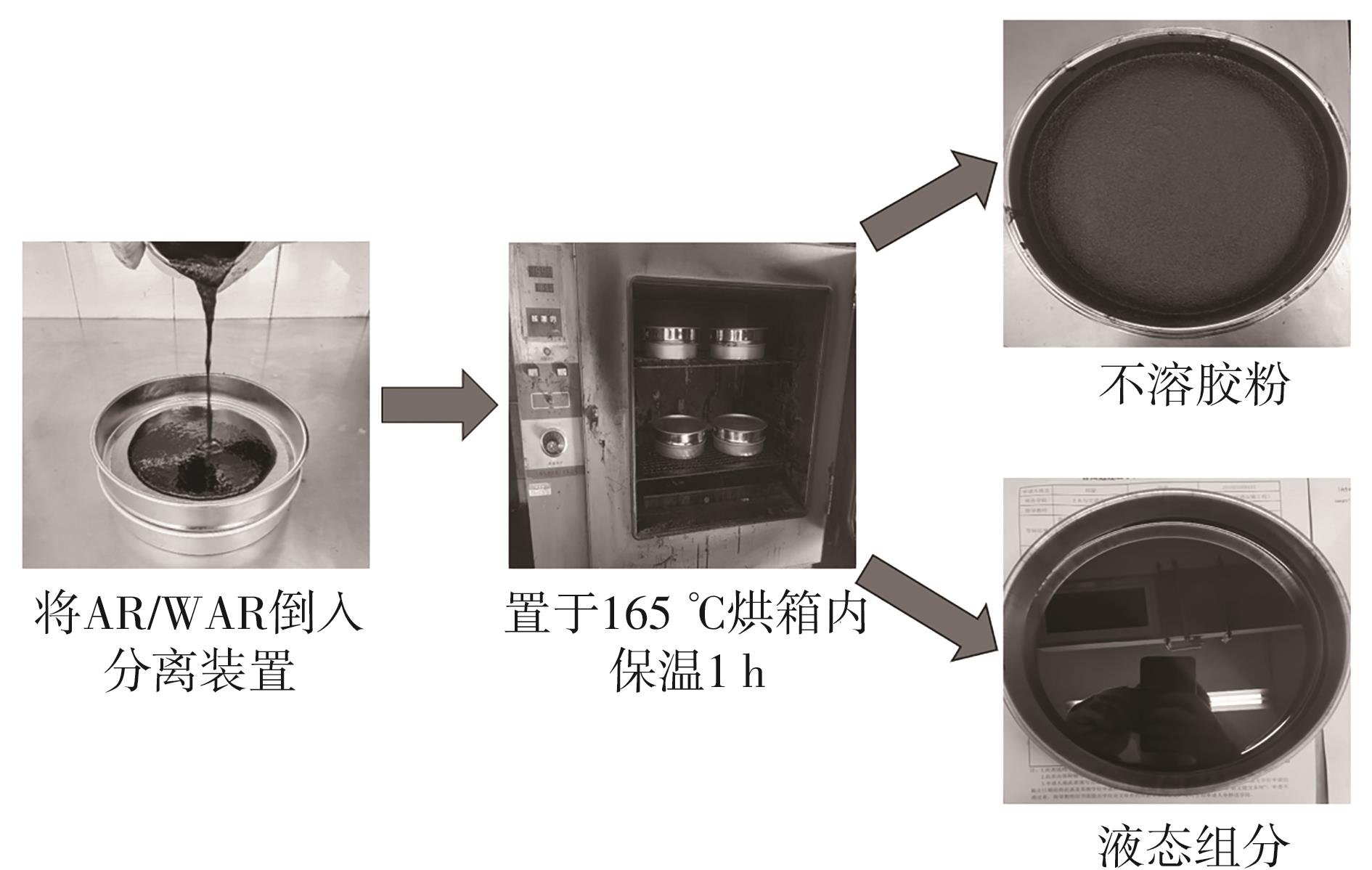
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 126-137.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230692
• Materials Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on the Modification Mechanism of Warm Asphalt Rubber Based on Stage-Extraction Method
YU Huayang1( ), ZHANG Zheng2, DENG Yihao1, YU Jiangmiao1(
), ZHANG Zheng2, DENG Yihao1, YU Jiangmiao1( )
)
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, Guangdong, China
2.China Construction Fourth Bureau Water Resources and Energy Development Co. , Ltd. , Guangzhou 510665, Guangdong, China
-
Received:2023-11-05Online:2024-08-25Published:2024-02-09 -
Contact:虞将苗(1979—),男,博士,教授,主要从事道路工程结构与材料研究。 E-mail:huayangyu@scut.edu.cn -
About author:于华洋(1988—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事道路工程结构与材料研究。E-mail: huayangyu@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51808228);the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2023A1515030287)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YU Huayang, ZHANG Zheng, DENG Yihao, et al. Study on the Modification Mechanism of Warm Asphalt Rubber Based on Stage-Extraction Method[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(8): 126-137.
