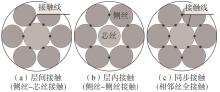
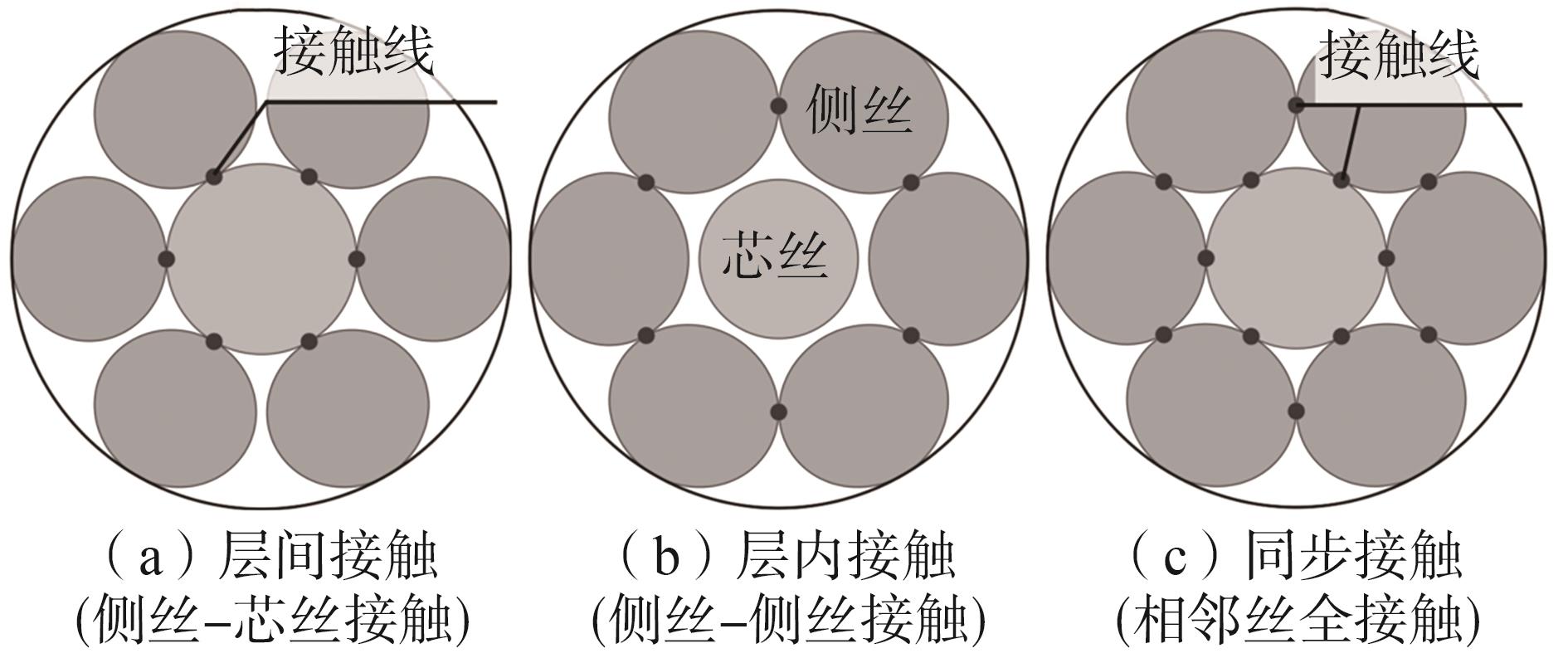
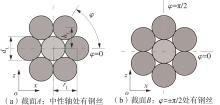
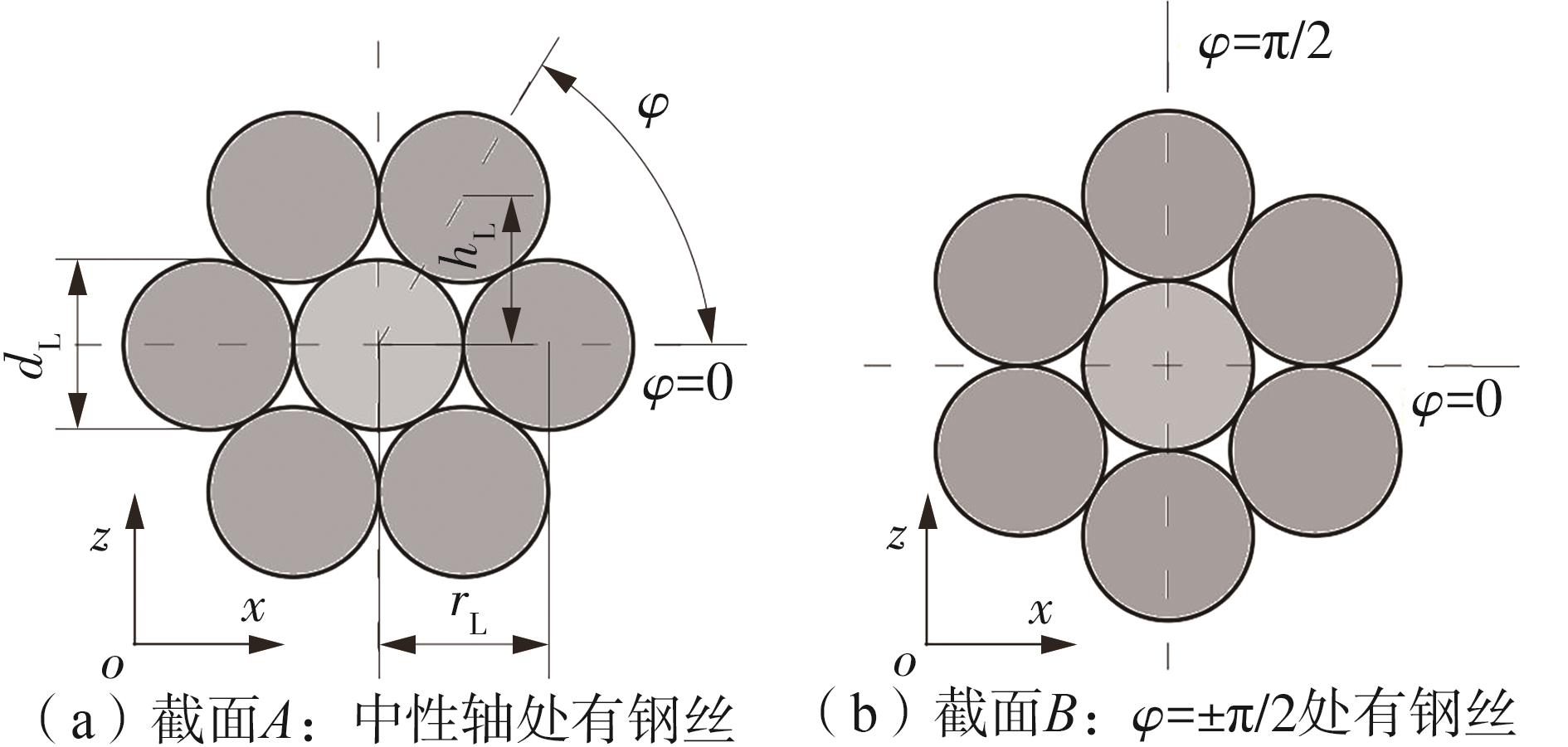
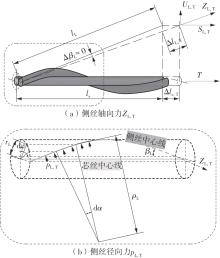
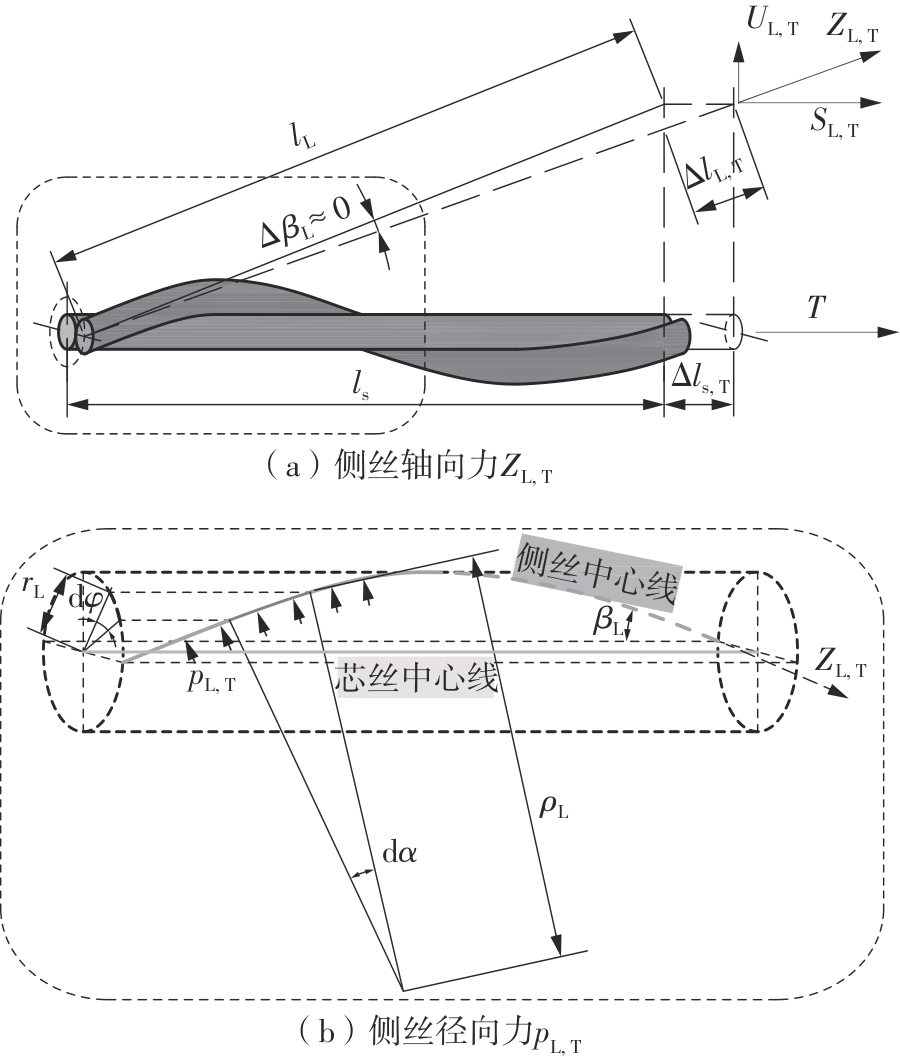
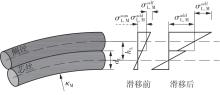
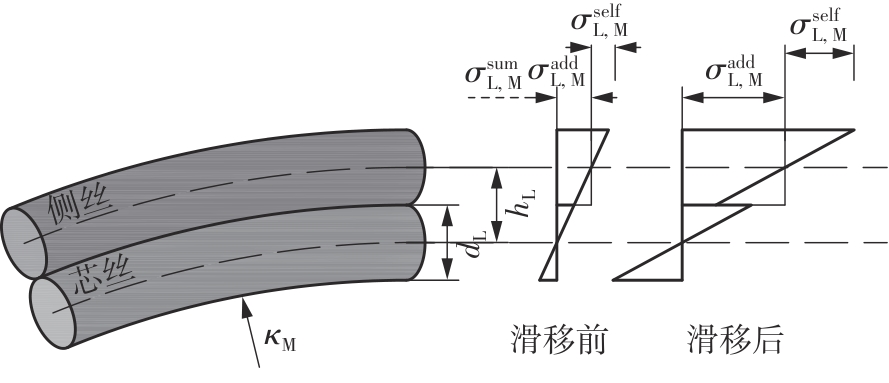
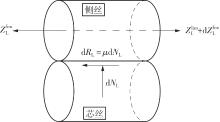
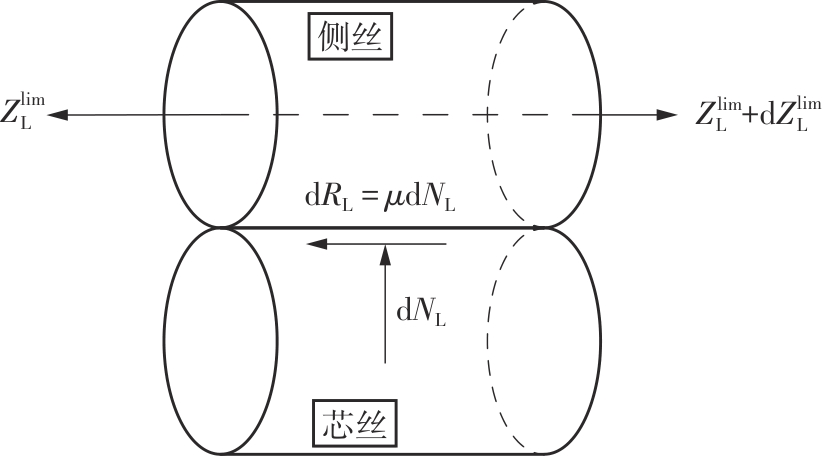
