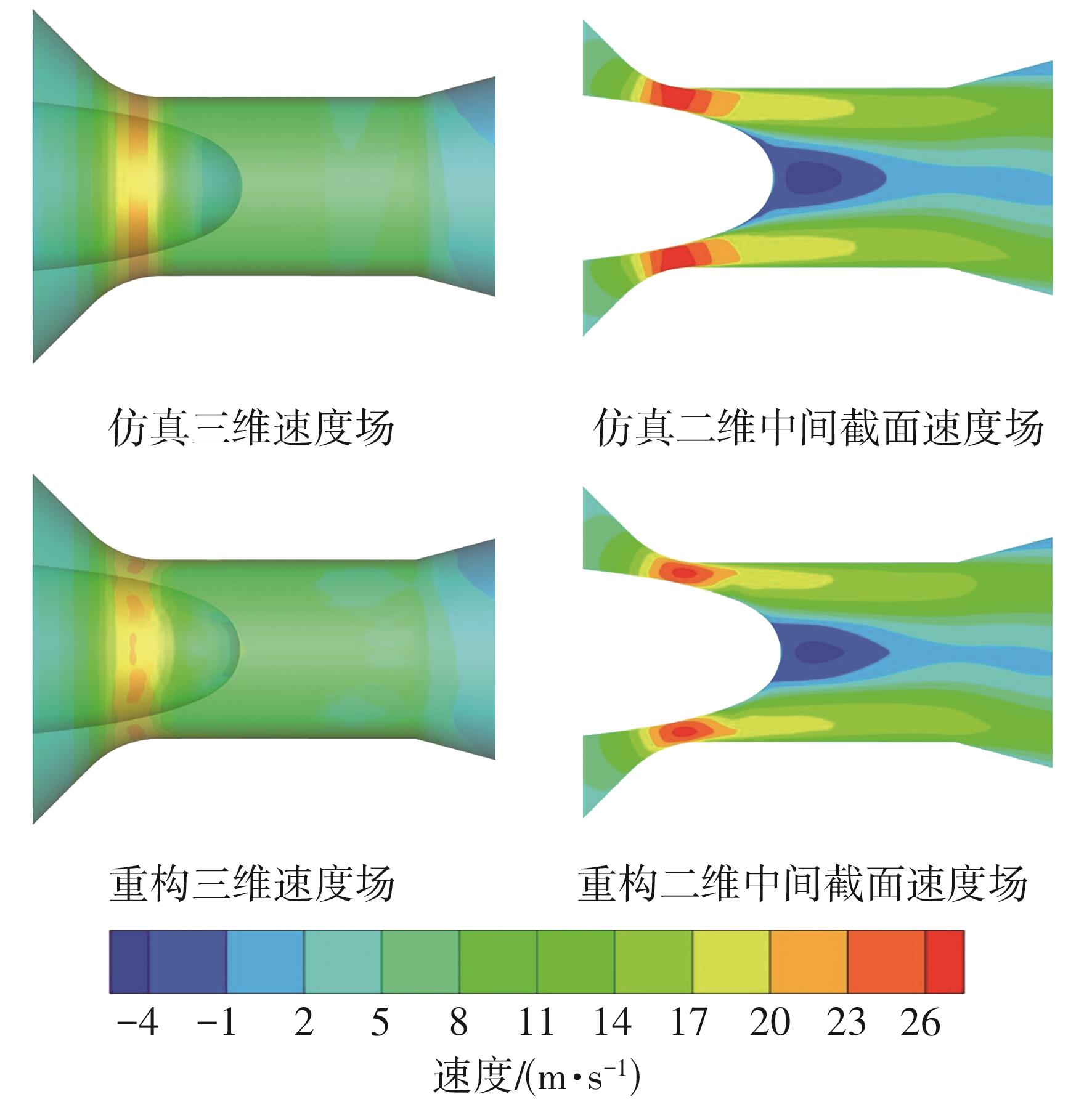
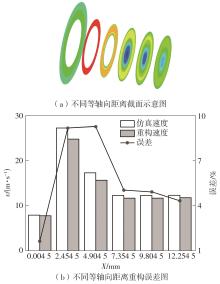
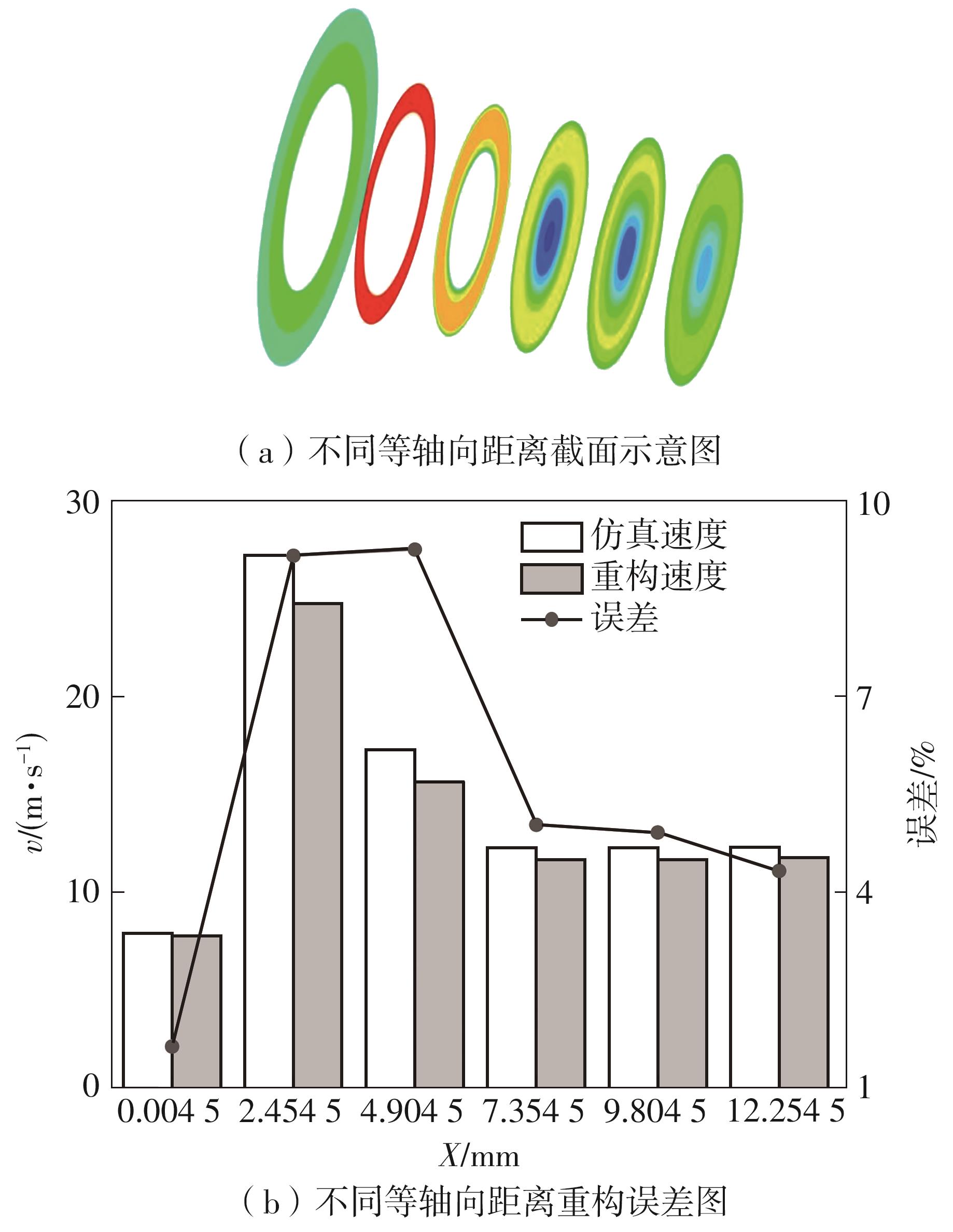
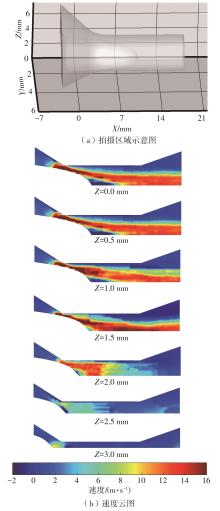
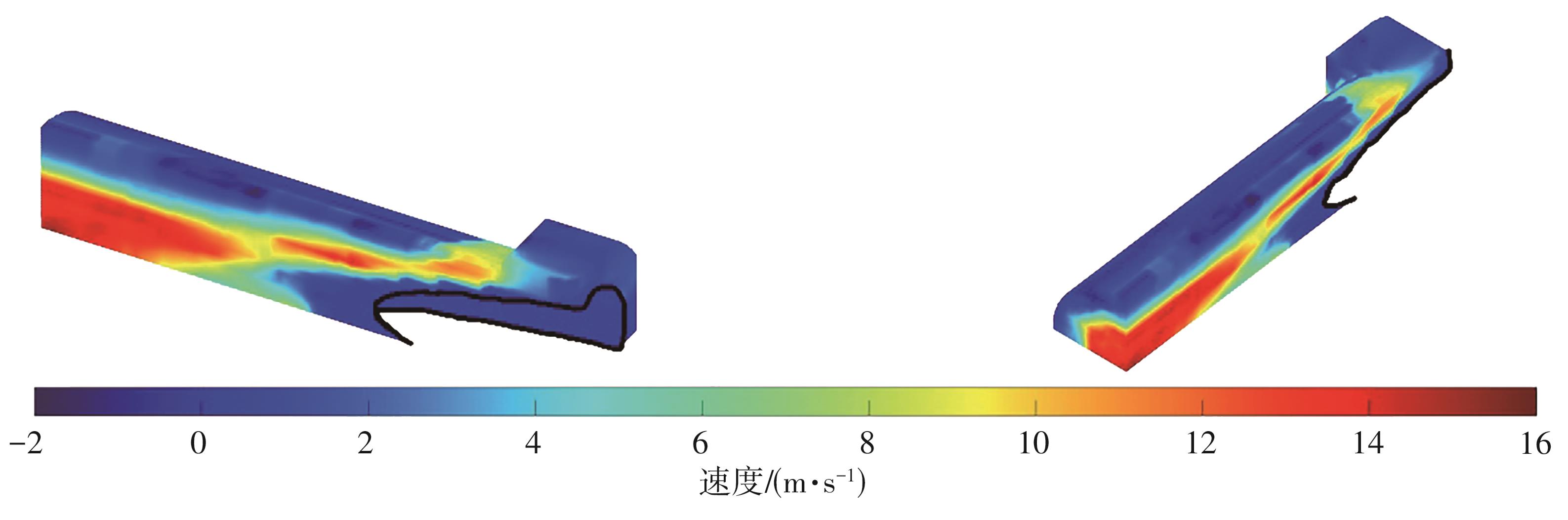
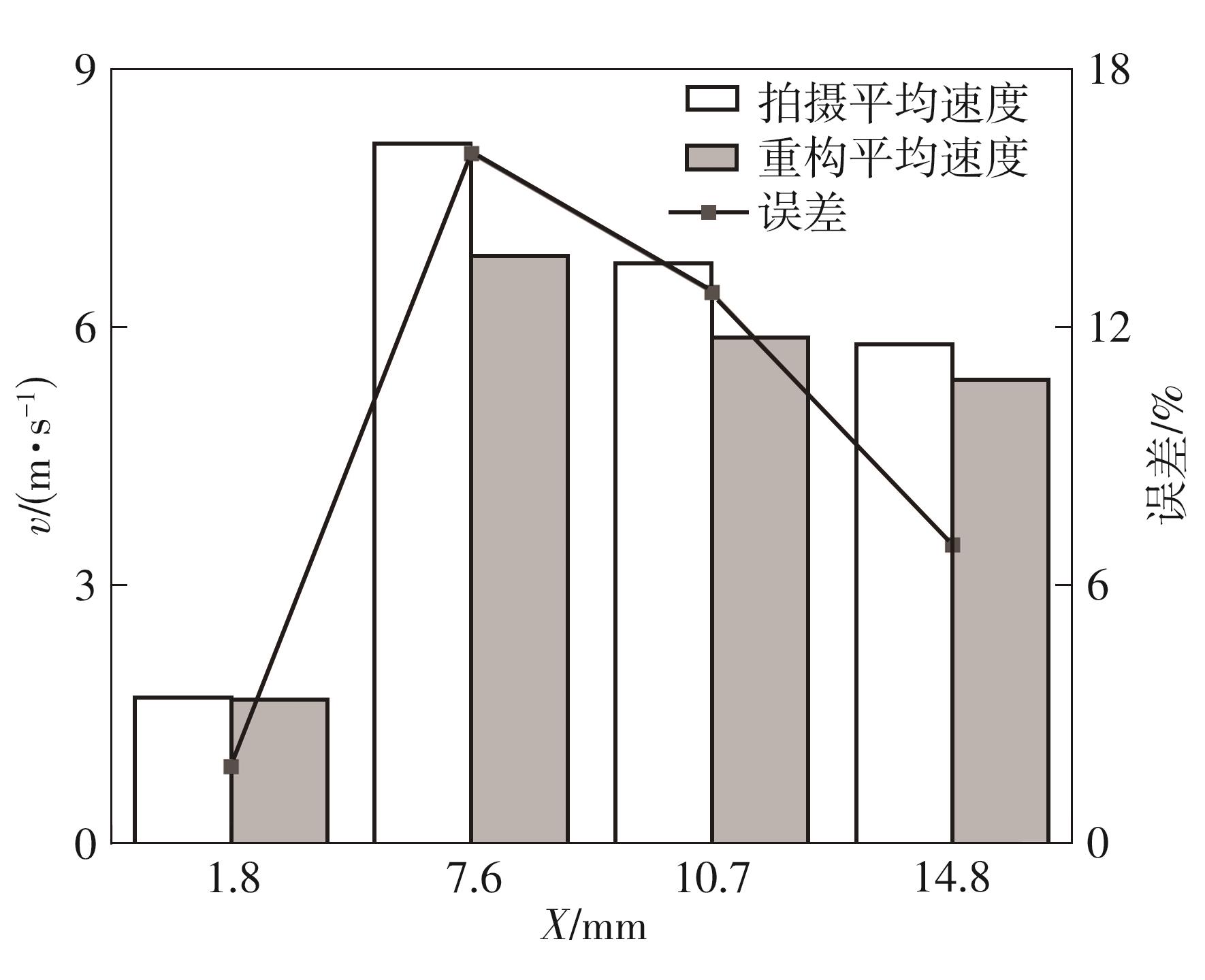
| 1 |
姜珊珊 .煤直接液化产品特性与产业应用[J].能源科技,2022,20(2):64-68.
|
|
JIANG Shanshan .Characteristics and industrial application of direct coal