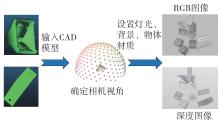
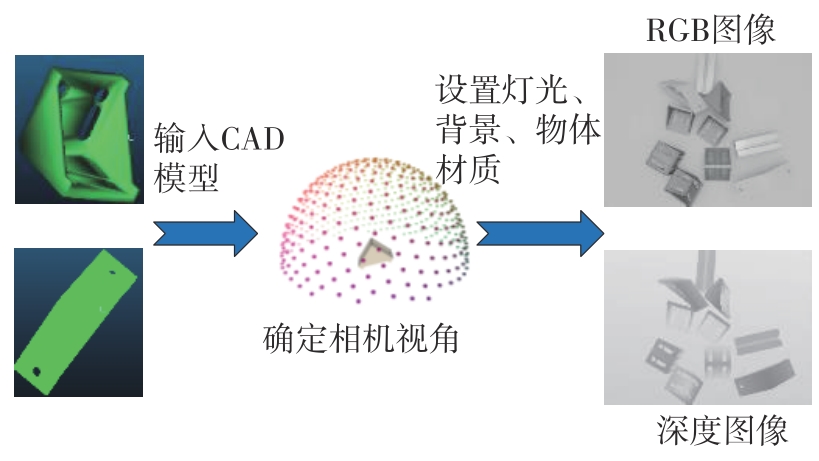
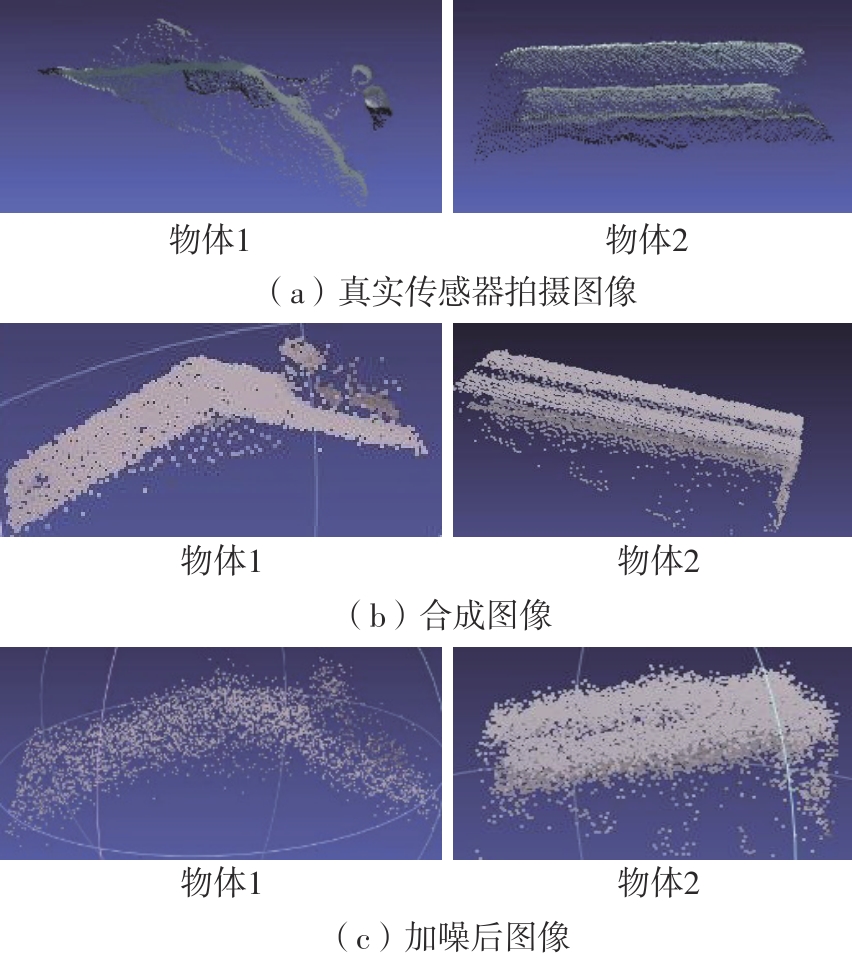
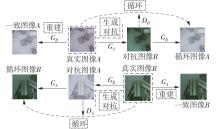
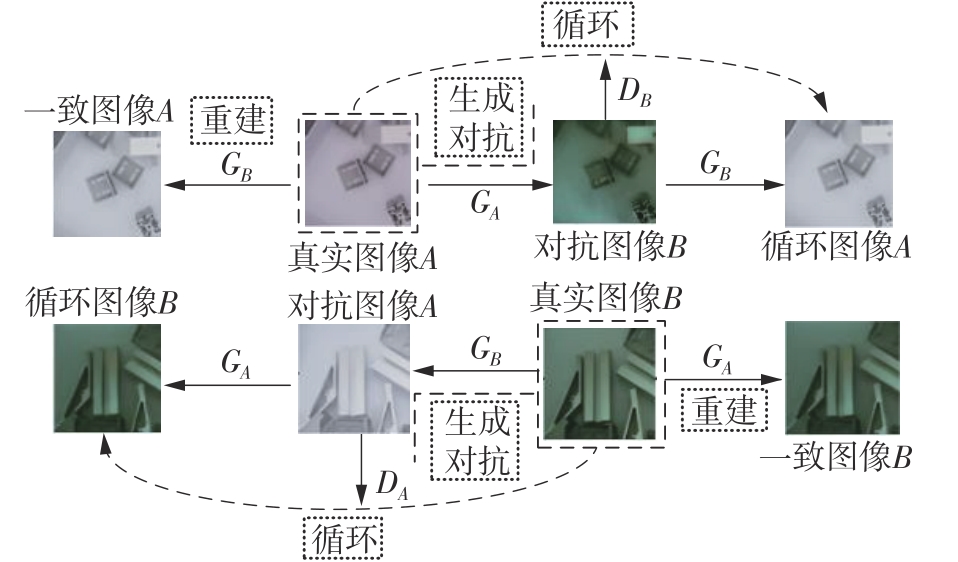
