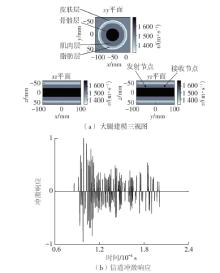
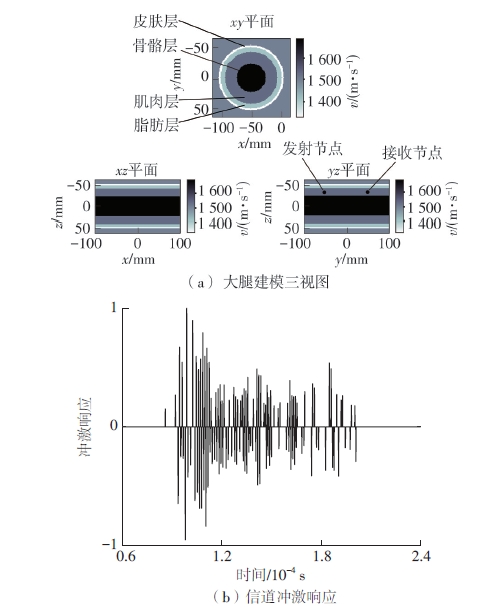
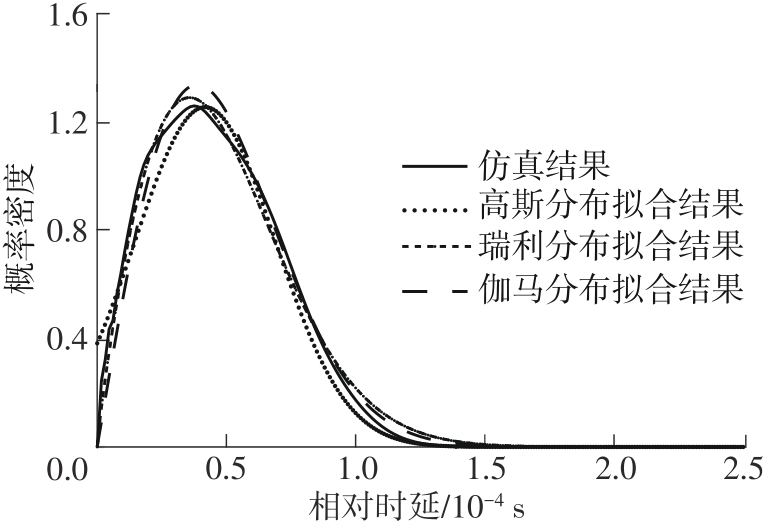
| 1 |
孙倩倩,周守君 .我国远程医疗的现状、问题及发展对策[J].南京医科大学学报(社会科学版),2022,22(1):25-30.
|
|
SUN Qianqian, ZHOU Shoujun .The development status problems and countermeasures of China’s telemedicine[J].Journal of Nanjing Medical University(Social Sciences),2022,22(1):25-30.
|
| 2 |
SANTAGATI G E, MELODIA T .A software-defined ultrasonic networking framework for wearable devices[J].IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking,2017,25(2):960-973.
|
| 3 |
MENG M, KIANI M .Design and optimization of ultrasonic wireless power transmission links for millimeter-sized biomedical implants[J].IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems,2017,11(1):98-107.
|
| 4 |
JAAFAR B, NEASHAM J A, DEGENAAR P .What ultrasound can and cannot do in implantable medical device communications[J].IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering,2021,16:357-370.
|
| 5 |
WANG M L, ARBABIAN A .Exploiting spatial degree of freedom for high data rate ultrasound communication with implantable devices[J].Applied Physics Letters,2017,111(13): 133-136.
|
| 6 |
MAZZILLI F, DEHOLLAIN C .184 μW ultrasonic on-off keying/amplitude-shift keying demodulator for downlink communication in deep implanted medical devices[J].Eletronics Letters,2016,52(7):502-504.