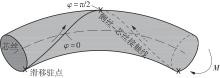
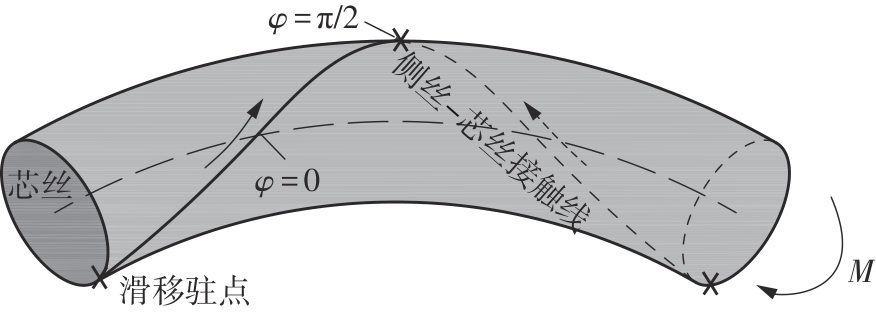
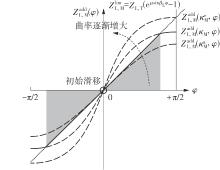
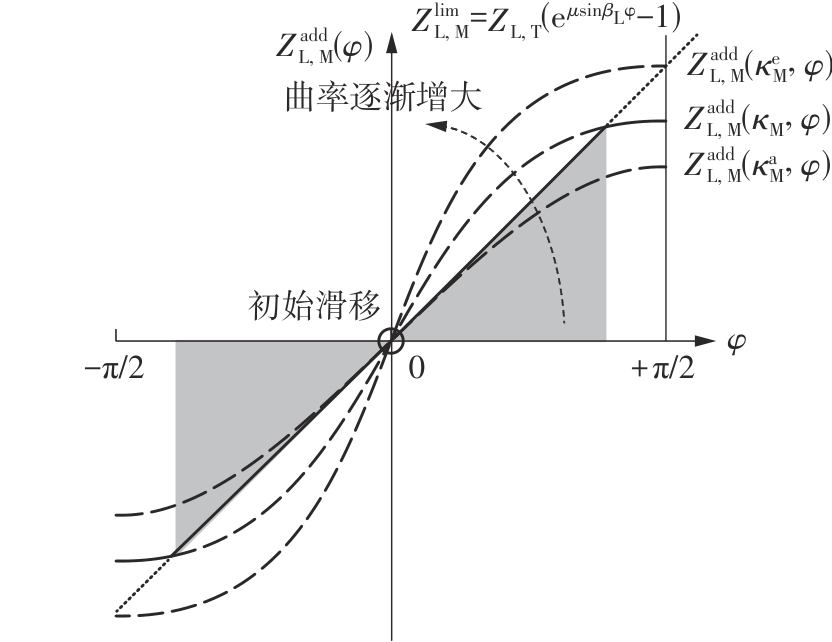
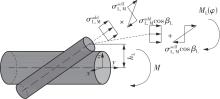
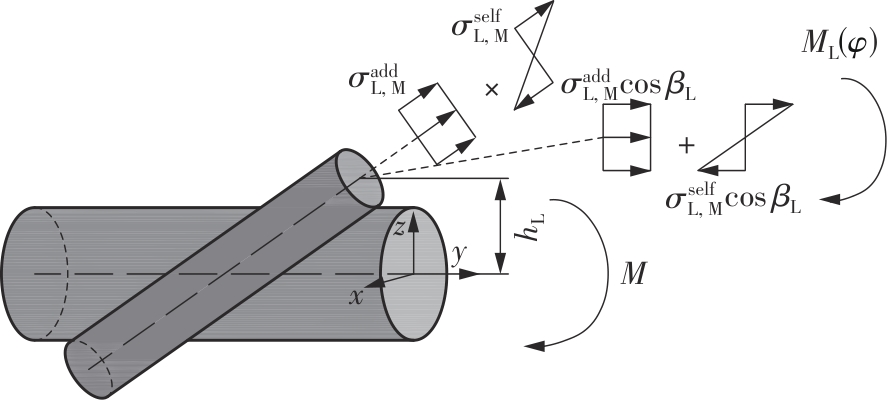
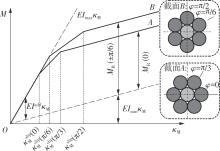
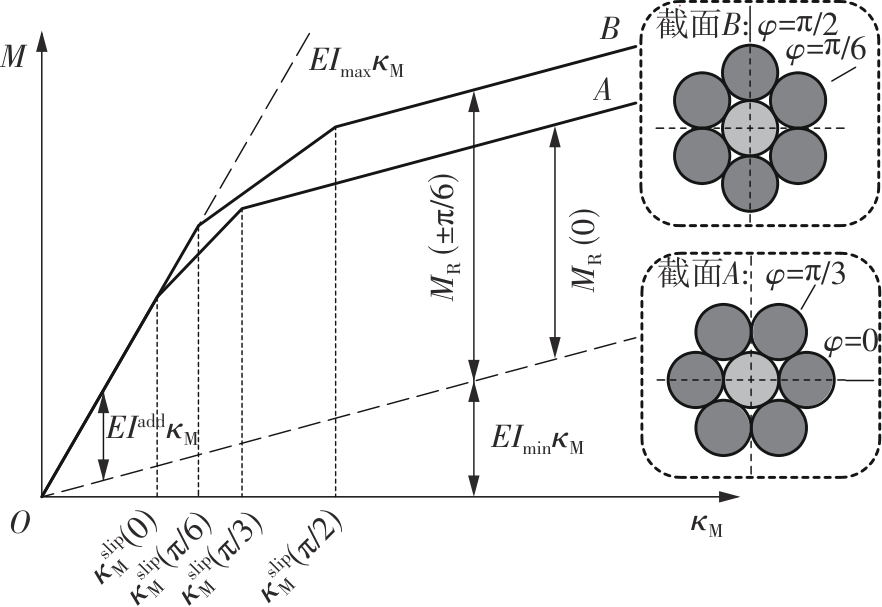
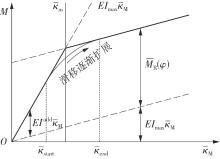
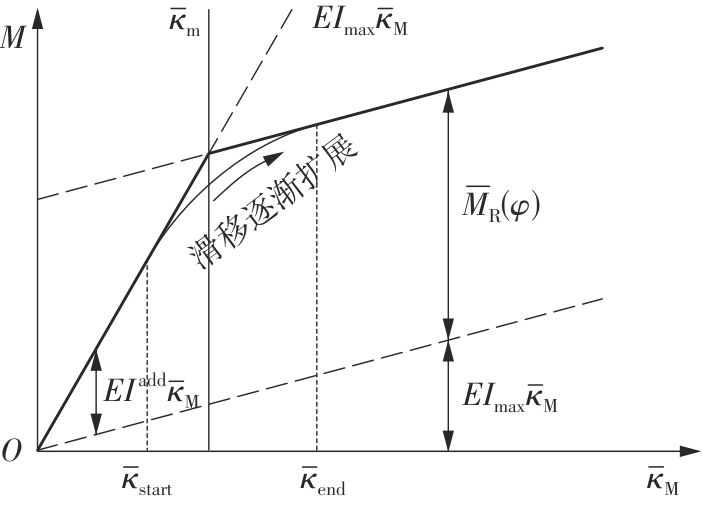
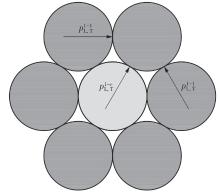
