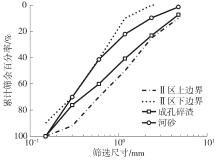
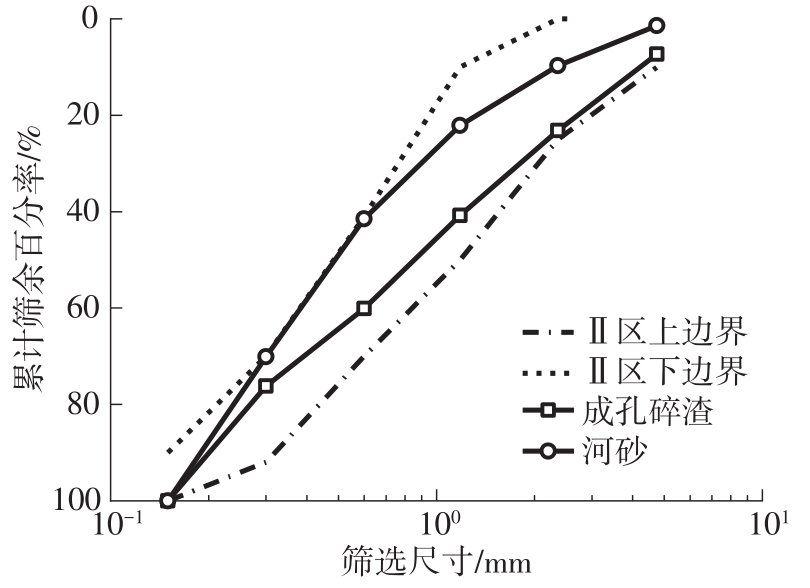
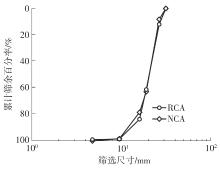
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (9): 120-128.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230008
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Compressive and Chloride Resistance Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Mixed with Hole Slag
WU Bo DING Jinpeng
- State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building Science,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-01-10Online:2023-09-25Published:2023-02-22 -
Contact:吴波(1968-),男,博士,研究员,主要从事建筑固废再生利用与结构抗灾研究。 E-mail:bowu@scut.edu.cn -
About author:吴波(1968-),男,博士,研究员,主要从事建筑固废再生利用与结构抗灾研究。 -
Supported by:the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province(2019B111107003)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WU Bo, DING Jinpeng. Compressive and Chloride Resistance Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Mixed with Hole Slag[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(9): 120-128.
share this article
Table 1
Main parameters of compression test specimens and chloride corrosion resistance test specimens"
| 组别 | 试件编号 | β/% | γ/% | 抗压试件数/个 | 抗氯盐侵蚀 试件数/个 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组1 | HS0-RCA0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| HS50-RCA0 | 50 | 0 | 3 | 3 | |
| HS70-RCA0 | 70 | 0 | 3 | 3 | |
| HS100-RCA0 | 100 | 0 | 3 | 3 | |
| 组2 | HS0-RCA50 | 0 | 50 | 3 | 3 |
| HS50-RCA50 | 50 | 50 | 3 | 3 | |
| HS70-RCA50 | 70 | 50 | 3 | 3 | |
| HS100-RCA50 | 100 | 50 | 3 | 3 | |
| 组3 | HS0-RCA70 | 0 | 70 | 3 | 3 |
| HS50-RCA70 | 50 | 70 | 3 | 3 | |
| HS70-RCA70 | 70 | 70 | 3 | 3 | |
| HS100-RCA70 | 100 | 70 | 3 | 3 | |
| 组4 | HS0-RCA100 | 0 | 100 | 3 | 3 |
| HS50-RCA100 | 50 | 100 | 3 | 3 | |
| HS70-RCA100 | 70 | 100 | 3 | 3 | |
| HS100-RCA100 | 100 | 100 | 3 | 3 |
Table 3
