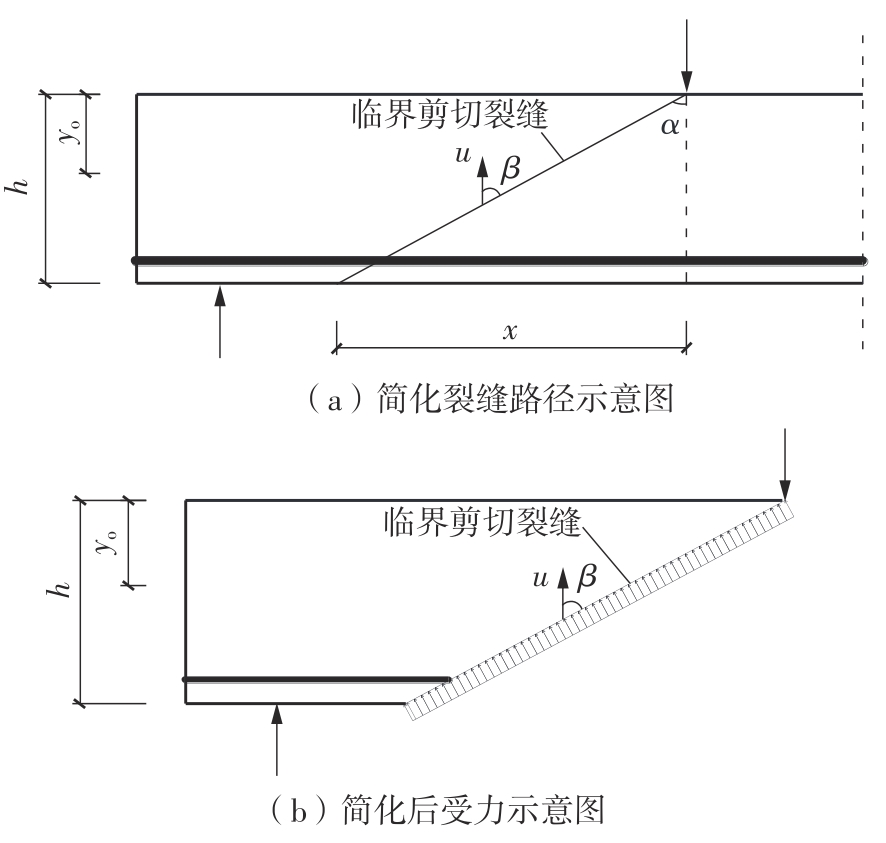
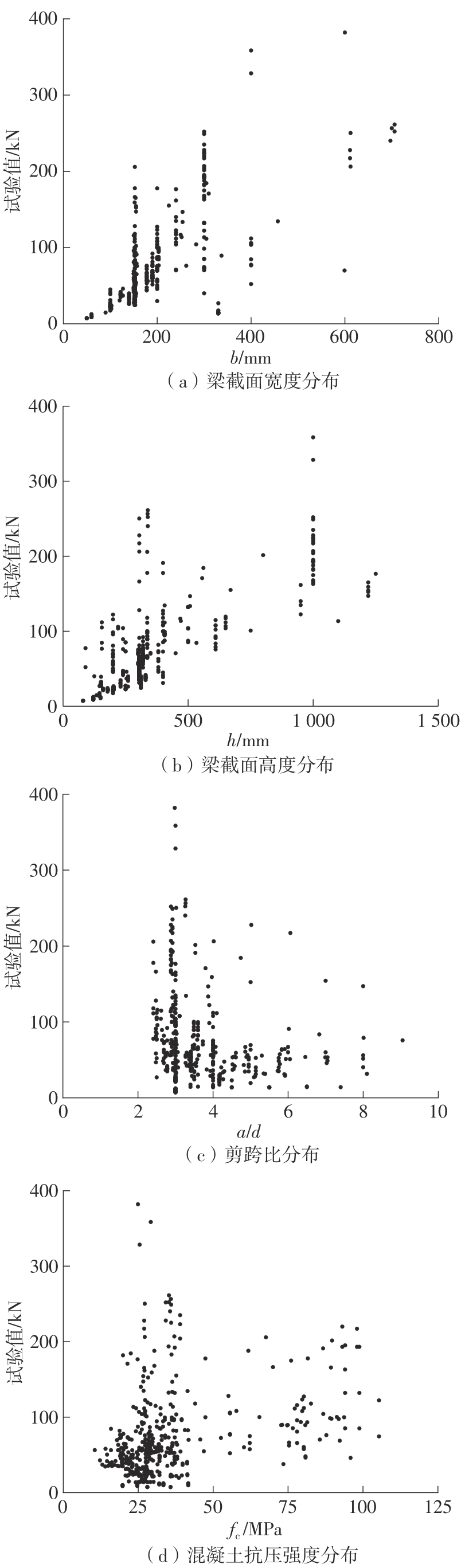
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 114-126.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230238
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shear Strength Calculation of RC Beams Without Shear Reinforcement Based on Crack Sliding Model
GONG Zhongwen( ), XIONG Ergang(
), XIONG Ergang( ), WANG Wenxiang, CAO Tao, FU Chongyang
), WANG Wenxiang, CAO Tao, FU Chongyang
- School of Civil Engineering,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710061,Shaanxi,China
-
Received:2023-04-13Online:2024-05-25Published:2023-05-26 -
Contact:熊二刚(1980-),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,主要从事工程结构抗震研究。 E-mail:xerg@chd.edu.cn -
About author:巩忠文(1997-),男,博士生,主要从事工程结构抗震研究。E-mail: 13571962851@163.com -
Supported by:the Key R&D Project of Shaanxi Province(2021SF-461)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
GONG Zhongwen, XIONG Ergang, WANG Wenxiang, et al. Shear Strength Calculation of RC Beams Without Shear Reinforcement Based on Crack Sliding Model[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 114-126.
share this article
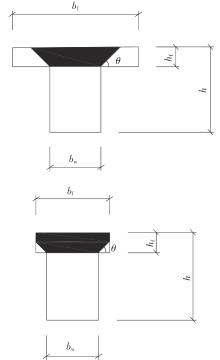
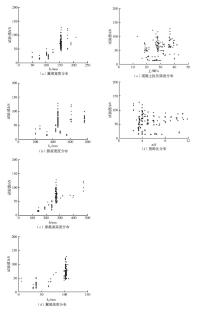
Table 2
T-beam dataset distribution"
| 参考文献 | 数据量 | bf /mm | bw /mm | hf /mm | h/mm | a/d | ρw /% | dg /mm | fc /MPa | φ/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACIdatabase[ | 40 | 330.2~609.6 | 76.2~177.8 | 6.35~101.5 | 139.7~469.9 | 7.4~2.5 | 1.473~4.091 | 6.4~19.0 | 13.23~43.11 | 9.5~28.7 |
| Kani等[ | 123 | 457~762 | 208~152 | 99~109 | 252~280 1) | 2.50~14.16 | 1.7~9.5 | — | 18.48~40.22 | — |
| Thamrin等[ | 9 | 250~610 | 50~190 | 65~102 | 212~399 1) | 3.3~10.4 | 0.49~5.20 | — | 32~40 | — |
| 1 | Mac GREGOR G J, HANSON M J .The shear strength of reinforced concrete members[J].ACI Journal,1973,99(6):471-473. |
| 2 | Committee ASCE-ACI 445 on shear and Torsion.Recent approaches to shear design of structural concrete[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,1998,124(12):1375-1417. |
| 3 | 戚家南,王景全 .考虑翼缘影响的钢筋混凝土T梁抗剪承载力[J].东南大学学报(自然科学版),2019,49(4):638-644. |
| QI Jianan, WANG Jingquan .Shear strength of reinforced concrete T-beams considering the effect of flange[J].Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition),2019,49(4):638-644. | |
| 4 | 易伟建 .混凝土结构试验与理论研究[M].北京:科学出版社,2012. |
| 5 | 冯浩雄,易伟建 .考虑翼缘有效宽度的钢筋混凝土T梁的抗剪承载力[J].江苏大学学报(自然科学版),2016,37(4):462-466. |
| FENG Haoxiong, YI Weijian .Shear strength of reinforced concrete T beams considering effective flange width[J].Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition),2016,37(4):462-466. | |
| 6 | GIACCIO C, Al-MAHAIDI R, TAPLIN G .Experimental study on the effect of flange geometry on the shear strength of reinforced concrete T-beams subjected to concentrated loads[J].Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering,2002,29(6):911-918. |
