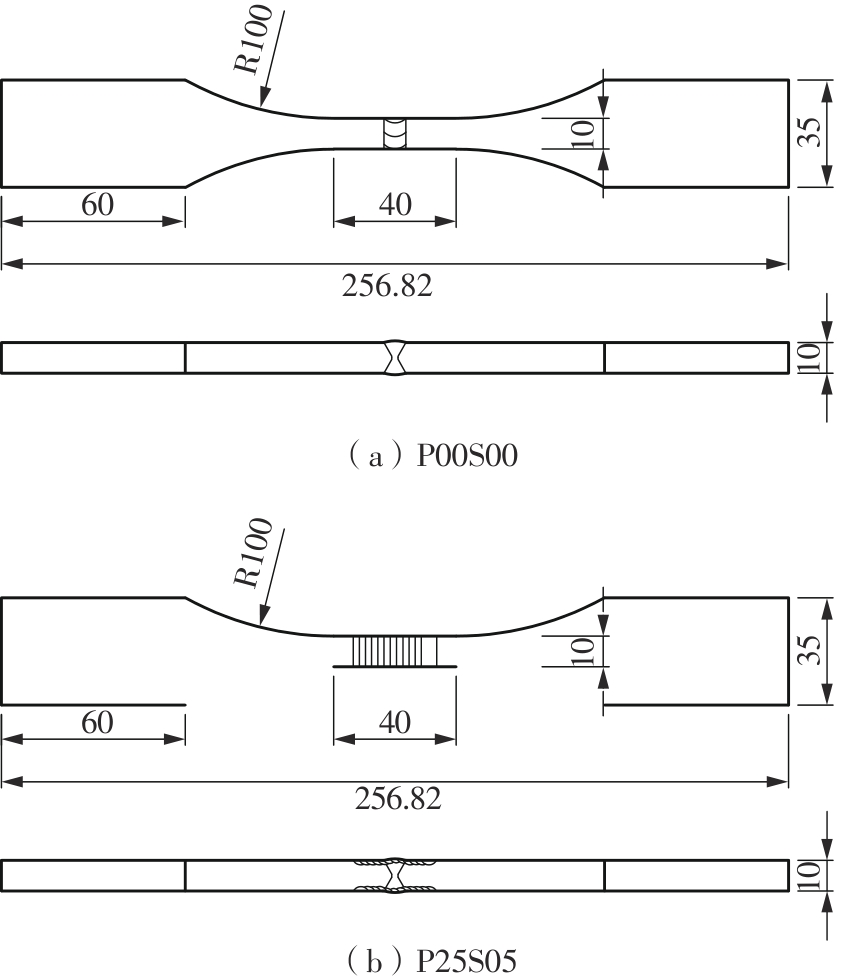
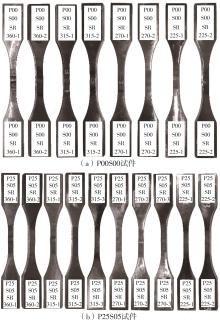
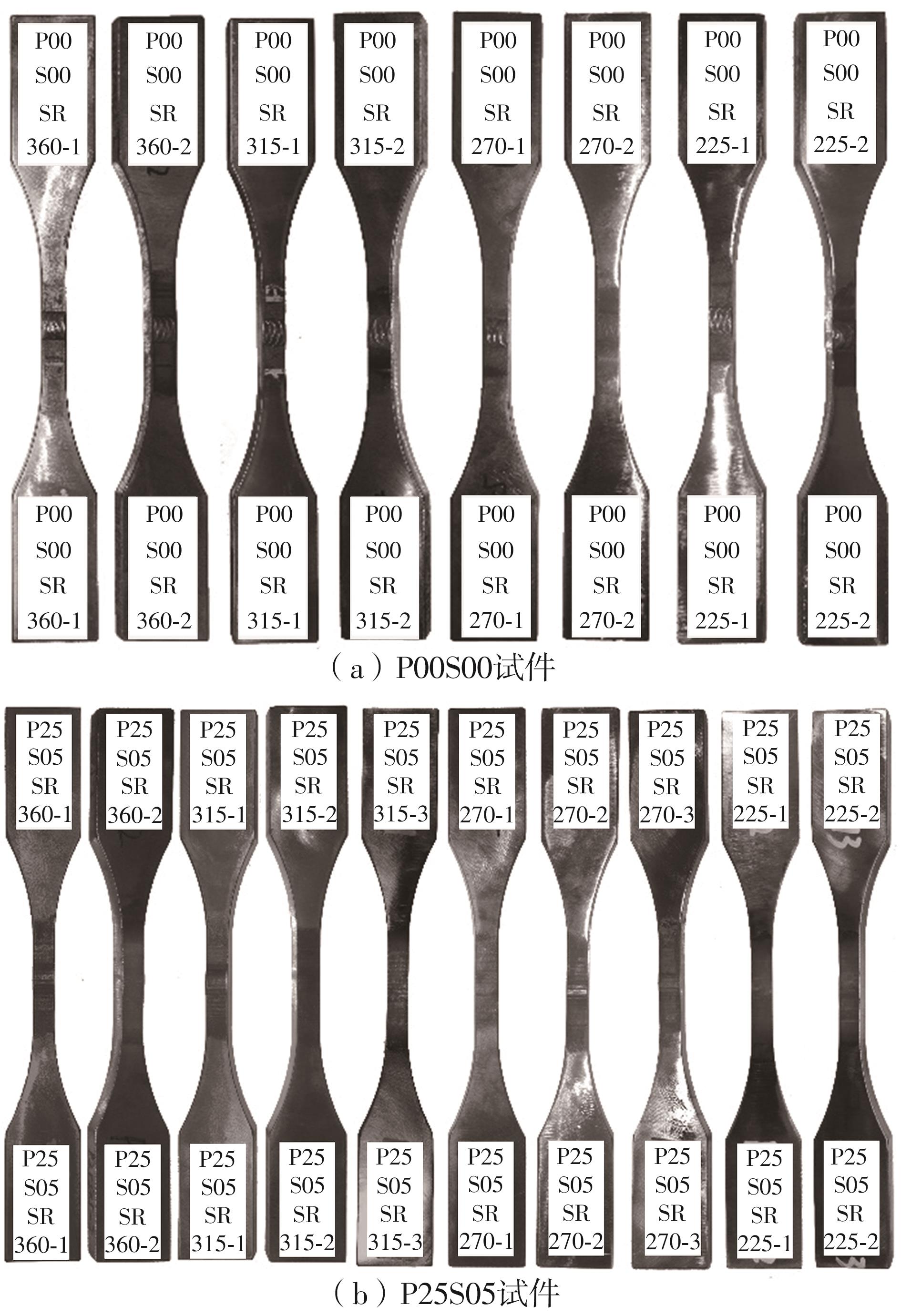
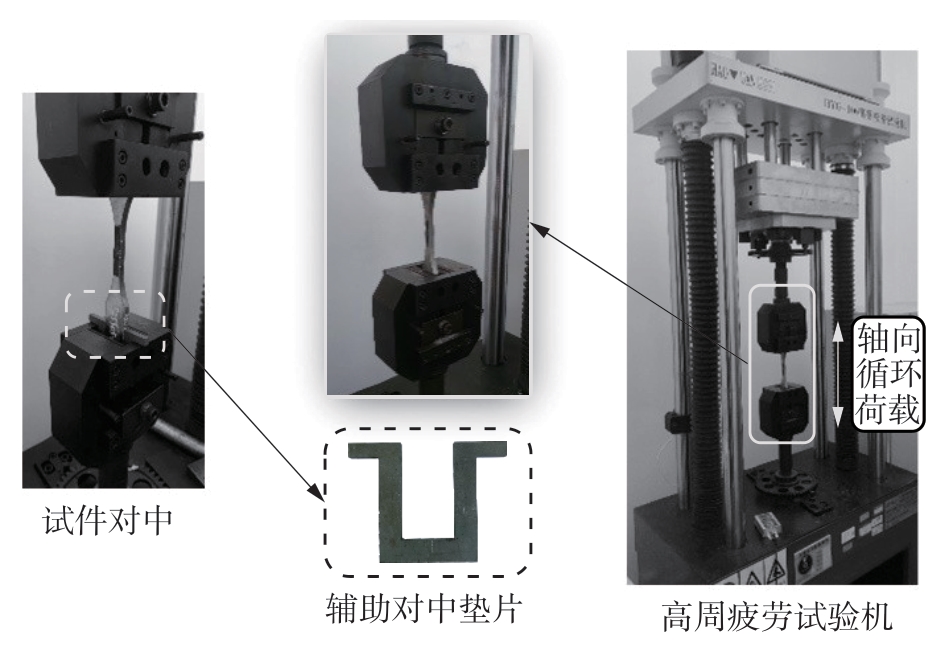
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1-11.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240357
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of Laser Remelting Treatment on Fatigue Performance of Steel Structure Welded Joints
KANG Lan1( ), LI Rongwen1, SU Jingyu1, FENG Lei2
), LI Rongwen1, SU Jingyu1, FENG Lei2
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.The Third Construction Engineering Co. ,Ltd of China Construction Third Engineering Bureau,Wuhan 430000,Hubei,China
-
Received:2024-07-15Online:2025-06-10Published:2024-09-27 -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52178286)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
KANG Lan, LI Rongwen, SU Jingyu, FENG Lei. Influence of Laser Remelting Treatment on Fatigue Performance of Steel Structure Welded Joints[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(6): 1-11.