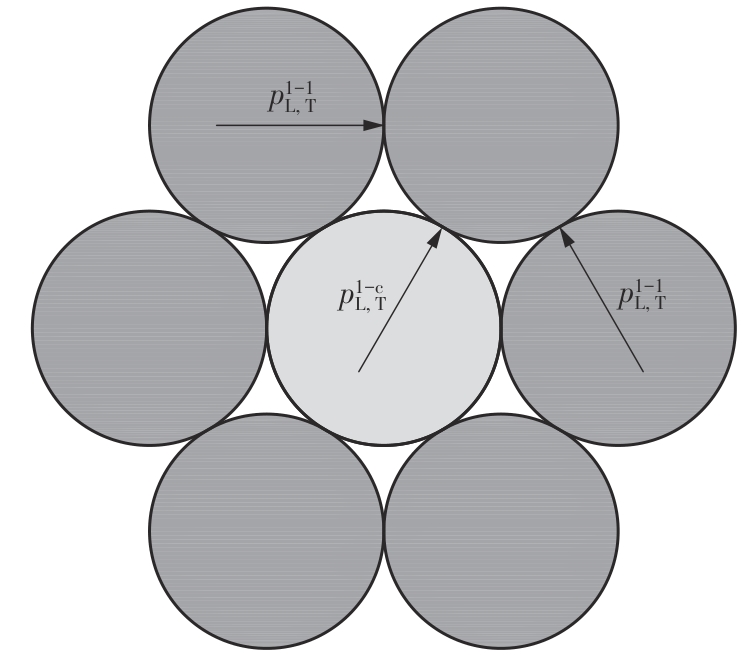
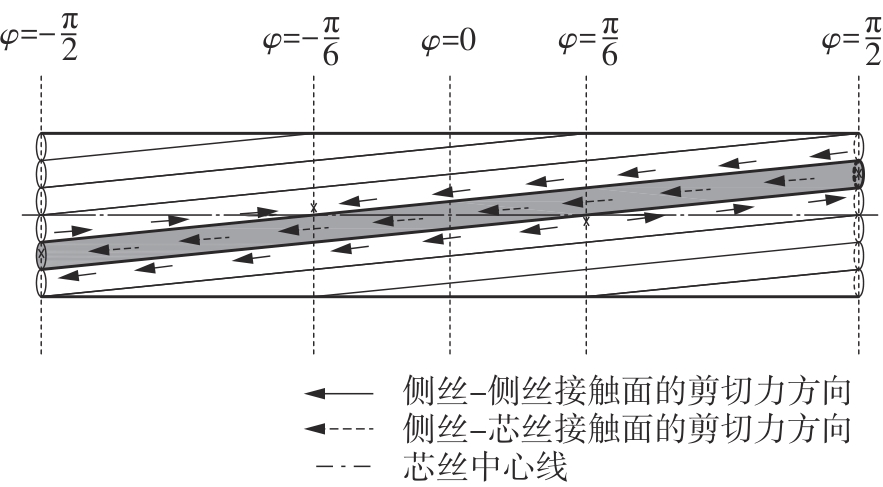
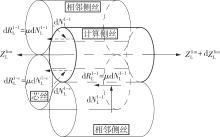
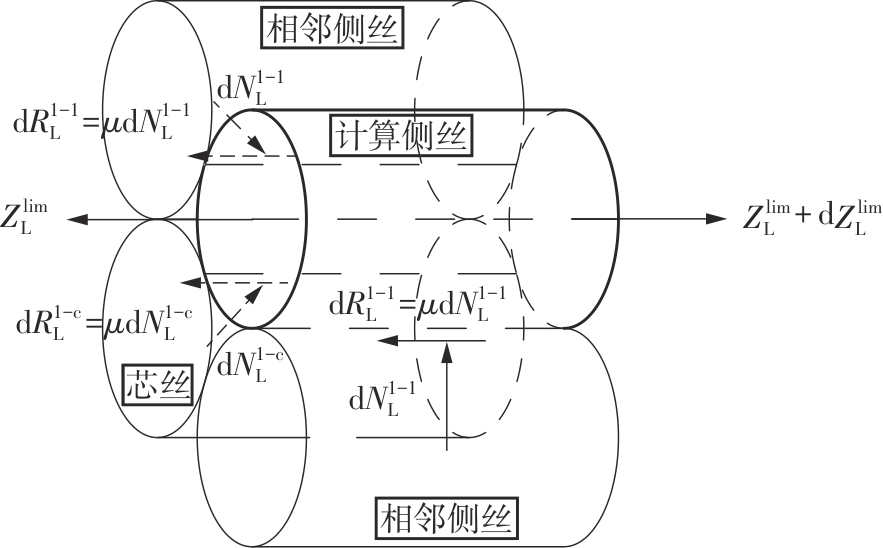
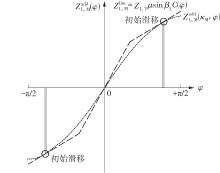
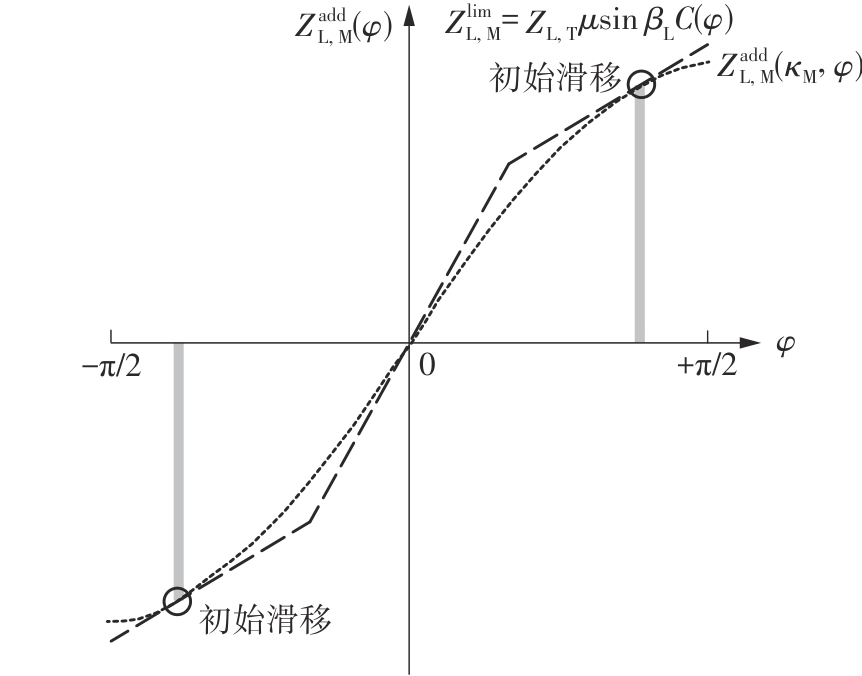
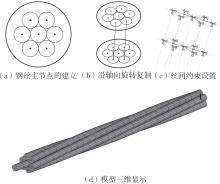
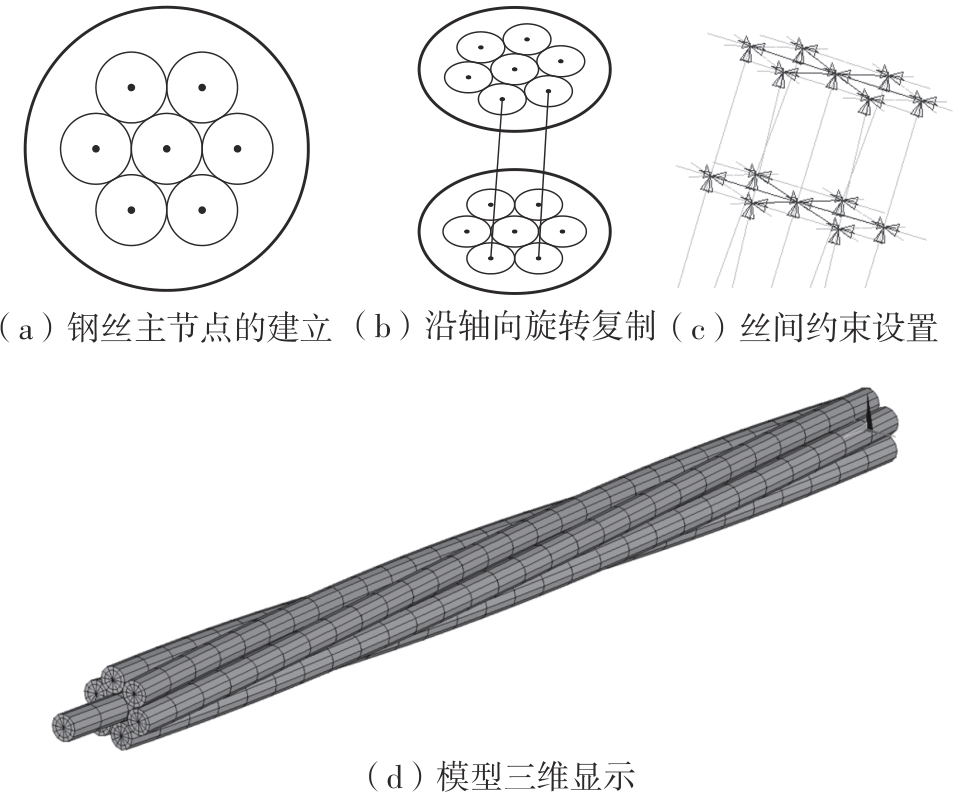
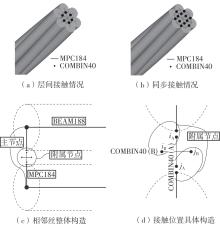
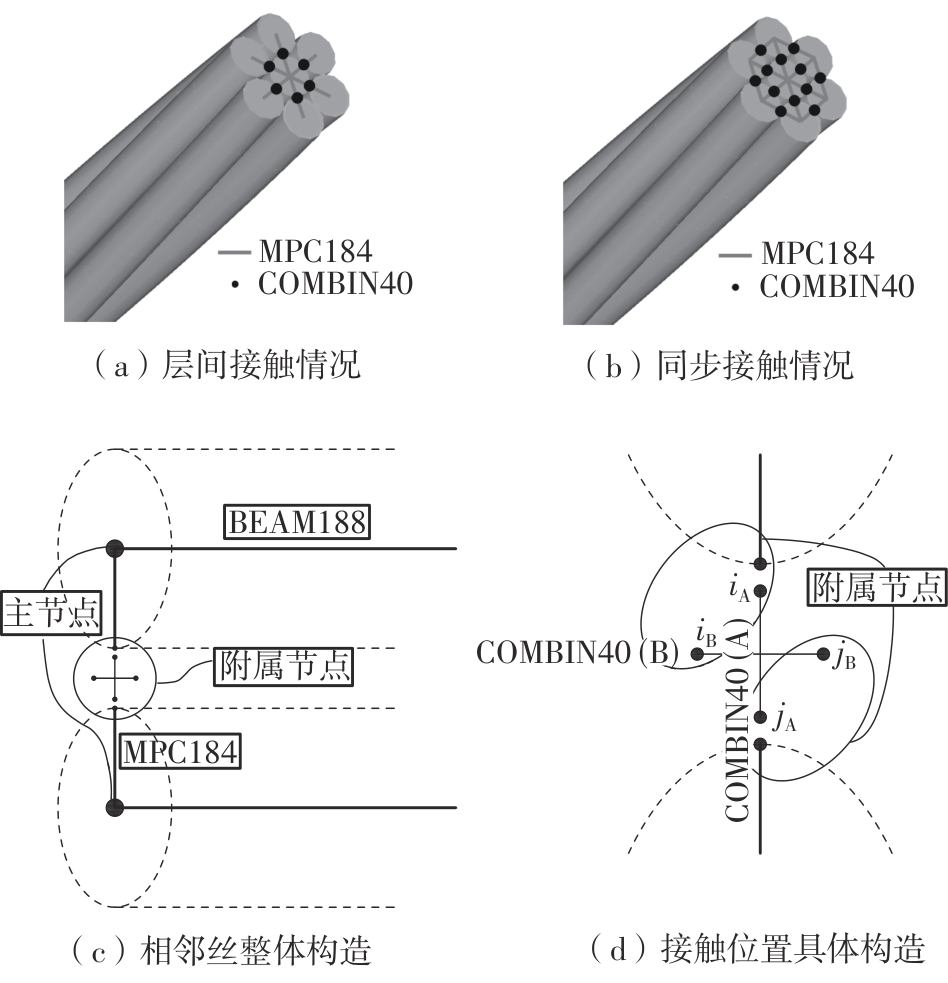