share this article
Table 1
Technical indicators of 70#BA"
| 试验项目 | 试验结果 | 试验方法 | 技术要求 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 ℃针入度/0.1 mm | 61.1 | T0604 | 60~80 | |
| 针入度指数 | -1.25 | T0604 | -1.5~+1.0 | |
| 软化点/℃ | 48.1 | T0606 | ≥47 | |
| 15 ℃延度/cm | >100 | T0605 | ≥100 | |
| 10 ℃延度/cm | 21 | T0605 | ≥15 | |
| 密度/(g∙cm-3) | 1.038 | T0603 | 实测记录 | |
| 溶解度(三氯乙烯)/ % | 99.7 | T0607 | ≥99.5 | |
| 闪点/℃ | 345 | T0611 | ≥260 | |
| 蜡含量/% | 1.67 | T0615 | ≤2.2 | |
| 60 ℃动力黏度/(Pa∙s) | 194 | T0620 | ≥180 | |
| 135 ℃旋转黏度/(Pa∙s) | 0.47 | T0625 | 未作要求 | |
| 旋转薄膜加热试验残留物 | 质量变化率/% | -0.011 | T0609 | ±0.8 |
| 针入度比/% | 64.3 | T0604 | ≥61 | |
| 10 ℃延度/cm | 6.7 | T0605 | ≥6 | |
Table 4
Rotational viscosity test results"
| 沥青类型 | 旋转黏度/(mPa∙s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 135 ℃ | 160 ℃ | 180 ℃ | |
| 70#BA | 469 | 185 | 74 |
| 40AR | 10 983 | 4 179 | 2 758 |
| 40ARE | 6 415 | 1 849 | 1 363 |
| 40ARS | 3 561 | 1 110 | 667 |
| 80AR | 12 584 | 5 598 | 3 011 |
| 80ARE | 7 325 | 2 142 | 1 550 |
| 80ARS | 4 135 | 1 408 | 914 |
| L-40AR | 842 | 277 | 142 |
| L-40ARE | 568 | 193 | 102 |
| L-40ARS | 537 | 188 | 98 |
| L-80AR | 870 | 286 | 154 |
| L-80ARE | 642 | 213 | 112 |
| L-80ARS | 597 | 202 | 108 |
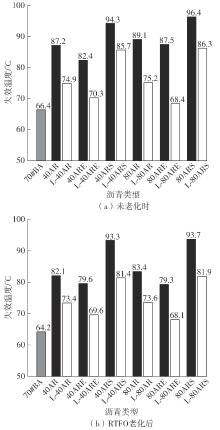
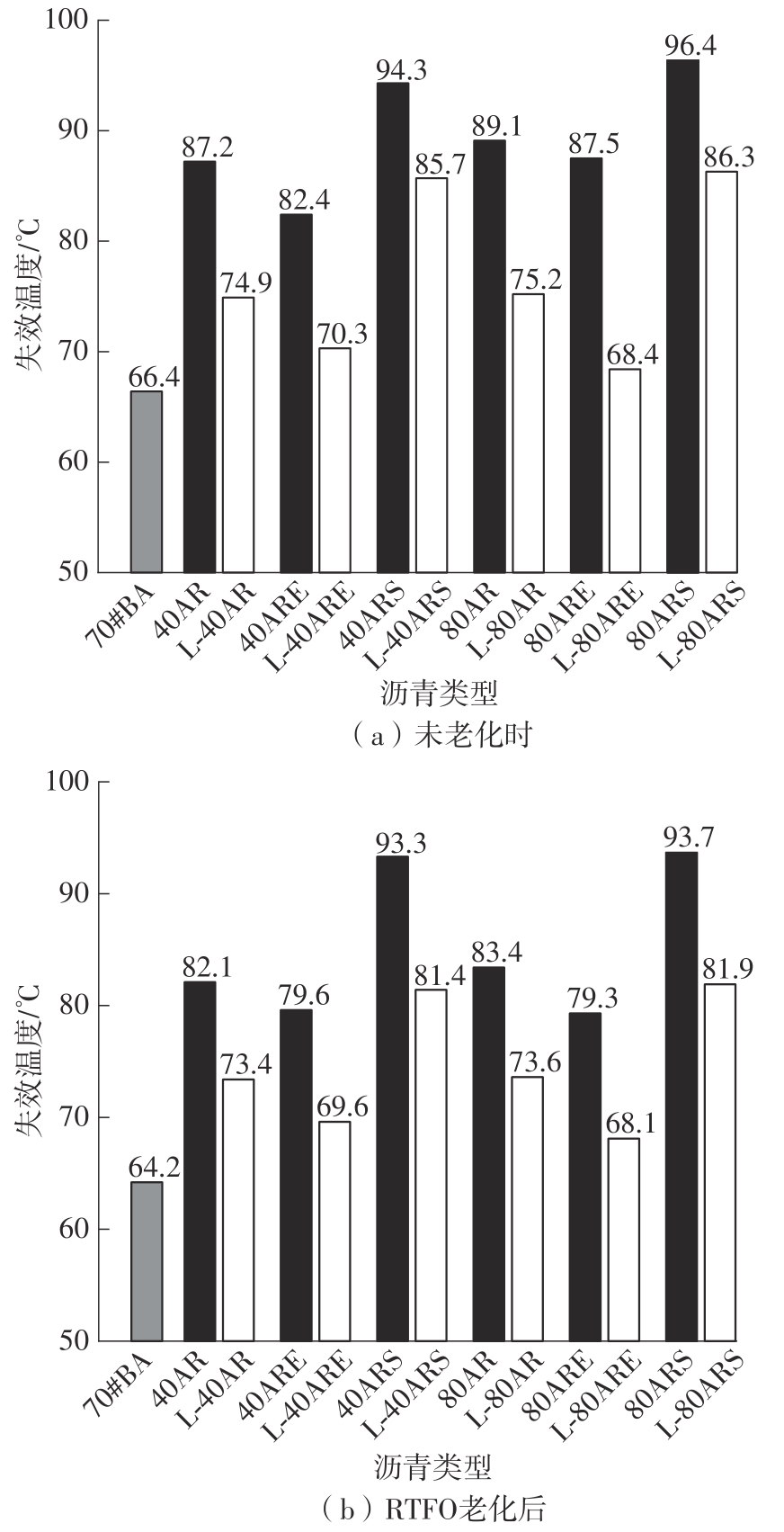
Table 5
High temperature PG grading of asphalt binders"
沥青 类型 | 高温PG分级 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 老化前 | 老化后 | 最终 | |
| 70#BA | PG64 | PG64 | PG64 |
| 40AR | PG82 | PG82 | PG82 |
| 40ARE | PG82 | PG76 | PG76 |
| 40ARS | PG94 | PG88 | PG88 |
| 80AR | PG88 | PG82 | PG82 |
| 80ARE | PG82 | PG76 | PG76 |
| 80ARS | PG94 | PG88 | PG88 |
| L-40AR | PG70 | PG70 | PG70 |
| L-40ARE | PG70 | PG64 | PG64 |
| L-40ARS | PG82 | PG76 | PG76 |
| L-80AR | PG70 | PG70 | PG70 |
| L-80ARE | PG64 | PG64 | PG64 |
| L-80ARS | PG82 | PG76 | PG76 |
Table 6
MSCR test results"
| 沥青类型 | Jnr/(kPa)-1 | R/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 kPa | 3.2 kPa | 0.1 kPa | 3.2 kPa | |
| 70#BA | 2.343 4 | 2.555 2 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| 40AR | 0.092 2 | 0.198 1 | 75.1 | 52.0 |
| 40ARE | 0.196 1 | 0.310 7 | 57.2 | 41.3 |
| 40ARS | 0.001 4 | 0.030 6 | 96.9 | 73.6 |
| 80AR | 0.073 6 | 0.235 1 | 80.7 | 47.5 |
| 80ARE | 0.103 0 | 0.341 2 | 78.0 | 39.7 |
| 80ARS | 0.001 2 | 0.024 3 | 97.4 | 79.8 |
