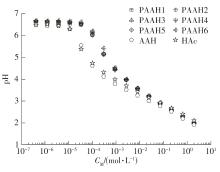
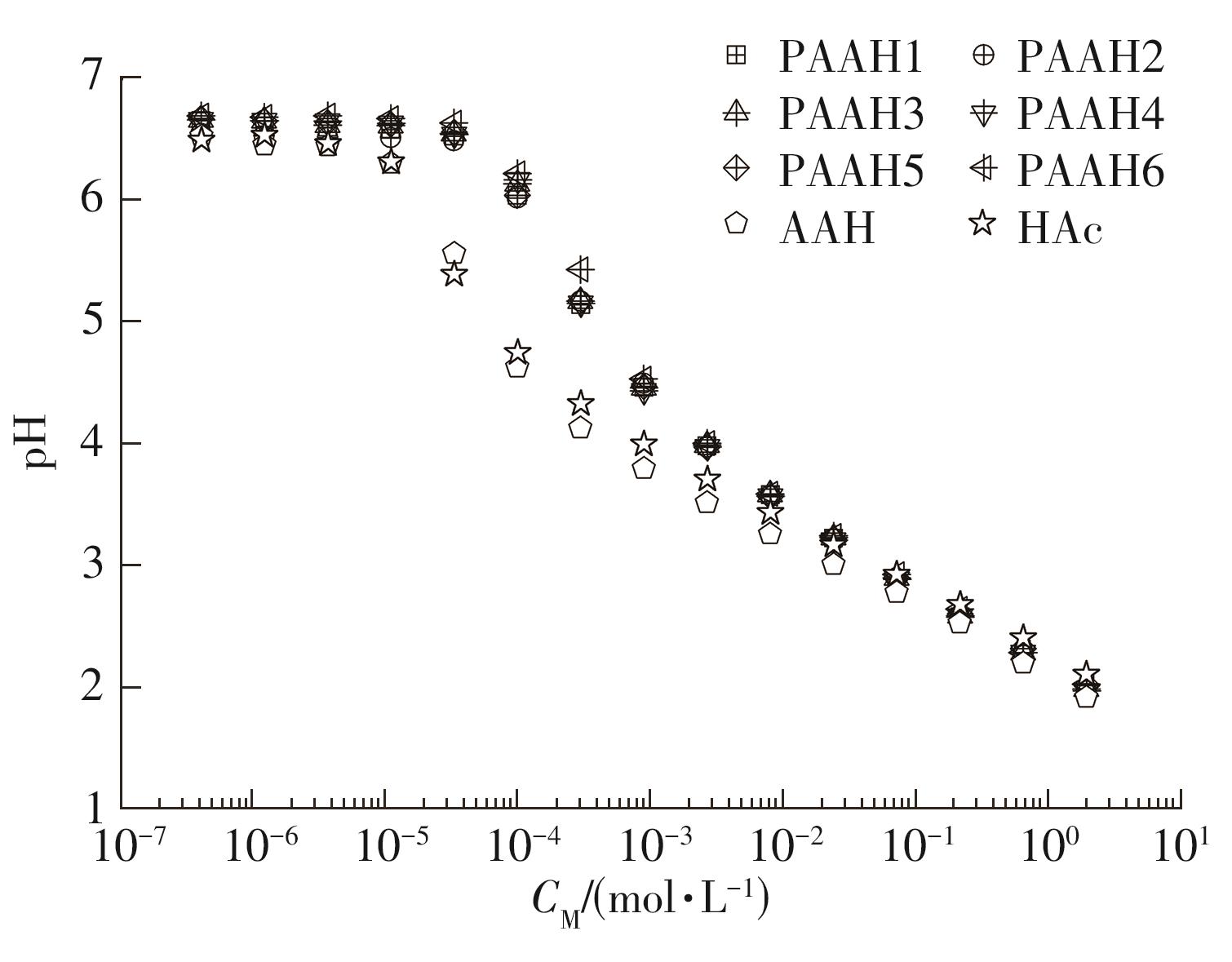
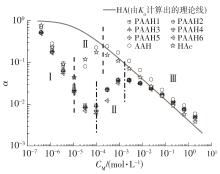
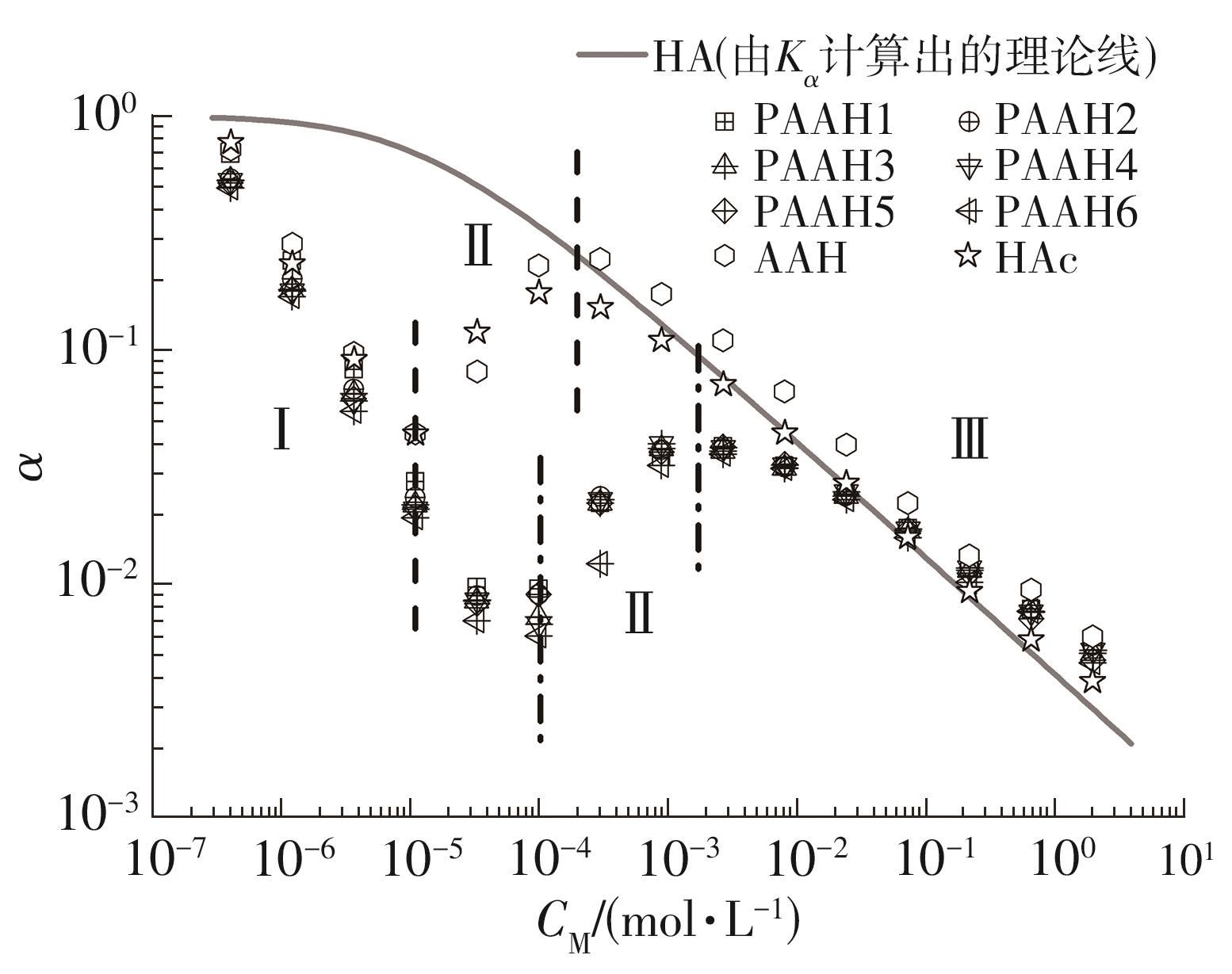
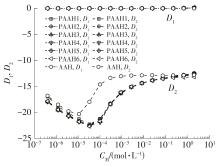