| 7 | LIU J, GAO Z .A comparative study of models for shear strength of reinforced concrete T-beams[J].Structures,2022,35:922-930. |
| 8 | PLACAS A, REGAN P E .Shear failure of reinforced concrete beams[J].ACI Journal,1971,68(10):763-773. |
| 9 | RIBAS GONZALEZ C R, FERNÁNDEZ RUIZ M .Influence of flanges on the shear-carrying capacity of reinforced concrete beams without web reinforcement[J].Structural Concrete,2017,18(5):720-732. |
| 10 | ZARARIS I P, KARAVEZIROGLOU M K, ZARARIS P D .Shear strength of reinforced concrete T-beams [J].ACI Structural Journal,2006,103(5):693-700. |
| 11 | CLADERA A, MARÍ A, RIBAS C,et al .Predicting the shear-flexural strength of slender reinforced concrete T and I shaped beams[J].Engineering Structures,2015,101:386-398. |
| 12 | KOTSOVOU G M, COTSOVOS D M .Shear failure criterion for RC T-beams[J].Engineering Structures,2018,160:44-55. |
| 13 | ZHANG T, OEHLERS D J, VISINTIN P .Shear strength of FRP RC beams and one-way slabs without stirrups[J].Journal of Composites for Construction,2014,18(5):04014007/1-15. |
| 14 | RAHMAN J, AHMED K S, KHAN N I,et al .Data-driven shear strength prediction of steel fiber reinforced concrete beams using machine learning approach[J].Engineering Structures,2021,233:111743/1-22. |
| 15 | CHOU J S, PHAM T P T, NGUYEN T K,et al .Shear strength prediction of reinforced concrete beams by baseline,ensemble,and hybrid machine learning models[J].Soft Computing,2020,24(5):3393-3411. |
| 16 | YU Y, ZHAO X, XU J,et al .Machine learning-based evaluation of shear capacity of recycled aggregate concrete beams[J].Materials,2020,13(20):4552/1-32. |
| 17 | CASTILLO R, OKUMUS P, KHORASANI N E,et al .Machine learning for shear strength of reinforced concrete beams[J].ACI Structural Journal,2022,119(5):83-94. |
| 18 | ZHANG J, SUN Y, LI G,et al .Machine-learning-assisted shear strength prediction of reinforced concrete beams with and without stirrups[J].Engineering with Computers,2022,38(2):1293-1307. |
| 19 | NIELSEN M P, HOANG L C .Limit analysis and concrete plasticity[M].Abingdon:CRC Press,2011. |
| 20 | ZHANG J P .Strength of cracked concrete,part 1:shear strength of conventional reinforced concrete beams,deep beams,corbels,and prestressed reinforced concrete beams without shear reinforcement[M].Lyngby:Danmarks Tekniske Universitet,1994. |
| 21 | CHOI K K, KIM J C, PARK H G .Shear strength model of concrete beams based on compression zone failure mechanism[J].ACI Structural Journal,2016,113(5):1095-1106. |
| 22 | ZARARIS P D, PAPADAKIS G C .Diagonal shear failure and size effect in RC beams without web reinforcement[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2001,127(7):733-742. |
| 23 | MUTTONI A, FERNÁNDEZ RUIZ M .Shear strength of members without transverse reinforcement as function of critical shear crack width[J].ACI Structural Journal,2008,105(2):163-172. |
| 24 | WALRAVEN J C .Fundamental analysis of aggregate interlock[J].Journal of the Structural Division,1981,107(11):2245-2270. |