| L-40AR | 0.575 7 | 0.697 7 | 11.4 | 7.2 |
| L-40ARE | 1.097 6 | 1.198 5 | 5.3 | 2.5 |
| L-40ARS | 0.005 1 | 0.084 7 | 92.0 | 49.9 |
| L-80AR | 0.531 3 | 0.573 5 | 19.0 | 7.9 |
| L-80ARE | 1.318 0 | 1.446 6 | 4.4 | 1.9 |
| L-80ARS | 0.004 9 | 0.079 2 | 92.7 | 51.7 |
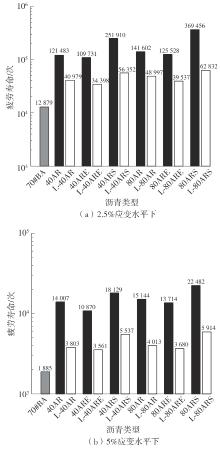
Table 7
BBR test results"
| 沥青类型 | -6 ℃ | -12 ℃ | -18 ℃ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S/MPa | m值 | S/MPa | m值 | S/MPa | m值 | |
| 70#BA | 142.0 | 0.293 | 332.9 | 0.195 | 674.7 | 0.181 |
| 40AR | 50.5 | 0.412 | 132.0 | 0.329 | 275.8 | 0.258 |
| 40ARE | 47.5 | 0.436 | 119.5 | 0.337 | 264.9 | 0.259 |
| 40ARS | 77.0 | 0.335 | 164.3 | 0.273 | 294.6 | 0.227 |
| 80AR | 47.3 | 0.439 | 126.1 | 0.346 | 255.5 | 0.265 |
| 80ARE | 44.8 | 0.443 | 111.0 | 0.358 | 220.4 | 0.273 |
| 80ARS | 70.1 | 0.341 | 150.4 | 0.282 | 264.5 | 0.249 |
| L-40AR | 135.2 | 0.339 | 314.3 | 0.228 | 652.9 | 0.204 |
| L-40ARE | 104.8 | 0.375 | 210.4 | 0.305 | 392.1 | 0.253 |
| L-40ARS | 207.5 | 0.269 | 371.8 | 0.173 | 675.8 | 0.169 |
| L-80AR | 129.4 | 0.341 | 261.2 | 0.284 | 460.2 | 0.225 |
| L-80ARE | 90.6 | 0.380 | 202.7 | 0.312 | 370.3 | 0.256 |
| L-80ARS | 194.5 | 0.278 | 359.3 | 0.186 | 591.9 | 0.172 |
| 1 | AKISETTY C K, LEE S J, AMIRKHANIAN S N .High temperature properties of rubberized binders containing warm asphalt additives[J].Construction and Building Materials,2009,23(1):565-573. |
| 2 | 何亮,凌天清,马育,等 .Sasobit温拌橡胶沥青及混合料高温蠕变特性[J].长安大学学报(自然科学版),2015,35(6):16-23. |
| HE Liang, LING Tian-qing, MA Yu,et al .High-temperature creep properties of asphalt-rubber and mixture with Sasobit warm mix additives[J].Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition),2015,35(6):16-23. | |
| 3 | YU H Y, ZHEN L, GAO Z M,et al .Thermal analysis on the component interaction of asphalt binders modified with crumb rubber and warm mix additives[J].Construction and Building Materials,2016,125:168-174. |
| 4 | LENG Z, YU H Y, ZHANG Z Y,et al .Optimizing the mixing procedure of warm asphalt rubber with wax-based additives through mechanism investigation and performance characterization[J].Construction and Building Materials,2017,144:291-299. |
| 5 | 潘睿 .应力吸收层温拌橡胶沥青混合料性能[J].长安大学学报(自然科学版),2019,39(6):49-56. |
| PANG Rui .Performance of warm mixed rubber asphalt mixture of stress absorbing layer[J].Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition),2019,39(6):49-56. | |