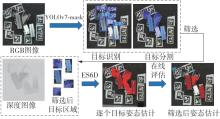
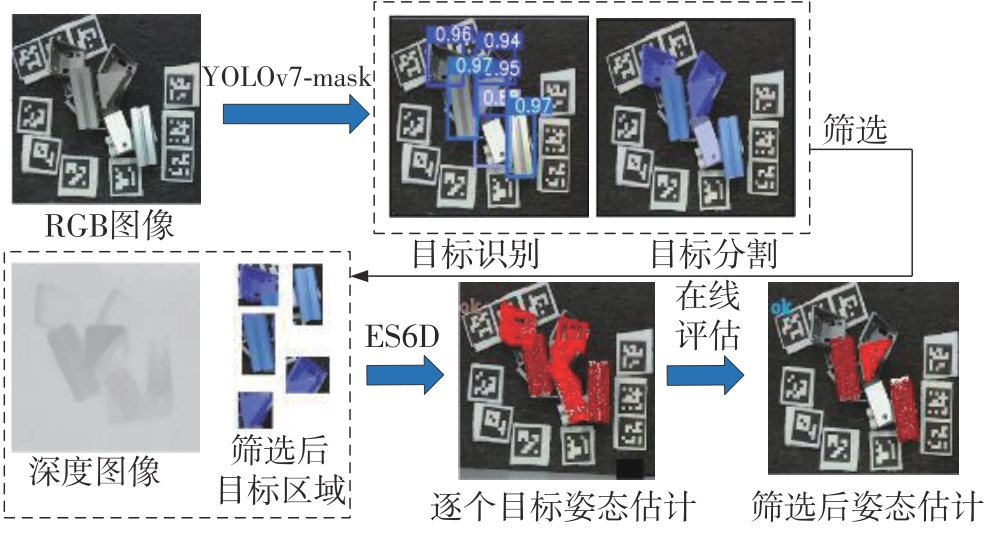
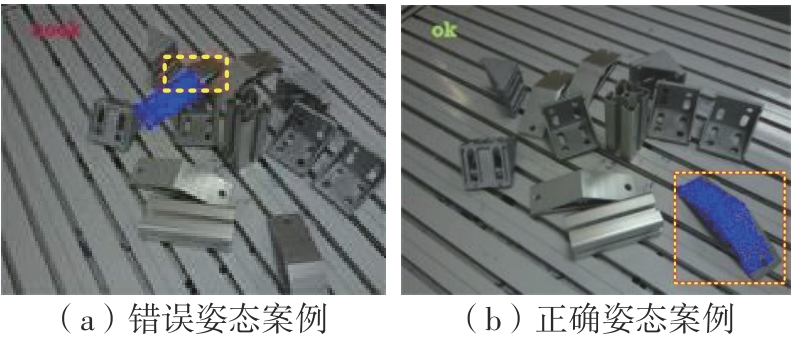
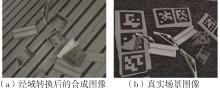
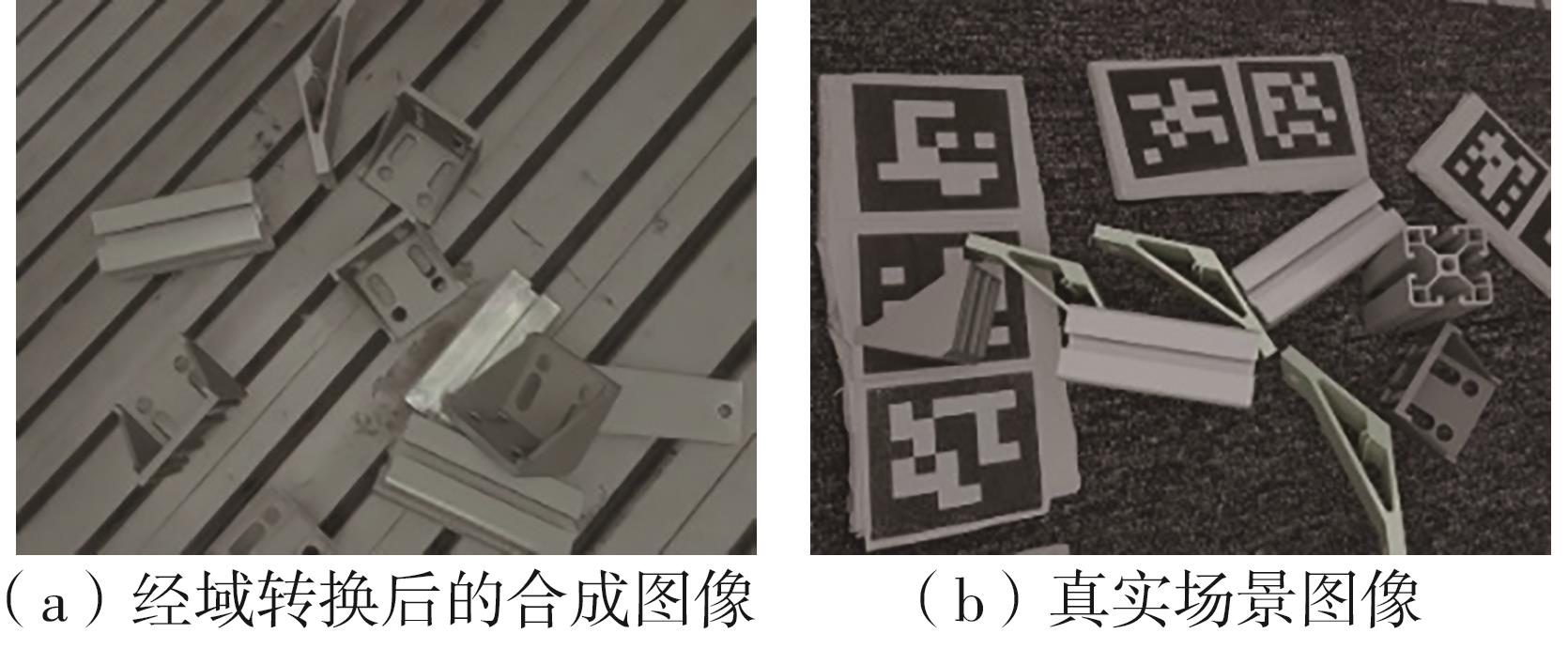