liquefaction products [J].Energy Science and Technology,2022,20(2):64-68.
|
| 2 |
李树勋,丁强伟,徐晓刚,等 .超(超)临界多级套筒调节阀空化抑制模拟研究[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(3):37-41.
|
|
LI Shuxun, DING Qiangwei, XU Xiaogang,et al .Numerical study on cavitation suppression in ultra-supercritical multistage sleeve control valve[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2015,43(3):37-41.
|
| 3 |
李连翠,王周杰,张含,等 .基于CFX的调节阀空化数值模拟及结构优化[J].动力工程学报,2021,41(12):1103-1108.
|
|
LI Liancui, WANG Zhoujie, ZHANG Han,et al .Numerical simulation of cavitation and structure optimization of a control valve based on CFX [J].Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering,2021,41(12):1103-1108.
|
| 4 |
CHATTOPADHYAY H, KUNDU A, SAHA B K,et al .Analysis of flow structure inside a spool type pressure regulating valve[J].Energy Conversion and Management,2012,53(1):196-204.
|
| 5 |
郝娇山,尚洪宝,蒋永兵,等 .煤化工专用黑水阀阀座流通性能研究[J].自动化与仪器仪表,2014(6):43-46.
|
|
HAO Jiaoshan, SHANG Hongbao, JIANG Yongbing,et al .Study on flow performance of blackwater valve seat for coal chemical industry[J].Automation and Instrumentation,2014(6):43-46.