| 6 | 冯志强 .超薄磨耗层温拌橡胶沥青混合料性能研究[J].公路,2021,66(11):14-20. |
| FENG Zhi-qiang .Research on the performance of ultra-thin wear layer warm-mix rubber asphalt mixture[J].Highway,2021,66(11):14-20. | |
| 7 | TURBAY E, MARTINEZ A G, NAVARRO D T,et al .Rheological behaviour of WMA-modified asphalt binders with crumb rubber[J].Polymers,2022,14(19),4148/1-22. |
| 8 | 《中国公路学报》编辑部 .中国路面工程学术研究综述·2020[J].中国公路学报,2020,33(10):1-66. |
| Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport .Review on China’s pavement engineering research·2020[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2020,33(10):1-66. | |
| 9 | 公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程: [S]. |
| 10 | BOWERS B F, HUANG B S, XIANG S,et al .Investigation of reclaimed asphalt pavement blending efficiency through GPC and FTIR[J].Construction and Building Materials,2014,50:517-523. |
| 11 | LU G Y, ZHANG S W, XU S F,et al .Rheological behavior of warm mix asphalt modified with foaming process and surfactant additive[J].Crystals,2021,11(4):410/1-14. |
| 12 | Standard method of test for determining the rheological properties of asphalt binder using a dynamic shear rheometer (DSR):AA [S]. |
| 13 | Standard method of test for multiple stress creep recovery (M ) test of asphalt binder using a dynamic shear rheometer (DSR):AASHTO TP 70[S]. |
| 14 | Standard method of test for estimating fatigue resistance of asphalt binders using the linear amplitude sweep (LAS):AA [S]. |
| 15 | 刘圣洁,林钰,李梦然,等 .基于MSCR试验的温拌阻燃沥青高温性能评价与分级[J].材料导报,2023,37(9):1-13. |
| LIU Shengjie, LIN Yu, LI Mengran,et al .High temperature performance evaluation and grading of warm-mixed flame retardant asphalt based on MSCR test[J].Material Reports,2023,37(9):1-13. | |
| 16 | ELKASHEF M, WILLIAMS R C .Improving fatigue and low temperature performance of 100% RAP mixtures using a soybean-derived rejuvenator[J].Construction and Building Materials,2017,151:345-352. |
| [1] | TAO Zhuohui, SHEN Shihui, SUN Yang, et al. Foaming Technology and Rheological Characteristics of Surfactant Additive-Foamed Asphalt [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(3): 41-49. |
| [2] | YIN Suhong GUAN Haiyu HU Jie HUANG Haoliang YU Qijun. Rheological Properties and Fluidity of Alkali-activated Fly Ash-slag Grouting Material [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(8): 120-128,135. |