| 25 | AUTRUP F, JOERGENSEN H B .Shear capacity of RC members without shear reinforcement:a modified crack sliding model[J].Engineering Structures,2021,239:112147/1-13. |
| 26 | KRAGH-Poulsen J C, NIELSEN M P, GOLTERMANN P .Shear strength of straight concrete members without shear reinforcement.reassessment of the effectiveness factors used in the crack sliding theory[J].Structural Concrete,2020,21(3):966-982. |
| 27 | VECCHIO F J, COLLINS M P .The modified compression-field theory for reinforced concrete elements subjected to shear[J].ACI Journal,1986,83(2):219-231. |
| 28 | REINECK K H .Ultimate shear force of structural concrete members without transverse reinforcement derived from a mechanical model (SP-885)[J].ACI Structural Journal,1991,88(5):592-602. |
| 29 | HUBER P, HUBER T, KOLLEGGER J .Investigation of the shear behavior of RC beams on the basis of measured crack kinematics[J].Engineering Structures,2016,113:41-58. |
| 30 | MÖRSCH E .Der Eisenbetonbau,seine theorie und anwendung[M].Stuttgart:Wittwer,1923. |
| 31 | YANG Y, WALRAVEN J, UIJL J .Shear behavior of reinforced concrete beams without transverse reinforcement based on critical shear displacement[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2017,143(1):04016146/1-13. |
| 32 | REGAN P E .Research on shear:a benefit to humanity or a waste of time?[J].Structural Engineer,1993,71(19):337-346. |
| 33 | TUREYEN A K, WOLF T S, FROSCH R J .Shear strength of reinforced concrete T-beams without transverse reinforcement[J].ACI Structural Journal,2006,103(5):656-663. |
| 34 | GIACCIO C, Al-MAHAIDI R, TAPLIN G .Flange strain measurement in shear critical RC T-beams[J].Advances in Structural Engineering,2006,9(4):491-505. |
| 35 | REINECK K H, BENTZ E C, FITIK B,et al .ACI-DAfStb database of shear tests on slender reinforced concrete beams without stirrups[J].ACI Structural Journal,2013,110(5):867-876. |
| 36 | KANI M W, HUGGINS M W, WITTKOPP R R .Kani on shear in reinforced concrete[D].Toronto:University of Toronto,1979. |
| 37 | THAMRIN R, TANJUNG J, ARYANTI R,et al .Shear strength of reinforced concrete T-beams without stirrups[J].Journal of Engineering Science and Technology,2016,11(4):548-562. |
| 38 | 混凝土结构设计规范: [S]. |
| 39 | Building code requirement for structural concrete and commentary:ACI 318-19 [S]. |
| 40 | Eurocode 2:design for concrete structures-part 1:general rules and rules for buildings:EN 1992-1-1:2004 [S]. |
| 41 | MUTTONI A .Schubfestigkeit und durchstanzen von platten ohne querkraftbewehrung[J].Beton-und Stahlbetonbau,2003,98(2):74-84. |
| 42 | ZSUTTY T C .Beam shear strength prediction by analysis of existing data[J].ACI Journal,1968,65(1):943-951. |
| [1] | ZHAO Jiandong, XU Huiling, LÜ Xing, et al. Recognition Model of Highway Toll Evasion Behavior Considering Cost-Sensitivity [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(5): 10-19. |