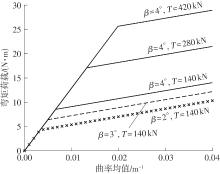
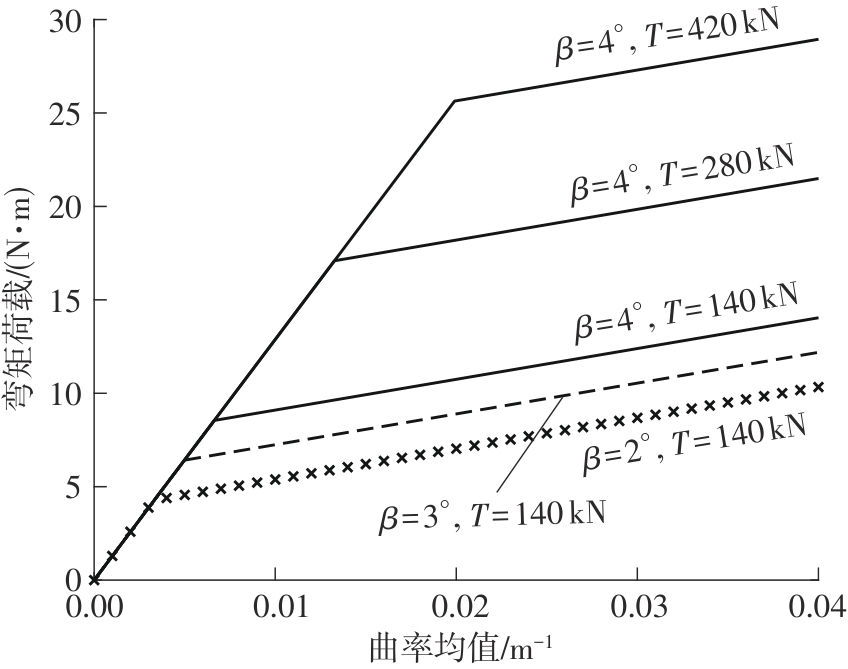
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 12-24.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240061
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bending Characteristics of 2-Layer Spiral Strand Under Typical Contact Conditions
WANG Ronghui1( ), LIU Xiyue1, ZHAO Yonglin1, ZHEN Xiaoxia1(
), LIU Xiyue1, ZHAO Yonglin1, ZHEN Xiaoxia1( ), ZHANG Zhuojie2,3
), ZHANG Zhuojie2,3
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Roads and Railway Engineering Safety Control,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,Hebei,China
3.Innovation Center for Wind Engineering and Wind Energy Technology of Hebei Province,Shijiazhuang 050043,Hebei,China
-
Received:2024-02-05Online:2025-06-10Published:2024-07-22 -
Contact:ZHEN Xiaoxia E-mail:rhwang@scut.edu.cn;xxzhen@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52178138);the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2024A1515012262)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Ronghui, LIU Xiyue, ZHAO Yonglin, ZHEN Xiaoxia, ZHANG Zhuojie. Bending Characteristics of 2-Layer Spiral Strand Under Typical Contact Conditions[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(6): 12-24.
