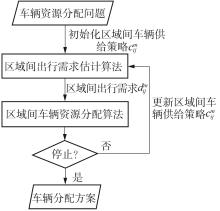
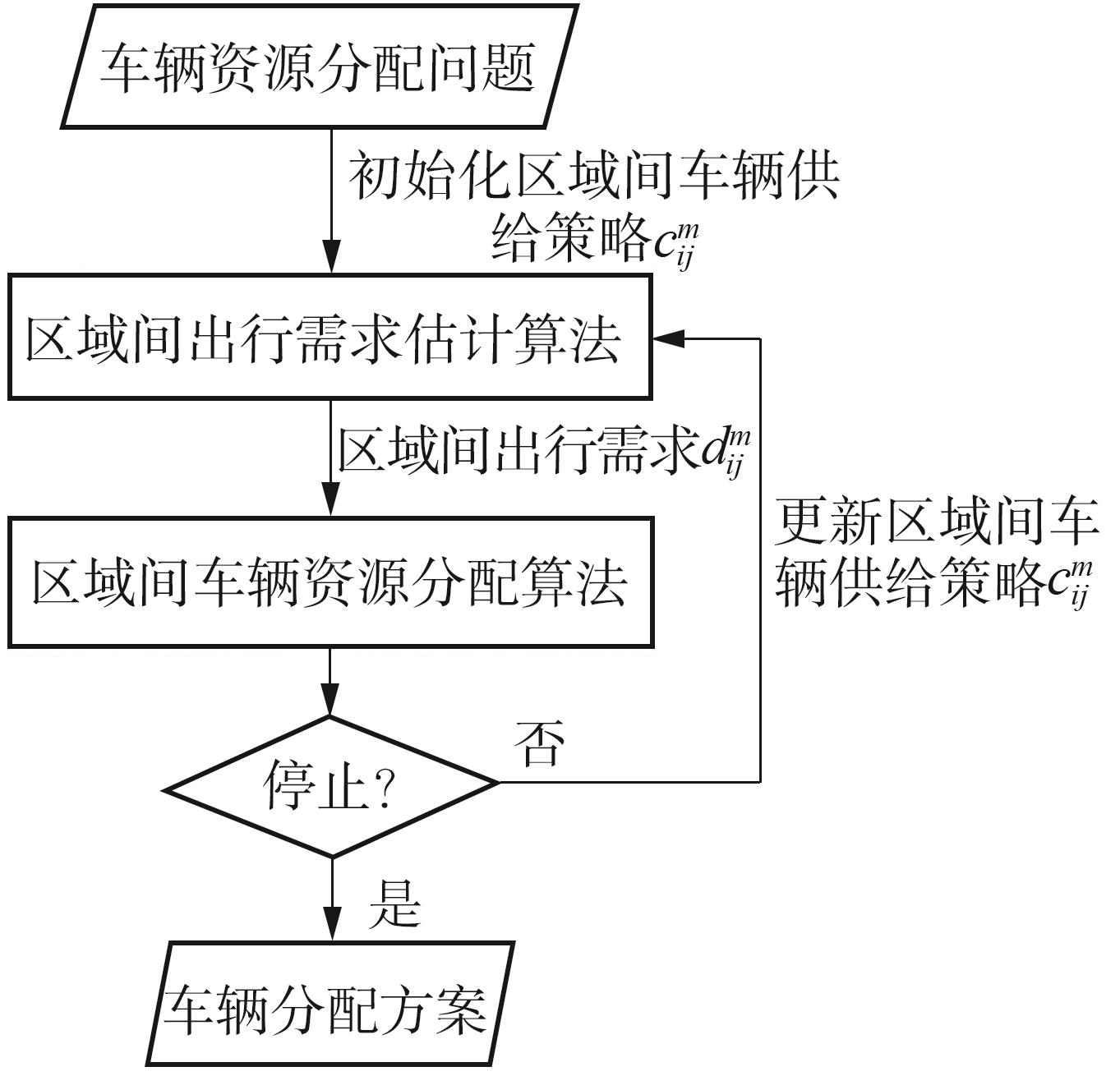
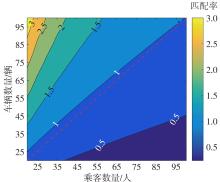
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (10): 89-98.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230182
Special Issue: 2023绿色智慧交通系统专辑
• Green, Intelligent Traffic System • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on the Multi-Period Allocation Method of Vehicle Resource in Hybrid Service Mode
SHEN Yutong1 LI Ming2 CUI Zhiyong1 YU Bin1
- 1.School of Transportation Science and Engineering,Beihang University,Beijing 102206,China
2.School of Transportation Engineering,Shandong Jianzhu University,Jinan 250101,Shandong,China
-
Received:2023-04-05Online:2023-10-25Published:2023-07-03 -
Contact:崔志勇(1993-),男,博士,副教授,主要从事交通交通数据科学、人工智能等研究。 E-mail:zhiyongc@buaa.edu.cn -
About author:沈羽桐(1993-),女,博士生,主要从事共享出行建模与优化等研究。E-mail:Shenyutong9368@163.com -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52202378)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
SHEN Yutong, LI Ming, CUI Zhiyong, et al. Study on the Multi-Period Allocation Method of Vehicle Resource in Hybrid Service Mode[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 89-98.
