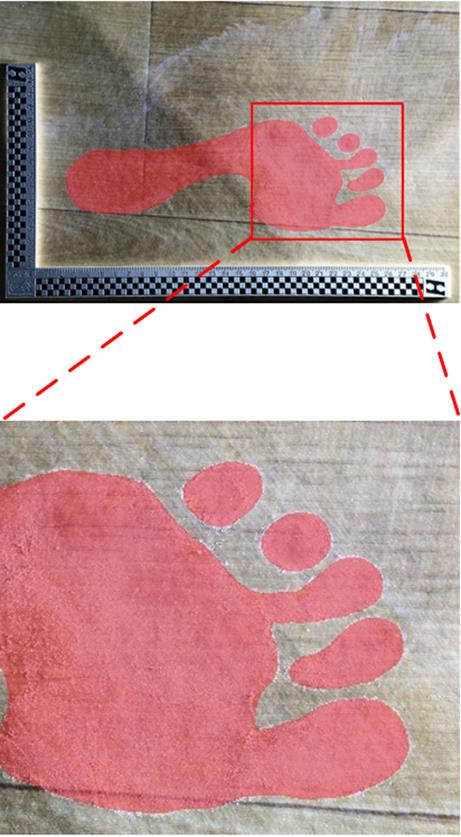
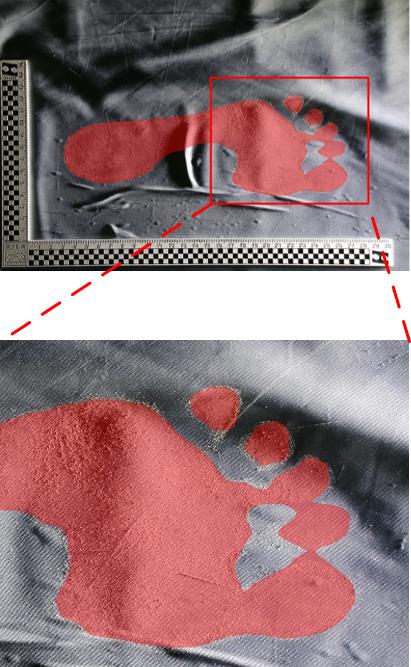
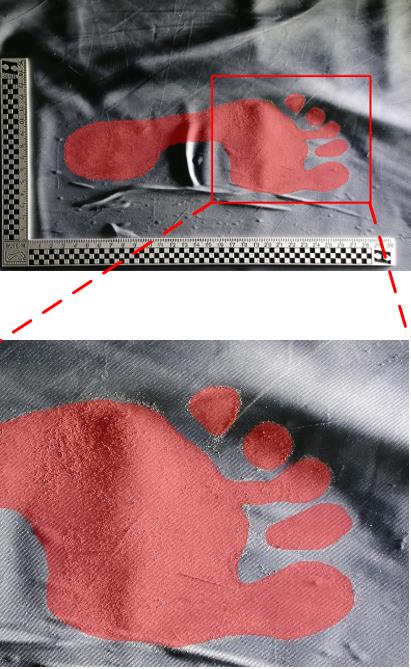
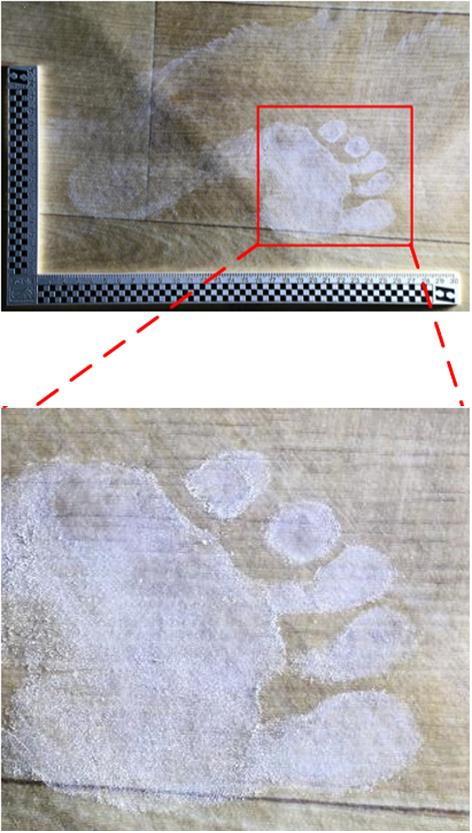
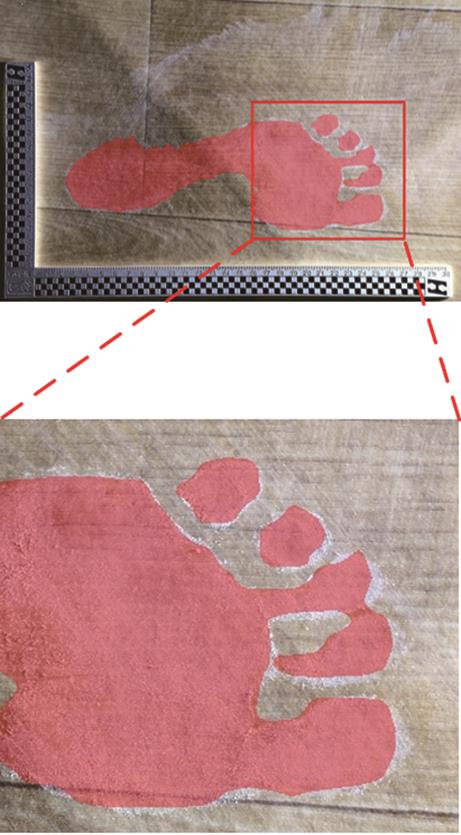
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 57-67.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240290
• Computer Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
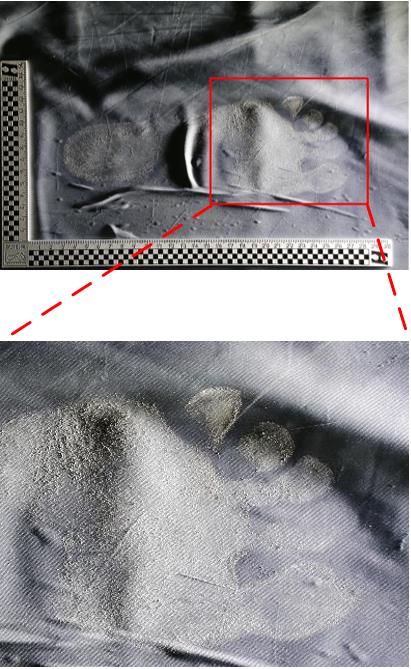