share this article
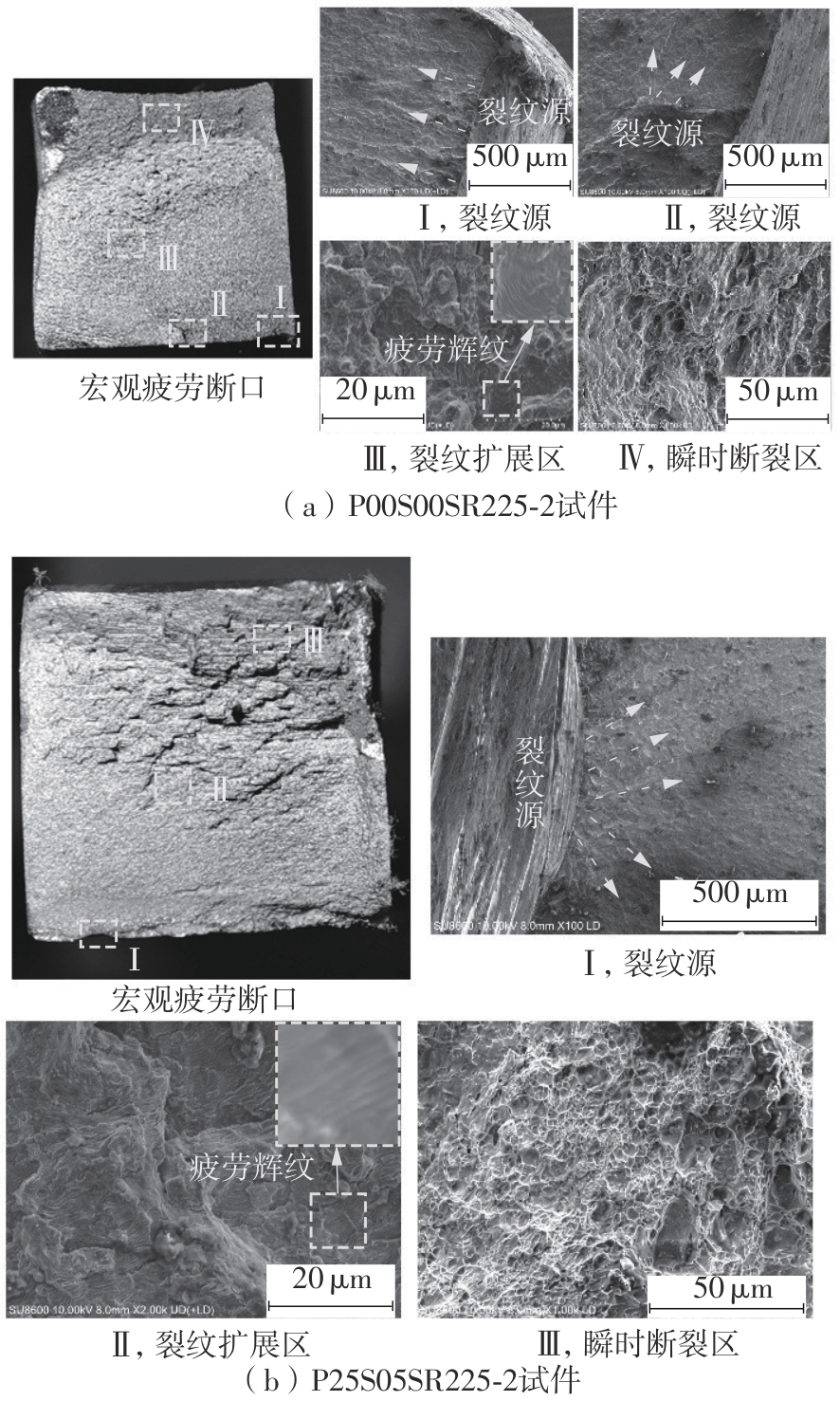
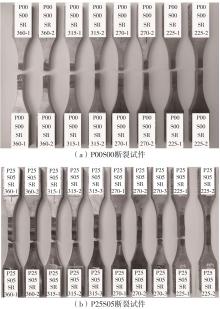
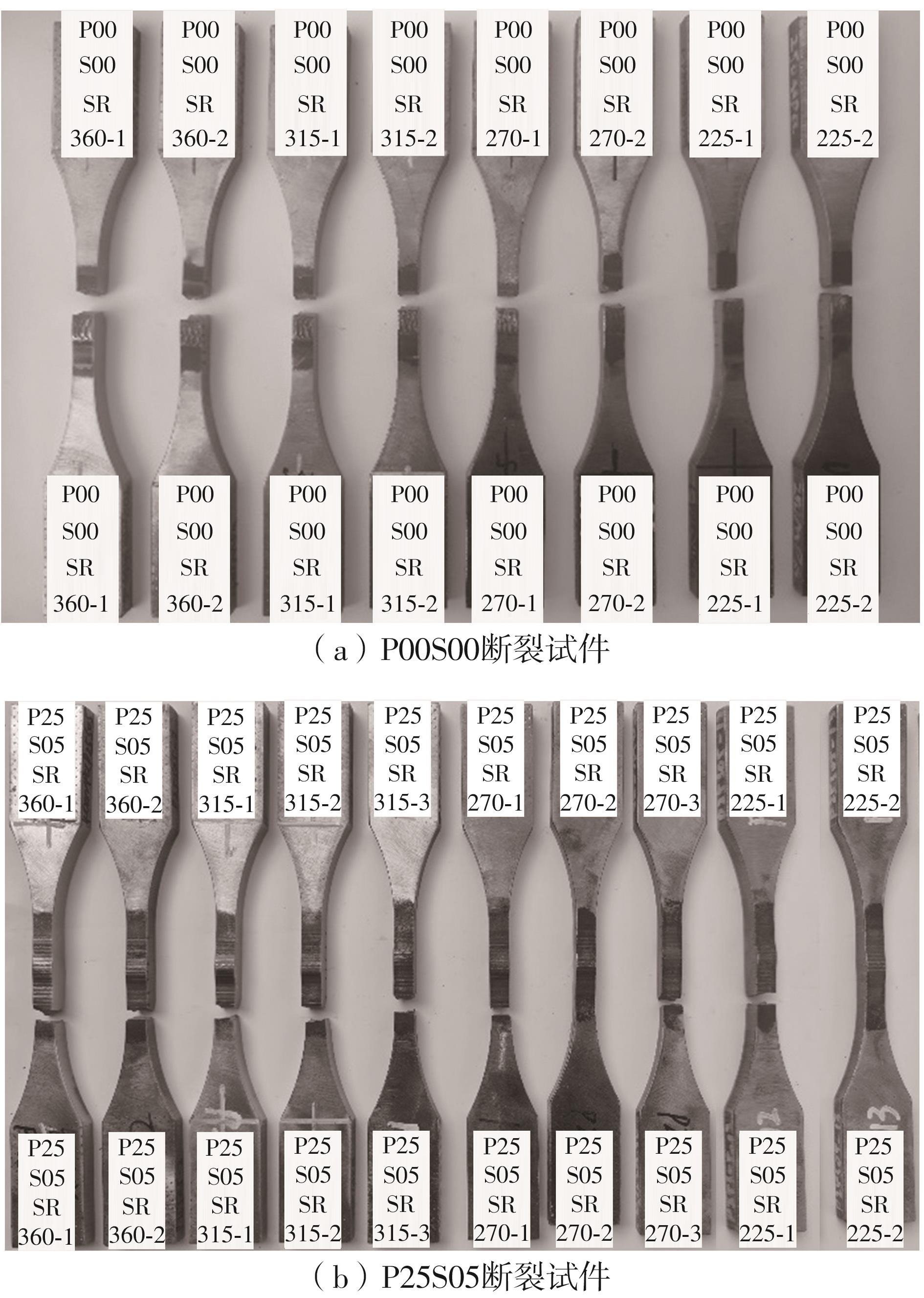
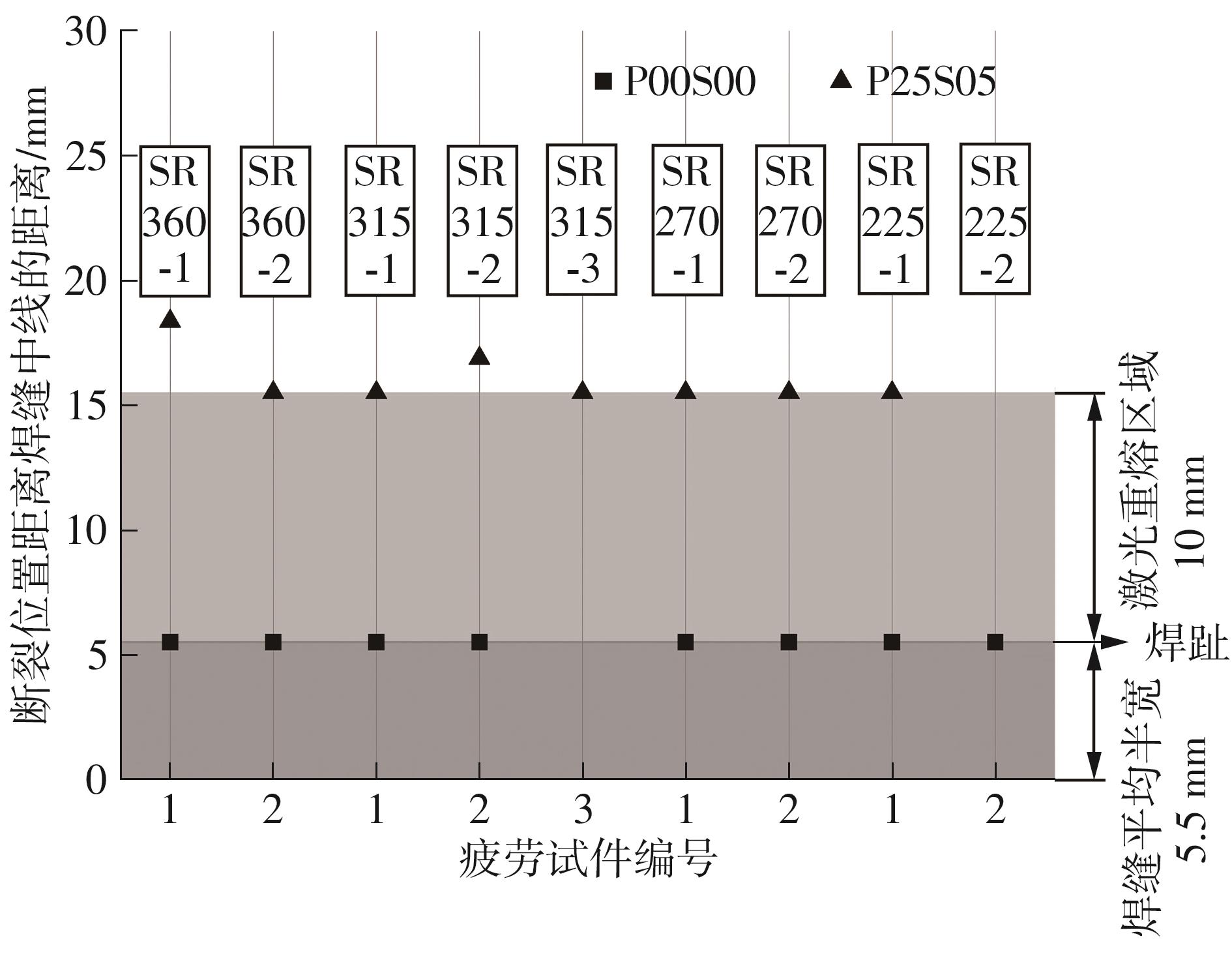
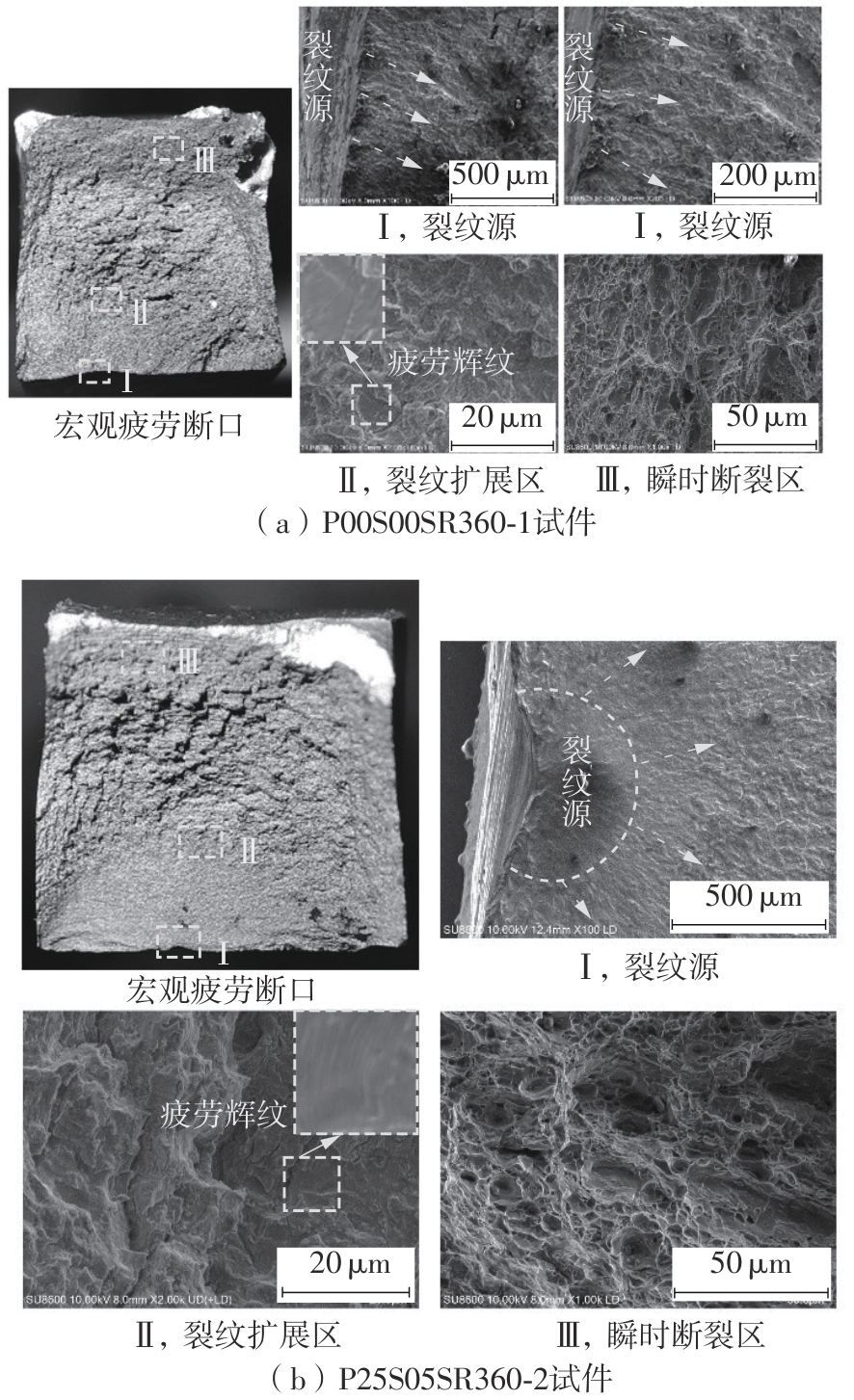
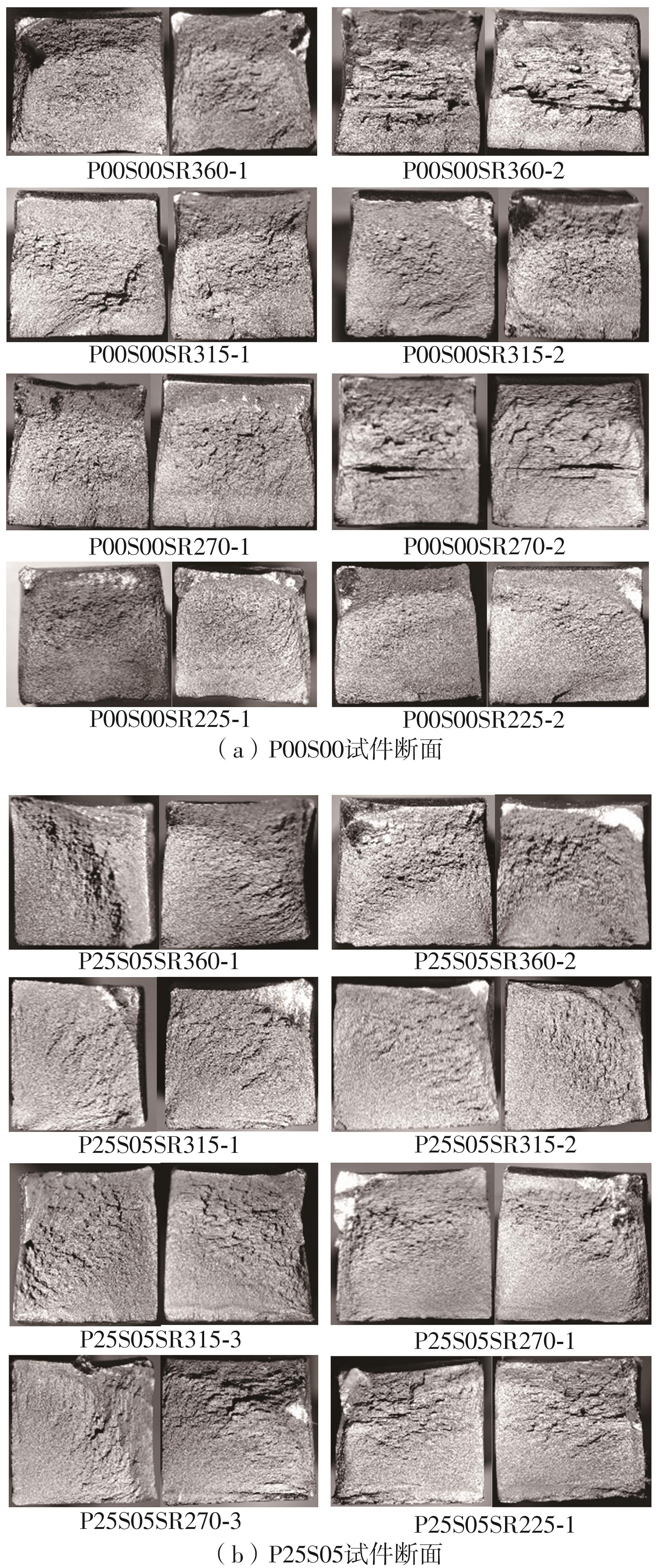
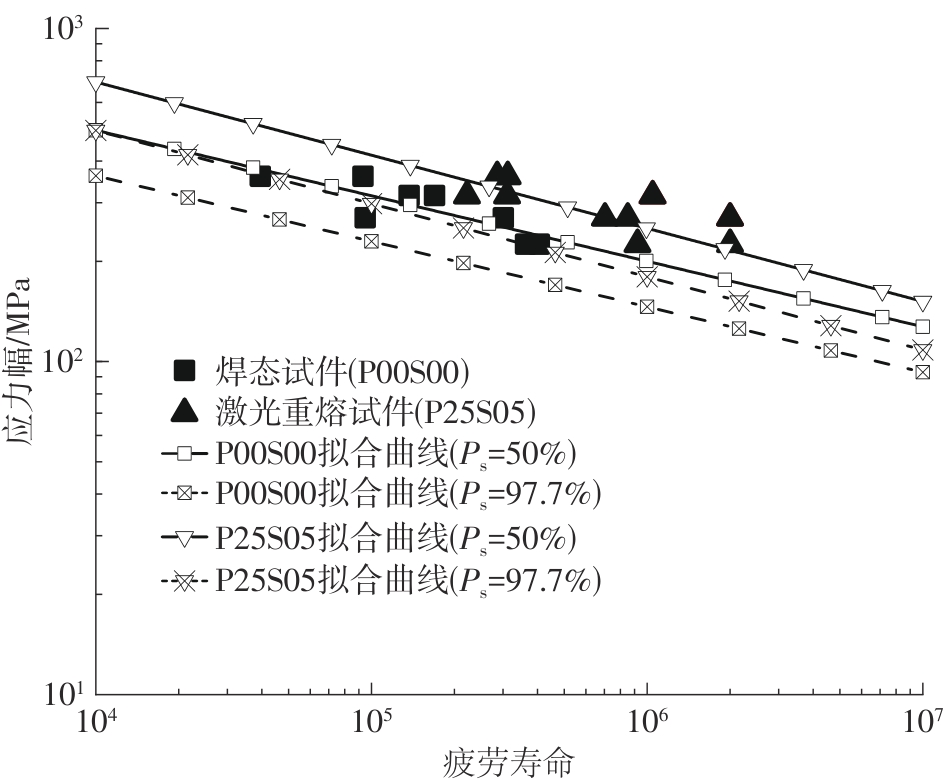
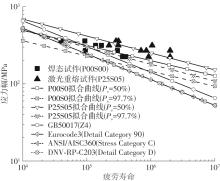
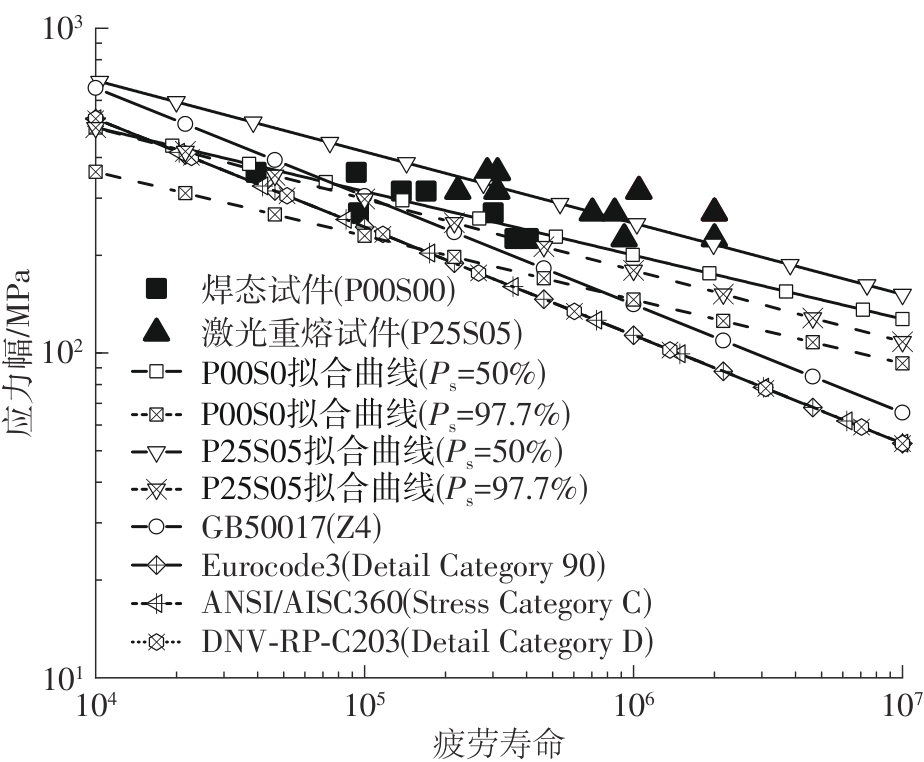
Table 3
High cycle fatigue test results of laser remelted specimens and as-welded specimens"
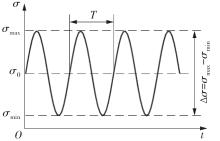
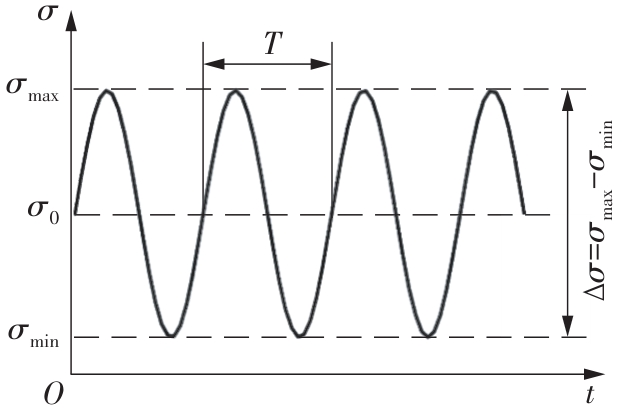
| 试件编号 | σmax/MPa | ∆σ/MPa | 最大荷载/kN | 最小荷载/kN | 循环次数 | 断裂位置 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P25S05SR360-1 | 400 | 360 | 37.90 | 3.790 | 285 981 | 母材 |
| P25S05SR360-2 | 312 223 | 母材 | ||||
| P25S05SR315-1 | 360 | 315 | 33.43 | 3.343 | 310 672 | 母材 |
| P25S05SR315-2* | 1 046 348 | 母材 | ||||
| P25S05SR315-3 | 222 185 | 母材 | ||||
| P25S05SR270-1 | 300 | 270 | 28.65 | 2.865 | 850 770 | 母材 |
| P25S05SR270-2* | 2 000 000 | 未断 | ||||
| P25S05SR270-3 | 703 375 | 母材 | ||||
| P25S05SR225-1 | 250 | 225 | 23.88 | 2.388 | 922 661 | 母材 |
| P25S05SR225-2 | 2 000 000 | 未断 | ||||
| P00S00SR360-1 | 400 | 360 | 37.90 | 3.790 | 39 520 | 焊趾 |
| P00S00SR360-2 | 93 127 | 焊趾 | ||||
| P00S00SR315-1 | 360 | 315 | 33.43 | 3.343 | 136 924 | 焊趾 |
| P00S00SR315-2 | 169 392 | 焊趾 | ||||
| P00S00SR270-1 | 300 | 270 | 28.65 | 2.865 | 94 991 | 焊趾 |
| P00S00SR270-2 | 300 727 | 焊趾 | ||||
| P00S00SR225-1 | 250 | 225 | 23.88 | 2.388 | 406 456 | 焊趾 |
| P00S00SR225-2 | 362 397 | 焊趾 |