| [2] | LI Baijian, HUANG Yan, FU Xinsha. Influence of Shapes of Corrugated Steel Plate on Load-Carrying Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Slab Culvert and Arch Effect with Lateral Restraint [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(1): 110-118. |
| [3] | XIE Xiaoli, GOU Wenxin, PANG Mulin, et al. Dynamic Characteristics of RC Rigid Frame Arch Bridge Strengthened by Plate-Truss Combination [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 31-43. |
| [4] | ZHOU Chuhao, LIN Peiqun, YAN Mingyue. Traffic Data Imputation Based on Self-Supervised Learning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(4): 101-114. |
| [5] | DONG Ping, WEI Shuyang, LIU Mingbo. Scheduling Strategies for Electric Vehicle Participation in Electricity Markets Under Multi-Network Collaboration [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(12): 83-94. |
| [6] | WANG Xiaofei, LI Siyu, CHEN Mi, et al. Influence of the Combination Equilibrium of Horizontal and Crest Vertical Curves on Highway Safety [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 76-84. |
| [7] | SONG Jian, WANG Wenlong, LI Dong, et al. Injection molding part size prediction method based on Stacking integration learning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(6): 19-26. |
| [8] | XIONG Ergang, ZU Kun, HU Qinbin, et al. Shear Capacity Prediction for RC Beams Without Stirrups Based on Mechanical Research [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(11): 115-124. |
| [9] | LIN Peiqun XIA Yu ZHOU Chuhao. Freeway Travel Time Prediction Based on Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Road Networks [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(8): 1-11. |
| [10] | JIA Ruo, DAI Shenghong, HUANG Ni, et al. Literature Review on Traffic Congestion Identification Methods [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(4): 124-139. |
| [11] | MA Yudong, MA Kaize, WEI Hui, et al. Shear Behavior of Steel Fiber Reinforced High-Strength Concrete Deep Beams [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(4): 20-27,38. |
| [12] | TIAN Wenling, LI Xinbo, ZHOU Jian, et al. Compressive Performance of Brick Columns Strengthened with Textile Reinforced Concrete [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(9): 34-42,70. |
| [13] | ZHAO Jing, WANG Xuancang, FAN Zhenyang, et al. Evaluation on Performance of Asphalt Pavement Based on Support Vector Machine [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(9): 116-123. |
| [14] | ZHANG Ziye, LI Mingchang, LIANG Lingrui, et al. Improved Transfer Learning Algorithm Based on Cross-domain in Recommendation System [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(11): 99-106. |
| [15] | XIONG Ergang, ZU Kun, ZHANG Qian, et al. Experimental Study on Mechanical Behavior of RC Beams Based on Compressive Force Path Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(10): 56-66,87. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||