Mix proportions of concrete and solid waste content in concrete"
| 编号 | 用量/(kg·m-3) | 固废含量/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水泥 | 水 | 附加水 | 河砂 | 成孔碎渣 | 天然粗骨料 | 再生粗骨料 | 减水剂 | ||
| HS0-RCA0 | 537.5 | 215 | 0.0 | 576.6 | 0.0 | 1 070.9 | 0.0 | 0.38 | 0.0 |
| HS50-RCA0 | 537.5 | 215 | 0.0 | 288.3 | 288.3 | 1 070.9 | 0.0 | 0.38 | 12.0 |
| HS70-RCA0 | 537.5 | 215 | 0.0 | 173.0 | 403.6 | 1 070.9 | 0.0 | 0.38 | 16.8 |
| HS100-RCA0 | 537.5 | 215 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 576.6 | 1 070.9 | 0.0 | 0.38 | 24.0 |
| HS0-RCA50 | 537.5 | 215 | 5.8 | 576.6 | 0.0 | 535.4 | 535.4 | 0.38 | 22.3 |
| HS50-RCA50 | 537.5 | 215 | 5.8 | 288.3 | 288.3 | 535.4 | 535.4 | 0.38 | 34.3 |
| HS70-RCA50 | 537.5 | 215 | 5.8 | 173.0 | 403.6 | 535.4 | 535.4 | 0.38 | 39.1 |
| HS100-RCA50 | 537.5 | 215 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 576.6 | 535.4 | 535.4 | 0.38 | 46.3 |
| HS0-RCA70 | 537.5 | 215 | 8.1 | 576.6 | 0.0 | 321.3 | 749.6 | 0.38 | 31.2 |
| HS50-RCA70 | 537.5 | 215 | 8.1 | 288.3 | 288.3 | 321.3 | 749.6 | 0.38 | 43.2 |
| HS70-RCA70 | 537.5 | 215 | 8.1 | 173.0 | 403.6 | 321.3 | 749.6 | 0.38 | 48.1 |
| HS100-RCA70 | 537.5 | 215 | 8.1 | 0.0 | 576.6 | 321.3 | 749.6 | 0.38 | 55.3 |
| HS0-RCA100 | 537.5 | 215 | 11.6 | 576.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1 070.9 | 0.40 | 44.6 |
| HS50-RCA100 | 537.5 | 215 | 11.6 | 288.3 | 288.3 | 0.0 | 1 070.9 | 0.40 | 56.6 |
| HS70-RCA100 | 537.5 | 215 | 11.6 | 173.0 | 403.6 | 0.0 | 1 070.9 | 0.40 | 61.4 |
| HS100-RCA100 | 537.5 | 215 | 11.6 | 0.0 | 576.6 | 0.0 | 1 070.9 | 0.40 | 68.6 |
Table 4
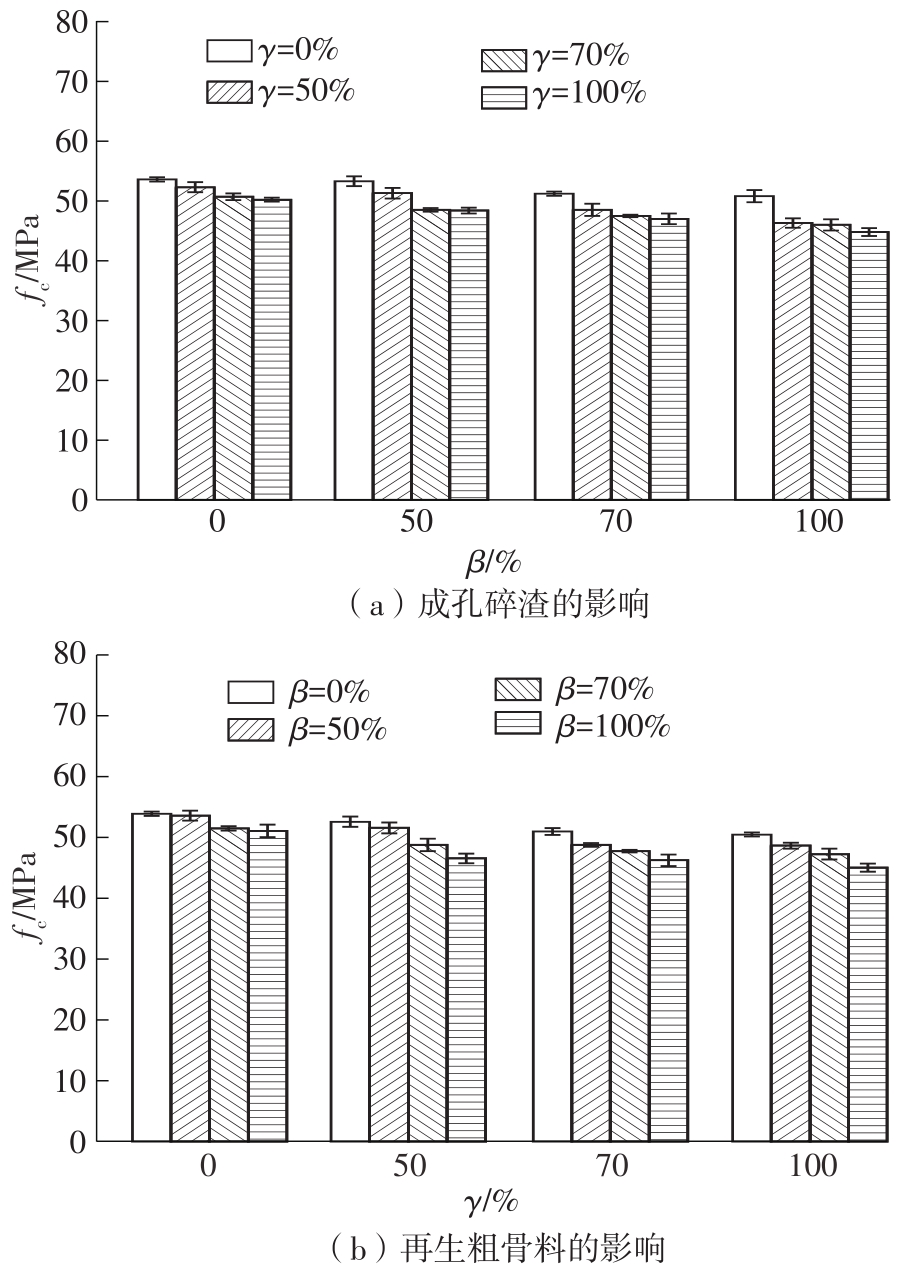
Measured results of compression test"
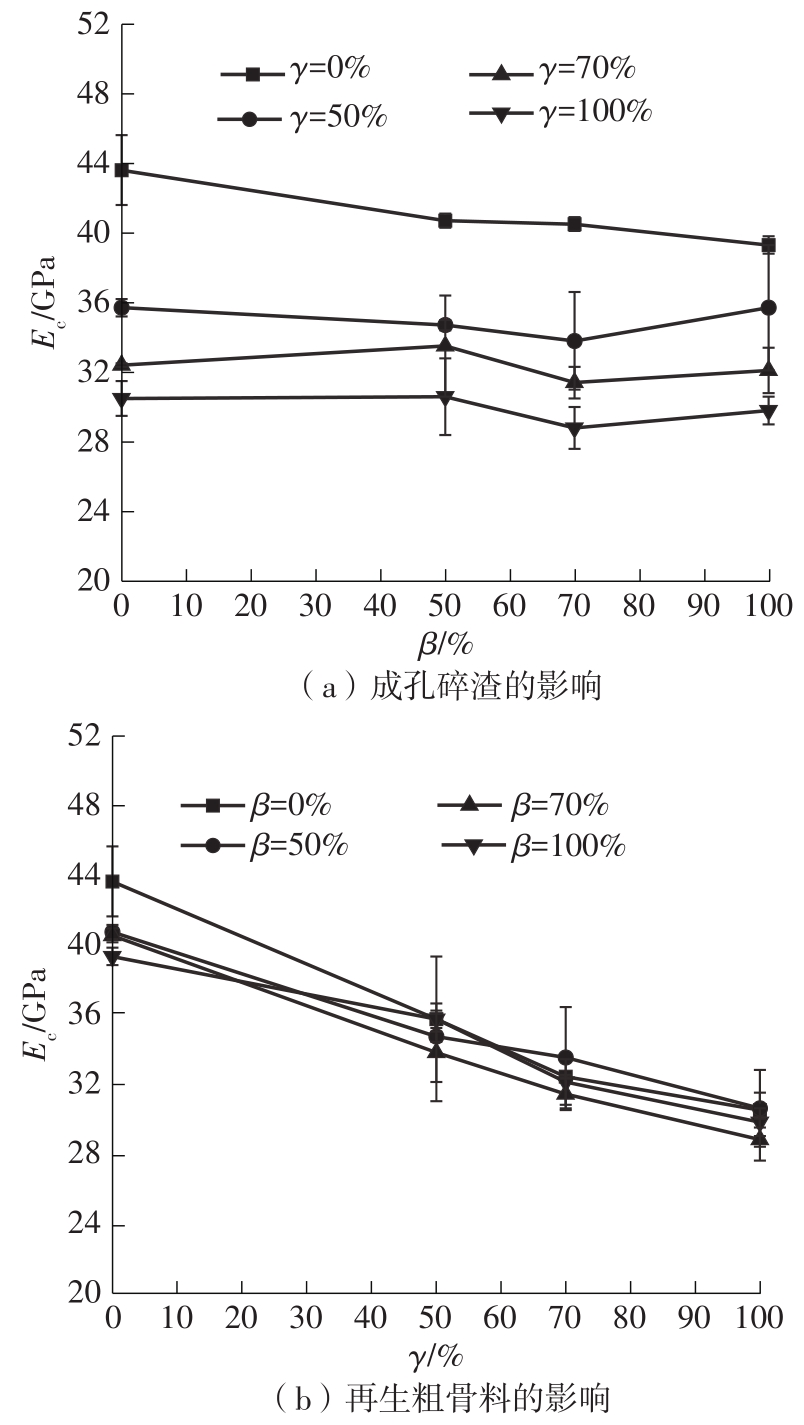
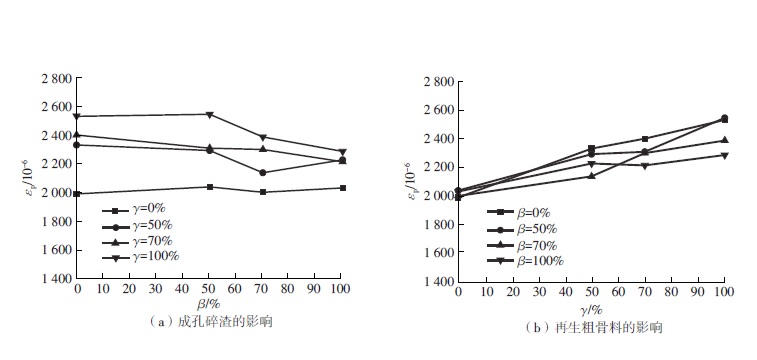
| 组别 | 试件编号 | fc/MPa | Ec/GPa | εp/10-6 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 标准差 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 平均值 | 标准差 | ||
| 组1 | HS0-RCA0 | 53.6 | 0.37 | 43.6 | 2.0 | 1 991 | 65 |