|
| 7 |
KERAMATZADEH K, SODAGAR A M .Design and implementation of an ultrasonic link for concurrent telemetry of multiple data streams to implantable biomedical microsystems[C]∥ Proceedings of 2018 IEEE the 61st International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems.Windor:IEEE,2018:1090-1093.
|
| 8 |
KOU Z, MILLER R J, SINGER A C,et al .High data rate communications in vivo using ultrasound[J].IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,2021,68(11):3308-3316.
|
| 9 |
TABAK G, YANG S, MILLER R J,et al .Video-capable ultrasonic wireless communications through biological tissues[J].IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics,Ferroelectrics,and Frequency Control,2021,68(3):664-674.
|
| 10 |
SANTAGATI G E, MELODIA T .Sonar inside your body:prototyping ultrasonic intra-body sensor networks[C]∥ Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications.Toronto:IEEE,2014:2679-2687.
|
| 11 |
SANTAGATI G E, MELODIA T .Design and performance evaluation of an implantable ultrasonic networking platform for the internet of medical things[J].IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking,2020,28(1):29-42.
|
| 12 |
WANG Q, GUAN Q, MA B,et al .Direct-sequence ultrasonic wideband technology for intra-body communications [J].IEEE Communications Letters,2019,23(10):1744-1747.
|
| 13 |
CAVALLARI R, MARTELLI F, ROSINI R,et al .A survey on wireless body area networks:technologies and design challenges [J].IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials,2014,16(3):1635-1657.
|
| 14 |
GUAN Z, SANTAGATI G E, MELODIA T .Ultrasonic intra-body networking:interference modeling,stochastic channel access and rate control[C]∥ Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications.Hong Kong:IEEE,2015:2425-2433.
|
| 15 |
刘娇蛟,王倩倩,马碧云,基于直扩超宽带的超声波人体通信技术仿真 [J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(3):18-23.
|
|
LIU Jiaojiao, WANG Qianqian, MA Biyun .Simulation of ultrasonic human body communication technology based on DS-UsWB[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2020,48(3):18-23.
|
| 16 |
TREEBY B,COX B, JAROS J .k-Wave:a Matlab toolbox for the time-domain simulation of acoustic wave fields [EB/OL].(2022-11-08)[2022-12-01]..
|
| 17 |
SANTAGATI G E, MELODIA T, GALLUCCIO L,et al .Distributed MAC and rate adaptation for ultrasonically networked implantable sensors[C]∥ Proceedings of 2013 the 10th Annual IEEE Communications Society Conference on Sensor,Mesh and Ad Hoc Communications and Networks.New Orleans:IEEE,2013:104-112.
|
| 18 |
PAUL S, RAJENDRAN S, SINGH M S .k-Wave toolbox for studying elastic property in photoacoustic imaging[C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Region 10 Conference.Kochi:IEEE,2019:91-95.
|
| 19 |
INSANA M F, BROWN D G .Acoustic scattering theory applied to soft biological tissues[M]∥ SHUNG K K,THIEME G A.Ultrasonics scattering in biological tissue.Boca Raton:CRC Press,1993:75-124.
|
| 20 |
TREEBY B, COX B T .k-Wave:Matlab toolbox for the simulation and reconstruction of photoacoustic wave fields[J].Journal of Biomedical Optics,2010,15(2):021314/1-12.
|
| 21 |
LEHNERT J, PURSLEY M .Error probabilities for binary direct-sequence spread-spectrum communications with random signature sequences[J].IEEE Transactions on Communications,1987, 35(1):87-98.
|
| 22 |
DAUTOV R, TSOURI G R .Dynamic off-body Rician channel modeling for indoor wireless body area networks[J].IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics,2020,24(5):1246-1254.
|
| 23 |
HOLTZMAN J M .A simple,accurate method to calculate spread-spectrum multiple-access error probabilities[J].IEEE Transactions on Communications,1992,40(3):461-464.
|