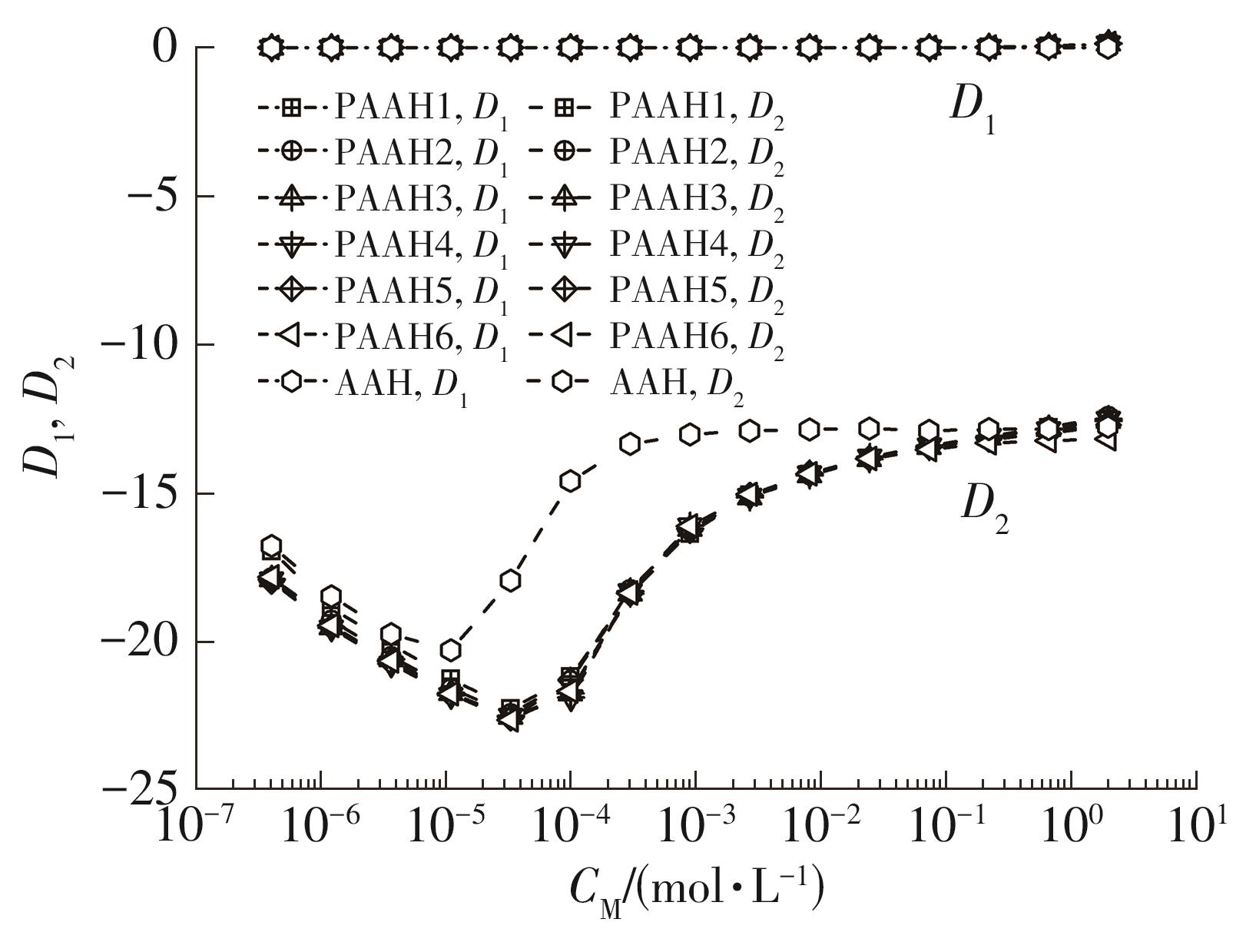
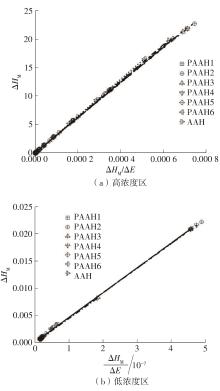
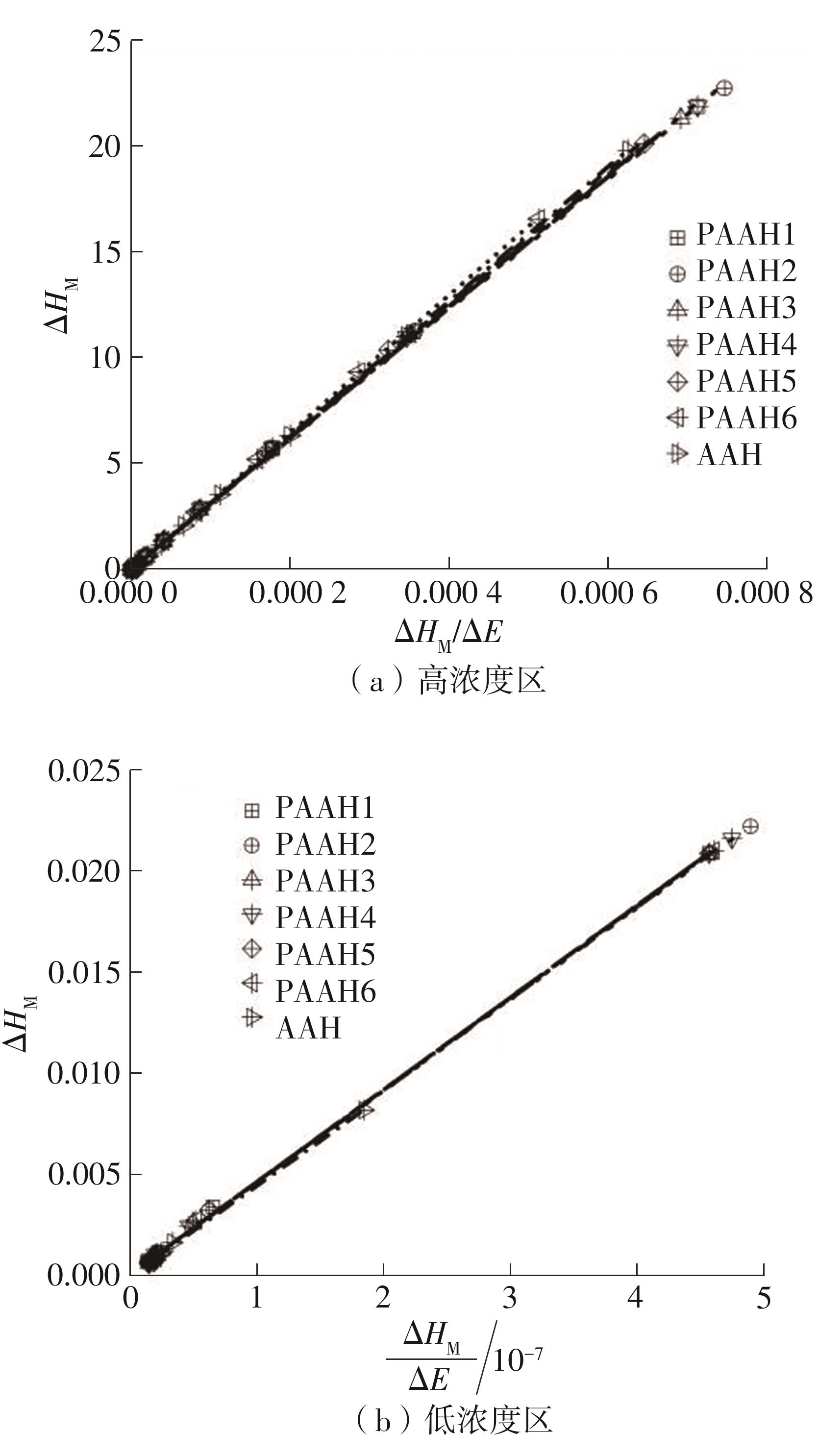
| 1 |
BORUKHOV I, ANDELMAN D, BORREGA R,et al .Polyelectrolyte titration:Theory and experiment [J].Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2000,104(47):11027-11034.
|
| 2 |
CARRILLO J M, DOBRYNIN A V .Salt effect on osmotic pressure of polyelectrolyte solutions:Simulation study [J].Polymers,2014,6(7):1897-1913.
|
| 3 |
LANDSGESELL J, NOVA L,RUD O,et al .Simulations of ionization equilibria in weak polyelectrolyte solutions and gels [J].Soft Matter,2019,15(6):1155-1185.