| HS50-RCA0 | 53.3 | 0.81 | 40.7 | 0.4 | 2 040 | 122 | |
| HS70-RCA0 | 51.2 | 0.37 | 40.5 | 0.4 | 2 002 | 146 | |
| HS100-RCA0 | 50.8 | 1.02 | 39.3 | 0.5 | 2 033 | 102 | |
| 组2 | HS0-RCA50 | 52.3 | 0.82 | 35.7 | 0.5 | 2 332 | 149 |
| HS50-RCA50 | 51.3 | 0.90 | 34.7 | 0.3 | 2 293 | 104 | |
| HS70-RCA50 | 48.5 | 1.03 | 33.8 | 2.8 | 2 139 | 73 | |
| HS100-RCA50 | 46.3 | 0.78 | 35.7 | 3.6 | 2 228 | 31 | |
| 组3 | HS0-RCA70 | 50.7 | 0.54 | 32.4 | 0.1 | 2 401 | 69 |
| HS50-RCA70 | 48.5 | 0.31 | 33.5 | 2.9 | 2 310 | 166 | |
| HS70-RCA70 | 47.5 | 0.21 | 31.4 | 0.9 | 2 301 | 89 | |
| HS100-RCA70 | 46.0 | 0.94 | 32.1 | 1.3 | 2 215 | 51 | |
| 组4 | HS0-RCA100 | 50.2 | 0.33 | 30.5 | 1.0 | 2 532 | 80 |
| HS50-RCA100 | 48.4 | 0.49 | 30.6 | 2.2 | 2 546 | 130 | |
| HS70-RCA100 | 47.0 | 0.90 | 28.8 | 1.2 | 2 388 | 92 | |
| HS100-RCA100 | 44.8 | 0.66 | 29.8 | 0.8 | 2 287 | 104 | |
| 1 | 柯晓军,叶春颖,陈世杰,等 .石粉含量及机制砂取代率对再生粗骨料混凝土流动性和抗压强度的影响[J].混凝土,2020(6):106-112. |
| KE Xiaojun, YE Chunying, CHEN Shijie,et al .Effect of stone powder content and machine-made sand replacement rates on fluidity and compressive strength of recycled coarse aggregate concrete [J].Concrete,2020(6):106-112. | |
| 2 | 范德科,马强,周宗辉,等 .石粉对机制砂混凝土性能的影响[J].硅酸盐通报,2016,35(3):913-917. |
| FAN De-ke, MA Qiang, ZHOU Zong-hui,et al .Influence of stone dust on properties of concrete with manufactured sand [J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2016,35(3):913-917. | |
| 3 | 杨海峰,蒋家盛,李德坤,等 .机制砂再生混凝土基本力学性能与微观结构分析[J].硅酸盐通报,2018,37(12):3946-3950. |
| YANG Hai-feng, JIANG Jia-sheng, LI De-kun,et al .Analysis on basic mechanical properties and microstructure of concrete made with manufactured sand and recycled coarse aggregate [J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2018,37(12):3946-3950. | |
| 4 | 谢开仲,刘振威,郑克西,等 .不同颗粒级配下机制砂混凝土性能研究[J].混凝土,2021(4):91-95. |
| XIE Kaizhong, LIU Zhenwei, ZHENG Kexi,et al .Research on the properties of manufactured sand concrete with different grain composition [J].Concrete,2021(4):91-95. | |