| 1 | 郭宏超,毛宽宏,万金怀,等 .高强度钢材疲劳性能研究进展[J].建筑结构学报,2019,40(4):17-28. |
| GUO Hongchao, MAO Kuanhong, WAN Jinhuai,et al .Research progress on fatigue properties of high strength steels[J].Journal of Building Structures,2019,40(4):17-28. | |
| 2 | RADAJ D, SONSINO C M, FRICKE W .Recent deve-lopments in local concepts of fatigue assessment of welded joints[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2009,31(1):2-11. |
| 3 | WANG D Q Q, YAO D D, GAO Z B,et al .Fatigue mechanism of medium-carbon steel welded joint:competitive impacts of various defects[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2021,151:106363/1-11. |
| 4 | BRAUN M, WANG X .A review of fatigue test data on weld toe grinding and weld profiling[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2021,145:106073/1-16. |
| 5 | RAMALHO A L, FERREIRA J A M, BRANCO C A G M .Fatigue behaviour of T welded joints rehabilitated by tungsten inert gas and plasma dressing[J].Materials & Design,2011,32(10):4705-4713. |
| 6 | GAN J, SUN D, WANG Z,et al .The effect of shot peening on fatigue life of Q345D T-welded joint[J].Journal of Constructional Steel Research,2016,126:74-82. |
| 7 | MALAKI M, DING H .A review of ultrasonic peening treatment[J].Materials & Design,2015,87:1072-1086. |
| 8 | DHAKAL B, SWAROOP S .Review:laser shock pee-ning as post welding treatment technique[J].Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2018,32:721-733. |
| 9 | CHAN W L, CHENG H K F .Hammer peening techno-logy—the past,present,and future[J].International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2022,118(3/4):683-701. |