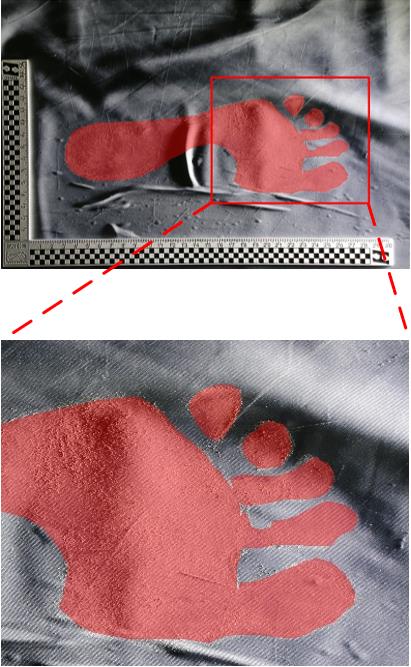
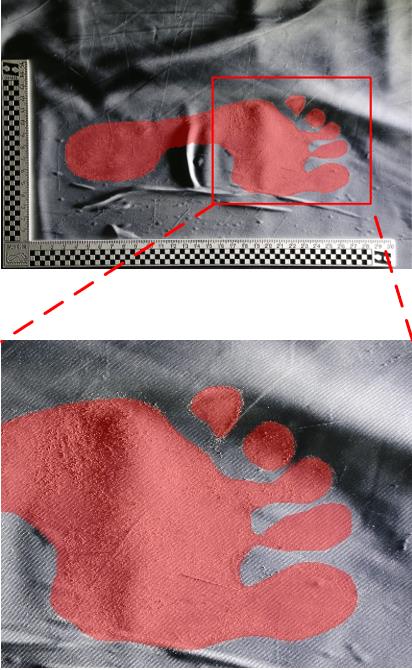
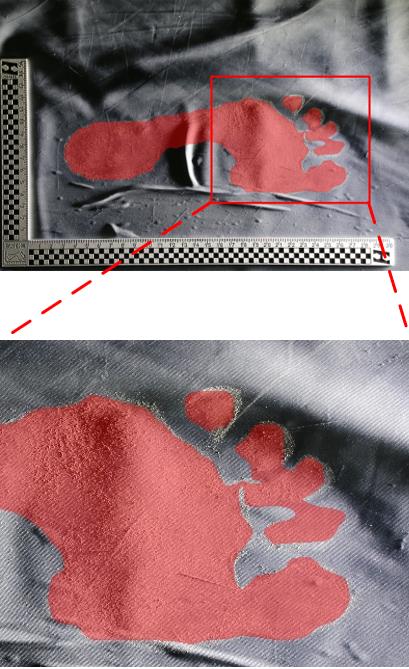
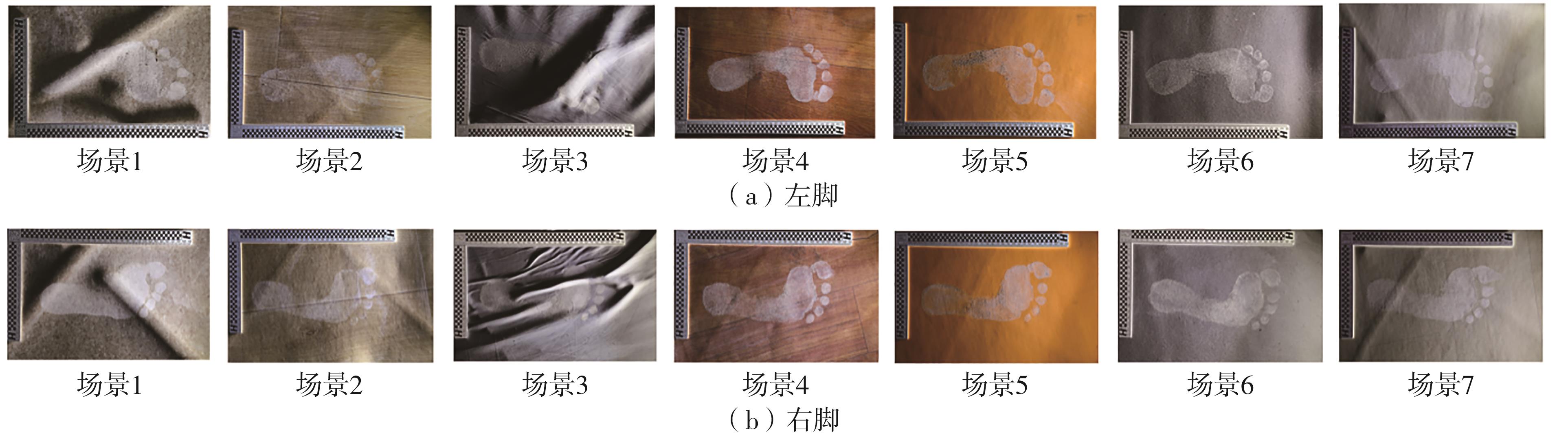
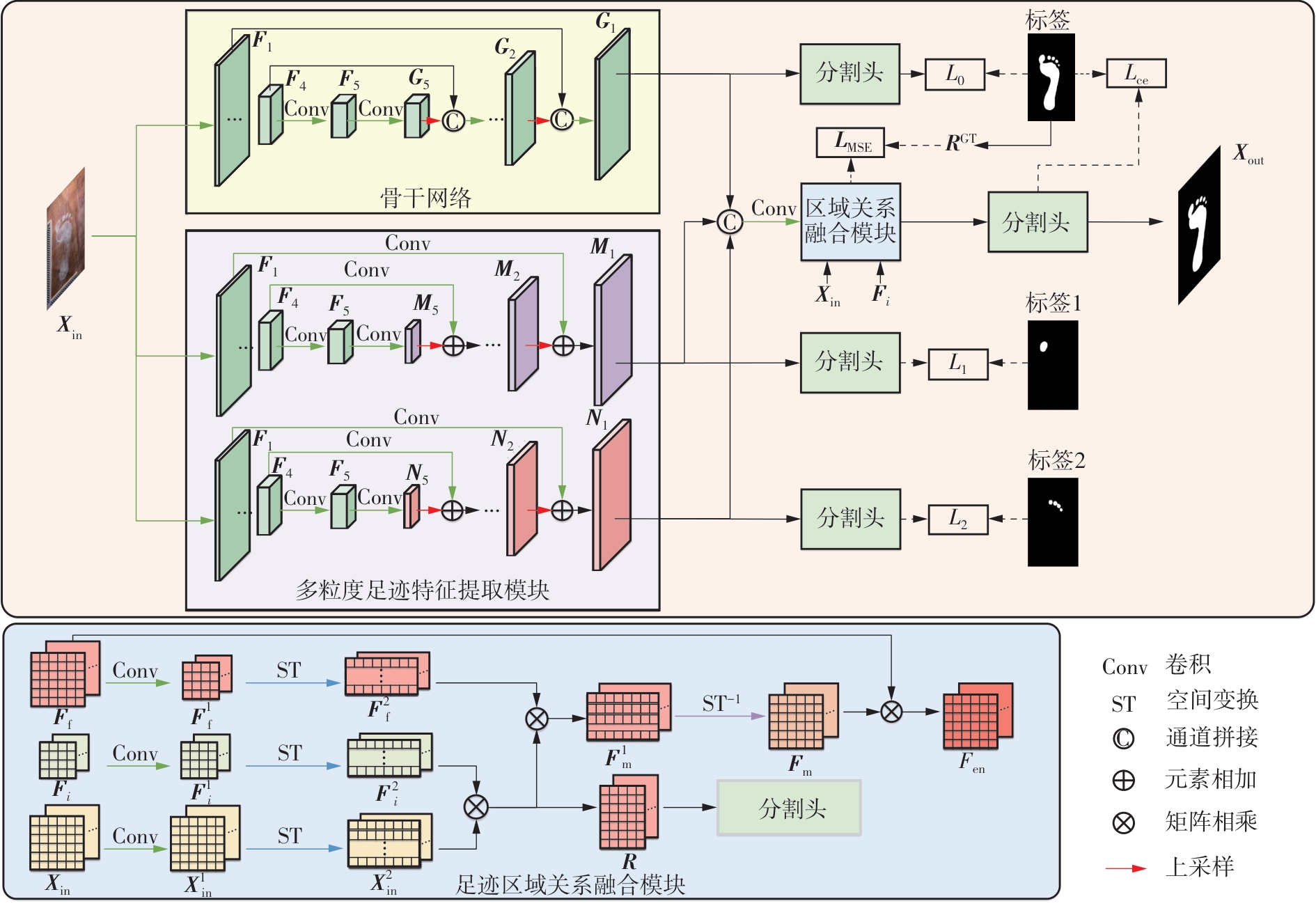
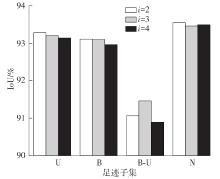
Segmentation Method of Barefoot Footprint Based on Multi-Granularity Feature and Region Relationship
ZHANG Yan( ), YAN Yi, WU Hongying, WANG Sitong, WU Yefeng, WANG Nian(
), YAN Yi, WU Hongying, WANG Sitong, WU Yefeng, WANG Nian( )
)
- School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Anhui University,Hefei 230601,Anhui,China
-
Received:2024-06-06Online:2025-03-10Published:2024-08-23 -
Contact:WANG Nian E-mail:zhangyan@ahu.edu.cn;wnianahu@163.com -
Supported by:the Key R & D Program of Anhui Province(2022k07020006);the University Natural Science Research Major Program of Anhui Province(KJ2021ZD0004);the University Collaborative Innovation Program of Anhui Pro-vince(GXXT-2022-038)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Yan, YAN Yi, WU Hongying, WANG Sitong, WU Yefeng, WANG Nian. Segmentation Method of Barefoot Footprint Based on Multi-Granularity Feature and Region Relationship[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(3): 57-67.