| 5 | 宁勇伟,陈迎周,范泽润,等 .机制砂颗粒特性对高强混凝土性能的影响[J].中国建材科技,2022,31(6):21-24. |
| NING Yongwei, CHEN Yingzhou, FAN Zerun,et al .Influence of manufactured sand with different particle characteristics on properties of high-strength concrete [J].China Building Materials Science and Technology,2022,31(6):21-24. | |
| 6 | 宋少民,程成,杨楠 .机制砂岩性对胶砂和混凝土性能影响的研究[J].混凝土,2019(9):67-70. |
| SONG Shaomin, CHENG Cheng, YANG Nan .Influence of manufactured sand lithology on mortar and concrete performance [J].Concrete,2019(9):67-70. | |
| 7 | 熊先达 .机制砂岩性和级配对混凝土氯离子渗透性的影响[D].南昌:南昌大学,2019. |
| 8 | 罗健勇,于本田,苏俊辉,等 .机制砂颗粒级配对混凝土性能的影响研究[J].公路,2022,67(9):384-388. |
| LUO Jianyong, YU Bentian, SU Junhui,et al .Study on the influence of manufactured sand particle grading on the performance of concrete [J].Highway,2022,67(9):384-388. | |
| 9 | FENG J C, DONG C Q, CHEN C H,et al .Effect of manufactured sand with different quality on chloride penetration resistance of high-strength recycled concrete [J].Materials,2021,14:7101. |
| 10 | LIN L, WU B .Water permeability behavior of recycled lump/aggregate concrete [J].Construction and Building Materials,2022,323:126508/1-16. |
| 11 | Standard test method for compressive strength of cylindrical concrete specimens: [S]. |
| 12 | LAMOND J F .Significance of tests and properties of concrete and concrete-making materials [M].West Conshohocken,PA:ASTM International,2006:194-206. |
| 13 | LI H J, WANG Z, HUANG F L,et al .Impact of different lithological manufactured sands on high-speed railway box girder concrete [J].Construction and Building Materials,2020,230:116943/1-9. |
| 14 | HTET P, CHEN W S, HAO H,et al .Physical and mechanical properties of quqternary blended concrete with recycled coarse aggregates and crushed waste glass [J].Construction and Building Materials,2022,353:129016/1-20. |
| 15 | 李旭平 .再生混凝土基本力学性能研究(Ι)——单轴受压性能[J].建筑材料学报,2007,10(5):598-603. |