| 10 | CHAISE T, LI J, NELIAS D,et al .Modelling of multiple impacts for the prediction of distortions and residual stresses induced by ultrasonic shot peening (USP)[J].Journal of Materials Processing Techno-logy,2012,212(10):2080-2090. |
| 11 | CUNHA A, GIACOMELLI R O, KAUFMAN J,et al .An overview on laser shock peening process:from science to industrial applications[C]∥Proceedings of the 2021 SBFoton International Optics and Photonics Conference (SBFoton IOPC).Sao Carlos,Brazil:IEEE,2021:1-6. |
| 12 | 李坤,房嘉辉,廖若冰,等 .高性能金属激光能量场表面热处理技术研究现状及展望(特邀)[J].中国激光,2024,51(4):121-137. |
| LI Kun, FANG Jiahui, LIAO Ruobing,et al .Current research status and future prospects for high-performance metal laser-energy-field surface heat treatment technologies (invited)[J].China Journal of Laser,2024,51(4):121-137. | |
| 13 | YU Y, ZHANG M, GUAN Y,et al .The effects of laser remelting on the microstructure and performance of bainitic steel[J].Metals,2019,9(8):912/1-12. |
| 14 | YAO Y, LI X, WANG Y Y,et al .Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Ti-Zr beta titanium alloy after laser surface remelting[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2014,583:43-47. |
| 15 | VIDYASAGAR K E C, RANA A, KALYANASUNDARAM D .Optimization of laser parameters for improved corrosion resistance of nitinol[J].Materials and Manufacturing Processes,2020,35(14):1661-1669. |
| 16 | 李鸿鹏,盛金马,黎彬,等 .激光表面强化316L不锈钢的组织与性能研究[J].激光与光电子学进展,2020,57(19):199-204. |
| LI Hongpeng, SHENG Jinma, LI Bin,et al .Microstructures and properties of laser surface-reinforced 316L stainless steel[J].Laser & Optoelectronics Progress,2020,57(19):199-204. | |