share this article
Table 1
Parameters and variables used in the model"
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| m | 参数上标, |
| i,j | 参数下标, |
| R | 区域集合 |
| 子交通网络集合 | |
| 匹配率相对于未匹配车辆数、等待乘客数及路网平均速度的弹性系数 | |
| 选择出行模式m的乘客的时间价值系数 | |
| 出行模式m下单位行驶里程的出行费用 | |
| 决策变量,平台预估区域i至区域j出行模式m的等待服务乘客数量 | |
| 从区域i至区域j内的等待响应乘客数量的最大值 | |
| 从区域i至区域j内的等待服务乘客数量 | |
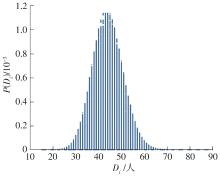
| 区域i内等待服务乘客数量 | |
| 决策变量,出行模式m下从区域i至区域j调派的车 辆数 | |
| 出行模式m下区域i内的平台在线车辆数量 | |
| 系统能够服务的从区域i至区域j选择出行模式m的乘客数量 | |
| 区域i至区域j独乘乘客的平均行驶里程 | |
| 出行模式m下从区域i至区域j的单位行驶里程运行 成本 | |
| 区域i至区域j选择出行模式m的效用值 | |
| 区域i和区域j路网的车辆平均运行速度 | |
| 出行模式m下从区域i至区域j乘客的平均出行时间 | |
| 出行模式m下从区域i至区域j乘客的平均等待时间 | |
| 合乘出行模式下从区域i至区域j乘客的平均绕行时间 | |
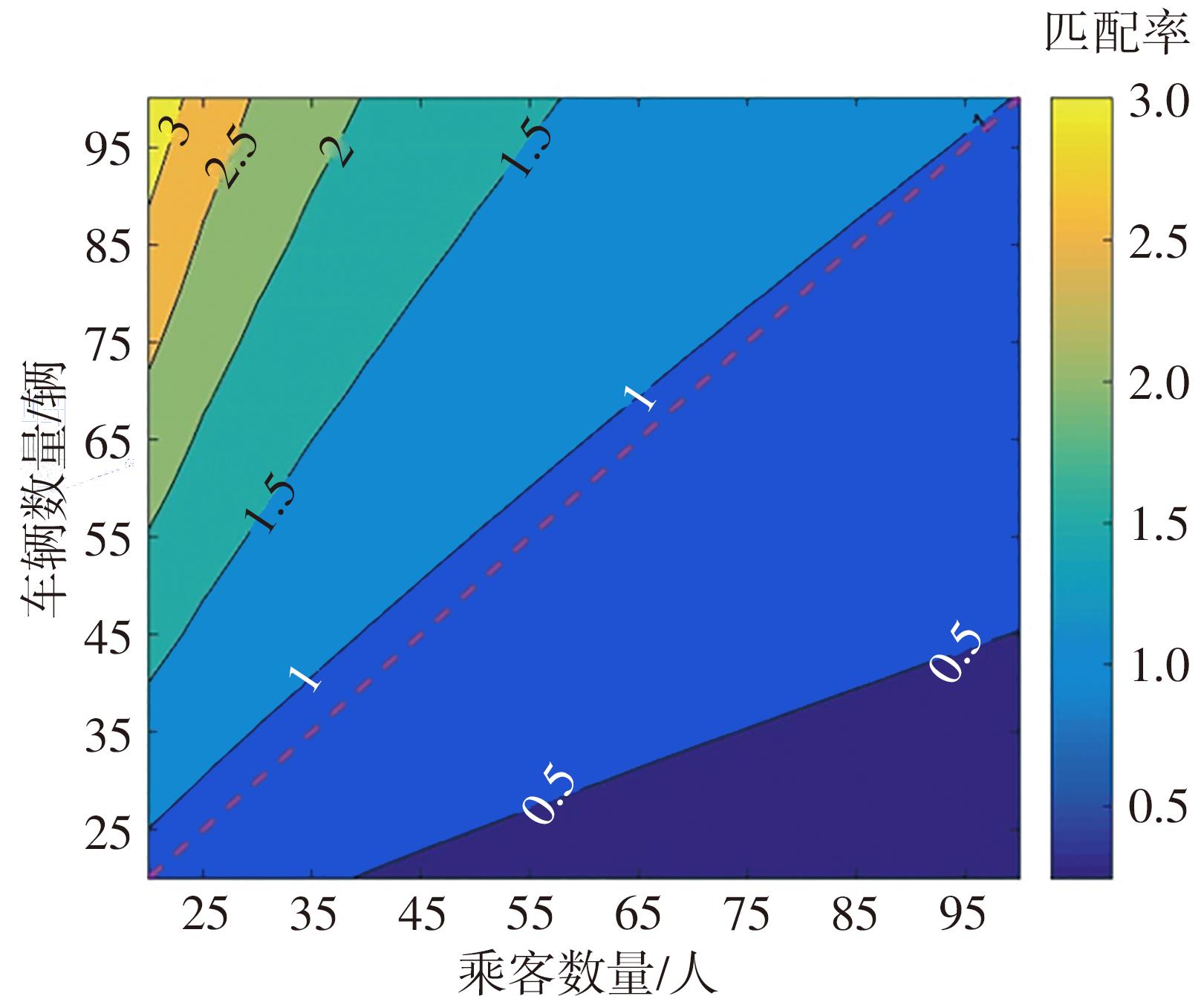
| 出行模式m下从区域i至区域j乘客的匹配率(%) |
Table 3
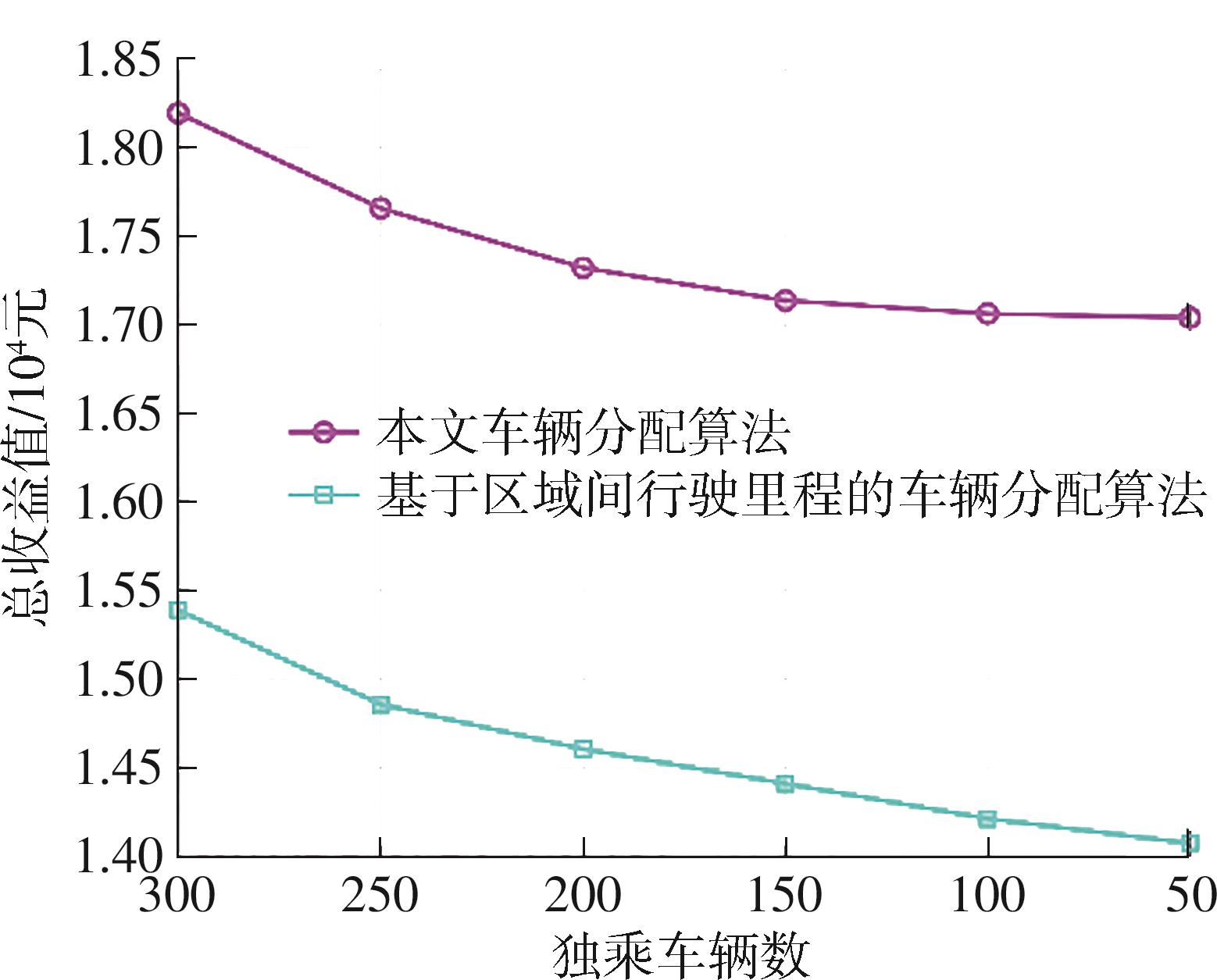
Comparison of the total revenue with different vehicle supplies"
| 车辆数量变化量 | 独乘车辆 | 合乘车辆 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 收益值/元 | 变化百分比/% | 收益值/元 | 变化百分比/% | |
| 0 | 18 188.72 | 18 188.72 | ||
| -50 | 17 652.51 | -2.90 | 16 857.65 | -7.32 |
| -100 | 17 317.51 | -4.78 | 15 675.89 | -13.82 |
| -150 | 17 132.98 | -5.80 | 14 711.37 | -19.12 |
| -200 | 17 058.79 | -6.21 | 14 013.83 | -22.95 |
| -250 | 17 036.16 | -6.34 | 13 574.83 | -25.37 |
| 1 | KRUEGER R, RASHIDI T H, ROSE J M .Preferences for shared autonomous vehicles[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2016,69:343-355. |
| 2 | MA J, LI X, ZHOU F,et al .Designing optimal autonomous vehicle sharing and reservation systems:a linear programming approach[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2017,84:124-141. |
| 3 | LEVIN M W .Congestion-aware system optimal route choice for shared autonomous vehicles[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2017,82:229-247 |