share this article
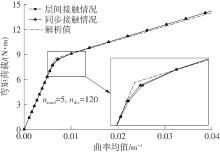
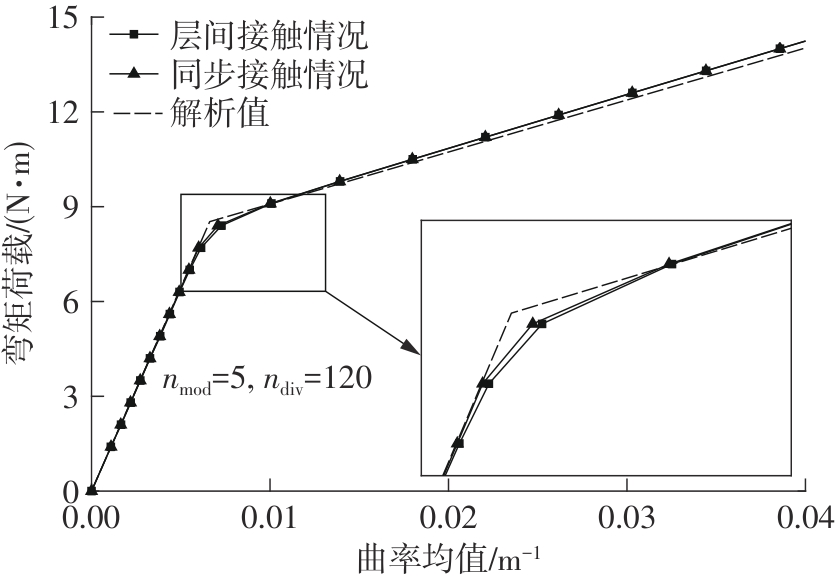
Table 1
Comparison of mean curvature under bending moment"
| 解析值 | ANSYS层间接触 | ANSYS同步接触 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相对 误差/% | 相对 误差/% | ||||
| 0.0 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 0 | 0.00 | 0.000 0 | 0.00 |
| 1.4 | 1.087 1 | 1.081 1 | -0.55 | 1.091 0 | 0.36 |
| 2.1 | 1.630 6 | 1.653 5 | 1.40 | 1.636 5 | 0.36 |
| 2.8 | 2.174 2 | 2.194 0 | 0.91 | 2.182 0 | 0.36 |
| 3.5 | 2.717 7 | 2.734 6 | 0.62 | 2.727 5 | 0.36 |
| 4.2 | 3.261 2 | 3.275 1 | 0.43 | 3.273 0 | 0.36 |
| 4.9 | 3.804 8 | 3.847 5 | 1.12 | 3.818 5 | 0.36 |
| 5.6 | 4.348 3 | 4.388 1 | 0.91 | 4.364 0 | 0.36 |
| 6.3 | 4.891 9 | 4.928 6 | 0.75 | 4.909 5 | 0.36 |
| 7.0 | 5.435 4 | 5.501 0 | 1.21 | 5.455 0 | 0.36 |
| 7.7 | 5.978 9 | 6.136 9 | 2.64 | 6.000 6 | 0.36 |
| 8.4 | 6.522 5 | 7.281 6 | 11.64 | 7.080 5 | 8.56 |
| 9.1 | 10.103 4 | 10.079 8 | -0.23 | 10.016 0 | -0.86 |
| 9.8 | 14.354 6 | 13.927 3 | -2.98 | 13.900 9 | -3.16 |
| 10.5 | 18.605 9 | 17.997 4 | -3.27 | 17.971 6 | -3.41 |
| 11.2 | 22.857 1 | 22.067 5 | -3.45 | 22.062 9 | -3.47 |
| 11.9 | 27.108 3 | 26.169 4 | -3.46 | 26.170 7 | -3.46 |
| 12.6 | 31.359 6 | 30.303 0 | -3.37 | 30.291 0 | -3.41 |
| 13.3 | 35.610 8 | 34.436 7 | -3.30 | 34.422 8 | -3.34 |
| 14.0 | 39.862 1 | 38.570 4 | -3.24 | 38.565 9 | -3.25 |
| 14.7 | 44.113 3 | 42.735 9 | -3.12 | 42.718 0 | -3.16 |
Table 2
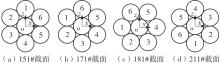
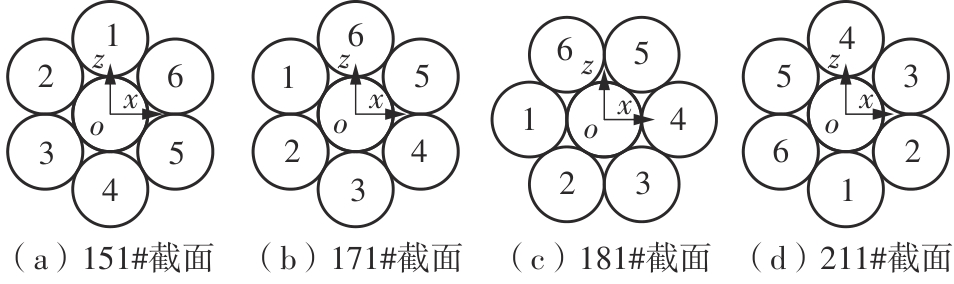
Applied bending moment and relative slip direction while COMBIN40 was slipping under inter-layer contact condition"
| 侧丝 | 151# (-90°) | 161# (-60°) | 171# (-30°) | 181# (0°) | 191# (30°) | 201# (60°) | 211# (90°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | 8 260 | 7 280 | 6 860 | 7 280 | 8 260 | × | |
| 7 280 | 6 860 | 7 280 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 280 | |
| 7 280 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 280 | 6 860 | 7 280 | |
| × | 8 260 | 7 280 | 6 860 | 7 280 | 8 260 | × | |
| 7 280 | 6 860 | 7 280 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 280 | |
| 7 280 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 280 | 6 860 | 7 280 |
Table 3
Applied bending moment and relative slip direction while COMBIN40 was slipping under synchronous contact condition"
| 接触点 | 151# (-90°) | 161# (-60°) | 171# (-30°) | 181# (0°) | 191# (30°) | 201# (60°) | 211# (90°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 840 | |
| × | 8 120 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 120 | × | |
| 7 840 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | |
| 7 840 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | |
| 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 120 | × | 8 120 | 7 840 | |
| × | 8 260 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 260 | × | |
| × | 8 260 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 260 | × | |
| 7 840 | 8 120 | × | 8 120 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | |
| 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 840 | |
| 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 840 | |
| × | 8 120 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 120 | × | |
| 7 840 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | |
| 7 840 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | |
| 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 120 | × | 8 120 | 7 840 | |
| × | 8 260 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 260 | × | |
| × | 8 260 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 260 | × | |
| 7 840 | 8 120 | × | 8 120 | 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | |
| 7 840 | 6 720 | 7 840 | 8 260 | × | 8 260 | 7 840 |
| 1 | 苏成,徐郁峰,韩大建 .频率法测量索力中的参数分析与索抗弯刚度的识别[J].公路交通科技,2005,22(5):75-78. |
| SU Cheng, XU Yu-feng, HAN Da-jian .Parameter analysis and identification of bending stiffness of cables during tension measurements by frequency method[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2005,22(5):75-78. | |