| 17 | LAGO J, BOKŮVKA O, NOVÝ F .The weld toe improvement of advanced HSLA steel by laser remelting[J].Materials Today:Proceedings,2016,3(4):1037-1040. |
| 18 | STAMM H, HOLZWARTH U, BOERMAN D J,et al .Effect of laser surface treatment on high cycle fatigue of AISI 316L stainless steel[J].Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures,1996,19(8):985-995. |
| 19 | ZHAO X, ZHANG H, LIU Y .Effect of laser surface remelting on the fatigue crack propagation rate of 40Cr steel[J].Results in Physics,2019,12:424-431. |
| 20 | SARKAR S, KUMAR C S, NATH A K. Effects of different surface modifications on the fatigue life of selective laser melted 15-5 PH stainless steel[J].Mate-rials Science & Engineering A,2019,762:138109/1-14. |
| 21 | FROSTEVARG J, TORKAMANY M J, POWELL J,et al .Improving weld quality by laser re-melting[J].Journal of Laser Applications,2014,26(4):041502/1-4. |
| 22 | POWELL J, ILAR T, FROSTEVARG J,et al .Weld root instabilities in fiber laser welding[J].Journal of Laser Applications,2015,27:S29008/1-5. |
| 23 | 邓德伟,马云波,马玉山,等 .重熔及退火对316L不锈钢激光熔覆层残余应力的影响[J].金属热处理,2020,45(8):113-118. |
| DENG Dewei, MA Yunbo, MA Yushan,et al .Influence of remelting and annealing on residual stress of 316L stainless steel laser clad layer[J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2020,45(8):113-118. | |
| 24 | GUENNEC B, UENO A, SAKAI T,et al .Effect of the loading frequency on fatigue properties of JIS S15C low carbon steel and some discussions based on micro-plasticity behavior[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2014,66:29-38. |
