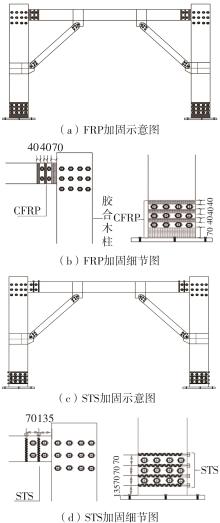
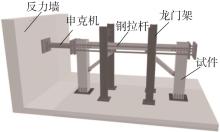
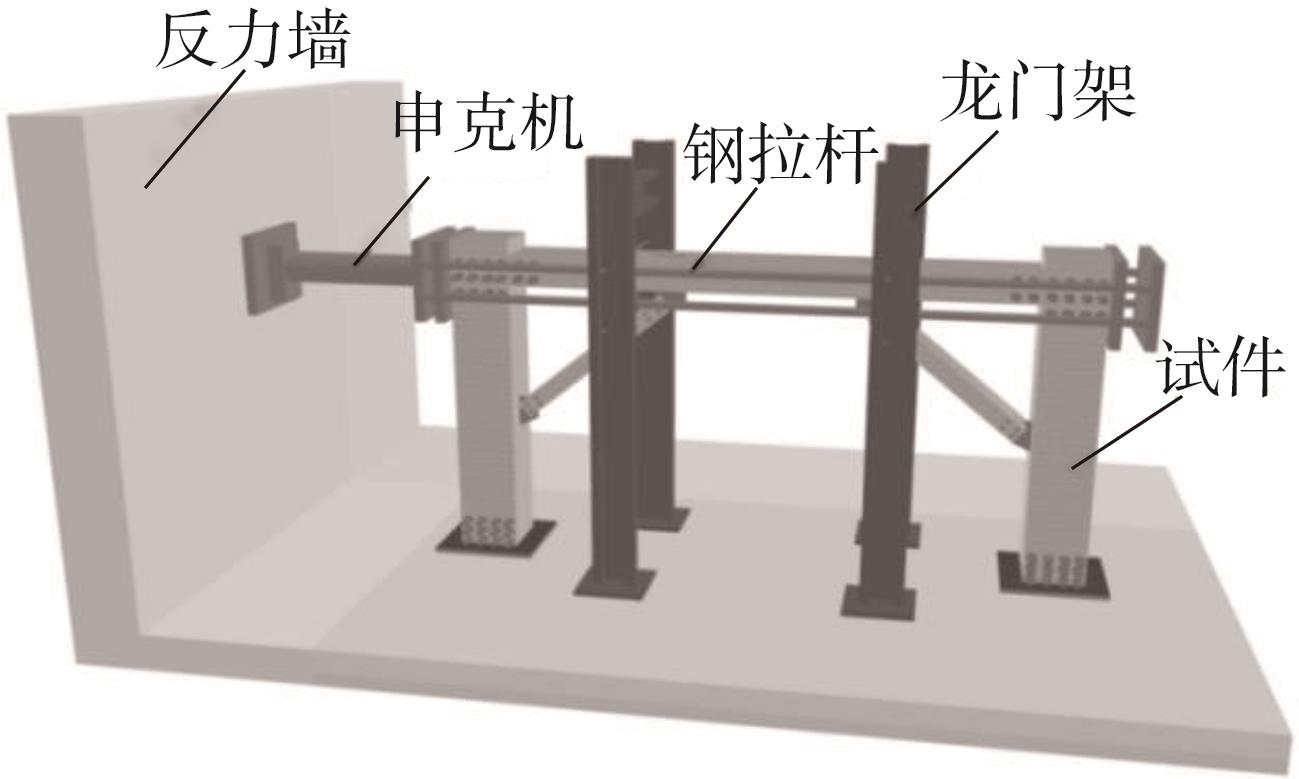
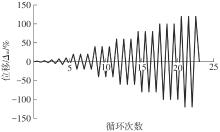
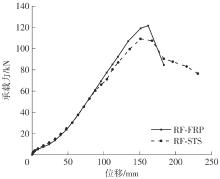
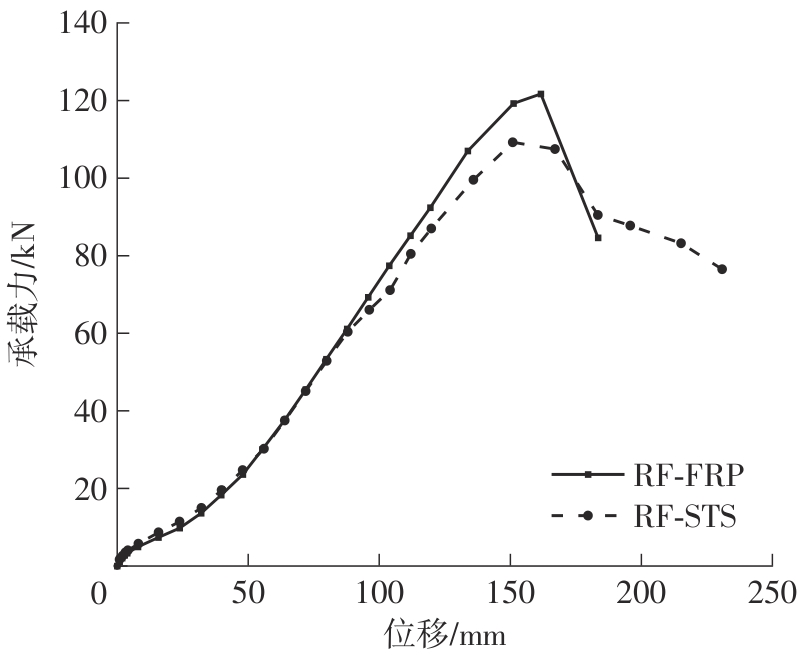
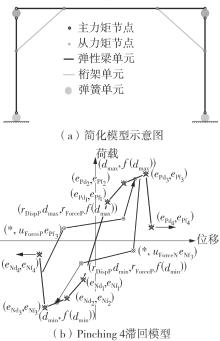
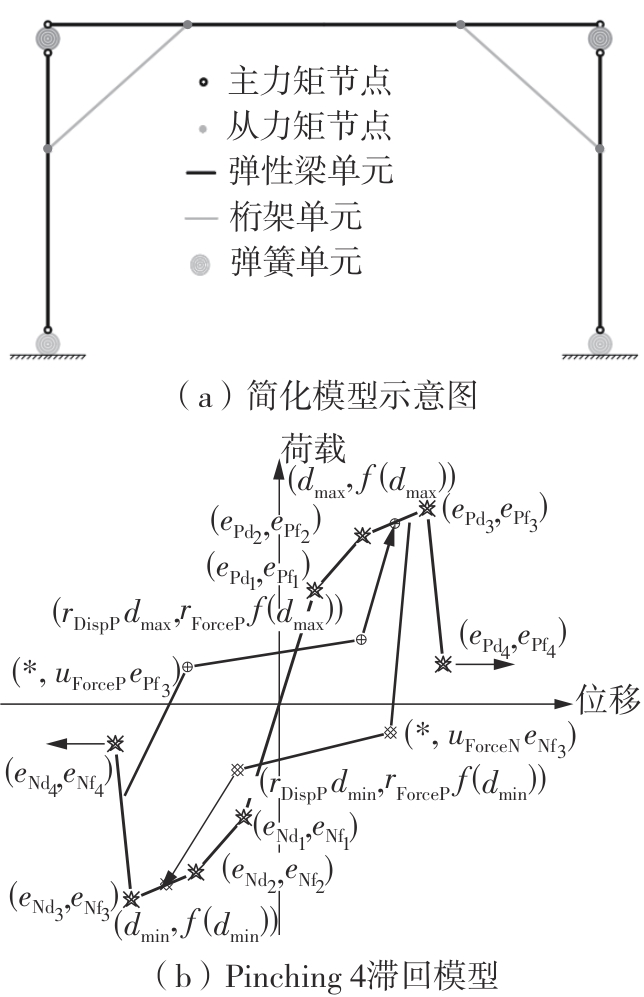
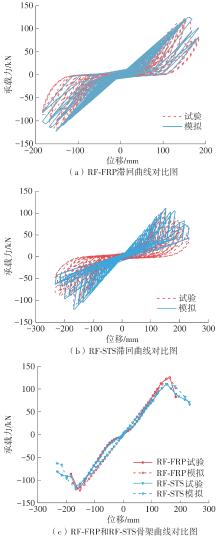
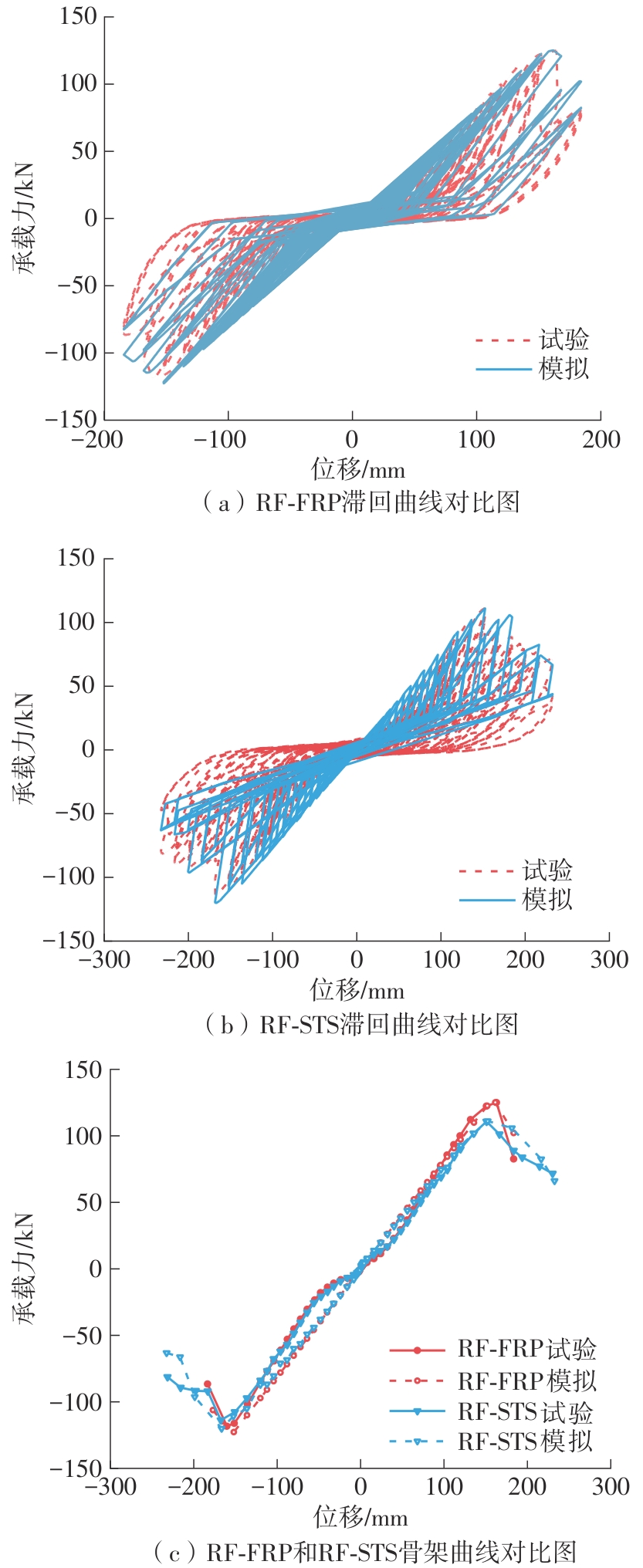