| [3] | Zhao Yong-qing Chen Fu-quan Wu Zheng-huan Feng Yan-hong Jin Gang Qu Jin-ping. Mechanical and Rheological Properties of Polybutylene Succinate / Epoxidized Soybean Oil Blends [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(10): 103-107,116. |
| [4] | Fan Fang-qiang Xia Zheng-bin Li Qing-ying Li Zhong Chen Huan-qin. Effects of Binder Resins on Expansion and Flame-Retardant Performances of Waterborne Fire-Retardant Coatings [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 40(9): 26-31,37. |
| [5] | Luo Zhi-gang Lu Jing-jing. Effect of Lysine on Properties of Tapioca Starch Paste [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(9): 12-16. |
| [6] | Peng Xin-wen Ren Jun-li Sun Run-cang. Investigation into Physicochemical Properties of Xylan Derivatives with High Degree of Substitution [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(8): 82-86. |
| [7] | Feng Yan-hong Li Zhan-hong Qu Jin-ping Liu Bin Xu Bai-ping Wang Zong-ming . Rheological Properties of PBS Composites Reinforced with Sisal Fibers [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(7): 101-106. |
| [8] | Liu Bin Luo Jie-wen Qu Jin-ping Cai Yi-xiang . Effects of Vibration Force Field on Melt Rheological Properties and Phase Isolation During Metal-Powder Injection Molding [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(6): 146-150. |
| [9] | Luo Fa-xing Huang Qiang Zhang Le-xing Li Lin . Viscosity Properties of Acetylated Distarch Adipate Waxy Potato Starch Paste [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(3): 45-49. |
| [10] | Gu Ren-guo Fang Ying-guang . Comparative Experimental Investigation into Effects of Organic Matter and Clayey Mineral on Rheological Properties of Soft Soil [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(10): 31-36. |
| [11] | Li Jian-bin Li Lin Chen Ling Li Bing Fu Xiao-qin. Rheological Properties of Potato Starch Paste Treated by Ultrasonic [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 34(3): 90-94. |
| [12] | Liu Guo-qin Li Lin Li Bing Lu Qi-yu Guo Si-yuan Wan Juan. Rheological Properties of Wet Gluten Protein of Wheat Flour [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 34(3): 86-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||