share this article
| 1 | 吴一全,朱丽,吴诗婳 .基于二维Arimoto灰度熵的图像阈值分割快速迭代算法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(5):48-57. |
| WU Yi-quan, ZHU Li, WU Shi-hua .Fast iterative algorithm for image threshold segmentation based on two-dimensional Arimoto gray entropy [J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2016,44(5):48-57. | |
| 2 | TREMEAU A, BOREL N .A region growing and mer-ging algorithm to color segmentation[J].Pattern Recognition,1997,30(7):1191-1203. |
| 3 | 王卫星,吴林春 .基于分数阶积分谷底边界检测的路面裂缝提取[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2014,42(1):117-122. |
| WANG Wei-xing, WU Lin-chun .Extraction of pavement cracks based on valley edge detection of fractional integral[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2014,42(1):117-122. | |
| 4 | 徐曼 .基于改进快速分水岭算法的图像分割技术研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2010. |
| 5 | LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T .Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017,39(4):640-651. |
| 6 | BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R .SegNet:a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,39(12):2481-2495. |
| 7 | RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T .U-Net:convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Munich:Springer,2015:234-241. |
| 8 | CHAURASIA A, CULURCIELLO E .LinkNet:exploi-ting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation [C] ∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing.St.Petersburg:IEEE,2017:1-4. |
| 9 | XIA X, KULIS B .W-Net:a deep model for fully unsuper-vised image segmentation[EB/OL].(2017-11-22) [2024-04-25].. |
| 10 | YUAN Y, CHEN X, WANG J .Object-contextual re-presentations for semantic segmentation[C]∥ Procee-dings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:173-190. |
| 11 | ZHAO H, SHI J, QI X,et al .Pyramid scene parsing network[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:6230-6239. |
| 12 | CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I,et al .DeepLab:semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets,atrous convolution,and fully connected CRFs[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,40(4):834-848. |
| 13 | CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F,et al .Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. (2017-06-17)[2024-04-25].. |
| 14 | LI H, XIONG P, AN J, et al .Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation [EB/OL].(2018-05-25)[2024-04-25].. |
| 15 | PUNN N S, AGARWAL S .Modality specific U-Net variants for biomedical image segmentation:a survey [J].Artificial Intelligence Review,2022,55(7):5845-5889. |
| 16 | 杨晋生,陈洪鹏,关欣,等 .一种多尺度轻量级脑胶质瘤图像分割网络[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(12):132-141. |
| YANG Jinsheng, CHEN Hongpeng, GUAN Xin,et al .A multi-scale lightweight brain glioma image segmentation network[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(12):132-141. | |
| 17 | XU J, XIONG Z, BHATTACHARYYA S P .PIDNet:a real-time semantic segmentation network inspired by PID controllers[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Vancouver:IEEE,2023:19529-19539. |
| 18 | CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G,et al .End-to-end object detection with transformers[C] ∥ Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:213-229. |
| 19 | DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A,et al .An image is worth 16×16 words:transformers for image recognition at scale[C] ∥ Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Learning Representations.[S.l.]: OpenReview.net,2021:1-21. |
| 20 | ZHENG S, LU J, ZHAO H,et al .Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Nashville:IEEE,2021:6877-6886. |
| 21 | STRUDEL R, GARCIA R, LAPTEV I,et al .Segmenter:transformer for semantic segmentation[C] ∥Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Confe-rence on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:7242-7252. |
| 22 | XIE E, WANG W, YU Z,et al .SegFormer:simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers [C] ∥ Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34:35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.San Diego:Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation,Inc.,2021:12077-12090. |
| 23 | RANFTL R, BOCHKOVSKIY A, KOLTUN V .Vision transformers for dense prediction[C] ∥ Procee-dings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2021:12159-12168. |
| 24 | CHEN Y, DAI X, CHEN D,et al .Mobile-Former:bridging MobileNet and transformer[C] ∥ Procee-dings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:5260-5269. |
| 25 | MEHTA S, RASTEGARI M .MobileVit:light-weight,general-purpose,and mobile-friendly vision transformer[C] ∥ Proceedings of the Tenth International Confe-rence on Learning Representations.[S.l.]:OpenReview.net,2022:1-26. |