| 25 | HONG Y, HU Y, ZHAO A .Effects of loading frequency on fatigue behavior of metallic materials:a li-terature review[J].Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures,2023,46(8):3077-3098. |
| 26 | LIAO X, WANG Y, WANG Z,et al .Effect of low temperatures on constant amplitude fatigue properties of Q345qD steel butt-welded joints[J].Engineering Failure Analysis,2019,105:597-609. |
| 27 | TONG L W, NIU L C, REN Z Z,et al .Experimental investigation on fatigue behavior of butt-welded high-strength steel plates[J].Thin-Walled Structures,2021,165:107956/1-11. |
| 28 | Specification for structural steel buildings:ANSI/AI [S]. |
| 29 | Eurocode 3:design of steel structure-Part 1-9:fatigue:EN 1993-1-9 [S]. |
| 30 | Fatigue design of offshore steel structures:DNV-RP-C203 [S]. |
| [1] | QIANG Xuhong, TIAN Weixiao, JIANG Xu, et al. Intelligent Method for Identifying Damage of Steel Members with Localized Random Pitting Based on Convolutional Neural Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(11): 43-54. |
| [2] | KANG Lan HONG Shutao. Experimental Investigation on Fatigue Properties of Q690D High Strength Steel [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(8): 35-42. |
| [3] | XU Daofen, CHEN Kanghua, XING Jun, et al. Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of 2219 Aluminum Alloy Forging's Joint by TIG Welding [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(3): 116-125. |