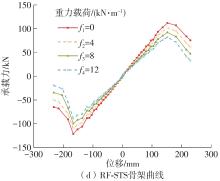
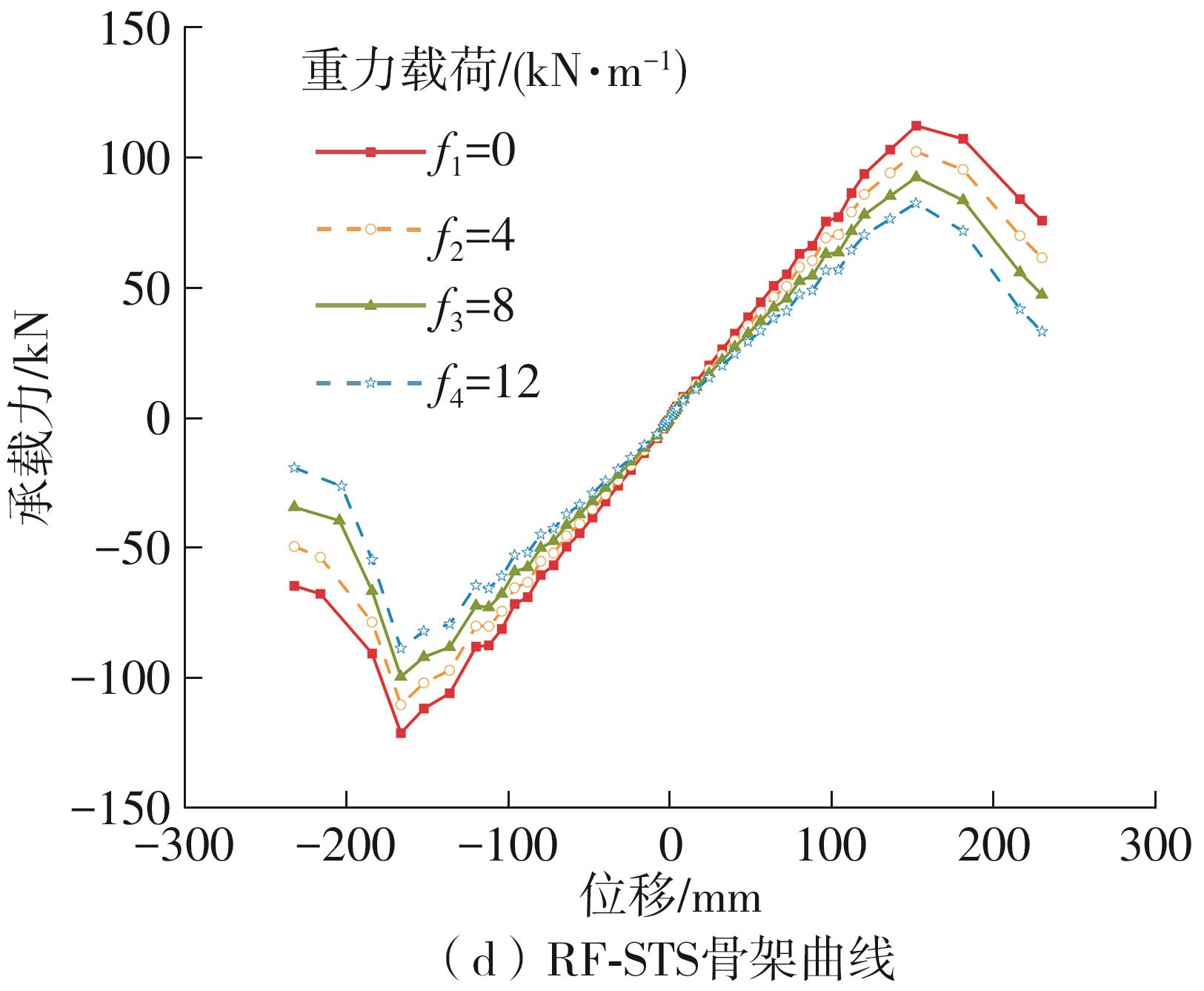
| 1 |
CORRADI M, BORRI A, RIGHETTI L,et al .Uncertainty analysis of FRP reinforced timber beams[J].Composites Part B:Engineering,2017,113:174-184.
|
| 2 |
CORRADI M, VEMURY C M, EDMONDSON V,et al .Local FRP reinforcement of existing timber beams[J].Composite Structures,2021,258:113363/1-13.
|
| 3 |
张风亮,陆建勇,薛建阳,等 .碳纤维布加固木结构残损节点性能分析与设计建议[J].建筑结构,2015,45(6):61-65,13.
|
|
ZHANG Fengliang, LU Jianyong, XUE Jianyang,et al .Performance analysis and design recommendations for damaged mortise-tenon joint of ancienttimber structures strengthened with CFRP[J].Building Structure,2015,45(6):61-65,13.
|
| 4 |
ELBASHIR D, BRANCO J M, RODRIGUES L G .Reinforcement of dowel-type timber joints with self-tapping screws[J].Institution of Civil Engineers-Structures and Buildings,2020,173(12):969-988.
|
| 5 |
孙兆洋,程小武,陆伟东 .钢板-自攻螺钉加固残损古建筑木结构直榫节点抗震性能试验研究[J].结构工程师,2018,34(5):106-112.
|
|
SUN Zhaoyang, CHENG Xiaowu, LU Weidong .Experimental study on seismic performance of damaged straight mortise-tenon joints of ancienttimber buildings strengthened with steel plates and self-tapping screws[J].Structural Engineers,2018,34(5):106-112.