| 4 | BONGIOVANNI C, KASPI M, GEROLIMINIS N .The electric autonomous dial-a-ride problem[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2019,122:436-456 |
| 5 | MAHMOUDI M, ZHOU X .Finding optimal solutions for vehicle routing problem with pickup and delivery services with time windows:a dynamic programming approach based on state-space-time network representations [J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2016,89:19-42 |
| 6 | MASOUD N, JAYAKRISHNAN R .A decomposition algorithm to solve the multi-hop Peer-to-Peer ride-matching problem[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2017,99:1-29. |
| 7 | 丁冉 .出租车动态合乘匹配问题研究[D].南京:东南大学,2015. |
| 8 | 肖强,何瑞春,张薇,等 .基于模糊聚类和识别的出租车合乘算法研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2014,14(5):119-125. |
| XIAO Qiang, HE Ruichun, ZHANG Wei,et al .Algorithm research of taxi carpooling based on fuzzy clustering and fuzzy recognition[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2014,14(5):119-125. | |
| 9 | HAME L, HAKULA H .A maximum cluster algorithm for checking the feasibility of dial-a-ride instances[J].Transportation Science,2015,49(2):295-310. |
| 10 | 郑建国,李园园 .基于改进差分进化算法的出租车合乘问题研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2018,18(1):121-126. |
| ZHENG Jianguo, LI Yuanyuan .Shared taxi problem based on the improved differential evolution algorithm[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2018,18(1):121-126. | |
| 11 | 郭羽含,伊鹏 .车辆合乘问题的分布式复合变邻域搜索算法[J].计算机科学与探索,2019,13(2):330-341. |
| GUO Yuhan, YI Peng .Distributed hybrid variable neighborhood search algorithm for carpooling problem[J].Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science & Technology,2019,13(2):330-341. | |
| 12 | YANG H, LEUNG C W Y, WONG S C,et al .Equilibria of bilateral taxi-customer searching and meeting on networks[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2010,44(8/9):1067-1083. |