| LI Xu-ping .Study on mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete (Ι)—behaviour under uniaxial compression [J].Journal of Building Materials,2007,10(5):598-603. | |
| 16 | BAO J W, LI S G, ZHANG P,et al .Influence of the incorporation of recycled coarse aggregate on water absorption and chloride penetration into concrete [J].Construction and Building Materials,2020,239:117845/1-9. |
| 17 | WU Y W, LIU C, LIU H W,et al .Pore structure and durability of green concrete containing recycled powder and recycled coarse aggregate [J].Journal of Building Engineering,2022,53:104584/1-20. |
| 18 | 陈昭南 .掺有花岗岩风化残积土再生砂的再生块体/骨料混凝土的收缩性能研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2022. |
| [1] | WU Bo, HUANG Tingting. Carbonation Properties and Pore Characteristics of Different Interfaces in Recycled Lump/Aggregate Concrete [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 52-60. |
| [2] | LIU Xin, YAO Yunlong, YAO Zirui, et al. Effect of Low Air Pressure on Performance and Pore Structure of Foamed Concrete in Pouring Period [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 72-80. |
| [3] | ZHOU Linren, LI Shaoji, CHEN Lan. Experimental Investigation into Effect of Surface Roughness on Convective Heat Transfer of Concrete [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(7): 81-89. |
| [4] | XIE Xiaoli, GOU Wenxin, PANG Mulin, et al. Dynamic Characteristics of RC Rigid Frame Arch Bridge Strengthened by Plate-Truss Combination [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 31-43. |
| [5] | Yu Qijun, Ma Ting, Zhang Tongsheng, et al. Effect of particle size on hydration kinetics and microstructure development of recycled brick powder-cement pastes [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(11): 63-73. |
| [6] | WU Bo, CHEN Zhaonan, WANG Hui. Creep Behavior of Reinforced and Unreinforced Recycled Lump/Aggregate Concrete [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 35-42. |