| 26 | ZHANG W, HUANG Z, LUO G,et al .TopFormer:token pyramid transformer for mobile semantic segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Confe-rence on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:12073-12083. |
| 27 | LI Y, YUAN G, WEN Y,et al .EfficientFormer: vision transformers at MobileNet speed[C] ∥ Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35:36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.San Diego:Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation,Inc.,2022:1-16. |
| 28 | WAN Q, HUANG Z, LU J,et al .SeaFormer: squeeze-enhanced axial transformer for mobile semantic segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations.[S.l.]:OpenReview.net,2023:1-19.. |
| 29 | LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R,et al .Feature pyramid networks for object detection [C] ∥ Procee-dings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:936-944. |
| 30 | GU J, KWON H, WANG D,et al .Multi-scale high- resolution vision transformer for semantic segmentation [C] ∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:12084-12093. |
| 31 | HUANG H, LIN L, TONG R,et al .UNet 3+:a full-scale connected UNet for medical image segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Confe-rence on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing.Barcelona:IEEE,2020:1055-1059. |
| 32 | CHEN L C, ZHU Y, PAPANDREOU G,et al . Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision.Munich:Springer,2018:833-851. |
| 33 | YUAN Y, HUANG L, GUO J,et al .OCNet:object context for semantic segmentation[J].International Journal of Computer Vision,2021,129:2375-2398. |
| 34 | FU J, LIU J, TIAN H,et al .Dual attention network for scene segmentation [C] ∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:3141-3149. |
| [1] | SUN Xiaohe, SHI Chenghua, LIU Linghui, et al. Concrete Crack Image Recognition System Based on Improved Seed Filling Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 127-136,146. |
| [2] | YANG Jinsheng, CHEN Hongpeng, GUAN Xin, et al. A Multi-Scale Lightweight Brain Glioma Image Segmentation Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(12): 132-141. |
| [3] | FAN Zizhu, WANG Song, ZHANG Hong, et al. W-Net-Based Segmentation for Remote Sensing Satellite Image of High Resolution [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(12): 114-124. |
| [4] | ZHENG Yunping LI Ruijun. Application of Binary Tree Model in Object Tracking [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(1): 42-50. |
| [5] | YANG Shun WU Jian JIANG Yuande WANG Guojun LIU Haizhen. Deep-Learning-Based Lane-Keeping Control Framework: From Virtuality to Reality [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(9): 90-97. |
| [6] |
FENG Bao CHEN Xiangmeng LI Pusheng CHEN Yehang YAO Nan LONG Wansheng.
Segmentation of the Partial Ground Glass Opacity Pulmonary Nodules with Wavelet Energy Guided Active Contour Model
|
| [7] | HONG Xiaobin WEI Xinyong HUANG Yesheng LIU Yanxia XIAO Guoquan. Local Path Planning Method for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Based on Image Recognition and VFH + [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(10): 24-33. |
| [8] | LIAO Yi-peng WANG Wei-xing. Improved Graph MST-Based Image Segmentation with Non-Subsampled Contourlet Transform [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(7): 143-152. |
| [9] | QIN Xiao SHEN Ai-qin GUO Yin-chuan ZHOU Sheng-bo HE Tian-qin. Evolution Rule of Microcosmic Cracks in Pavement Concrete Under Multi-Field Coupling [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(6): 81-88,102. |
| [10] | WO Yan JIN Xuan. A Graph-Based Color Image Segmentation Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(9): 1-8. |
| [11] | WU Yi-quan ZHU Li WU Shi-hua. Fast Iterative Algorithm for Image Threshold Segmentation Based on Two-Dimensional Arimoto Gray Entropy [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(5): 48-57. |
| [12] | Zhou Zhi-heng Zhong Hui-qiang Dai Ming. A Dynamic Gradient Vector Flow Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(9): 20-26,33. |
| [13] | Yang Zhen-lun Min Hua-qing Luo Rong-hua. Multi-Threshold Image Segmentation Algorithm Based on Improved Quantum-Behaved Particle Swarm Optimization [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(5): 126-131,138. |
| [14] | Zhou Xiao- ming Li Zhao Liu Xiong- ying. An Automatic Image Segmentation Algorithm Based on Improved FCM [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(3): 1-7. |
| [15] | Wang Wei- xing Wu Lin- chun. Extraction of Pavement Cracks Based on Valley Edge Detection of Fractional Integral [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(1): 117-122. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||