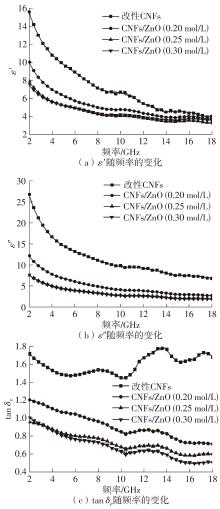
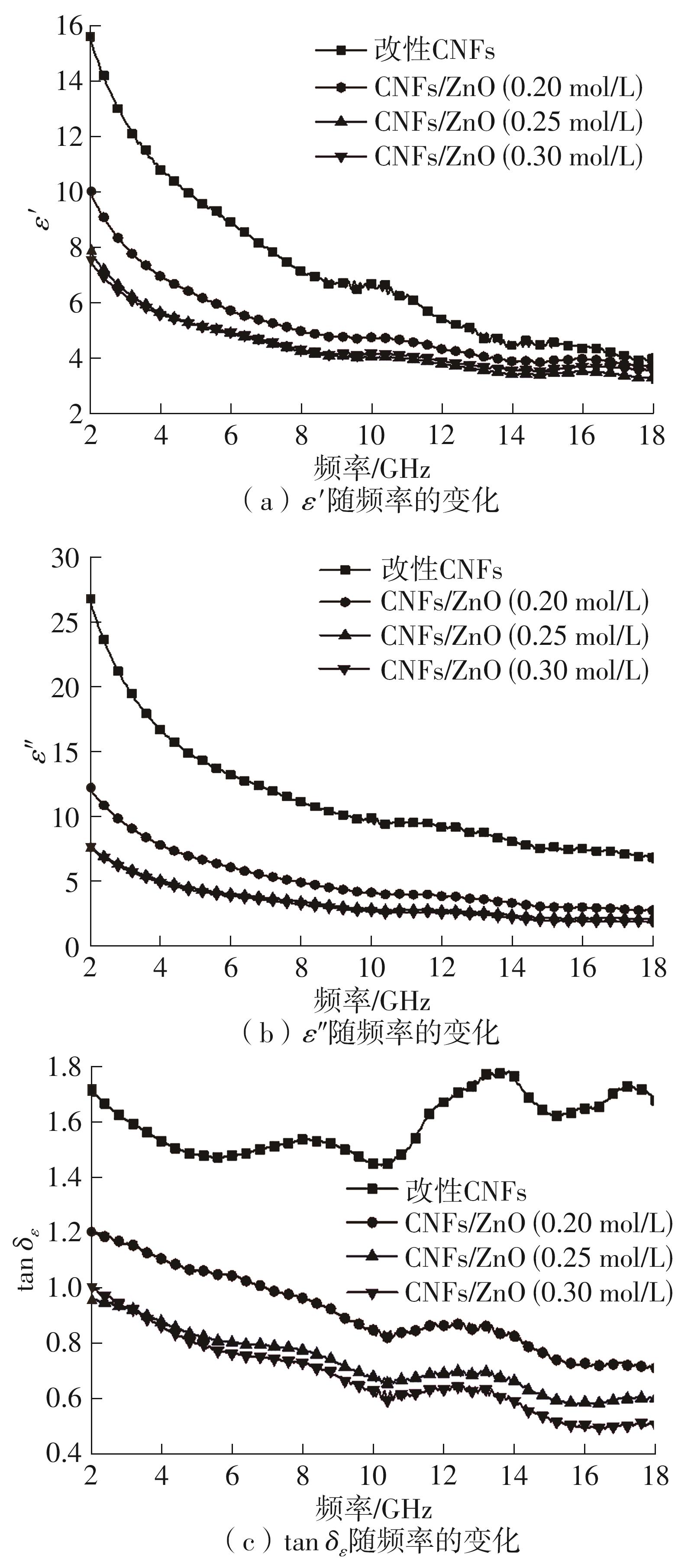
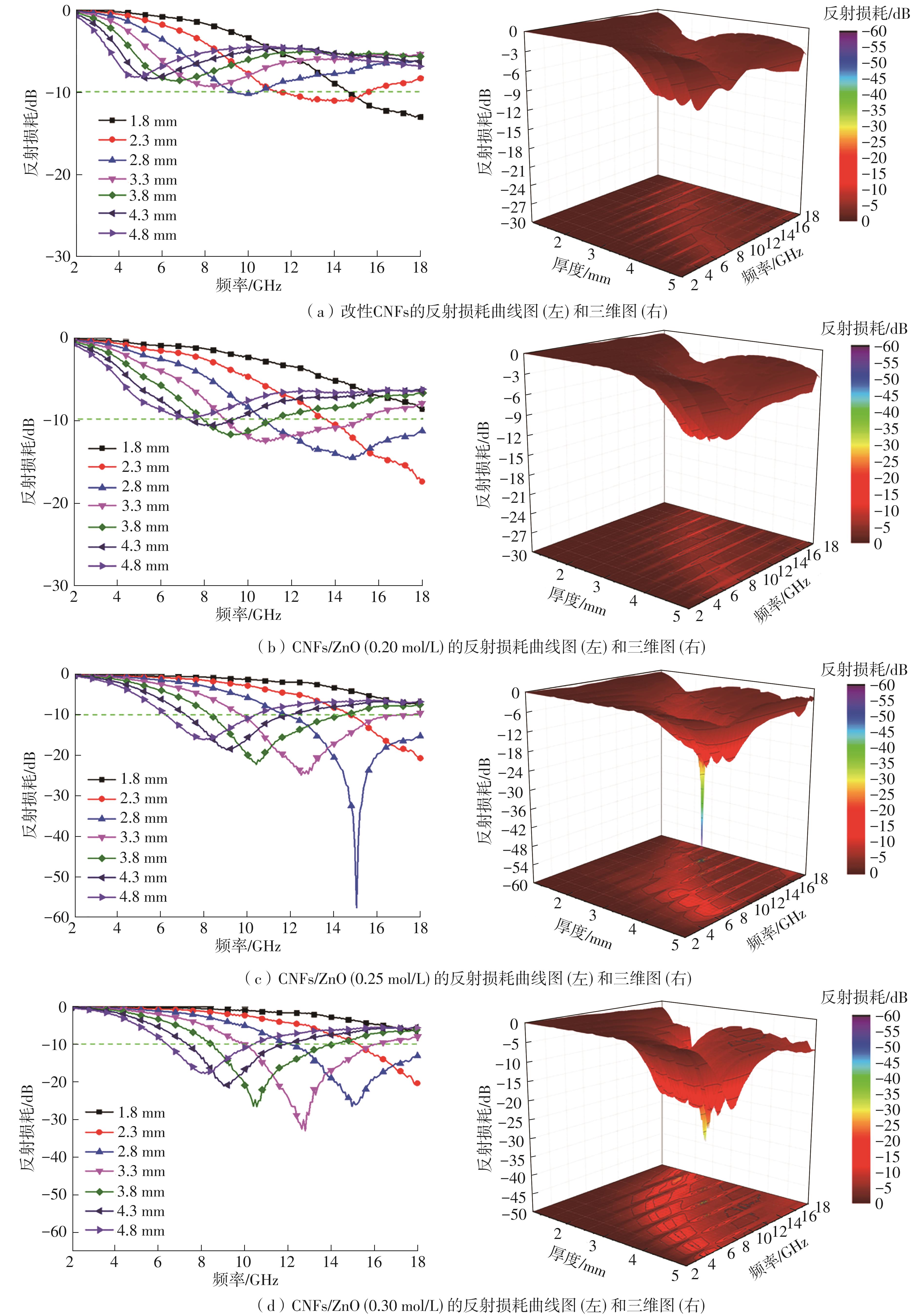
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 138-145.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230743
• Materials Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and Properties of Bacterial Cellulose Based CNFs/ZnO Microwave Absorbing Materials
LIU Pingan( ), LIN Baoshun, DING Huiling, XIAO Liang, ZHANG Zhijie
), LIN Baoshun, DING Huiling, XIAO Liang, ZHANG Zhijie
- School of Materials Science and Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China