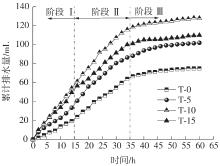
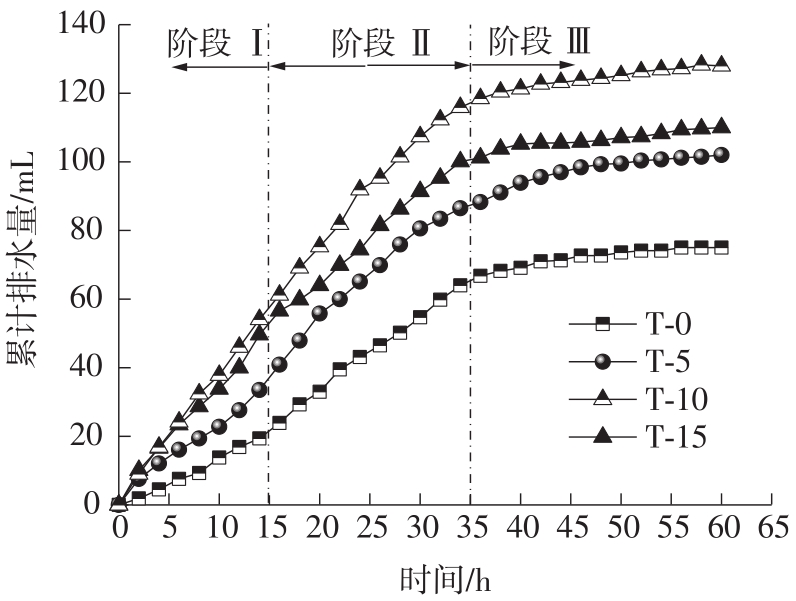
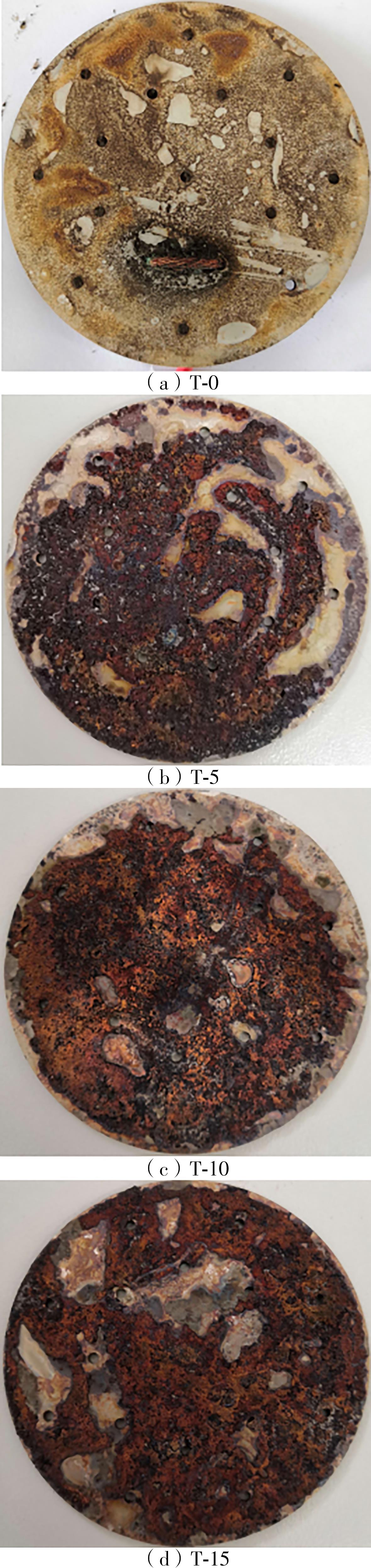
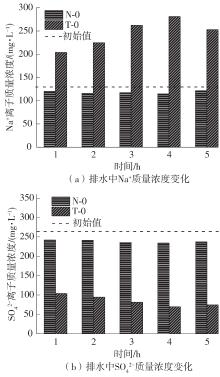
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 53-60.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220359
Special Issue: 2023年土木建筑工程
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
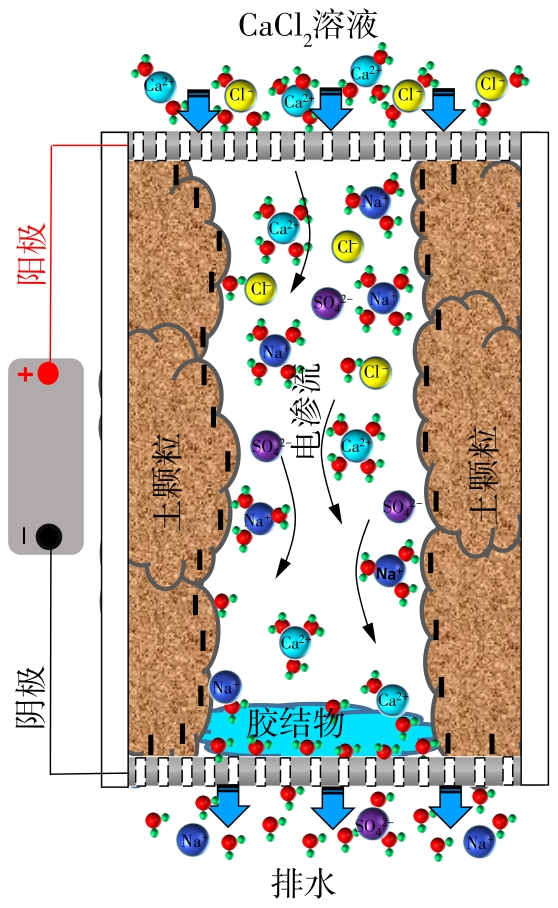
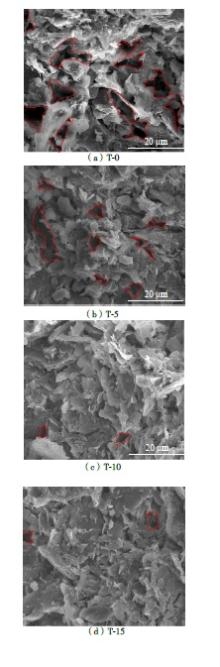
Influence of Electroosmosis-Calcium Chloride Treatment on the Deformation of Sodium Sulfate Saline Soil
ZHANG Heng1,2,3,4 HUANG Junguang4 LI Weike4 LI Jianbin4
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangzhou Municipal Construction Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510030,Guangdong,China
3.Guangzhou Construction Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510030,Guangdong,China
4.Guangzhou Design Institute Group Co. ,LTD,Guangzhou 510620,Guangdong,China