|
| 6 |
王燕,徐晓刚,胡建,等 .多级套筒调节阀流场数值模拟与流量特性研究[J].石油化工自动化,2013,49(1):50-53.
|
|
WANG Yan, XU Xiaogang, HU Jian,et al .Numerical simulation of flow field and research of flow characteristics of multi-stage cage control valve [J].Automation in Petro-chemical Industry,2013,49(1):50-53.
|
| 7 |
ZHENG Z J, OU G F, YI Y W,et al .A combined numerical-experiment investigation on the failure of a pressure relief valve in coal liquefaction[J].Enginee-ring Failure Analysis,2016,60:326-340.
|
| 8 |
吴姿宏,刘秀梅,李贝贝,等 .基于图像灰度统计的调节阀空化分布特性研究[J].机械工程学报,2023,59(2):307-316.
|
|
WU Zihong, LIU Xiumei, LI Beibei,et al .Research on cavitation distribution characteristics in regulate valve based on image gray statistics[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2023,59(2):307-316.
|
| 9 |
柴博森,王广义,朱国仁,等 .制动工况下液力变矩器大涡模拟流场仿真及可视化试验验证[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(3):95-105.
|
|
CHAI Bosen, WANG Guangyi, ZHU Guoren,et al .Large eddy simulation flow field analysis and visualization test verification of hydraulic torque converter under braking conditions[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(3):95-105.
|
| 10 |
YANG S, LI S, TIAN H,et al .Tomographic PIV investigation on coherent vortex structures over shark- skin-inspired drag-reducing riblets[J].Acta Mechanica Sinica,2016,32(2):284-294.
|
| 11 |
田海平,伊兴睿,钟山,等 .基于Stereo-PIV技术的三维发卡涡结构定量测量研究[J].力学学报,2020,52(6):1666-1677.
|
|
TIAN Haiping, YI Xingrui, ZHONG Shan,et al .Experimental study on quantitative measurement of three-dimensional structure of hairpin vortex by Stereo-PIV [J].Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2020,52(6):1666-1677.
|
| 12 |
高琪,王洪平,王晋军 .一种单相机三维体视PIV技术及其应用[J].中国科学:技术科学,2012,42(9):985-996.
|
|
GAO Qi, WANG Hongping, WANG Jinjun .A single camera volumetric particle image velocimetry and its application[J].Science China:Technological Sciences,2012,42(9):985-996.
|
| 13 |
张皎丹 .基于PIV的单弯管下游三维流场测量方法研究[D].天津:天津大学,2014.
|
| 14 |
朱效宇,张彪,李健,等 .基于预识别技术及SART算法的单光场相机三维流场重建[J].工程热物理学报,2020,41(6):1445-1451.
|
|
ZHU Xiao-yu, ZHANG Biao, LI Jian,et al .Reconstruction of tracer particle distribution in light field PIV using pre-recognition-based SART algorithm[J].Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2020,41(6):1445-1451.
|
| 15 |
李庆浩,赵陆海波,张彪,等 .基于光场成像的气液两相流中气泡三维测量方法[J].东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,48(6):1143-1151.
|
|
LI Qinghao, ZHAO Luhaibo, ZHANG Biao,et al .Three-dimensional measurement of bubble in gas-liquid flow by light field photography [J].Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition),2018,48(6):1143-1151.
|
| 16 |
ZHAO Z, BUCHNER A, ATKINSON C,et al .Volumetric measurements of a self-similar adverse pressure gradient turbulent boundary layer using single-camera light-field particle image velocimetry[J].Experiments in Fluids,2019,60(9):141/1-14.
|
| 17 |
KRAVTSOVA A Y, MARKOVICH D M, PERVUNIN K S,et al .High-speed visualization and PIV measurements of cavitating flows around a semi-circular leading-edge flat plate and NACA0015 hydrofoil[J].International Journal of Multiphase Flow,2014,60:119-134.
|
| 18 |
WANG G, QIN X J, SHEN J N,et al .Quantitative analysis of microscopic structure and gas seepage characteristics of low-rank coal based on CT three-dimensional reconstruction of CT images and fractal theory[J].Fuel,2019,256:115900/1-11.
|