| [4] | SHI Kairong PAN Wenzhi JIANG Zhengrong Lü Junfeng LUO Bin . Mechanical Behaviors of Large-tonnage Complex Steel Spherical Hinged Support: Rotation Behavior Subjected to Axial Compressive Load [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(8): 9-15. |
| [5] | HONG Xiaobin ZI Wenjiang YU Rong LUO Zongqiang HE Zhenwei . Fusion Assessment on the Credibility of Cloud Nondestructive Testing for Large-Scale Steel Structures [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(3): 70-77. |
| [6] | LI Wanrun ZHANG Guangli LIU Yufei FANG Zhao LI Aiqun DU Yongfeng. Welding Residual Stress Simulation and Experimental Verification in Beamto-Column Joints of Q345B Steel [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(10): 114-123. |
| [7] | Hu Yun Liu Shao- jun Liao Ya- shi Ding Sheng. Fatigue Strength Probability Distribution Inference Based on Monte Carlo Simulation Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(9): 35-40. |
| [8] | Zhang Shu-kuan Huang Pei-yan Zhao Chuan-yu. Numerical Analysis of Stress Intensity Factor of Surface Crack in Steel Plate Strengthened with CFL Under Bending Load [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(4): 162-168. |
| [9] | Pan Duo-zhong Wei De-min. Simulation Method of Step-by-Step Construction of Long-Span Steel Structures [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(9): 123-126,137. |
| [10] | Ye Bang-yan Peng Rui-tao Tang Xin-zi Liang Zhong-wei . Residual Stress and Surface Morphology of Pre-Stress Hard Cutting [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(4): 6-9. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||