| 13 | RAMEZANI M, NOURINEJAD M .Dynamic modeling and control of taxi services in large-scale urban networks:A macroscopic approach[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2018,94:203-219. |
| 14 | CAO Z, CEDER A .Autonomous shuttle bus service timetabling and vehicle scheduling using skip-stop tactic[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2019,102:370-395. |
| 15 | ABE R .Introducing autonomous buses and taxis:quantifying the potential benefits in Japanese transportation systems[J].Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice,2019,126:94-113. |
| 16 | FISHER M L .An applications oriented guide to Lagrangian relaxation[J].Interfaces,1985,15(2):10-21. |
| [1] | . Review of the Impact of Spatiotemporal Constraints on Active Travel [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(2): 113-123. |
| [2] | ZHUANG Yan, DONG Chunjiao, MI Xueyu, WANG Jing, YANG Miaoyan. Identification of Accident Black Spots Based on Improved Network Kernel Density and Negative Binomial Regression [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 119-126. |
| [3] | ZHAO Xiaomei, HAO Guoyu, NIU Xiaojing, ZHOU Zhiqian. Traffic Boundary Control Strategy Based on Macroscopic Fundamental Diagram Under Different Rainfall [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 72-82. |
| [4] | HU Xinghua, CHEN Xinghui, WANG Ran, et al. Optimization Model of Bus Priority Control Considering Carbon Emissions with Stochastic Characteristics [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 160-170. |
| [5] | XU Lunhui, YU Jiaxin, PEI Mingyang, et al. Repositioning Strategy for Ride-Hailing Vehicles Based on Geometric Road Network Structure and Reinforcement Learning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(10): 99-109. |