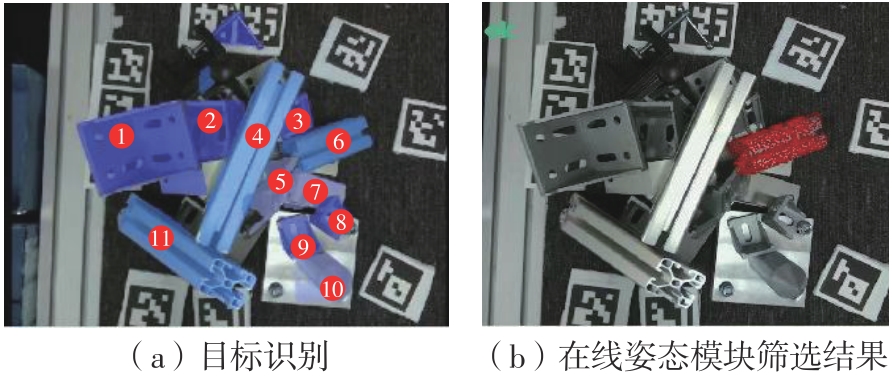
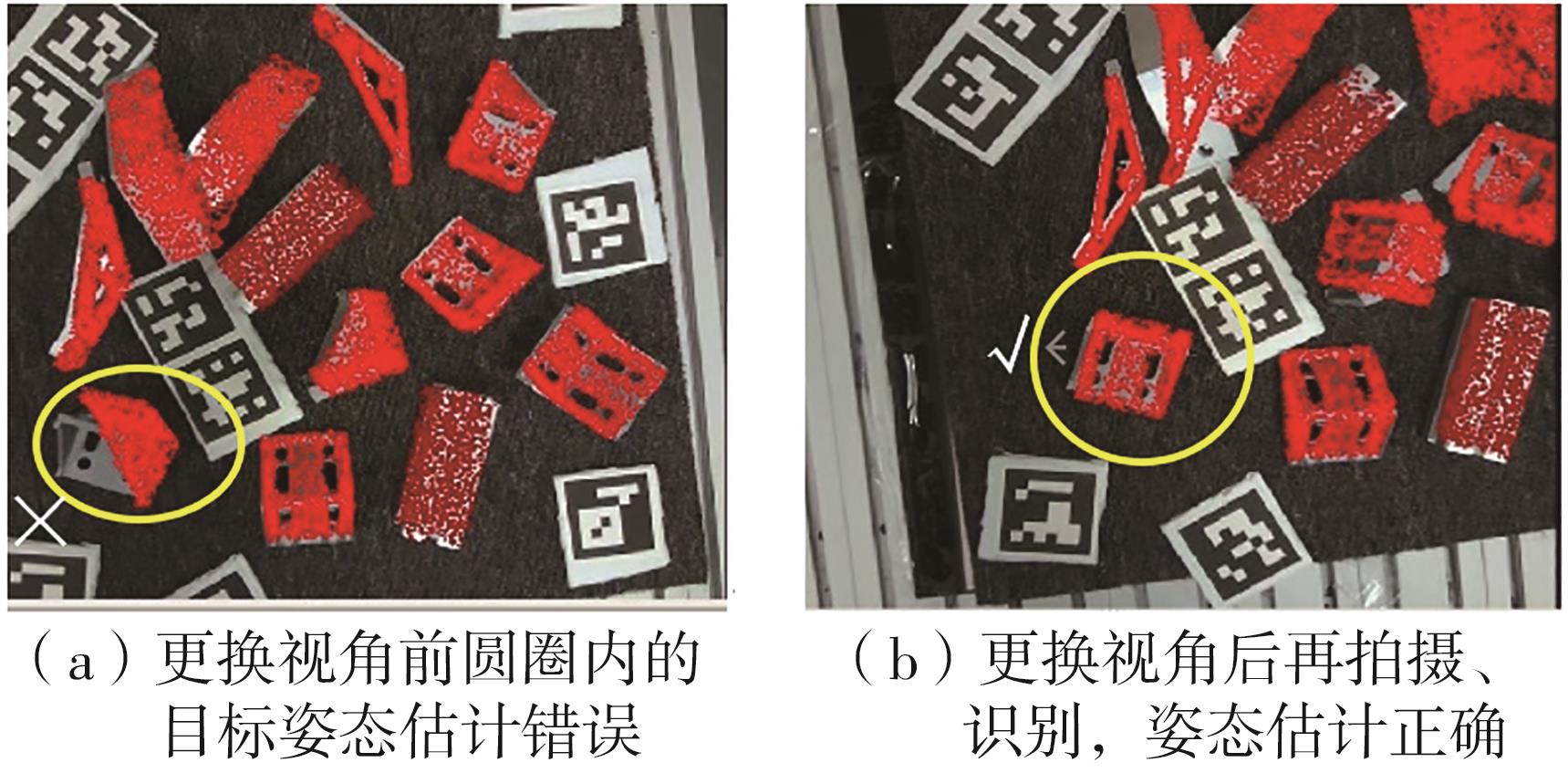
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 42-50.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230327
• Mechanical Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Multi-Object Recognition and 6-DoF Pose Estimation Based on Synthetic Datasets
HU Guanghua OU Meitong LI Zhendong
- School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China