|
| 6 |
ZHU Xiaodong, LIU Yu .Nondestructive testing and system reliability based on finite element modeling in GFRP-reinforced timber beams[J].BioResources,2014,9(3):5501-5510.
|
| 7 |
BEDON C, FRAGIACOMO M .Numerical analysis of timber-to-timber joints and composite beams with inclined self-tapping screws[J].Composite Structures,2019,207:13-28.
|
| 8 |
BEDON C, SCIOMENTA M, FRAGIACOMO M .Mechanical characterization of timber-to-timber composite (TTC) joints with self-tapping screws in a standard push-out setup[J].Applied Sciences,2020,10(18):6534/1-23.
|
| 9 |
KILDASHITI K, ALINOORI F, MOSHIRI F,et al .Computational simulation of light timber framing connections strengthened with self-tapping screws[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2021,44:103003.
|
| 10 |
熊海贝,刘应扬,杨春梅,等 .梁柱式胶合木结构体系抗侧力性能试验[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2014,42(8):1167-1175.
|
|
XIONG Haibei, LIU Yingyang, YANG Chunmei,et al .Experimental study on lateral resistance of glued-laminated timber post and beam systems[J].Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2014,42(8):1167-1175.
|
| 11 |
熊海贝,李冰阳,刘应扬,等 .梁柱式木框架-支撑体系低周反复试验研究[J].结构工程师,2015,31(1):147-154.
|
|
XIONG Haibei, LI Bingyang, LIU Yingyang,et al .Experimental study on timber post and beam frame-brace structure systems under lateral cyclic loading[J].Structural Engineers,2015,31(1):147-154.
|
| 12 |
熊海贝,刘应扬,姚亚,等 .梁柱式木结构加固方法及抗侧力性能试验研究[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(5):695-702.
|
|
XIONG Haibei, LIU Yingyang, YAO Ya,et al .Experimental study of reinforcement methods and lateral resistance of glued-laminated timber post and beam structures[J].Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2016,44(5):695-702.
|
| 13 |
熊海贝,刘应扬,姚亚,等 .碳纤维布加固梁柱式胶合木结构抗侧性能试验[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(10):1463-1470.
|
|
XIONG Haibei, LIU Yingyang, YAO Ya,et al .Experimental study on lateral resistance of timber post and beam structures strengthened with carbon fiber reinforced polymer[J].Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2015,43(10):1463-1470.
|
| 14 |
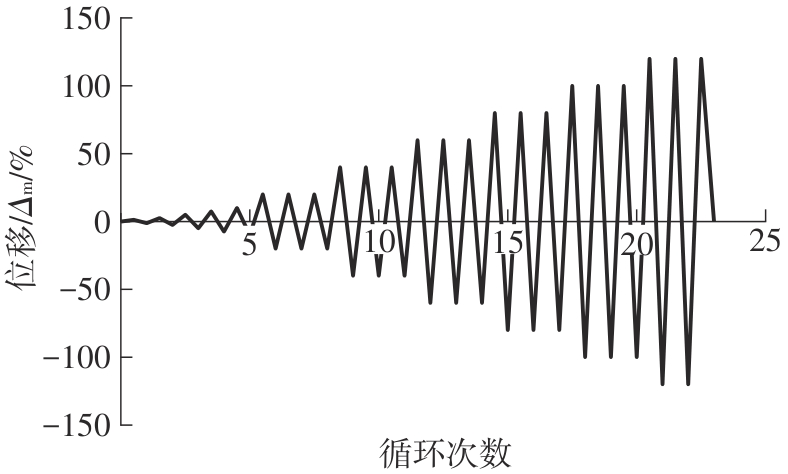
Standard test methods for cyclic (reversed) load test for shear resistance of vertical elements of the lateral force resisting systems for buildings: [S].
|
| 15 |
SOROUSHIAN S, MARAGAKIS E M, JENKINS C. Capacity evaluation of suspended ceiling components, part 2: analytical studies[J].Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 2015, 19(5): 805-821.
|
| 16 |
RAHMANISHAMSI E, SOROUSHIAN S, MARAGAKIS E M .Cyclic shear behavior of gypsum board-to-steel stud screw connections in nonstructural walls[J].Earthquake Spectra,2016,32(1):415-439.
|
| 17 |
SHEN Y L, SCHNEIDER J, TESFAMARIAM S,et al .Hysteresis behavior of bracket connection in cross-laminated-timber shear walls[J].Construction and Building Materials,2013,48:980-991.
|