| [6] | WANG Hao, XIE Ning . Coordinated Optimization Model of Arterial Segmented Green Waves Considering the Efficiency of Tram Operation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(1): 95-105. |
| [7] | ZHAO Jiandong, ZHU Dan, LIU Jiaxin. Metro Transfer Passenger Flow Prediction Based on STL-GRU [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 22-31. |
| [8] | WU Jiaorong XIE Jinhong WANG Yuqin. The Profiling Method of Instability of Bus Route Operation and Its Application [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(2): 15-22. |
| [9] | CHEN Xiaohong, HU Fang . Interval Optimization Model of Signal Control at Intersection Based on Possibility Degree [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(10): 29-40. |
| [10] | YU Lijun. Generalized System-Optimal Traffic Assignment with Link Capacity Constraints [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(4): 140-148. |
| [11] | YAO Enjian LU Muyang LIU Yuhuan YUAN Ling. Electric Bus Area Driving Plan Preparation Considering Charging Constraints [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(9): 68-73. |
| [12] | LIU Zhongbo ZHAO Xiaohui. A Dynamic Allocation and Guidance Model for Parking Spaces with Minimum Total Parking Costs#br# [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 92-98. |
| [13] | LU Kai LIN Maowei DENG Xingdong XU Guanghui XU Jianmin. A model of area dynamic allocation and guidance of parking space with the minimum total parking cost [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(9): 82-91,98. |
| [14] |
CHEN Xiaohong ZHANG Xiekui CHEN Shimiao.
Interval Decision Making Model of Cycle Length at Signal Intersection
|
| [15] | TIAN Sheng XU Kai . Evolutionary Model of Traffic Flow in Crowded and Charged Routes Considering Heterogeneous Travelers [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(11): 110-116. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||