| [7] | SUN Xiaohe, SHI Chenghua, LIU Linghui, et al. Concrete Crack Image Recognition System Based on Improved Seed Filling Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 127-136,146. |
| [8] | ZHENG Hongyu, YU Yuqi, XU Dixin, et al. Axial Compression Test of Seawater Sea-Sand Concrete Circular Column Inner-Confined by BFRP Spiral Strip [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 96-108. |
| [9] | LUO Xiaoyong, CHENG Qian, CHENG Junfeng, et al. Mechanical Properties of Hydrochloric Acid Corroded Concrete Under Cyclic Loading [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 73-85. |
| [10] | XIONG Ergang, ZU Kun, HU Qinbin, et al. Shear Capacity Prediction for RC Beams Without Stirrups Based on Mechanical Research [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(11): 115-124. |
| [11] | LING Yuhong, LIAO Haopeng, XU Jinghang, et al. Study on Mechanical Behavior of New Type Middle Joint of CFST Composite Column-Concrete Beam [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(11): 82-94. |
| [12] | ZHOU Zhong, DENG Zhuoxiang, CHEN Yun, et al. Strength Prediction of Foam Light Soil Based on GA-BP Neural Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(11): 125-132. |
| [13] | LING Yuhong, WEN Xingui, ZHENG Wenli, 等. Experimental Study on Mechanical Behavior of New Type Side Joint of CFST Composite Column-Concrete Beam [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(1): 38-49. |
| [14] | YANG Youfu GUO Hongxin. Axial Compression Behavior of the Stiffened Concrete-Filled Thin-Walled High-Strength Square Steel Tube Stub Columns [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(8): 43-52. |
| [15] | TIAN Li LI Jie LI Menghui. Damage of Concrete Sandwich Wall Subjected to Synergistic Effects of Blasts and Fragments [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(8): 53-64. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||