|
| 4 |
WANDREY C .Concentration regimes in polyelectrolyte solutions [J].Langmuir,1999,15(12):4069-4075.
|
| 5 |
XU G F, LUO S J, YANG Q B,et al .Single chains of strong polyelectrolytes in aqueous solutions at extreme dilution:Conformation and counterion distribution[J].Journal of Chemistry Physics,2016,145(14):144903-1-7.
|
| 6 |
刘全伟,李艺,王治流,等 .丙烯酸-丙烯酸钠共聚物在水溶液中的离解 [J].高分子学报,2005(4):484-485.
|
|
LIU Quan-wei, LI Yi, WANG Zhi-liu,et al .Dissociation of acrylic acid sodium acrylate copolymer in aqueous solution [J].Acta Polymerica Sinica,2005(4):484-485.
|
| 7 |
FUKUSHIMA M, TATSUMI K, WADA S .Evaluation of the intrinsic acid-dissociation constant of alginic acid by considering the electrostatic effect [J].Analytical Sciences,1999,15:1153-1155.
|
| 8 |
YEKYMOV E, ATTIA D, LEVI-KALISMAN Y,et al .Effects of non-ionic micelles on the acid-base equilibria of a weak polyelectrolyte [J].Polymers,2022,14(9):1926.
|
| 9 |
PAN Y, CHENG R S .A novel interpretation of concentration dependence of viscosity of dilute polymer solution [J].Chinese Journal of Poylmer Science,2000,18(1):57-67.
|
| 10 |
KAJI K, URAKAWA H, KANAYA T,et al .Phase diagram of polyelectrolyte solutions [J].Journal de Physique France,1988,49(6):993-1000.
|
| 11 |
TANAHATOE J J, KUIL M E .Dynamic light scattering of a flexible highly charged polyelectrolyte in the dilute concentration regime [J].Macromolecules,1997,30(20):6102-6106.
|
| 12 |
蔡佳利,薄淑琴,程镕时 .聚电解质溶液浓度区域的划分 [J].高分子学报,2004(5):625-627.
|
|
Cai Jia-li, Bo Shu-qin, Cheng Rong-shi .Division of concentration region of polyelectrolyte solution [J].Acta Polymerica Sinica,2004(5):625-627.
|
| 13 |
NISHIDA K, KAJI K, KANAYA T .Improved phase diagram of polyelectrolyte solutions [J].Journal of Chemical Physics,2001,115(17):8217-8220.
|
| 14 |
NISHIDA K, KAJI K, KANAYA T .High concentration crossovers of polyelectrolyte solutions [J].Journal of Physical Chemistry,2001,114(19):8671-8677.
|
| 15 |
WANDREY C .Concentration regimes in polyelectrolyte solutions [J].Langmuir,1999,15(12):4069-4075.
|
| 16 |
MUTHUKUMAR M .Theory of counter-ion condensation on flexible polyelectrolytes:Adsorption mechanism [J].Journal of Chemical Physics,2004,120(19):9343-9350.
|
| 17 |
蔡正春,杨琥,程镕时 .聚电解质在水溶液中的离解行为[C]∥2007年全国高分子学术论文报告会论文摘要集(上册).成都:[s.n.],2007:237.
|
| 18 |
CHENG R S .On the concentration regimes of a flexible-chain polymer solution [J].Macromolecular Symposia,1997,124:27-34.
|
| 19 |
蔡正春 .聚丙烯酸在水溶液中的离解与电迁移行为 [D].南京:南京大学,2008.
|
| 20 |
陈环环 .聚电解质在溶液中的电离行为 [D].广州:华南理工大学,2016.
|
| 21 |
蔡正春,杨琥,程镕时 .羧酸离子在水中的水合数 [J].化学学报,2008,66(7):831-833.
|
|
CAI Zheng-chun, YANG Hu, CHENG Rong-shi .Hydration number of carboxylic acid ions in water [J].Acta Chimica Sinica,2008,66(7):831-833.
|
| 22 |
LI W B, ZHENG Y, CHENG R S .Transition of hydration states of poly(vinyl alcohol) in aqueous solution [J].Polymer,2008,49(21):4740-4744.
|
| 23 |
LI W B, XUE F, CHENG R S .States of water in partially swollen poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels [J].Polymer,2005,46(25):12026-12031.
|