| 2 | MCCONNELL K G, ZEMKE W P .The measurement of flexural stiffness of multistranded electrical conductors while under tension[J].Experimental Mechanics,1980,20(6):198-204. |
| 3 | 余玉洁 .基于拉索半精细化有限元模型的拉索弯曲及断丝研究[D].天津:天津大学,2016. |
| 4 | COSTELLO G A .Theory of wire rope[M].New York:Springer Science & Business Media,1997. |
| 5 | RAOOF M, HOBBS R E .Analysis of multilayered structural strands[J].Journal of Engineering Mecha-nics,1988,114(7):1166-1182. |
| 6 | JOLICOEUR C, CARDOU A .Semicontinuous ma-thematical model for bending of multilayered wire strands [J].Journal of Engineering Mechanics,1996,122(7):643-650. |
| 7 | PAPAILIOU K O .Bending of helically twisted cables under variable bending stiffness due to internal friction,tensile force and cable curvature[D].Zurich:Swiss Federal Institute of Technology,1995. |
| 8 | PAPAILIOU K O .On the bending stiffness of transmission line conductors[J].IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery,1997,12(4):1576-1588. |
| 9 | HONG K J, KIUREGHIAN A D, SACKMAN J L .Bending behavior of helically wrapped cables[J].Journal of Engineering Mechanics,2005,131(5):500-511. |
| 10 | FOTI F, MARTINELLI L .Mechanical modeling of metallic strands subjected to tension,torsion and ben-ding[J].International Journal of Solids and Structures,2016,91:1-17. |
| 11 | JIANG W G, WARBY M K, HENSHALL J L .Statically indeterminate contacts in axially loaded wire strand[J].European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids,2008,27(1):69-78. |
| 12 | GNANAVEL B K, GOPINATH D, PARTHASARATHY N S .Effect of friction on coupled contact in a twisted wire cable[J].Journal of Applied Mechanics,2009,77(2):024501/1-6. |
| 13 | JIANG W G .A concise finite element model for pure bending analysis of simple wire strand[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2012,54(1):69-73. |
| 14 | ZHANG D, OSTOJA-STARZEWSKI M .Finite element solutions to the bending stiffness of a single-layered helically wound cable with internal friction [J].Journal of Applied Mechanics,2015,83(3):031003/1-9. |
| 15 | STANOVA E, FEDORKO G, FABIAN M,et al .Computer modelling of wire strands and ropes part Ⅱ:finite element-based applications[J].Advances in Engineering Software,2011,42(6):322-331. |
| 16 | 陈原培 .钢丝绳股力学与摩擦磨损性能研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2016. |
| 17 | 预应力热镀锌钢绞线: [S]. |
| 18 | 斜拉桥用热挤聚乙烯高强钢丝拉索: [S]. |
| 19 | FEYRER K .Wire ropes[M].Berlin:Springer,2007. |
| 20 | 李红,郑罡,陈璨 .斜拉索内平行钢丝间摩擦系数的确定[J].重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2011,30(2):196-199. |
| LI Hong, ZHENG Gang, CHEN Can .Determination of friction coefficients between steel wires in stay cables[J].Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science),2011,30(2):196-199. |
| [1] | ZHEN Xiaoxia, LIU Guiyuan, DONG Chunguang, et al. Study on Natural Vibration Characteristics of Cable Network-Damper System [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 61-71. |
| [2] | DU Yunwei, WANG Ronghui, ZHEN Xiaoxia, et al. Calculation of Elastic Stiffness of Shear Connector in Steel Concrete Bridge Tower Joint Section [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(2): 76-87. |
| [3] | YU Xianbin, WANG Ronghui, CHEN Shanting, et al. High-Accuracy and Non-iteration Methods for Control Tension of Parallel-Strand Stay Cables [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 43-55. |
| [4] | Zhang Zhuo- jie Wang Rong- hui. Numerical Method of Determining Installation Force for Parallel Strand Cables [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(2): 88-95,102. |
| [5] | Peng Chong- mei Zhang Qi- wei Li Yuan- bing. Static Model and Parameter Analysis of Multilayered Semi- Parallel Wire Cable Under Tensile Load [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(8): 115-119,126. |
| [6] | Li Zhou Wei Yuan-cheng. Parametric Vibration and Corresp0nding Impact Parameters Analysis of Suspender Cable Considering the First Two Order M odals [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(2): 94-100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||